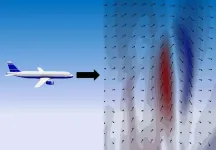
Supercomputer used to simulate winds that cause clear air turbulence
2023-07-12
A research group from Nagoya University has accurately simulated air turbulence occurring on clear days around Tokyo using Japan’s fastest supercomputer. They then compared their findings with flight data to create a more accurate predictive model. The research was reported in the journal Geophysical Research Letters.
Although air turbulence is usually associated with bad weather, an airplane cabin can shake violently even on a sunny and cloudless day. Known as clear air turbulence (CAT), these turbulent ...
Sea snake vision evolved to regain color
2023-07-12
An international team of scientists examining the genetic history of sea snakes have found that the species has enhanced their colour vision in response to living in brighter and more colourful marine environments.
“Our research has found that the annulated sea snake possesses four intact copies of the opsin gene SWS1,” said PhD candidate Isaac Rossetto, from the University of Adelaide’s School of Biological Sciences who led the study.
“Two of these genes have the ancestral ultraviolet sensitivity, and two have evolved a new sensitivity to the longer wavelengths that dominate ocean habitats.
“The earliest ...
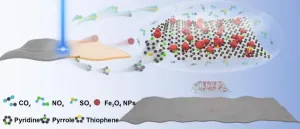
Scientists developed 180% relative bandwidth microwave absorber by ultrafast UV laser
2023-07-12
Scientists from Chinese Academy of Sciences Ningbo Institute of Materials Technology and Engineering, National Physical Laboratory (UK), The University of Manchester (UK) and National University of Singapore have developed a new approach, published in International Journal of Extreme Manufacturing (IF: 14.7), to fabricate a specifically designed wideband microwave absorption metamaterial with well-controlled electrical and magnetic characteristics on a polyethylene terephthalate (PET) substrate using ultraviolet (UV) laser irradiation.
The process involves using a UV laser to precisely control the characteristics of 2-D pattern on a specially formulated donor ...
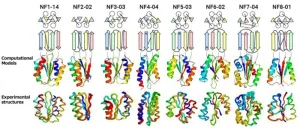
Beyond nature's imagination: Scientists discover extensive array of protein folds unexplored in nature
2023-07-12
A groundbreaking study has shed new light on the astonishing diversity of protein structures and their folds in nature. Researchers set out to reveal the extent to which nature has explored the vast landscape of possible protein topologies. The results have unveiled an astounding array of unexplored protein folds, expanding our understanding and uncovering the depth of the protein universe.
This research has been published in the journal Nature Structural and Molecular Biology on July 3, 2023.
Proteins, ...
Bound states in the continuum is possible in the acoustoelastic coupling
2023-07-12
Let’s imagine a hypothetical scenario where two individuals are gripping a rope, each holding one end. Person A proceeds to shake the rope in an up-and-down motion, thus generating a propagating wave that travels towards person B. Now, if person C, positioned between person A and B, engages in a comparable frequency of waving motion as that of the rope’s wave, could the wave be redirected back to person A rather than reaching person B? Initially, this situation appears implausible, as person C does not physically ...
Pre-operative exercise substantially helps with recovery – study
2023-07-12
Policy-makers are being urged to take notice of a University of Otago study that confirms that undertaking a short programme of high intensity interval training before surgery can substantially help with recovery.
The study, published in the journal Surgery, reviewed and analysed 12 studies including 832 patients who had undertaken preoperative high-intensity interval training. Such training involves repeated aerobic high-intensity intervals at about 80 per cent of the maximum heart rate followed by active recovery.
Lead investigator Dr Kari Clifford says the study included all types of major surgeries – those expected ...
Scientists developing way to make cheaper Lithium batteries
2023-07-12
Lyon, France: Lithium is becoming the new gold, with rocketing use in lithium-ion batteries in electric cars, computers, and portable devices driving up the price and affecting the supply of the relatively rare metal. Scientists are on the verge of developing a way of using sodium to replace some of the lithium, so driving down costs and guaranteeing the supply.
Recently scientists have looked at dispensing with lithium altogether and instead using sodium or other elements in high quality batteries. Sodium is cheaper and more available (it’s found in seawater, as sodium chloride), but they have ...
Plant Biology 2023 plenary closeup: Connecting the dots
2023-07-12
This year’s Presidential Symposium places plant science within a larger context, spotlighting the connections between plants and humanity. Accordingly, ASPB President Gustavo MacIntosh selected speakers with a broad array of backgrounds and expertise. Yet when the Presidential Symposium takes place Saturday, August 5, at 1:30 pm, you’ll find they agree on critical fundamentals.
“Humans are totally dependent on plants for food,” began Barbara Schaal of Washington University.
“When it comes to agriculture, plants and people are really ...
Tiny fish surprise scientists in ‘volunteer’s dilemma’
2023-07-12
Tiny fish called Trinidadian guppies have surprised scientists when faced with the so-called “volunteer’s dilemma”.
The idea of the dilemma is that individuals are less likely to cooperate if they are in a large group.
Various studies have demonstrated this in humans – but guppies appear to buck the trend.
In the new study, by the University of Exeter, guppies in larger groups were more likely to risk approaching a predator to gather information for the shoal.
“When faced with a possible predator, guppies have to balance risks,” said Rebecca Padget, from Exeter’s Centre for Research in Animal Behaviour.
“At least one ...
Six research centers will lead innovation towards a fully sustainable energy sector
2023-07-12
An investment of £53 million in six research centres will drive forward change in the energy system and help to meet the UK’s net zero target by 2050.
The energy research centres will boost knowledge, create innovative green technologies and reduce demand for energy to achieve greener, cleaner domestic, industrial and transport energy systems.
UK Research and Innovation (UKRI) has awarded:
£15 million for a new Energy Demand Research Centre that will provide solutions for energy demand reduction, understand the impact on consumers, and enable equitable policy decision-making.
£17.5 ...
Training robots how to learn, make decisions on the fly
2023-07-12
Mars rovers have teams of human experts on Earth telling them what to do. But robots on lander missions to moons orbiting Saturn or Jupiter are too far away to receive timely commands from Earth. Researchers in the Departments of Aerospace Engineering and Computer Science at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign developed a novel learning-based method so robots on extraterrestrial bodies can make decisions on their own about where and how to scoop up terrain samples.
“Rather than simulating how to scoop every possible type of rock or granular material, ...
Substance use linked to long-lasting brain changes, cognitive decline
2023-07-12
An estimated 50 million individuals in the United States struggle with the challenges of cocaine or alcohol use disorders, according to the National Institutes of Health (NIH). Beyond the well-documented health risks, addiction to these substances detrimentally affects our cognitive flexibility, which is the ability to adapt and switch between different tasks or strategies. Although previous research has hinted at this connection, the underlying reasons for this cognitive impairment remain elusive.
Cognitive flexibility is a crucial element in various domains of our life, including ...
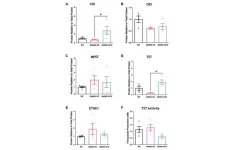
CU Anschutz study shows CBD use in pregnancy could impact the fetal brain
2023-07-12
AURORA, Colo. (July 11, 2023) – Researchers at the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus have found that cannabidiol (CBD), often used to treat anxiety and nausea, can potentially harm a developing fetus.
The paper was published in Molecular Psychiatry today.
People consume cannabis or a non-psychoactive component cannabidiol (CBD) to help with nausea and anxiety during pregnancy because they think it is safe and healthy. But CBD crosses the placenta and accumulates in the fetal brain.
Until now, no one knew how fetal exposure to CBD affected brain development, said Emily ...
Paths for reducing harmful air pollution in South Asia identified
2023-07-11
Fine particulate matter comes from wood burning, power generation, motor vehicles and other combustion sources that emit tiny particles into the air. At only 2.5 micrometers or smaller, these particles are small enough to be inhaled and cause lasting damage to the heart and lungs. Known as PM2.5, exposure to these particles is a leading mortality risk factor in India and the surrounding region of South Asia.
A new study by researchers in Randall Martin’s lab in the McKelvey School of Engineering at Washington University in St. Louis evaluated the contribution of various emission sectors and fuels to PM2.5 mass for 29 states in India ...
Zoonotic researcher receives ORAU Ralph E. Powe Junior Faculty Enhancement Award
2023-07-11
Daniel Becker, Ph.D., an assistant professor of Biology in the Dodge Family College of Arts and Sciences, has received an Oak Ridge Associated Universities Ralph E. Powe Junior Faculty Enhancement Award for his continued research on bat migration in western Oklahoma.
“We’re studying migratory Mexican free-tailed bats and the pathogens they might carry that are possible threats to human or wildlife health,” Becker said. “This award allows us to purchase the microchips we implant in the bats and ...
Cancer disparities: Sylvester researchers, collaborators seek answers to prostate, breast cancer among people of African ancestry
2023-07-11
MIAMI, FLORIDA (July 11, 2023) – “Please, please do it (cancer screening), if not for yourself, then for the next generation. We need to see the day when we end cancer.”
Those are the impassioned words of Charinus Johnson-Davis, who was diagnosed with breast cancer a dozen years ago but is now cancer-free after a double-mastectomy and 28 rounds of chemotherapy plus radiation. She is on a mission to help address cancer disparities affecting Black women and men, and is one of the first to enroll in the African Cancer Genome Registry, a new study at Sylvester Comprehensive Cancer ...
AGS supports CMS decision to require real-world data for monoclonal antibodies
2023-07-11
New York (July 11, 2023) — The American Geriatrics Society (AGS) supports the recently announced decision from the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) to require the collection of real-world information via a registry to study monoclonal antibodies directed against amyloid for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease. This decision applies to monoclonal antibodies that receive traditional approval from the Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Currently, lecanemab (trade name ...
GSA Connects 2023: A premier international scientific meeting
2023-07-11
11 July 2023
The Geological Society of America
Release no. 23-25
Contact: Justin Samuel
+1-303-357-1026
jsamuel@geosociety.org
For immediate release
GSA Connects 2023: A Premier International Scientific Meeting
The Geological Society of America visits Pittsburgh
Boulder, Colo., USA: Media registration is open now for The
Geological Society of America’s Connects 2023
meeting, to be held 15–18 October 2023 at the David L Lawrence Convention
Center (1000 Fort Duquesne Blvd) in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, USA. The
organizing committee is pleased to be planning a dynamic meeting centered
around ...
Generative AI ‘fools’ scientists with artificial data, bringing automated data analysis closer
2023-07-11
The same AI technology used to mimic human art can now synthesize artificial scientific data, advancing efforts toward fully automated data analysis.
Researchers at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign have developed an AI that generates artificial data from microscopy experiments commonly used to characterize atomic-level material structures. Drawing from the technology underlying art generators, the AI allows the researchers to incorporate background noise and experimental imperfections into the generated ...
Satisfaction with online dating app depends on what you’re looking for
2023-07-11
With an estimated 75 million active users each month, Tinder is the most popular dating app in the world. But a new study by Stanford Medicine researchers and collaborators has found, surprisingly - though perhaps not to users of the app - that many users are not swiping for dates.
In a survey of more than a thousand Tinder users, half said they were not interested in meeting offline, and nearly two-thirds were already married or "in a relationship."
In fact, the psychological motivations behind people's use of the app varied widely and had a strong influence on their satisfaction with the app and the dates it led to, according to the study published June 23 ...
University of Illinois study finds turning food waste into bioenergy can become a profitable industry
2023-07-11
URBANA, Ill. — Food waste is a major problem around the world. In the United States, an estimated 30 to 40% of edible food is lost or wasted, costing billions of dollars each year. One potential solution is to divert food waste from landfills to renewable energy production, but this isn’t done on a large scale anywhere. A new study from the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign investigates the feasibility of implementing energy production from food waste in the state of Illinois.
“We have a large amount of organic waste in the U.S., which eventually enters landfills and emits greenhouse gasses. However, this material ...
Hepatic hydrogen sulfide levels are reduced in mouse model of progeria
2023-07-11
“To date, no studies have directly measured [hydrogen sulfide] production in Hutchinson-Gilford Progeria Syndrome [...]”
BUFFALO, NY- July 11, 2023 – A new research paper was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science) Volume 15, Issue 12, entitled, “Hepatic hydrogen sulfide levels are reduced in mouse model of Hutchinson-Gilford progeria syndrome.”
Hutchinson-Gilford progeria syndrome (HGPS) is a rare ...
Missing a rare cause of hereditary cancer
2023-07-11
New research from Cedars-Sinai Cancer investigators could warrant reconsideration of current screening guidelines to include a poorly recognized cause of Lynch syndrome, the most common cause of hereditary colorectal and endometrial cancers. Their study, published today in the JNCCN—Journal of the National Comprehensive Cancer Network, concluded that the guidelines leave a significant number of patients undiagnosed.
“When patients with Lynch syndrome—whose first cancers generally appear at an early age—aren’t diagnosed promptly, they don’t get appropriate follow-up or surveillance,” said Megan Hitchins, ...
U of M Medical School receives DARPA award to develop detection tools for early symptoms of depression, psychosis and suicidality
2023-07-11
MINNEAPOLIS/ST. PAUL (07/11/2023) — Researchers at the University of Minnesota Medical School recently received a four-year award from the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency’s (DARPA’s) Neural Evidence Aggregation Tool program. The goal of their project— titled Fast, Reliable Electrical Unconscious Detection (FREUD)—is to develop tools to better detect early symptoms of depression, psychosis and suicidality, with the intent that treatment can be started as early in a condition’s trajectory as possible.
“It’s exactly those early moments when getting someone therapy or mental health services could save their life or ...
Research aims to identify better COPD diagnosis in African American patients
2023-07-11
DENVER — Recently published research suggests that despite showing clear symptoms of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), many African Americans are not officially diagnosed with the disease due to flaws in diagnosis methods. The Research was led by National Jewish Health and recently published in the Journal of General Internal Medicine from the COPDGene study.
Fixed-ratio spirometry, a standard method of measuring respiratory capacity, has long been used as a method of detecting COPD. ...
[1] ... [1799]
[1800]
[1801]
[1802]
[1803]
[1804]
[1805]
[1806]
1807
[1808]
[1809]
[1810]
[1811]
[1812]
[1813]
[1814]
[1815]
... [8818]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.