World’s first glue derived from industrial bio-waste will make furniture recyclable
2023-06-28
An innovative new adhesive, derived from purified and refined industrial bio-waste, should enable 90 percent of engineered wood products, such as furniture and construction boards, to become fully recyclable and helping to develop a sustainable circular economy in this sector.
Currently, formaldehyde adhesives used by manufacturers, are toxic petrochemicals that are carcinogenic in nature. This prevents recycling and incineration meaning most construction panels and furniture made from engineered wood ends up in landfill. The new adhesive, derived from extracted and purified waste is ...
McMaster University team discovers hormonal pathway that increases calorie burning during weight loss
2023-06-28
Hamilton, ON (June 28, 2023) - Researchers led by McMaster University professor Gregory Steinberg and postdoctoral research fellow Dongdong Wang have uncovered a key mechanism for promoting weight loss and maintaining the burning of calories during dieting.
The research team studied a hormone called GDF15 that they had previously shown to reduce appetite in response to the type 2 diabetes drug metformin. Their latest findings, published in Nature on June 28, showed that GDF15 also has the potential to help with weight loss.
The research opens new possibilities to help people maintain weight loss ...
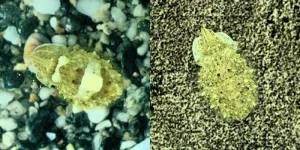
Cuttlefish camouflage: more than meets the eye
2023-06-28
Cuttlefish, along with other cephalopods like octopus and squid, are masters of disguise, changing their skin color and texture to blend in with their underwater surroundings.
Now, in a study published 28 June in Nature, researchers at the Okinawa Institute of Science and Technology (OIST) and the Max Planck Institute for Brain Research have shown that the way cuttlefish generate their camouflage pattern is much more complex than previously believed.
Cuttlefish create their dazzling skin patterns by precisely controlling millions of tiny skin pigment cells, ...
Outcomes of financial penalties to encourage hospital price transparency
2023-06-28
About The Study: Hospital compliance with federal price transparency regulations is high and increasing. The results of this study suggest that financial penalties may be a useful policy enforcement mechanism in health care. These findings are relevant for the enforcement of other regulations designed to promote transparency in health care.
Authors: Yunan Ji, Ph.D., of Georgetown University in Washington, D.C., is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link ...
Brain volume changes in aging individuals with normal cognition
2023-06-28
About The Study: In this study of adults without dementia, age-dependent brain structure volumes and volume change rates in various brain structures were characterized using serial magnetic resonance imaging scans. These findings clarified the normal distributions in the aging brain, which are essential for understanding the process of age-related neurodegenerative diseases.
Authors: Shohei Fujita, M.D., Ph.D., of the University of Tokyo, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.18153)
Editor’s Note: Please ...
Long-range neuronal connections drive glioblastoma invasion
2023-06-28
Glioblastoma (GBM) is the most aggressive and lethal form of brain tumor. Despite treatment, GBM recurrence is inevitable and tends to occur outside surgical margins or in locations remote to the primary tumor, highlighting the central role played by tumor infiltration in this malicious disease.
Little is known about the underlying molecular mechanisms driving GBM infiltration, but in a new study published in the journal Nature, researchers at Baylor College of Medicine working with animal models reveal a novel process by which neurons in locations remote to the primary tumor provoke expression of genes from gliomblastoma that subsequently ...
Largest-ever atlas of normal breast cells brings unprecedented insights into mammary biology
2023-06-28
HOUSTON ― A new study led by researchers at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer, University of California, Irvine and Baylor College of Medicine has created the world’s largest and most comprehensive map of normal breast tissue, providing an unprecedented understanding of mammary biology that may help identify therapeutic targets for diseases such as breast cancer.
The Human Breast Cell Atlas, published today in Nature, used single-cell and spatial genomic methods to profile more than 714,000 cells from 126 women. The breast atlas highlights 12 major cell types ...
Research breakthrough could be significant for quantum computing future
2023-06-28
Scientists using one of the world’s most powerful quantum microscopes have made a discovery that could have significant consequences for the future of computing.
Researchers at the Macroscopic Quantum Matter Group laboratory in University College Cork (UCC) have discovered a spatially modulating superconducting state in a new and unusual superconductor Uranium Ditelluride (UTe2). This new superconductor may provide a solution to one of quantum computing’s greatest challenges.
Their finding has been published in the prestigious journal Nature.
Lead author Joe Carroll, a PhD researcher working with UCC Prof. of Quantum Physics Séamus Davis, explains the subject of the paper.
“Superconductors ...
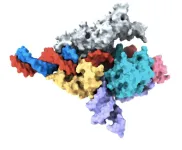
Researchers uncover new CRISPR-like system in animals that can edit the human genome
2023-06-28
A team of researchers led by Feng Zhang at the Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard and the McGovern Institute for Brain Research at MIT has uncovered the first programmable RNA-guided system in eukaryotes — organisms that include fungi, plants, and animals.
In a study in Nature, the team describes how the system is based on a protein called Fanzor. They showed that Fanzor proteins use RNA as a guide to target DNA precisely, and that Fanzors can be reprogrammed to edit the genome of human cells. The compact Fanzor systems have the potential to be more easily delivered to cells and tissues as therapeutics than CRISPR/Cas systems, ...
Starlight and the first black holes: researchers detect the host galaxies of quasars in the early universe
2023-06-28
New images from the James Webb Space Telescope have revealed, for the first time, starlight from two massive galaxies hosting actively growing black holes – quasars – seen less than a billion years after the Big Bang. A new study in Nature this week finds the black holes have masses close to a billion times that of the Sun, and the host galaxy masses are almost one hundred times larger, a ratio similar to what is found in the more recent universe. A powerful combination of the Subaru Telescope and the JWST has paved a new path to study the distant universe.
The existence of such massive black holes in the distant universe has created more questions ...
Life after death: Hawaiʻi astronomers find a planet that shouldn’t exist
2023-06-28
Maunakea, Hawaiʻi - When our Sun reaches the end of its life, it will expand to 100 times its current size, enveloping the Earth. Many planets in other solar systems face a similar doom as their host stars grow old. But not all hope is lost, as astronomers from the University of Hawaiʻi Institute for Astronomy (UH IfA) have made the remarkable discovery of a planet’s survival after what should have been certain demise at the hands of its sun.
The Jupiter-like planet 8 UMi b, officially named Halla, ...
Genetic variant linked with faster progression of multiple sclerosis
2023-06-28
Contact: Bess Connolly, 203-432-1324 or elizabeth.connolly@yale.edu
Embargoed For Release: 11 A.M. ET June 28, 2023
Genetic variant linked with faster progression of multiple sclerosis
New Haven, Conn. — A study of more than 22,000 people with multiple sclerosis (MS) has for the first time identified a genetic variant associated with faster progression of the disease, an accumulation of disability that can rob patients of their mobility and independence over time.
Multiple sclerosis begins as an autoimmune disease where the immune system attacks the brain and the spinal cord, resulting in symptom flares, called relapses, as well as longer-term degeneration known ...
High-speed proton transaction
2023-06-28
How did life begin on Earth? Experts have long been fascinated by this question and over the years have come up with a variety of theories. One hypothesis is that the origin of life can be traced back to warm little ponds which are thought to have existed on Earth four billion years ago. The water in these ponds probably contained urea molecules; these were exposed to ultraviolet radiation from the sun, which at that time would have penetrated to the surface of the earth largely unimpeded. This high-energy radiation was able to convert ...
The complex role of pyroptosis in lung cancer: a Chinese Medical Journal Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine Review
2023-06-28
Lung cancer, one of the most aggressive forms of cancer, continues to be a leading cause of death worldwide. Although several new therapies have been developed for this disease, it has a poor prognosis in its advanced stages. A primary reason underlying this poor response to treatment is the formation of a tumor microenvironment (TME)— the environment that surrounds a tumor and plays a crucial role in its growth. To develop approaches that can overcome treatment resistance during the advanced stages of this cancer, we need to understand ...
The American Association for Anatomy calls for ethical treatment and justice for human body donors
2023-06-28
ROCKVILLE, MD—JUNE 15, 2023 – In response to the allegations of illicit buying and selling of stolen body parts from Harvard Medical School's body donation program, the American Association for Anatomy (AAA) stands united in strong condemnation of the commercialization of human body donors and any action that violates donor ethics and trust. Our heartfelt support goes out to the affected families.
Any act that violates the principles of respect and dignity owed to every individual, in life or death, undermines the sanctity of ...
Scientists design a nanoparticle that may improve mRNA cancer vaccines
2023-06-28
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE
Johns Hopkins Medicine scientists say they have developed a nanoparticle — an extremely tiny biodegradable container — that has the potential to improve the delivery of messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA)-based vaccines for infectious diseases such as COVID-19, and vaccines for treating non-infectious diseases including cancer.
Results of tests in mice, reported June 20 in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, show that the degradable, polymer-based nanoparticle carrying an mRNA-based vaccine, when injected into the ...
Undergrad-driven project reveals drought’s effects on painted turtles
2023-06-28
A projected rise in droughts could muddy the waters for painted turtles and some fellow freshwater-dwelling reptiles, says 11 years of data collected by 50-plus undergraduates from the University of Nebraska–Lincoln.
Two recent studies based on the data suggest that drought can lower the survival odds, slow the growth and even skew the ratio of female-to-male painted turtles inhabiting the ponds of the Cornhusker State. Those outcomes emerged despite the water level of a sampled pond in southwestern Nebraska remaining relatively steady throughout the observed periods ...
One-two punch: Novel drug pairing could beat pancreatic cancer
2023-06-28
Mutations in the KRAS gene are the major driver of pancreatic cancer. The resulting protein controls multiple signaling pathways involved in cell growth and survival. In cancer, the gene is mutated to be permanently “on,” driving cells to excessively multiply and form tumors.
New drugs have recently been developed to inhibit KRAS and appear to be therapeutically promising. However, pancreatic cancer is especially prone to drug resistance. Most drugs only work for a short period of time before the cancer finds its way around them.
Previous experiments revealed a potential reason why: a group ...
Field-controlled microrobots fabricated by photopolymerization
2023-06-28
A review paper by scientists at the Beijing Institute of Technology summarized the recent research on field-controlled microrobots fabricated by photopolymerization.
The new review paper, published on Jun. 6 in the journal Cyborg and Bionic Systems, provided an overview the photopolymerization technologies utilized in the fabrication of field-controlled microrobots and introduced the photopolymerized microrobots actuated by different field forces and their functions.
“Field-controlled microrobots have attracted extensive research in the ...
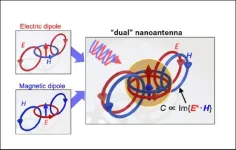
Developing a nano-antenna that forms a near field of circularly polarized light: Promising applications in highly sensitive sensing and asymmetric photochemical reactions for molecular chirality
2023-06-28
Main Points
The research group proposed and tested a nano-antenna that uses the specific optical resonance of dielectric nanoparticles to form a near field of circularly polarized light.
This technique bolsters the circularly polarized light-selective response of chiral molecules.
The results of this study should provide applications in chirality analysis and asymmetric photochemical reactions for biomolecules, chemical substances, and pharmaceuticals.
Research Background
“Chirality” refers to the property of a substance that cannot be superimposed on its mirror image. Since the mirror image isomers of chiral molecules ...
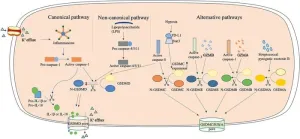
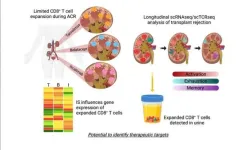
Research reveals novel insights into transplant rejection and new drug development targets
2023-06-28
CINCINNATI -- Imagine a day when a urine test could inform a doctor precisely why a kidney transplant patient was experiencing organ rejection and suggest the best medication for specifically addressing the problem.
That day took a leap closer to reality thanks to a remarkable set of single-cell analyses that have identified the most specific cellular signatures to date for kidney transplant rejection. The findings were detailed May 25, 2023, in JCI The Journal of Clinical Investigation.
The study results reflect eight years of teamwork led by experts at Cincinnati Children’s and the University of Cincinnati College of Medicine with contributions ...
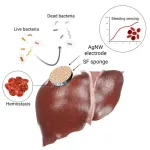
All-in-one device for hemorrhage control
2023-06-28
(LOS ANGELES) – June 28, 2023 - A multi-faceted device for effectively treating deep, non-compressible, and irregularly-shaped wounds has been engineered by the scientists at the Terasaki Institute for Biomedical Innovation (TIBI). As outlined in their recent paper in Advanced Science, the device provides rapid hemorrhage management, has minimal inflammatory effects, and provides infection control. It also has tunable biodegradation rates, making it usable for both internal and external use, and features sensing capabilities for long-term hemorrhage monitoring. This versatile device is highly beneficial ...
Boom! Detecting gregarious goliath groupers using their low-frequency pulse sounds
2023-06-28
From growls to pulses to booms, whales, fish and crustaceans all produce sounds. In fact, more than 800 species of fish are capable of making noises for a variety of functions such as courtship and mating, defending their turf or responding to threats. Each of these species has a characteristic waveform that is unique to their “calls.” As such, detecting structures in these signals can be used to identify the sounds of different species.
Classifying sounds produced by fish will help to understand how they respond to environmental changes ...
Squid-inspired soft material is a switchable shield for light, heat, microwaves
2023-06-28
With a flick of a switch, current technologies allow you to quickly change materials from being dark to light, or cold to hot, just by blocking or transmitting specific wavelengths. But now, inspired by squid skin, researchers in ACS Nano report a soft film that can regulate its transparency across a large range of wavelengths — visible, infrared and microwave — simultaneously. They demonstrated the material in smart windows and in health monitoring and temperature management applications.
Unique to the skin of squid and other cephalopods, iridocytes and chromatophores reversibly ...
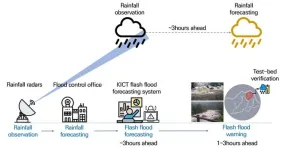
Forecasting flash floods an hour in advance
2023-06-28
Korea has recently seen a surge in localized torrential rain and floods due to global warming. Frequent flash floods are hard to forecast and, when forecast, the accuracy is low. This often leads to major disasters that take hundreds of lives, as seen in Germany and China (Henan) in July 2021. Floods are one of the deadliest types of natural disasters, but climate change has made the forecasting of them even more challenging.
Researchers at the Korea Institute of Civil Engineering and Building Technology (KICT, President Kim Byung-Suk) have developed a system that can forecast ...
[1] ... [1823]
[1824]
[1825]
[1826]
[1827]
[1828]
[1829]
[1830]
1831
[1832]
[1833]
[1834]
[1835]
[1836]
[1837]
[1838]
[1839]
... [8819]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.