An easier way to learn quantum processes
2023-07-05
Imagine a world where computers can unravel the mysteries of quantum mechanics, enabling us to study the behavior of complex materials or simulate the intricate dynamics of molecules with unprecedented accuracy.
Thanks to a pioneering study led by Professor Zoe Holmes and her team at EPFL, we are now closer to that becoming a reality. Working with researchers at Caltech, the Free University of Berlin, and the Los Alamos National Laboratory, they have found a new way to teach a quantum computer how to understand and predict the behavior of quantum systems, even with a few simple examples.
Quantum neural networks (QNNs)
The researchers worked on “quantum neural networks” ...
Fast, automated, affordable test for cement durability developed at U of I
2023-07-05
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — Engineers at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign have developed a new test that can predict the durability of cement in seconds to minutes – rather than the hours it takes using current methods. The test measures the behavior of water droplets on cement surfaces using computer vision on a device that costs less than $200. The researchers said the new study could help the cement industry move toward rapid and automated quality control of their materials.
The results of the study, led by Illinois civil and environmental engineering professor Nishant ...
Study finds younger kidney cancer survivors at significant risk for heart problems
2023-07-05
New research out of VCU Massey Cancer Center indicates that many adolescent and young adult kidney cancer survivors are at a significantly elevated risk for heart issues.
Cardiovascular disease is a leading cause of health complications and death among adolescents and young adults (AYAs) diagnosed with cancer, where AYAs are characterized as patients between the ages of 15 and 39.
A study publishing July 5 in the Journal of the National Comprehensive Cancer Network assessed the incidence and risk of hypertension — high blood pressure — and heart failure among AYA patients diagnosed ...
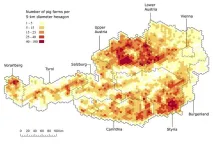
Researchers map Austria's pig trade network for the first time
2023-07-05
The transfer of pigs from one place to another poses the risk of spreading infectious diseases. Knowing how holdings (e.g., farms, markets, etc.) are connected is therefore of crucial importance. In a study by the Complexity Science Hub, the University of Veterinary Medicine Vienna, and the Austrian Agency for Health and Food Safety (AGES), researchers are now drawing a map of the Austrian pig trade for the first time.
Every year, around 250,000 transfers of pigs take place in Austria. Each of these transfers carries a certain risk of spreading swine infectious diseases. To identify possible risks of disease spread and ...
Migrant orangutans learn which foods are good to eat by watching the locals
2023-07-05
Orangutans are dependent on their mothers longer than any other non-human animal, nursing until they are at least six years old and living with her for up to three years more, learning how to find, choose, and process the exceedingly varied range of foods they eat. But how do orangutans that have left their mothers and now live far from their natal ranges, where the available foods may be very different, decide what to eat and figure out how to eat it? Now, an international team of authors has shown that in such cases, migrants follow the rule ‘observe, and do as the locals do’. The results are published in Frontiers in Ecology and Evolution.
“Here we ...
Pure capped mRNA vaccine opens the door to more effective vaccines with lower chances of inflammation
2023-07-05
A research group from Japan has developed a method to produce highly active mRNA vaccines at high purity using a unique cap to easily separate the desired capped mRNA. This ‘Purecap’ technique extracted up to 100% pure Cap2-type mRNA, which showed 3-4 times better production of the protein that stimulates the immune system. These results open up the possibility of purer vaccines with a lower risk of inflammation caused by impurities. Their findings were published in Nature Communications.
mRNA vaccines have been used successfully as therapy against variants ...
New understanding of how the brain processes and stores words we hear
2023-07-05
WASHINGTON – Georgetown University Medical Center neuroscientists say the brain’s auditory lexicon, a catalog of verbal language, is actually located in the front of the primary auditory cortex, not in back of it -- a finding that upends a century-long understanding of this area of the brain. The new understanding matters because it may impact recovery and rehabilitation following a brain injury such as a stroke.
The findings appear in Neurobiology of Language on July 5, 2023.
Riesenhuber’s lab showed the existence of a lexicon for written words at the base of the brain’s left hemisphere in a region ...
Similar to humans, elephants also vary what they eat for dinner every night
2023-07-05
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] — Elephants eat plants. That’s common knowledge to biologists and animal-loving schoolchildren alike. Yet figuring out exactly what kind of plants the iconic herbivores eat is more complicated.
A new study from a global team that included Brown conservation biologists used innovative methods to efficiently and precisely analyze the dietary habits of two groups of elephants in Kenya, down to the specific types of plants eaten by which animals in the group. Their findings on the habits of ...
Endometriosis linked to reduction in live births before diagnosis of the disease
2023-07-05
Endometriosis is linked to a reduction in fertility in the years preceding a definitive surgical diagnosis of the condition, according to new research published today (Wednesday) in Human Reproduction [1], one of the world’s leading reproductive medicine journals.
In the first study to look at birth rates in a large group of women who eventually received a surgical verification of endometriosis, researchers in Finland found that the number of first live births in the period before diagnosis was half that of women without the painful condition. ...
Apex predator of the Cambrian likely sought soft over crunchy prey
2023-07-05
Biomechanical studies on the arachnid-like front “legs” of an extinct apex predator show that the 2-foot (60-centimeter) marine animal Anomalocaris canadensis was likely much weaker than once assumed. One of the largest animals to live during the Cambrian, it was probably agile and fast, darting after soft prey in the open water rather than pursuing hard-shelled creatures on the ocean floor. The study is published today in the journal Proceedings of the Royal Society B.
First discovered in the late 1800s, Anomalocaris canadensis—which means “weird shrimp from Canada” in Latin—has long been thought to be responsible ...
Warmer and murkier waters favour predators of guppies, study finds
2023-07-05
Changes in water conditions interact to affect how Trinidadian guppies protect themselves from predators, scientists at the University of Bristol have discovered.
Known stressors, such as increased temperature and reduced visibility, when combined, cause this fish to avoid a predator less, and importantly, form looser protective shoals.
The findings, published today in the journal Proceedings of the Royal Society B, show guppies’ responses are more affected by the interaction of these stressors than if they acted independently.
Natural ...
Vineyard fungicides pose a threat to survival of wild birds
2023-07-04
New research reveals that wild birds living in vineyards can be highly susceptible to contamination by triazole fungicides, more so than in other agricultural landscapes. Exposure to these fungicides at a field-realistic level were found to disrupt hormones and metabolism, which can impact bird reproduction and survival.
“We found that birds can be highly contaminated by triazoles in vineyards,” says Dr Frédéric Angelier, Senior Researcher at the French National Center for Scientific Research, France. “This contamination was much higher in vineyards relative to other crops, emphasizing that contaminants may especially put birds at risk in these ...
World’s most threatened seabirds visit remote plastic pollution hotspots, study finds
2023-07-04
UNDER STRICT EMBARGO UNTIL 16:00 LONDON TIME (BST) / 11:00 (US ET) ON TUESDAY 4TH JULY 2023
Analysis of global tracking data for 77 species of petrel has revealed that a quarter of all plastics potentially encountered in their search for food are in remote international waters – requiring international collaboration to address.
The extensive study assessed the movements of 7,137 individual birds from 77 species of petrel, a group of wide-ranging migratory seabirds including the Northern Fulmar and European Storm-petrel, and the Critically Endangered Newell’s Shearwater.
This is ...
Sea of plastic: Mediterranean is the area of the world most at risk for endangered seabirds
2023-07-04
New study reveals the areas most at risk of plastic exposure by the already endangered seabirds.
The study, now published in Nature Communications, brings together more than 200 researchers worldwide around a pressing challenge, widely recognized as a growing threat to marine life: the pollution of oceans by plastic. Coordinated by Dr. Maria Dias, researcher at the Centre for Ecology, Evolution and Environmental Changes (cE3c) at the Faculty of Sciences of the University of Lisbon (Ciências ULisboa), ...
Omega-3 oil counteracts toxic effects of pesticides in pollinators
2023-07-04
New research suggests that the use of an omega-3 rich oil called “ahiflower oil” can prevent damage to honey bee mitochondria caused by neonicotinoid pesticides. This research is part of an ongoing project by PhD student Hichem Menail of the Université de Moncton in New Brunswick, Canada.
“Pesticides are a major threat to insect populations and as insects are at the core of ecosystem richness and balance, any loss in insect biodiversity can lead to catastrophic outcome,” says Mr Menail, adding that pesticide-related pollinator declines are also a huge concern for food crops globally.
Imidacloprid, ...
Global efforts to reduce infectious diseases must extend beyond early childhood
2023-07-04
Global efforts to reduce infectious disease rates must have a greater focus on older children and adolescents after a shift in disease burden onto this demographic, according to a new study.
The research, led by Murdoch Children’s Research Institute and the Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation, has found that infectious disease control has largely focused on children aged under five, with scarce attention on young people between five and 24 years old.
Published in The Lancet, the study found three million children and adolescents die from infectious diseases every year, equivalent to one death every 10 seconds. It looked at data across 204 countries ...
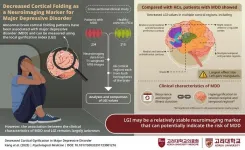
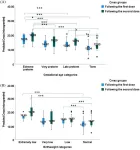
Korea University Medicine study highlights a new biomarker for major depressive disorder
2023-07-04
In appearance, the human brain’s outermost layer, called the cortex, is a maze of tissue folds. The peaks or raised surfaces of these folds, called gyri, play an important role in the proper functioning of the brain. Improper gyrification—or the development of gyri—has been implicated in various neurological disorders, one of them being the debilitating and widespread mental illness­, major depressive disorder (MDD). Although prior studies have shown that abnormal cortical folding patterns are associated with MDD, ...
Luísa Figueiredo was elected as an EMBO member
2023-07-04
The European Molecular Biology Organization (EMBO) has announced today that it will award the lifetime honor of EMBO Membership to Luísa Figueiredo, group leader at the Instituto de Medicina Molecular João Lobo Antunes (iMM, Lisbon, Portugal), in recognition of the excellence of her research and outstanding achievements in the life sciences. EMBO is an international organization of more than 2000 life scientists in Europe and around the world, committed to build a European research environment where scientists can achieve their best work. Aside from Luísa Figueiredo, 68 other EMBO Members have been elected this year.
Luísa ...
Fat-free mass-based dosing: A superior antibiotic regimen for newborns
2023-07-04
Gentamicin is a common antibiotic used to treat critically ill neonates. It is water soluble and is primarily eliminated from the body through urine. For this reason, total body weight, which factors in the weight of the body’s water content, is used to determine gentamicin dosage. However, the total water content of a healthy neonate differs significantly from that of a premature baby. As such, using total body weight to calculate gentamicin dose may lead to non-optimal dose prescription. Premature babies also have weaker kidneys, which means that discrepancy in ...
How mercury emissions from industry can be greatly reduced
2023-07-04
Sulphuric acid is the world’s most used chemical. It is an important reagent used in many industries and it is used in the manufacture of everything from paper, pharmaceuticals and cosmetics to batteries, detergents and fertilisers. It is therefore a worldwide challenge that sulphuric acid often contains one of the most toxic substances – mercury. Researchers at Chalmers University of Technology, Sweden, have now developed a method that can reduce the levels of mercury in sulphuric acid by more than 90 per cent – even from low levels.
“Until now, there has been no viable method for purifying finished sulphuric ...
Long COVID not caused by COVID-19 immune inflammatory response, new research finds
2023-07-04
Long Covid, which affects nearly two-million people in the UK1, is not caused by an immune inflammatory reaction to COVID-19, University of Bristol-led research finds. Emerging data demonstrates that immune activation may persist for months after COVID-19.
In this new study, published in eLife today [4 July], researchers wanted to find out whether persistent immune activation and ongoing inflammation response could be the underlying cause of long Covid.
To investigate this, the Bristol team collected and analysed immune responses in blood samples from 63 patients hospitalised ...
How the ear can inform the brain of whether hearing is impaired
2023-07-04
A cochlear signal, the exact role of which has been unclear since its discovery around 70 years ago, probably gives the brain information on whether the ear is functioning normally or not. This is the conclusion of a study from Linköping University, Sweden. Its findings are an important piece of the puzzle in explaining what happens in the ear in hearing impairment caused by harmful noise, and may in the long run contribute to diagnosing noise-induced hearing injury.
When the ear is exposed to loud sounds, as at a concert or when being in a noisy environment, hearing can be temporarily impaired. Being repeatedly exposed to loud sounds may cause permanent ...
Nanosheet technology developed to boost energy storage dielectric capacitors
2023-07-04
A research group led by Professor Minoru Osada at the Institute for Materials and Systems for Sustainability (IMaSS), Nagoya University in Japan, in collaboration with NIMS, has developed a nanosheet device with the highest energy storage performance yet seen. Their results were published in Nano Letters.
Innovations in energy storage technology are vital for the effective use of renewable energy and the mass production of electric vehicles. Current energy storage technology, such as lithium-ion batteries, has long charging times ...
Older adults who remain more active have a better quality of life, study finds
2023-07-04
A reduction in the amount of time spent physically active when adults are over sixty years old is linked to lower quality of life, a Cambridge study of almost 1,500 adults has shown.
The same was also true for increases in the amount of sedentary time, such as watching TV or reading. The researchers say this highlights the need to encourage older adults to remain active.
Physical activity – particularly when it is moderate-intensity and raises your heart rate – is known to reduce the risk of a number of diseases, including heart disease, stroke, diabetes and cancer. The NHS recommends that adults do at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity activity ...
Joint research team from Korea and Germany seeks to enhance production efficiency of fuel cells with laser machining technology
2023-07-04
Fuel cells used for vessels and airplanes are becoming increasingly lighter to improve efficiency, and this is leading to a decline in the thickness of bipolar plate. In this regard, a laser machining technology for thin bipolar plate, which can help to enhance the production efficiency and quality of fuel cells, has been developed through international R&D innovative collaboration project.
Through international joint research between Korea and Germany, the joint research team consisting of the Korea Institute of Machinery and Materials (President Sang-jin Park, hereinafter referred to as KIMM), an institute under the jurisdiction of the Ministry ...
[1] ... [1813]
[1814]
[1815]
[1816]
[1817]
[1818]
[1819]
[1820]
1821
[1822]
[1823]
[1824]
[1825]
[1826]
[1827]
[1828]
[1829]
... [8818]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.