Trends in state-level maternal mortality by racial and ethnic group
2023-07-03
About The Study: While maternal mortality remains unacceptably high among all racial and ethnic groups in the U.S., American Indian and Alaska Native and Black individuals are at increased risk, particularly in several states where these inequities had not been previously highlighted. Maternal mortality persists as a source of worsening disparities in many U.S. states and prevention efforts during this study period (1999 to 2019) appear to have had a limited impact in addressing this health crisis.
Authors: Gregory A. ...
Global, regional, and national epidemiology of diabetes in children
2023-07-03
About The Study: Childhood diabetes is an increasing global health challenge with rising incidence. Results of this study suggest that despite the global decline in deaths and disability-adjusted life-years (DALYs), the number of deaths and DALYs remains high among children with diabetes, especially in low Sociodemographic Index regions. Improved understanding of the epidemiology of diabetes in children may facilitate prevention and control.
Authors: Xiaodong Sun, M.D., Ph.D., and Ningning Hou, M.D., of the Affiliated Hospital of Weifang Medical ...
Trends in mortality from poisonings, firearms, and all other injuries by intent
2023-07-03
About The Study: The results of this study suggest that from 1999 to 2020, death rates due to poisonings, firearms, and all other injuries increased substantially in the U.S. The rapid increase in deaths due to unintentional poisonings and firearm homicides is a national emergency that requires urgent public health interventions at the local and national levels.
Authors: Wayne R. Lawrence, Dr.P.H., of the National Institutes of Health in Bethesda, Maryland, is the corresponding author.
To ...
Preventing stroke disability in a community with high rate of poverty
2023-07-03
· Use of successful medications to break up blood clots rose from 4% to 14% due to new approach
Suspected stroke victims now bypass emergency room for CT scanner and nurse stroke experts, who support patient care team
Community educators went to beauty and barber shops, churches and water distribution centers to deliver stroke-awareness talks
Approach can be duplicated by other communities to improve treatment
CHICAGO --- The use of thrombolysis, medications to break up blood clots, for acute ischemic stroke reduces post-stroke disability, but it is underutilized. This particularly affects Black individuals, who experience ...
Everything in balance? How a molecular switch controls lipid metabolism
2023-07-03
Our body’s fat metabolism plays a vital role in energy production in our body. A research team at the University of Basel, Switzerland, has discovered a molecular switch that regulates lipid metabolism in our cells. This switch controls the storage or conversion of lipids into energy.
All organisms need energy to live. We get energy from various components of our food. Our body uses a part of this energy directly and stores the rest. While glucose serves as an immediately available energy source, fats are stored as energy reserve in form of lipid droplets within our cells.
When the body needs energy from these fat stores, lipids are transported ...
AI and CRISPR precisely control gene expression
2023-07-03
Artificial intelligence can predict on- and off-target activity of CRISPR tools that target RNA instead of DNA, according to new research published in Nature Biotechnology.
The study by researchers at New York University, Columbia Engineering, and the New York Genome Center, combines a deep learning model with CRISPR screens to control the expression of human genes in different ways—such as flicking a light switch to shut them off completely or by using a dimmer knob to partially turn down their activity. These precise gene controls could be used to develop new CRISPR-based therapies.
CRISPR is a gene ...
Older frail patients have a 1-in-3 chance of surviving CPR during surgery
2023-07-03
It’s estimated that around 25% of patients who have a cardiac arrest and receive cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) in a normal hospital setting will survive. Those odds shoot up to 50% for patients who receive CPR during or in the immediate period following surgery, where they are closely monitored by specialists who know their medical history and can intervene without delay. But it’s unclear whether that trend applies to frail patients, who are often older and at a higher risk of experiencing CPR-related trauma and complications. Such uncertainty has led some doctors ...
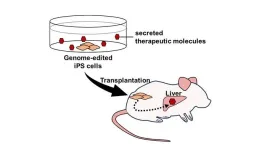
Transplantation of genome-edited iPS cells delivers therapeutic molecules in vivo
2023-07-03
Induced pluripotent stem (iPS) cells have a great impact on biology and medicine, and they are expected to improve regenerative medicine. Since 2014 when a sheet of retinal pigment epithelial cells derived from iPS cells was transplanted into patients with age-related macular degeneration, clinical trials have been conducted with various cell types derived from iPS cells. While iPS cells derived from healthy individuals have been used so far, it is expected that transplantation therapy using iPS cells can be enhanced through genetic modification in the future.
Therefore, we addressed this possibility by utilizing a Fabry disease mouse model, ...
A spatiotemporal intelligent framework and experimental platform for urban digital twins
2023-07-03
Research Background
The era of Big Data features intelligence, ubiquity, and interconnection of all things. It comes with other advanced information technologies, such as the Internet, Cloud Computing (CC), Internet of Things (IoT), and Artificial Intelligence (AI) . Human society has also gradually entered the Ternary Space from the Binary Space. That is, from the Social Space (the sum of human behavior and social activities) to the Information Space (the computer, Internet, and data information built on physical space and social space) . The Ternary Space maps and digitally connect the urban physical and social ...
Sheep and cattle-killing disease carriers never take a break
2023-07-03
Bluetongue virus, an incurable cattle and sheep-killing disease, is spread by tiny flies once thought to disappear in winter. New research demonstrates that though they are harder to find when it’s cold, they remain active.
Bluetongue virus is common in cattle throughout most of the United States, particularly in the southwestern U.S. with nearly 20% of some California cattle herds infected. Due to concerns about spread of this virus, exports of U.S. cattle and cattle products to parts of Europe and Asia have been restricted to prevent contamination.
However, not all infected animals die. The main symptoms are elevated temperatures, lethargy, ...
2023 EPS Europhysics Prize
2023-07-03
Prof. Claudia Felser is a director at the Max Planck Institute for Chemical Physics of Solids in Germany, Prof. B. Andrei Bernevig is a Professor of Physics at Princeton University in the United States and Visiting Ikerbasque Professor at Donostia International Physics Center in Spain.
The Prize will be presented on Wednesday 6th September 2023, during the Awards Session of the 30th General Conference of the EPS Condensed Matter Division (CMD30), to be held in Milan (joint organization with FisMat in Italy). This prize has been awarded since 1975 (this is the 40th edition) and is one ...
A UCLA-led team has received a $925,000 CDC grant to track mpox outbreaks across the US
2023-07-03
The effort is led by Dr. David Talan, a professor of emergency medicine and infectious diseases in the UCLA Department of Emergency Medicine at the David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA.
Summer 2022 saw an outbreak of the disease that infected people in several countries across the globe. That outbreak receded by the following fall after widespread public attention and vaccination of high-risk individuals, prompting the World Health Organization on May 11, 2023 to declare an end to mpox as a global health emergency.
But a recent outbreak among 20 people in Chicago, including some vaccine breakthrough ...
Endocrine Society’s Journal of the Endocrine Society earns first Impact Factor
2023-07-03
WASHINGTON—The Endocrine Society’s Journal of the Endocrine Society (JES) received its first Impact Factor score in 2022, while the Society’s other journals maintained high rankings on the prestigious measure of scholarly publishing.
The 2022 Impact Factors were released June 28 by Journal Citation Reports, an annual publication of Clarivate Analytics.
JES, which launched in 2017, is an open access journal providing rapid publication of clinical research, clinical practice information, and basic research in all areas of endocrinology. The publication also ...
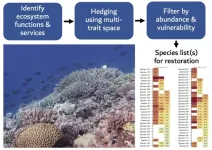
Hedging strategy for coral restoration balances diversity, ecosystem benefits
2023-07-03
Resource managers and conservationists have been offered an innovative, new approach to selecting coral species for reef restoration. An international team of scientists worked together to develop this approach during a workshop organized by the University of Melbourne (U Melbourne) and the Australian Institute of Marine Science (AIMS). In a study published today in the Journal of Applied Ecology, this international team of scientists, led by a University of Hawai‘i (UH) at Mānoa researcher, revealed a strategy for choosing a set of key ...
New approaches against the consequences of birth asphyxia
2023-07-03
Brain damage caused by oxygen deficiency at birth is one of the main causes of death in newborns worldwide. Using a small animal model, researchers from the University Hospital Bonn (UKB) and DZNE tested treatment with 25 different active agents. Seven substances proved to be more effective than the standard therapy of artificial cooling: caffeine performed best. The results, published in the scientific journal Scientific Reports, could pave the way for new treatment options for newborns.
Children, who experience ...
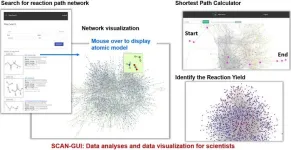
Virtual exploration of chemical reactions
2023-07-03
A new online platform to explore computationally calculated chemical reaction pathways has been released, allowing for in-depth understanding and design of chemical reactions.
Advances in computational chemistry have proven a great boon in the field of reaction design, leading to the discovery of new reaction pathways for the synthesis of high-value compounds. Computational chemistry generates much data, and the process of organizing and visualizing this data is vital to be able to utilize it for future research.
A team of researchers from Hokkaido University, led by Professor Keisuke Takahashi at the Faculty of Chemistry and Professor Satoshi ...
Vaginal suppository containing lactobacilli can prevent recurrent cystitis in women
2023-07-03
Recurrent cystitis (RC) is a frequent infection of the urinary tract and bladder, which is highly prevalent among postmenopausal women. Under healthy circumstances, the human vagina is home to a host of beneficial intestinal bacteria, such as Lactobacilli. However, in the case of urinary tract infections (UTIs), there is a decrease in the abundance of Lactobacilli and an increase in pathogenic bacteria, such as Escherichia coli (E. coli).
Previous studies have shown that changes in vaginal microbiota are a key underlying reason for the development of UTIs. Further, a few clinical trials have demonstrated the utility of Lactobacillus-containing vaginal ...
Amazon dolphins at risk from fishing, dams and dredging
2023-07-03
Amazon river dolphins are under threat from fishing and proposed new dams and dredging, research shows.
Scientists used satellite tags to track eight dolphins in the Peruvian Amazon, to discover where they went in relation to fishing areas and proposed dams and dredging sites.
On average, 89% of the dolphins’ home “range” (the area they live in) was used for fishing.
Dolphins were found to be an average of 252km from the nearest proposed dam and 125km from the nearest proposed dredging site.
While these are significant distances, the dolphins’ ranges ...
Fewer teens now perceive themselves as overweight – international study of more than 745,000 adolescents
2023-07-03
A study involving more than 745,000 adolescents from 41 countries across Europe and North America identified an increase in the amount of teenagers who underestimate their body weight.
Tracking data from 2002 to 2018, the peer-reviewed findings, published today in Child and Adolescent Obesity, demonstrate a noticeable decrease in those who overestimate their weight too.
The team of international experts, who carried out the research, warn these shifting trends in body weight perception could reduce the effectiveness of public health interventions aimed at weight reduction in young people.
“During this impressionable age, body weight perception ...
Aston University appoints UK’s only Regius Professor of Pharmacy
2023-07-03
Professor Ian Wong has been appointed as Regius Professor of Pharmacy at Aston University
A Regius Professorship is a rare award bestowed on a university by the monarch - a mark of exceptionally high standards of research and teaching
Aston University’s Pharmacy School can trace its roots back to 1847.
Under embargo until 00:01 hrs BST 3 July 2023| Birmingham, UK
Aston University has appointed Professor Ian Wong as its new Regius Professor of Pharmacy.
Professor Wong is a pharmacoepidemiologist. His research focuses on the application ...
Why do we articulate more when speaking to babies and puppies?
2023-07-01
Babies and puppies have at least two things in common: aside from being newborns, they promote a positive emotional state in human mothers, leading them to articulate better when they speak. This finding is the result of research by an international team1 that included Alejandrina Cristia, a CNRS Researcher at the Laboratoire de sciences cognitives et psycholinguistique (LSCP) (CNRS/EHESS/ENS-PSL). Scientists studied the vocal behaviour of ten mothers to better understand why mothers articulate more when speaking to infants. Participants were asked to ...
COVID-19 vaccination reduced disease disparities between low- and high-income communities
2023-07-01
COVID-19 vaccination helped reduce disparities in disease incidence between low- and high-income communities, according to a new analysis led by Cedars-Sinai investigators.
While lower-income communities had lower vaccination rates than higher-income communities, the impact of vaccination on disease incidence was larger in lower-income communities. As a result, investigators say, vaccination led to reduced income-related disparities in COVID-19 incidence.
The findings were published today in the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report, a publication of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
“This study is a unique demonstration ...
Immune-boosting therapy helps honey bees resist deadly viruses
2023-07-01
Scientists have successfully tested a novel way of boosting honey bees’ immune systems to help them fend off deadly viruses, which have contributed to the major losses of the critical pollinator globally.
In a new study, the research team, which includes entomologists with the University of Florida, the Agricultural Research Service-USDA, Louisiana State University and the University of Nebraska-Lincoln, showed that prompting honey bees’ cells to produce free radicals helped the bees weather a host of viruses. In fact, the treatment greatly reduced, and in some cases, nearly eliminated virus ...
Biomedical Sciences researcher gets $2.67 million grant to study cardiac disease in diabetes
2023-07-01
ATLANTA — Dr. Jun Zou, a research assistant professor in the Institute for Biomedical Sciences at Georgia State University, has received a five-year, $2.67 million federal grant to study the link between gut dysbiosis, an imbalance in the microbiota, and cardiac disease in diabetes.
The grant from the National Institutes of Health’s National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute will be used to explore the role of diabetes-induced alteration of gut microbiota ...
US Department of Energy releases plan to ensure free, immediate, and equitable access to federally funded research
2023-06-30
WASHINGTON, D.C. — The U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) today released a plan to ensure the Department’s Federally funded research is more open and accessible to the public, researchers, and journalists as part of a broader effort by the Biden-Harris Administration to make government data more transparent. With 17 National Laboratories and scores of programs that fund university and private research, DOE directly supports thousands of research papers per year, and, when this plan goes into effect, those findings will be available ...
[1] ... [1815]
[1816]
[1817]
[1818]
[1819]
[1820]
[1821]
[1822]
1823
[1824]
[1825]
[1826]
[1827]
[1828]
[1829]
[1830]
[1831]
... [8818]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.