With a comfort promise, new clinic aims to eliminate pain in kids
2023-07-11
Each year, too many kids in the East Bay suffer needlessly from pain related to long-term serious illness, including migraines, joint and abdominal pain, sickle cell anemia and more. A new UCSF Health pain clinic in Walnut Creek is opening to provide relief.
The new clinic extends the reach of the Stad Center for Pediatric Pain, Palliative & Integrative Medicine beyond UCSF Benioff Children’s Hospitals in San Francisco and Oakland. The Center is one of the nation’s most innovative and comprehensive integrative ...
Potential targets to delay motor aging revealed by C. elegans genome-wide screen
2023-07-11
Genome-wide screen in the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans reveals potential targets to delay motor aging, including the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase VPS-34; genetic and pharmacological partial inhibition of VPS-34 improves neurotransmission and muscle integrity through increased PI(3)P-PI-PI(4)P conversion, ameliorating motor aging in both worms and mice.
#####
In your coverage, please use this URL to provide access to the freely available paper in PLOS Biology: http://journals.plos.org/plosbiology/article?id=10.1371/journal.pbio.3002165
Article ...
Scientists build a healthy dietary pattern using ultra-processed foods
2023-07-11
GRAND FORKS, N.D., July 11, 2023 ̶ Scientists at the USDA Agricultural Research Service’s (ARS) Grand Forks Human Nutrition Research Center led a study that demonstrates it is possible to build a healthy diet with 91 percent of the calories coming from ultra-processed foods (as classified using the NOVA scale) while still following the recommendations from the 2020-2025 Dietary Guidelines for Americans (DGA). The study highlights the versatility of using DGA recommendations in constructing healthy menus.
“The study is a proof-of-concept that shows a more balanced view of healthy ...
Low-glucose sensor in the brain promotes blood glucose balance
2023-07-11
The body’s blood glucose level needs to be maintained in a relatively narrow range. It cannot be too high, as it can lead to diabetes, and it cannot be too low because it can cause fainting or even death.
“There are many glucose-sensing neurons in the brain that are thought to actively participate in detecting small changes of glucose levels in the body and then trigger responses accordingly to return the level to a healthy range,” said Dr. Yong Xu, professor of pediatrics – nutrition, ...
New study is first to find exposure to neurotoxic rodenticide bromethalin in birds of prey
2023-07-11
In 2020, Tufts Wildlife Clinic Director Maureen Murray, V03, published a study that showed 100% of red-tailed hawks tested at the clinic were positive for exposure to anticoagulant rodenticides (ARs). Such exposure occurs when these chemicals are used to kill mice or rats, which eat the poison, and the birds eat the poisoned prey. Now, Murray is expanding that research with a new study published recently in the journal Environmental Pollution, which found that another type of rodenticide—a neurotoxicant called bromethalin—also ...
Changing the way we deliver immune-based cancer drugs could reduce costs by 14%
2023-07-11
ANN ARBOR, Michigan — A new analysis finds that up to millions of dollars could be saved annually on cancer immunotherapy treatments across the Veterans Health Administration by reconsidering how those drugs are delivered.
It’s a concept that could be applied to all cancer centers nationwide. Immune checkpoint inhibitors were initially tested and approved at weight-based dosages but then moved to one-size-fits-all flat doses, in part to reduce drug waste. But researchers from the University of Michigan Rogel Cancer Center found that if vials intended for a single ...
Damage to gut bacteria linked with chemo-induced weight gain in breast cancer patients
2023-07-11
EDMONTON — Researchers have found a link between chemotherapy-induced changes to gut bacteria and the unhealthy weight gain seen in breast cancer patients, pointing the way to potentially help survivors avoid obesity-related illness later in their lives.
In newly published research, a team at the University of Alberta found that the patients treated with chemotherapy lost muscle mass and gained abdominal fat, which has been linked to heart disease, diabetes and even cancer recurrence. The chemo patients also exhibited signs of inflammation and significant changes to the number and variety of bacteria in their guts.
“Changes in the bacterial populations ...
Nurse researcher casts new light on bruise detection in patients with darker skin tones
2023-07-11
July 11, 2023 – A leading forensic nurse researcher has developed new approaches to detecting bruises in patients with darker skin tones – thus helping to overcome barriers to diagnosing injuries in patients of color, according to a special article on nurse innovators in the July issue of the American Journal of Nursing (AJN). The journal is published in the Lippincott portfolio by Wolters Kluwer.
The article highlights the work of Katherine Scafide, PhD, RN, of George Mason University, Fairfax, Va., whose "nonconventional program ...
Warmer weather makes venomous snake bites more likely, especially in spring
2023-07-11
American Geophysical Union
Press Release No. 23-27
For Immediate Release
11 July 2023
This press release is available online at: https://news.agu.org/press-release/warmer-weather-makes-venomous-snake-bites-more-likely-especially-in-spring
AGU press contact:
Rebecca Dzombak, news@agu.org, +1 (202) 777-7492 (UTC-4 hours)
Emory University press contact:
Rob Spahr, rob.spahr@emory.edu (UTC-4 hours)
Interview requests should be sent to Rob.
WASHINGTON — Climate change is not only making Georgia hotter but also increasing the likelihood of snake bite, according to a new study. Every degree Celsius of daily temperature increase corresponds with about ...
Aston University researcher turns one of the basic rules of construction upside down
2023-07-11
1675 theory states a hanging chain mirrors shape of an upstanding rigid arch
Research from Aston University shows that this common-held belief is incorrect
Explained using transition from Newtonian to Lagrangian mechanics and mathematical rigour.
Monday 10 July 2023 | Birmingham, UK
An Aston University researcher has turned one of the basic rules of construction on its head.
For centuries a hanging chain has been used as an example to explain how masonry arches stand.
Structural engineers are familiar ...
Software creates entirely new views from existing video
2023-07-11
ITHACA, N.Y. -- Filmmakers may soon be able to stabilize shaky video, change viewpoints and create freeze-frame, zoom and slow-motion effects – without shooting any new footage – thanks to an algorithm developed by researchers at Cornell University and Google Research.
The software, called DynIBar, synthesizes new views using pixel information from the original video, and even works with moving objects and unstable camerawork. The work is a major advance over previous efforts, which ...
Working to make steel greener, cleaner
2023-07-11
CLEVELAND–Case Western Reserve University chemical engineer Rohan Akolkar is leading a research team working to develop a new zero-carbon, electrochemical process to produce iron metal from ore.
If successful, the project could be a first step toward eliminating harmful greenhouse gas emissions by eventually replacing century-old, blast-furnace ironmaking with a new electrolytic-iron production process.
Reducing iron ore to metal is carbon- and energy-intensive, leading to significant carbon-dioxide emissions that drive global warming.
“We don’t use carbon at all in our process, so ...
Crawford Lake chosen as the primary marker to identify the start of the Anthropocene epoch
2023-07-11
EMBARGOED: Not for Release Until 18:00 BST 11 July 2023.
Crawford Lake chosen as the primary marker to identify the start of the Anthropocene epoch
Anthropocene proposes human activity has become a dominant influence on the planet, especially since the mid-twentieth century
Nuclear bomb tests have left a ‘stark plutonium fingerprint’ of this change in human activity
Evidence from Crawford Lake in Canada and 12 secondary locations will be assessed by International Commission on Stratigraphy to decide if we have entered a new geological era
Today [11 July 2023] an international team of researchers has chosen the location ...
New study finds U.S. military veterans living in discriminatory ‘redlined’ areas suffered higher rates of cardiovascular disease
2023-07-11
CLEVELAND—U.S. military veterans who lived in what were once known as “redlined” areas had a higher risk for heart attacks and other cardiovascular issues, according to a new study by researchers at Case Western Reserve University, University Hospitals and the Cleveland VA Medical Center.
In the 1930s, the federal government-sponsored Homeowners’ Loan Corp. (HOLC) established maps of U.S. neighborhoods that identified levels of mortgage risk. This practice led to disinvestments and segregation in “redlined” neighborhoods.
Judicial rulings--and, later, federal legislation--prohibited such government practices, but research has shown their ...
$1.5 million donation supports research on effects of psychedelic DMT on the brain
2023-07-11
One of the most powerful psychedelics known, N,N-dimethyltryptamine (DMT) has been described as causing imaginative visuals akin to the dream state. It is typically consumed on its own or in ayahuasca, a ceremonial brew that has been used for spiritual and visionary purposes by indigenous cultures for centuries. Some have expressed that DMT helped address psychological ailments such as depression and addiction, promoting emotional well-being. However, the way that DMT impacts the brain, body and health is largely unknown.
A ...
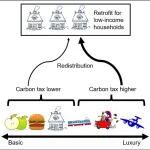
Carbon taxes that focus on luxury consumption are fairer than those that tax all emissions equally
2023-07-11
Not all carbon emissions are made for the same reason—they range from more essential purposes like heating a home to nonessential “luxury” activities like leisure travel. However, proposals for the implementations of carbon taxes tend to apply to all emissions at an equal rate. This can give rise to and exacerbate inequalities. A new analysis published on July 11 in the journal One Earth suggests taxing luxury carbon emissions at a higher rate instead; if all 88 countries analyzed in this study adopted the luxury-focused policy, this would achieve 75% of the emissions reduction needed to reach the Paris Agreement’s goal of limiting climate change ...
Thermal cloak passively keeps electric vehicles cool in the summer and warm in the winter
2023-07-11
When an electric vehicle is parked outside, its temperature can swing wildly from day to night and season to season, which can lead to deterioration of the battery. To dampen these fluctuations and extend the battery’s lifespan, researchers have designed an all-season thermal cloak that can cool an electric vehicle by 8°C on a hot day and warm it by 6.8°C at night. The cloak, made predominantly of silica and aluminum, can do so passively without outside energy input and operates without any modification between hot or cold weather. This prototype is described July 11 in the newly launched Device, an application-oriented sister journal ...
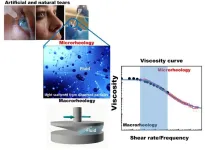
Breaking into tears with microrheology to design custom eye drops
2023-07-11
WASHINGTON, July 11, 2023 – Compared to artificial tears, or eye drops, human tears are significantly more complex liquids, with a wide range of components including lipids, carbohydrates, proteins, water, and salt. It is this complex mixture that gives tears the perfect thickness and ability to moisturize the eye, a design that is hard to replicate with fewer ingredients.
In Physics of Fluids, from AIP Publishing, Vega et al. researched human tears at the micron level to reveal new ways of customizing artificial tears to address individual symptoms of dry eye disease. The detailed insights they gained about the composition and behavior ...
Unborn babies use ‘greedy’ gene from dads to ‘remote-control’ mums into feeding them extra food
2023-07-11
Unborn babies use ‘greedy’ gene from dads to ‘remote-control’ mums into feeding them extra food
Fetuses use a copy of a gene inherited from their dad to force their mum to release as much nutrients as possible during pregnancy, Cambridge scientists have discovered.
The unborn baby ‘remote controls’ its mother’s metabolism so the two are in a nutritional tug of war. The mother’s body wants the baby to survive but needs to keep enough glucose and fats circulating in her system for her own health, to be able to deliver ...
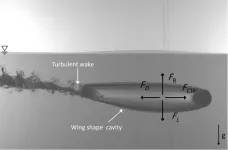
The science behind skipping stones
2023-07-11
WASHINGTON, July 11, 2023 – Inspired by the need to safeguard marine animals and promote sustainable solutions within marine environments, an interdisciplinary team of researchers from King Abdullah University of Science and Technology in Saudi Arabia and Sofia University in Bulgaria are delving into the hydrodynamics of buoyant objects at the air-water interface.
By studying these dynamics, their goal is to expand the understanding of fluid hydrodynamics and complex surface interactions – and advance fields such as the design and performance of marine engineering systems, buoy systems, and ...
Association of racial discrimination with obesity in children and adolescents
2023-07-11
About The Study: The findings of this study suggest that personally mediated racial discrimination may be a risk factor for developing obesity in children and adolescents, above and beyond socioeconomic status. The results highlight the need for a multifaceted approach to address racial discrimination and its impact on the health of children and adolescents.
Authors: Adolfo G. Cuevas, Ph.D., of the New York University School of Global Public Health in New York, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.22839)
Editor’s Note: Please ...
Association between historical neighborhood redlining and cardiovascular outcomes among veterans
2023-07-11
About The Study: In this cohort study of U.S. veterans, the findings suggest that those with atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease who reside in historically redlined neighborhoods continue to have a higher prevalence of traditional cardiovascular risk factors and higher cardiovascular risk. Even close to a century after this practice was discontinued, redlining appears to still be adversely associated with adverse cardiovascular events.
Authors: Sadeer Al-Kindi, M.D., of University Hospitals in Cleveland, and Salil V. Deo, ...
Genome sequencing nearly twice as effective as a targeted gene-sequencing test at diagnosing genetic disorders in newborns and infants
2023-07-11
July 11, 2023 (BOSTON) – A new national study, led by researchers at Tufts Medical Center in Boston, has found whole genome sequencing (WGS) to be nearly twice as effective as a targeted gene sequencing test at identifying abnormalities responsible for genetic disorders in newborns and infants. The study, “A Comparative Analysis of Rapid Whole Genomic Sequencing and a Targeted Neonatal Gene Panel in Infants with a Suspected Genetic Disorder: The Genomic Medicine for Ill Neonates and Infants ...
Racial discrimination increases risk for childhood obesity
2023-07-11
Children who experience racial discrimination are more likely to later have a higher body mass index (BMI) and larger waistline, according to a new study published in JAMA Network Open. The findings illustrate that racial discrimination may be a risk factor for young people developing obesity—above and beyond other socioeconomic factors such as family income.
“Exposure to racial discrimination must be acknowledged as both a social determinant of obesity and a significant contributor to obesity disparities among children and adolescents,” said Adolfo Cuevas, assistant professor of social and behavioral sciences at the NYU School of Global Public Health and the study’s ...
First large US clinical trial of cytisinicline finds the smoking cessation medication effective and well tolerated
2023-07-11
BOSTON – The first large-scale U.S. clinical trial of cytisinicline, led by a Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) investigator, found the smoking cessation medication to be effective and well tolerated in adults who wished to break their nicotine dependence. In the Phase 3 study published in JAMA, researchers reported that cytisinicline could offer adults who smoke a potential new treatment option.
“Cigarette smoking remains the leading preventable cause of death worldwide, yet no new smoking cessation medication has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for nearly two decades,” says Nancy Rigotti, MD, director of MGH’s ...
[1] ... [1800]
[1801]
[1802]
[1803]
[1804]
[1805]
[1806]
[1807]
1808
[1809]
[1810]
[1811]
[1812]
[1813]
[1814]
[1815]
[1816]
... [8818]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.