AI finds a way to people’s hearts (literally!)
2023-07-07
Body
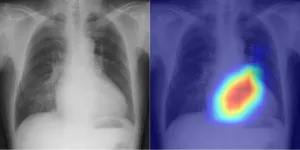
Osaka, Japan - AI (artificial intelligence) may sound like a cold robotic system, but Osaka Metropolitan University scientists have shown that it can deliver heartwarming—or, more to the point, “heart-warning”—support. They unveiled an innovative use of AI that classifies cardiac functions and pinpoints valvular heart disease with unprecedented accuracy, demonstrating continued progress in merging the fields of medicine and technology to advance patient care. The results will be published in The Lancet Digital ...
Mid-life structural jawbone changes may signal women’s subsequent height loss
2023-07-07
Mid-life structural changes to the jawbone may signal subsequent height loss in women, suggests research published in the open access journal BMJ Open.
Dentists, who are likely to spot these on mouth x-rays during routine check-ups, should collaborate with patients’ doctors as this may open up opportunities for prevention, suggest the researchers.
Height loss in women tends to speed up over the age of 75 and is associated with increased risks of ill health and death, say the researchers.
Various explanations have been mooted for this loss, including progressive skeletal deformation, fallen arches in the feet and altered posture, and/or degenerative processes ...
Patient aggression towards doctors’ receptionists in general practice “serious workplace safety concern”
2023-07-07
Patient aggression towards receptionists working in general practice is a “serious workplace safety concern,” concludes a review of the available published evidence, published in the open access journal Family Medicine and Community Health.
Not only does it affect the wellbeing of the individuals concerned, but it also has operational effects by boosting levels of workplace absenteeism and the numbers of staff leaving the healthcare workforce, say the researchers.
Acts of incivility perpetrated against general practice staff, including doctors, are common, but few studies have included the perspectives of the receptionists, ...
Wildlife crossing guards
2023-07-07
Oak Ridge National Laboratory researchers developed a model framework that identifies ways to ensure wildlife can safely navigate their habitats while not unduly affecting infrastructure.
The project centered on the 32,000-acre Oak Ridge Reservation in Tennessee, home to Department of Energy facilities and several at-risk species like the four-toed salamander.
Scientists identified habitats and simulated solutions like conservation buffers and open-bottom culverts to allow safe passage for salamanders and other wildlife, which cost far less than large-scale barrier removal ...
School nurses may be crucial to reducing childhood obesity
2023-07-07
School nurses do much more than bandage scraped knees and take temperatures. A Rutgers study, published in the journal Pediatric Nursing, suggests they also may play a key role in reducing childhood obesity.
Elaine Elliott, a school nurse in Newark, teamed up with Cheryl Holly and the late Sallie Porter, professors at Rutgers University School of Nursing, to test a family-centered, school-based intervention using parents and teachers as role models for healthy eating and other behaviors.
“An important reason for the success of this program was the trust nurses have with parents ...
Leading the way to cyber safety on roads and highways
2023-07-06
A new research center led by the University of Houston is helping prevent potential cyberattacks that could threaten to impede the safe and efficient movement of people and goods in the United States and throughout the world.
CYBER-CARE – the Transportation Cybersecurity Center for Advanced Research and Education – is a U.S. Department of Transportation (USDOT) University Transportation Center (UTC), Tier 1. The center is supported by a $2 million USDOT grant for its first year with anticipated total federal funding of $10 million over five years.
“We all use transportation. Therefore, maintaining ...
Reduced levels of FKBP5 promote atrial fibrillation
2023-07-06
Atrial fibrillation (AFib) is the most common type of heart arrhythmia. This serious condition occurs when the heart beats so fast that the upper chambers of the heart quiver. This irregular heartbeat can lead to severe conditions, including heart failure, dementia and a fivefold increase in the risk of stroke.
AFib affects more than 33.5 million people worldwide, and its prevalence is increasing. Despite intense research to better understand AFib, the molecular mechanism underlying the progression of this condition remains poorly understood.
At Baylor College of Medicine, Dr. ...
Older adults experiencing social isolation are more likely to smoke
2023-07-06
Aging brings wisdom and experience; however, for some individuals getting older can also mean health challenges, loss of friends, and decreased mobility, leading to social isolation. Both the U.S. Surgeon General and the National Academy of Medicine have issued recent warnings about the growing public health concern of social isolation and loneliness and its association with premature death among the elderly.
Not having anyone to call (via phone or online) or not interacting with people in the community are forms of social isolation, which affects nearly a fifth of U.S. ...
Pennington Biomedical working to give children the best chance at a healthy life
2023-07-06
BATON ROUGE – One in five children have obesity in the U.S., and even more are considered overweight. Dr. Amanda Staiano, associate professor at Pennington Biomedical Research Center and director of the Pediatric Obesity and Health Behavior Laboratory, believes childhood obesity is at the top of the list for public health issues of this century because children with obesity are much more likely to develop heart disease, diabetes, asthma, sleep problems and other issues.
Dr. Staiano's background is in developmental psychology, and she studies how to make sure children are growing in a healthy way and in ...
Multiple factors delay timely endometriosis diagnosis, study shows
2023-07-06
Reviewing qualitative studies from the past 20 years, the researchers found a range of contributing factors including: a continuing stigma around periods; society’s normalisation of menstrual pain; and a lack of medical training about the condition.
Endometriosis, which affects 10% of women globally and 1.5 million women in the UK alone, is caused by endometrial (womb) tissue growing outside the womb. It’s extremely painful, exhausting, interferes with daily life and can lead to infertility if untreated.
The researchers found that women in the studies often weren’t sure if their pain was unusual or severe enough to seek treatment. ...
Food labels offer consumer choices but also confusion about animal welfare
2023-07-06
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. – Animal-based food products often come packaged in a wide array of information labels, including organic, natural, grass-fed, humanely raised and pasture-raised.
“There’s some confusion about food labels related to animal welfare,” said Purdue University’s Marisa Erasmus, associate professor of animal sciences and a specialist in animal behavior and welfare. “It’s typically up to the consumer to do their homework and figure out what these different claims mean. Labels do provide consumers with a choice because, in theory, you can ...
Department of Energy announces $2.2 million for U.S.-Japan cooperative research in high energy physics
2023-07-06
WASHINGTON, D.C. - Today, the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) announced $2.2 million for 11 collaborative research projects in high energy physics that involve substantial collaboration with Japanese investigators.
For over forty years, collaboration between U.S. and Japanese scientists has enabled progress in some of the most challenging areas in high energy physics. Working together, researchers explore the universe at the smallest and largest scales, from the most elementary constituents of matter and energy to the nature of space and time. ...
Multistakeholder collaborations are vital to advancing technologies in Parkinson’s
2023-07-06
TUCSON, Ariz., July 6, 2023 — Critical Path Institute (C-Path) and the Center for Health + Technology (CHeT) at University of Rochester today announced the release of two seminal publications about digital health technologies for Parkinson’s. These technologies, such as smartphones and wearable sensors, offer an opportunity for objective, frequent and remote assessment of people with Parkinson’s.
With 10 million people living with Parkinson’s worldwide, collaboration and data sharing are crucial for driving innovation in drug development for the fastest-growing degenerative neurological condition.
Research leaders at CHeT have joined ...
THC use during pregnancy linked to changes in fetal development
2023-07-06
Oregon Health & Science University researchers showed that consuming THC while pregnant could potentially affect development of the fetus and lead to life-long health impacts for offspring.
The preclinical study was published today in the journal Clinical Epigenetics.
Delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol, or THC, is the main psychoactive ingredient in cannabis, a substance growing in popularity and availability in the United States. The prevalence of cannabis use in pregnancy is also rapidly increasing, especially during the first trimester — a time when the fetus is most vulnerable to environmental exposures — ...
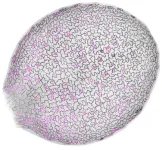
New insight into how plant cells divide
2023-07-06
Every time a stem cell divides, one daughter cell remains a stem cell while the other takes off on its own developmental journey. But both daughter cells require specific and different cellular materials to fulfill their destinies. Animal stem cells use the cytoskeleton – a transient network of structural tubules – to physically pull the correct materials from the parent cell into each daughter cell during the split. Plants also have stem cells that need to distribute different materials ...
Eliminating extra chromosomes in cancer cells prevent tumor growth
2023-07-06
New Haven, Conn. — Cancer cells with extra chromosomes depend on those chromosomes for tumor growth, a new Yale study reveals, and eliminating them prevents the cells from forming tumors. The findings, said the researchers, suggest that selectively targeting extra chromosomes may offer a new route for treating cancer.
The study was published July 6 in the journal Science.
Human cells typically have 23 pairs of chromosomes; extra chromosomes are an anomaly known as aneuploidy.
“If you look at normal skin or normal lung tissue, for example, 99.9% of the cells will have the right number of chromosomes,” said ...
Fantasy football in math class?
2023-07-06
While mathematics is a fundamental skill crucial to daily life, U.S. parents today see math education as boring, outdated, and disconnected from the real world. (1) At the national level, short and long-term achievement trends paint a disconcerting picture of the need for innovative math education strategies:
Math scores among eighth graders dropped in 2022, to the lowest score since 20031
Math scores declined for students regardless of racial and ethnic group, gender, parental education, or disability status1
The COVID-19 pandemic exacerbated declines in math achievement; the median school district lost about ...
Mobile phone data used for public health underrepresent vulnerable populations
2023-07-06
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — Mobile phone data are increasingly used in public health management and disease outbreak response, as demonstrated during the COVID-19 pandemic when location data were used as a proxy for human movement and contacts and informed exposure notification apps. However, a new study led by researchers at Penn State revealed that phone data may not accurately reflect under-resourced or particularly vulnerable populations, who are often underrepresented in other data as well.
If this bias is not acknowledged or complemented with additional ...
Researchers discover potential molecular indicators for Parkinson’s symptoms
2023-07-06
Hand tremors and slowed movements are two of the most widely recognized hallmarks of Parkinson’s disease, and for many sufferers the first indication that something is amiss. But by the time these symptoms manifest, those patients have already lost 50–80 percent of their dopamine neurons—a mass die-off that causes the neurodegenerative disease. Malfunctions in dopamine-dependent areas of the brain are responsible for many of the symptoms, which differ from person to person in an unpredictable way.
A diagnosis at an early age, typically before age 50, can stave off the most severe symptoms for years; when the disease is identified later, its trajectory is often swift ...
Study supports “catch up” HPV test in older women
2023-07-06
For women over the age of 65 who have never had a high-risk human papillomavirus (HPV) test, a “catch up” HPV screening intervention may improve cervical cancer prevention by detecting more cervical pre-cancer lesions as compared to women not offered screening. That is the conclusion of a new study publishing July 6th in the open access journal PLOS Medicine by Mette Tranberg, University Research Clinic for Cancer Screening, Randers Regional Hospital, Denmark, and colleagues.
High-risk human papillomavirus (HPV) test is replacing cytology as the primary cervical cancer screening test in most countries, but many women over 65 years have never had an HPV ...
The solstice switch: Warming’s effects on autumn leaf senescence depend on timing
2023-07-06
How temperate and boreal trees’ leaves respond to climate change remains uncertain. Now, a new study of northern forests reports that while early-season climate warming – that occurring before the summer solstice – tends to be associated with earlier autumn leaf senescence, late-season warming (after the summer solstice) has the opposite impact, delaying onset of leaf senescence in fall. “Improved models of plant development and growth under climate change will need to incorporate the reversal of warming effects after the summer solstice,” write Constantin Zohner and colleagues, authors of the study. Climate change ...
Two studies report: Perovskite-silicon tandem cells that break the 30% efficiency threshold
2023-07-06
In two separate studies, researchers present novel methods that enable the fabrication of high-performance perovskite-silicon tandem solar cells with power conversion efficiencies exceeding 30%. Silicon solar cells – the most commonly deployed photovoltaic (PV) technology – are rapidly approaching their theoretical power conversion efficiency (PCE) limit of 29%. One way to increase the efficiency of a solar cell is to optimize the spectrum of sunlight for conversion into energy. This can be done by stacking two or more interconnected photoactive materials into a singular device, improving ...
Precipitation tolerance helped explain which vertebrate species spread between newly joined continents
2023-07-06
A new study helps explain why rates of species exchange are at least twice as high from west to east than in the opposite direction across Wallace’s Line. The study included an analysis of more than 20,000 species belonging to all 227 families of terrestrial vertebrates present in the Indo-Australian archipelago. As tectonic plates merge, once disparate continents can connect and create new opportunities for biotic exchange. Species movement across newly connected continents millions of years ago continues to shape assemblages of flora and fauna today. One of the most well-known ...
Ready for its close-up: The electron’s permanent electric dipole moment
2023-07-06
A new study with direct implications for one of the most important unresolved questions in physics – the imbalance of matter and antimatter in our universe – reports “the most precise measurement yet” of the size of the electron’s permanent electric dipole moment. The imbalance between matter and antimatter in the Universe can be explained via the breaking of charge parity symmetry. The standard model (SM) of particle physics predicts a slight breaking of this symmetry, but it is insufficient to explain the imbalance actually observed. Many extensions to the standard ...
Policymakers should consider animal welfare in decisions
2023-07-06
Incorporating animal welfare into policymaking may improve policy and practice, according to Rutgers research.
The article, published in Science, notes that animal welfare rarely is considered during policymaking, explains why current tools make it difficult to incorporate the well-being of animals into public policy and identifies methods for remedying these issues.
“Animal welfare is often ignored in policymaking, despite its relevance across many domains ranging from food systems to biomedical research to climate policy,” said Mark ...
[1] ... [1821]
[1822]
[1823]
[1824]
[1825]
[1826]
[1827]
[1828]
1829
[1830]
[1831]
[1832]
[1833]
[1834]
[1835]
[1836]
[1837]
... [8832]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.