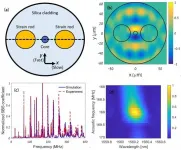
(Press-News.org) The gold standard in functional brain imaging for over two decades, functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) has transformed the landscape of research and clinical care. Yet, because of its cost and functional limitations, scientists have continued to look for new ways to see into the human brain.
Researchers from the Keck School of Medicine of USC and the California Institute of Technology (Caltech), with the help of patients recovering from traumatic brain injury, have now demonstrated an alternative way to produce highly detailed images of the human brain. Their work, published in END
Breakthrough in brain imaging may offer future alternative to functional MRI
Keck School of Medicine of USC researchers, working with a Caltech team, demonstrate possibilities of innovative imaging technology to visualize brain function
2021-06-14
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Olfactory virtual realities show promise for mental health practices and integrative care
2021-06-14
BURLINGTON, VT -- Findings from a study on the feasibility of addressing anxiety, pain and stress with Olfactory Virtual Reality (OVR) -- a new form of VR that incorporates the sense of smell into its augmented reality -- paint a clearer picture for clinical psychiatrists about how it could be used to safely and effectively help mental health and mood disorders. What's more, it holds promise for improved access and inclusion of patients impacted by physical limitations or constraints, such as patient mobility, comorbidities and safety.
Building on previous research proving VR's effectiveness in "distraction for pain and medical procedures, relaxation and calming, and immersion therapy for trauma, PTSD and ...
Data from community science is underutilized; new study aims to change that
2021-06-14
SAN FRANCISCO, CA (June 11, 2021) -- In recent years, community science--also known as citizen science--has become a global phenomenon, engaging millions of people through wildlife observation platforms like END ...
Opto-mechanical non-reciprocity in fiber
2021-06-14
The internet era that we live in depends completely on the transfer of vast information over optical fibers. Optical fibers are literally everywhere. In fact, the overall length of optical fibers installed on our planet is sufficient to reach planet Uranus and back. However, the transfer of information from point A to point B is not enough. The information that we send and receive must also be processed. Light waves take up an increasing role in addressing that task as well. In addition, optical fibers can do more for us than just relay information: They constitute an exceptional sensing platform. Optical fibers support measurements from a long stand-off distance, simply installed within structures, ...
How firms can navigate competitors' pitfalls without being 'tarred by the same brush'
2021-06-14
Researchers from University of Adelaide published a new paper in the Journal of Marketing that examines how advertising can increase the informativeness of a firm's stock price by reducing its stock price synchronicity.
The study, forthcoming in the Journal of Marketing, is titled "Tarred with the Same Brush? Advertising Share of Voice and Stock Price Synchronicity" and is authored by Chee Cheong, Arvid Hoffmann, and Ralf Zurbruegg.
Firms are sometimes "tarred with the same brush" by investors instead of being traded based on firm-specific information. ...
Lazy, hazy days no more: A call-to-action to better understand air pollution mechanisms
2021-06-14
Earth's atmosphere has a budget, and when expenses outpace savings, secondary aerosols form in areas of excessive pollution. Greenhouse gases enter the atmosphere, and free radicals bond to the molecules, rendering them inert. But when there are more pollution molecules than free radicals, they are left to recombine and form ozone and visible particulate matter -- smog and haze.
The precise mechanisms underlying this atmospheric oxidation capacity are not well understood, leaving the process inadequately described or completely missed in research, according to Yuesi Wang, professor with the State Key Laboratory of Atmospheric Boundary Layer Physics and ...
Black and white women have same mutations linked to breast cancer risk
2021-06-14
PHILADELPHIA-- The prevalence of genetic mutations associated with breast cancer in Black and white women is the same, according to a new JAMA Oncology study of nearly 30,000 patients led by researchers in the Basser Center for BRCA at the Abramson Cancer Center. About five percent of both Black and white women have a genetic mutation that increases their risk of breast cancer.
"The findings challenge past, smaller studies that found Black women face a greater genetic risk and the suggestion that race should be an independent factor when considering genetic testing," said first author Susan Domchek, MD, executive director of the Basser Center for BRCA. "We shouldn't make changes to testing guidelines based on race alone. Rather, our efforts should ...
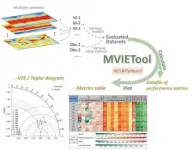
Meteorologists improve multivariable integrated evaluation method for climate model
2021-06-14
The Multivariable Integrated Evaluation (MVIE) method can help meteorologists to quantitatively evaluate the overall performance of a climate model in simulating multiple variables like air temperature, precipitation, and vector wind, against observed ones.
Recently, researchers from Nanjing University and the Institute of Atmospheric Physics (IAP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences developed a simple-to-use Multivariable Integrated Evaluation Tool (MVIETool) coded with Python/NCL to facilitate climate model evaluation and models inter-comparison, improving the MVIE method.
The study was published in Geoscientific Model Development.
"The improved MVIE method can provide a more comprehensive and precise evaluation of climate model performance. With the support of ...
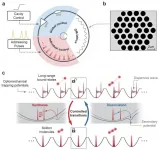
PCF-based 'parallel reactors' unveils collective matter-light analogies of soliton molecules
2021-06-14
Optical solitons are nonlinear optical wave-packets that can maintain their profile during the propagation even in the presence of moderate perturbations, offering useful applications in optical communications, all-optical information processing as well as ultrafast laser techniques. The interaction between optical solitons exhibit many particle-like properties, and has been widely investigated for decades. Particularly, the bound-states of optical solitons in nonlinear dissipative systems, as a result of balanced interactions, have been found to manifest unique matter-light analogies and are epitomized by the "soliton molecules" - compact ...
Hope for infertile men; mice could hold the secret
2021-06-14
Male infertility affects more than 20 million men globally and is a contributing cause to around 50% of infertility in couples. Frequently, male infertility is the result of defects in the sperm tail, the flagellum, which allows the sperm to swim toward an egg. Males with severe infertility can experience multiple sperm malformations, including flagella that are shortened, irregular, coiled or even absent, preventing them from swimming.
In humans, several genetic mutations lead to malformed sperm, including those affecting the sheath that covers the sperm; the mitochondria, which power sperm as they swim; and ...
Study effects paradigm shift in the understanding of how red rot attacks sugarcane
2021-06-14
The fungus Fusarium verticillioides is one of the causes of red rot, the most serious sugarcane disease. Losses average around USD 1 billion per harvest in Brazil alone.
The traditional approach to the etiology of this disease is that it is triggered by Diatraea saccharalis, a moth usually referred to as the sugarcane borer. In the caterpillar stage, this insect bores into the stem of the plant, which is later infected opportunistically by the fungus.
However, a study conducted in Brazil by the University of São Paulo's Luiz de Queiroz College of Agriculture (ESALQ-USP) has turned this model upside down, showing that the trigger is not the insect but the fungus. "It's the first scientifically demonstrated case of a pathogenic ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
Electric field tunes vibrations to ease heat transfer
[Press-News.org] Breakthrough in brain imaging may offer future alternative to functional MRIKeck School of Medicine of USC researchers, working with a Caltech team, demonstrate possibilities of innovative imaging technology to visualize brain function