Survival of children with acute lymphatic leukemia further increased
2023-07-17
The five-year survival of all children with acute lymphatic leukemia (ALL) has continued to increase to 94%. This is evident from a study of 800 Dutch children. Within the study, modified treatment protocols for four subgroups were examined. The modifications were found to have positive effects on survival and quality of life. For example, the risk of disease recurrence became as much as three times smaller for children with an aggressive form of leukemia. Says Prof. Dr. Rob Pieters: ‘The five-year ...
Bacteria discreetly dwelling in throat revealed to be primary source of Strep A transmission
2023-07-17
Breakthrough research has found that Group A Streptococcus (GAS) infections are more likely transmitted from asymptomatic throat carriage than skin-to-skin contact in communities with high rates of infection.
This major discovery has far-reaching implications for public health approaches, vaccine development and future research as it challenges previous understanding of how the bacterium is spread.
GAS (Streptococcus pyogenes), commonly found on the skin and in the throat, can cause infections ranging from sore throats and impetigo (skin infections) to deadly bloodstream infections. In places like remote First Nations communities where the pathogen is ...
First study to directly compare gene mutation type in individuals with CHAMP1 disorder indicates key differences
2023-07-17
New research led by the Seaver Autism Center for Research and Treatment at Mount Sinai has illuminated genetic differences among children with a rare neurodevelopmental condition and could point the way toward a precision medicine approach to caring for these children.
The study is the first of its kind to directly assess differences between individuals with mutations in the CHAMP1 gene and those with deletions of the gene. The analysis was published in Human Genetics on July 17.
CHAMP1 disorder is a genetic, neurodevelopmental condition associated with intellectual disability, medical comorbidities (e.g., seizures, gastrointestinal problems), and dysmorphic ...
Innovative infection prevention program reduces surgical site infections, results in hospital days reduced and $500,000 savings
2023-07-17
Chicago — An innovative anesthesiologist-led infection prevention program helped reduce the number of surgical site infections (SSIs) in colorectal patients by 50%, the number of days in the hospital by 46%, and led to significant cost savings over a two-year period, according to research presented at the virtual American Society of Anesthesiologists’ Anesthesia Quality and Patient Safety Meeting.
“With the skyrocketing cost of medical care for patients and health care institutions, one area physicians can focus on is reducing SSIs,” ...
Shrinking light: Nanoscale optical breakthrough
2023-07-17
Imagine shrinking light down to the size of a tiny water molecule, unlocking a world of quantum possibilities. This has been a long-held dream in the realms of light science and technology. Recent advancements have brought us closer to achieving this incredible feat, as researchers from Zhejiang University have made groundbreaking progress in confining light to subnanometer scales.
Traditionally, there have been two approaches to localize light beyond its typical diffraction limit: dielectric confinement and plasmonic confinement. However, challenges such as precision fabrication and optical loss have hindered the confinement of optical fields to sub-10 nanometer (nm) or even ...
UMD researchers uncover privacy risks in cellphones purchased at police auctions
2023-07-17
Law enforcement agencies nationwide regularly sell items that are seized in criminal investigations or are unclaimed from lost-and-found inventories. Many of these items—vehicles, jewelry, watches and electronic devices like cellphones—end up at online auction houses.
People looking for a bargain can bid on cellphones in bulk, snatching up dozens at rock bottom prices for parts or other uses. This ultimately provides revenue for the police agencies, making for a good deal for everyone involved. Or is it?
A recent study by University of Maryland security experts found that many of the phones sold ...
Bacterial protein found in the urogenital tract may contribute to reduced fertility, birth defects
2023-07-17
A team of researchers from the University of Maryland School of Maryland’s (UMSOM) Institute of Human Virology (IHV), a Center of Excellence of the Global Virus Network (GVN), published new findings that emphasize the crucial role of the urinary and genital tract microbiota in adverse pregnancy outcomes and genomic instability that originate in the womb during fetal development.
The study, published on July 17 in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America (PNAS), established a new link between genomic instability and a protein from Mycoplasma fermentans, a kind of bacterium that commonly ...
Picky green sea turtle has travelled to the same place to eat for generations
2023-07-17
For approximately 3,000 years, generations of green sea turtles have returned to the same seagrass meadows to eat. This was discovered by Willemien de Kock, a historical ecologist at the University of Groningen, by combining modern data with archaeological findings. Sea turtles migrate between specific breeding places and eating places throughout their lives–this much was known. But the fact that this stretches over many generations highlights the importance of protecting seagrass meadows along the coasts of North Africa. The results were published in PNAS on July 17.
When young green ...
How skin cancer virus outcompetes host cell replication
2023-07-17
University of Pittsburgh researchers have shown for the first time how Merkel cell polyomavirus (MCV), which causes an aggressive skin cancer called Merkel cell carcinoma, initiates DNA replication in host cells.
Published today in the journal PNAS, the study sheds light on the fundamental question of how viruses override their host cells’ carefully regulated DNA replicating system to make hundreds of new copies of themselves.
“Understanding how MCV replicates gives us really important clues about ...
All about the Benjamins: Researchers decipher the secrets of Benjamin Franklin’s paper money
2023-07-17
Benjamin Franklin may be best known as the creator of bifocals and the lightning rod, but a group of University of Notre Dame researchers suggest he should also be known for his innovative ways of making (literal) money.
During his career, Franklin printed nearly 2,500,000 money notes for the American Colonies using what the researchers have identified as highly original techniques, as reported in a study published this week in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
The research team, led by Khachatur ...
Redlining linked to higher heart failure risk among Black adults in US
2023-07-17
Research Highlights:
An analysis of more than two million adults in the U.S. found that present day heart failure risk was higher among Black adults who lived in zip codes historically impacted by redlining compared to Black adults living in non-redlined areas.
Redlining did not have the same impact on heart failure risk among white adults living in historically redlined zip codes.
Among Black adults living in historically redlined communities, approximately half of the excess risk of heart failure appeared to be explained by higher levels of socioeconomic distress.
Embargoed until 1 p.m. CT/2 p.m. ET Monday, July 17, ...
Racial disparities discovered in patients with cardiac devices
2023-07-17
Black patients with implantable cardioverter defibrillators (ICDs) have a significantly higher burden of disease than white patients with the same device, according to a new study from University of Rochester Medical Center (URMC) cardiology researchers. Analyzing data from clinical trials conducted over a 20-year period by the Clinical Cardiovascular Research Center (CCRC) at URMC, investigators concluded that not only did Black patients with ICDs tend to be significantly younger than white patients, but they also had a higher ...
SwRI team identifies giant swirling waves at the edge of Jupiter’s magnetosphere
2023-07-17
SAN ANTONIO — July 17, 2023 —A team led by Southwest Research Institute (SwRI) and The University of Texas at San Antonio (UTSA) has found that NASA’s Juno spacecraft orbiting Jupiter frequently encounters giant swirling waves at the boundary between the solar wind and Jupiter’s magnetosphere. The waves are an important process for transferring energy and mass from the solar wind, a stream of charged particles emitted by the Sun, to planetary space environments.
Jake Montgomery, a doctoral student in the joint space physics program ...
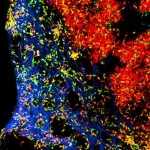
Immune cells in single file
2023-07-17
The cells of the immune system circulate mainly in the blood and migrate into the body's tissues after an inflammation. Some types of immune cells, however, are permanently located in the tissues, where they come together to form three-dimensional networks.
How do these networks form and how are they maintained? For the long-lived macrophages (phagocytes), the answer is already known: They settle in so-called niches. These are environments of connective tissue cells that supply the macrophages with nutrients and keep them ...
New research shows babies’ immunological weak spot and strength
2023-07-17
NEW YORK, NY--A pair of new studies led by researchers at Columbia University explains why babies get so many common respiratory infections and identifies a specialized cluster of immune cells found only in babies that help them better cope with new pathogens.
“We know little about how the immune system develops throughout life, and most of what we know about immune system development in children comes from animal studies,” says Donna Farber, PhD, an expert in immune system development at Columbia University ...
National Poll: Less than half of parents utilize patient portal benefits for their children
2023-07-17
ANN ARBOR, Mich. – For many busy families, online access to a child’s health provider for medical advice, health records or prescription refills is likely a convenient option.
Yet, only 43% of parents have set their child up for a patient portal – an online tool allowing communication between patients and medical providers – and others may not be optimizing portal use, suggests the University of Michigan Health C.S. Mott Children’s Hospital National Poll on Children’s Health.
“Patient portals offer a wide range of benefits, including decreasing unnecessary hassles for providers and patients and improving access to both the medical ...
The missing Americans: Unprecedented US mortality far exceeds other wealthy nations
2023-07-17
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE
Monday, July 17, 2023
Contact:
Jillian McKoy, jpmckoy@bu.edu
Michael Saunders, msaunder@bu.edu
##
The Missing Americans: Unprecedented US Mortality Far Exceeds Other Wealthy Nations
A new study found that more than one million US deaths a year—including many young and working-age adults—could be avoided if the US had mortality rates similar to its peer nations.
In 2021, 1.1 million deaths would have been averted ...
Addressing the future challenges of global surface water quality
2023-07-17
As the world's population continues to grow, ensuring access to clean and safe water has become an increasingly important concern, yet little is known about how surface water quality will change in the future. Recent scientific research has shed light on the potential challenges that surface water quality may face in the coming years, particularly in Sub-Saharan Africa. “While surface water quality is projected to improve in most developed countries, there is an important caveat: the outlook for the poorest nations is bleak”.
A recent study, published in Nature Water, has projected an increase in surface water pollution in Sub-Saharan Africa. These findings ...
Study finds how to reduce risk of kids playing with a found gun
2023-07-17
COLUMBUS, Ohio – In a lab at The Ohio State University masquerading as a playroom, pairs of kids ages 8 to 12 participating in a study found a variety of toys and games to play with – as well as a mysterious file cabinet.
Inside one of the drawers of the unlocked cabinet were two disabled 9-mm handguns.
As they played in the room, nearly all the children eventually found the guns. But some kids in the study were much more likely to tell an adult they found a gun, less likely to touch the gun, and were less reckless if they did touch it – and they were the kids who had watched a one-minute gun safety video a week earlier.
The study may be the ...
Trading sickness for health: Swapping brain cells points to new Huntington's therapies
2023-07-17
NNew research appearing in the journal Nature Biotechnology answers important questions about the viability of treatments that seek to replace diseased and aged cells in the central nervous system with healthy ones. Its findings have implications for a number of neurological and psychiatric disorders—including Huntington’s disease, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), and schizophrenia—that have been linked to glia, a population of cells that support brain health and function.
“A broad variety of disorders we associate with neuronal loss now appear to be caused ...
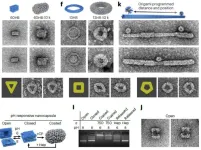
Researchers craft ‘origami DNA’ to control virus assembly
2023-07-17
Griffith University researchers have played a key role in using DNA ‘origami’ templates to control the way viruses are assembled.
The global team behind the research, published in Nature Nanotechnology, developed a way to direct the assembly of virus capsids – the protein shell of viruses - at physiological conditions in a precise and programmable manner.
Dr Frank Sainsbury and Dr Donna McNeale from the Griffith Institute for Drug Discovery were part of the research team and said forcing viruses to assemble onto DNA folded into different shapes “like origami” was a question that this project answered.
“We achieved control over the virus protein ...
Cap top 20% of energy users to reduce carbon emissions
2023-07-17
Consumers in the richer, developed nations will have to accept restrictions on their energy use if international climate change targets are to be met, warn researchers.
The big challenge is to identify the fairest and most equitable way that governments can curtail energy use, a process known as energy demand reduction.
Writing in the journal Nature Energy, the research team - led by Milena Büchs, Professor of Sustainable Welfare at the University of Leeds - analysed several scenarios to identify a potential ...
Excess mortality with Alzheimer disease and related dementias as an underlying or contributing cause during pandemic
2023-07-17
About The Study: This study found that large increases in mortality with Alzheimer disease and related dementias as an underlying or contributing cause of death occurred in COVID-19 pandemic year 1 but were largely mitigated in pandemic year 2. The most pronounced declines were observed for deaths in nursing home/long-term care settings. Conversely, excess deaths at home and in medical facilities remained high in year 2.
Authors: M. Maria Glymour, Sc.D., of the Boston University School of Public Health ...
Comparison of history of present illness summaries generated by a chatbot and senior internal medicine residents
2023-07-17
About The Study: History of present illnesses generated by a chatbot or written by senior internal medicine residents were graded similarly by internal medicine attending physicians. These findings underscore the potential of chatbots to aid clinicians with medical documentation.
Authors: Ashwin Nayak, M.D., M.S., of Stanford University in Stanford, California, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2023.2561)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, ...
Addressing adaptation inequalities in climate research
2023-07-17
A new study proposes ways to better incorporate adaptation in climate change research, addressing the uneven distribution of adaptation capacities and needs worldwide.
Research on adaptation to the risks posed by climate change has witnessed significant growth in the past decade, with increasing recognition of its urgency in policy agendas at the international, national, and local levels. Adaptation needs and capacities are not evenly distributed worldwide, with countries in the Global South generally experiencing the highest challenges. ...
[1] ... [1802]
[1803]
[1804]
[1805]
[1806]
[1807]
[1808]
[1809]
1810
[1811]
[1812]
[1813]
[1814]
[1815]
[1816]
[1817]
[1818]
... [8832]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.