National Cancer Institute grant targets cancer disparities
2023-06-26
Weill Cornell Medicine and Columbia University have been awarded a $9.8 million, five-year grant from the National Cancer Institute (NCI), part of the National Institutes of Health, to help combat cancer disparities fueled by persistent poverty.
The competitive award, will engage faculty members from Weill Cornell Medicine, Columbia University Mailman School of Public Health, Columbia University School of Nursing and SUNY Downstate Health Sciences University in a collaborative effort to develop a specialized research center and spearhead two large projects in ...
SNMMI elects Jean-Luc C. Urbain, MD, PhD, FASNC, as Vice President-Elect at 2023 Annual Meeting
2023-06-26
Chicago, Illinois (Embargoed until 9:30 am CDT, Monday, June 26, 2023)—Jean-Luc C. Urbain, MD, PhD, FASNC, professor of radiology/nuclear medicine and medicine, vice chair of theranostics, and director of nuclear medicine at Roswell Park Cancer Center at the University of Buffalo in New York, has been elected vice president-elect for the Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging (SNMMI). SNMMI introduced a new slate of officers during its 2023 Annual Meeting, held June 24-27.
“With the advent of new precision oncology nuclear therapies and the explosion of the field of theranostics, there has never been a more exciting ...
Umar Mahmood, MD, PhD, receives first annual SNMMI Minoshima-Pappas Transformational Leadership Award
2023-06-26
Chicago, Illinois (Embargoed until 9:30 am, CDT, Monday, June 26, 2023)—Umar Mahmood, MD, PhD, chief of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging, director of the Center for Precision Imaging, and associate chair for imaging sciences in the Department of Radiology at Massachusetts General Hospital and professor of radiology at Harvard Medical School in Boston, Massachusetts, has been named as the first recipient of the new Minoshima-Pappas Transformational Leadership Award. Mahmood was presented the award by the Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging (SNMMI) at its 2023 Annual Meeting.
The Minoshima-Pappas Transformational Leadership Award was ...
Peter J. H. Scott, PhD, receives SNMMI Sam Gambhir Trailblazer Award
2023-06-26
Chicago, Illinois (Embargoed until 9:30 am, CDT, Monday, June 26, 2023)—Peter J. H. Scott, PhD, associate professor of radiology and pharmacology, division director of nuclear medicine, and director of the PET Center at the University of Michigan in Ann Arbor, Michigan, has been named as the 2023 recipient of the Sam Gambhir Trailblazer Award. Scott was presented the award by the Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging (SNMMI) at its 2023 Annual Meeting.
Scott's nuclear medicine and molecular imaging research spans ...
Act now to prevent uncontrolled rise in carbon footprint of computational science, say Cambridge scientists
2023-06-26
Cambridge scientists have set out principles for how computational science – which powers discoveries from unveiling the mysteries of the universe to developing treatments to fight cancer to improving our understanding of the human genome, but can have a substantial carbon footprint – can be made more environmentally sustainable.
Writing in Nature Computational Science, researchers from the Department of Public Health and Primary Care at the University of Cambridge argue that the scientific community needs to act now if it is to ...
Study of Earth’s stratosphere reduces uncertainty in future climate change
2023-06-26
New research led by the University of East Anglia (UEA) reduces uncertainty in future climate change linked to the stratosphere, with important implications for life on Earth.
Man-made climate change is one of the greatest challenges facing us today, but uncertainty in the exact magnitude of global change hampers effective policy responses.
A significant source of uncertainty relates to future changes to water vapour in the stratosphere, an extremely dry region of the atmosphere 15–50 km above the Earth’s surface.
Future increases in water vapour here risk amplifying climate change and slowing down the recovery ...
New study reveals brain's potential to regulate fentanyl consumption, offering hope in the fight against opioid addiction
2023-06-26
The opioid crisis continues to pose a grave public health concern, with synthetic opioids such as fentanyl posing a major risk for development of addiction and death due to overdose. In a ground-breaking development, a recent study by the research group led by Prof. Ami Citri at the Hebrew University of Jerusalem's Edmond and Lily Safra Center for Brain Sciences has unveiled crucial insights into the brain's potential ability to regulate the urge to consume fentanyl. This discovery offers a glimmer of hope in the ongoing battle against ...
Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program access and racial disparities in food insecurity
2023-06-26
About The Study: Racial disparities in food insecurity were found among low-income households that do not participate in Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (SNAP) but not among those that do, suggesting that access to SNAP should be improved. These results also highlight the need to examine the structural and systemic racism in food systems and in access to food assistance that may contribute to disparities.
Authors: Laura J. Samuel, Ph.D., R.N., of the Johns Hopkins School of Nursing in Baltimore, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.20196)
Editor’s ...
Study of deep-sea corals reveals ocean currents have not fuelled rise in atmospheric carbon dioxide
2023-06-26
Pioneering analysis of deep-sea corals has overturned the idea that ocean currents contributed to increasing global levels of carbon dioxide in the air over the past 11,000 years.
The study, led by the University of Bristol in the UK and Nanjing University in China, examined historic deep-sea corals to shed intriguing new light on the history of ocean chemistry.
Understanding what has led to the pre-industrial rise in carbon dioxide (CO2) levels during the Holocene period, which dates back some 11,700 years to the present day, is a source of scientific debate. One theory suggests the increase in physical ...
Tuning T cell traits and functions with biomechanical materials
2023-06-26
By Benjamin Boettner
(Boston) — The successful campaign of adoptive T cell therapies, a type of immunotherapy in which immune T cells are collected from a patient, enhanced outside of the body, and reinfused back into the same patient, especially against blood cancers is well under way. But improving the ability to create patient-specific T cell populations with specific traits and functions could broaden clinicians’ repertoire of T cell therapies.
One way to approach this goal is to better understand how T cells’ traits and functions, including their cytotoxic effects on ...
New understanding of why kidney cancers become metastatic discovered by MD Anderson researchers
2023-06-26
HOUSTON ― Researchers at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer have engineered a new model of aggressive renal cell carcinoma (RCC), highlighting molecular targets and genomic events that trigger chromosomal instability and drive metastatic progression.
The study, published today in Nature Cancer, demonstrates that the loss of a cluster of interferon receptor (IFNR) genes plays a pivotal role in allowing cancer cells to become tolerant of chromosomal instability. This genomic feature may be used to help clinicians predict a tumor’s potential to become metastatic and treatment resistant.
Researchers led by Luigi Perelli, ...
Dry days trigger leaves to send a surprising growth signal telling roots to keep growing
2023-06-26
Scientists at the Sainsbury Laboratory Cambridge University (SLCU) have discovered a new molecular signalling pathway, triggered when leaves are exposed to low humidity, that ensures plant roots keep growing towards water.
In dry soil conditions, plants take action to try and conserve water by producing the drought stress hormone abscisic acid (ABA). For decades plant scientists thought that in response to dry soil, ABA was made in the roots and then transported to the leaves. In this root-to-shoot signalling pathway, ABA closes microscopic leaf pores, called stomata, to prevent water loss from leaves. In recent years, scientists ...
Study on rare antibodies hints at strategy tweaks that may future-proof COVID-19 vaccines
2023-06-26
New research examining how frequently our bodies produce broadly neutralizing antibodies (bnAbs) capable of thwarting a range of SARS-CoV-2 variants offers clues on the strategy tweaks that could potentially future-proof COVID-19 vaccines.
To counter invading viruses, our body deploys specific antibodies, among them the neutralizing kind targeting the receptor-binding domain (RBD) — the “Velcro hooks” used by pathogens to fasten onto our cells. As SARS-CoV-2 accumulates genetic mutations, new variants emerge donning sneaky disguises to outsmart our defenses. So-called bnAbs are elite neutralizing antibodies that can keep up ...
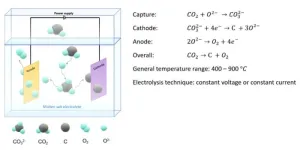
Overview of CO2 capture and electrolysis technology in molten salts: operational parameters and their effects
2023-06-26
Carbon dioxide capture, storage, and utilization have been widely researched to achieve CO2 zero emission and resolve climate change issues. Molten salt electrolysis is one promising method to simultaneously capture and convert CO2 into valuable carbon materials and oxygen with high current efficiencies, to provide a promisingly positive cash flow. However, this method still requires investigation for future scale-up applications. A team of scientists reviews the molten salt CO2 electrolysis’s ...
Researchers urge caution in gene editing early human embryos following findings that it could have unexpected and dangerous consequences Further research to refine gene editing technology is needed
2023-06-26
Copenhagen, Denmark: Scientists have discovered that the cells of early human embryos are often unable to repair damage to their DNA. The researchers say that this has important implications for the proposed use of gene editing techniques to remove serious inherited diseases from embryos, as well as for IVF in general.
Presenting the research to the 39th annual meeting of the European Society of Human Reproduction and Embryology (ESHRE) [1], Dr Nada Kubikova from the University of Oxford (UK), said: “Gene editing has the potential to correct defective genes, a process that usually involves first breaking and then ...
New sensor chip advances rapid, cost-effective disease diagnostics
2023-06-26
Media Inquiries to Laura Muntean, laura.muntean@ag.tamu.edu, 6012481891
Written by Gabe Saldana, 956-408-5040, gabe.saldana@ag.tamu.edu
Texas A&M AgriLife Research scientists and collaborators at Iowa State University have developed a sensor chip that can detect many disease pathogens with 10 times the sensitivity of currently available methods.
The chip also eliminates the need for chemical dye reagents typically used in the diagnostic process. The new technology shows promise for rapid, low-cost point-of-care diagnostic capabilities in plants, foods, animals and humans, including detecting foodborne pathogens, bird flu and COVID-19.
An ...
Opting to freeze eggs can help women have babies when they are older, but many do not use their frozen eggs
2023-06-26
Copenhagen, Denmark: More than 40% of women who chose to freeze their eggs in their 30s were able to have babies later in life when they returned to the fertility clinic, according to research presented today (Monday) at the 39th annual meeting of the European Society of Human Reproduction and Embryology (ESHRE) [1].
However, many of the women in the study who had frozen their eggs (known as elective oocyte cryopreservation) had not returned to the fertility clinic and many who did return chose fertility treatments that did not involve their frozen eggs.
The research was presented by Dr Ezgi Darici, a clinical fellow at the Centre for Reproductive Medicine at ...
Fertility may decline early in women treated for Hodgkin lymphoma in childhood, but most who try for babies when they are young are successful
2023-06-26
Copenhagen, Denmark: Women treated for childhood Hodgkin lymphoma may face declining fertility at a younger age, according to research presented today (Monday) at the 39th annual meeting of the European Society of Human Reproduction and Embryology (ESHRE) [1].
The research also found that women treated for Hodgkin lymphoma may have to try for longer to become pregnant; however, the majority of women in the study who had tried to become pregnant were ultimately successful.
The research was presented by Dr Katja Drechsel from the Princess Máxima Centre for Paediatric Oncology, ...
NSF invests $162 million in research centers to accelerate materials science from lab to factory
2023-06-26
A $162 million investment from the U.S. National Science Foundation will drive the creation of advanced materials capable of remarkable things — from being tough enough to withstand the heat of a fusion reactor to processing information at the quantum level. Nine Materials Research Science and Engineering Centers (MRSECs) will each receive $18 million over six years. The centers aim to transform fundamental scientific breakthroughs into tangible benefits for multiple sectors of the U.S. economy and innovations ...
Towards synthesis of phenanthridine-based pharmaceutical compounds
2023-06-26
Phenanthridines are heterocyclic compounds consisting of two six-membered benzene rings fused to a six-membered ring containing nitrogen. They are found in many naturally occurring organic compounds known for their anticancer and antitumor properties. Due to their potential medicinal applications, there is a significant interest in synthesizing phenanthridine derivatives in laboratories. A promising synthesis approach involves radical isonitrile insertion to produce imidoyl radical intermediates, which then cyclize to form phenanthridine. However, the exact mechanism of isonitrile insertion is not well understood.
Recently, a team of researchers, led by Associate Professor ...
Arsenic levels decline for most highly exposed U.S. communities served by public water systems following final arsenic ruling
2023-06-26
June 26, 2023-- Reductions in arsenic exposure among the U.S. population were reported for users of public water systems in the South and West, and among Mexican American participants, according to a new study by Columbia University Mailman School of Public Health. Differences in change over time were reported by educational attainment in addition to by region, race/ethnicity, and public water arsenic level. The full findings are published in the journal Environmental Pollution.
The Final Arsenic Rule, first enforced since 2006, reduced the arsenic maximum contaminant level to 10 μg/L in public water systems.
“We ...
No simple answer for why people believe in conspiracy theories
2023-06-26
People can be prone to believe in conspiracy theories due to a combination of personality traits and motivations, including relying strongly on their intuition, feeling a sense of antagonism and superiority toward others, and perceiving threats in their environment, according to research published by the American Psychological Association.
The results of the study paint a nuanced picture of what drives conspiracy theorists, according to lead author Shauna Bowes, a doctoral student in clinical psychology at Emory ...
Wiley and the European College of Sport Science announce partnership
2023-06-26
HOBOKEN, N.J. – June 26, 2023 – Wiley, a knowledge company and global leader in research, publishing and knowledge solutions, today announced that it will publish the European Journal of Sport Science (EJSS) on behalf of the European College of Sport Science (ECSS) beginning in January 2024, spearheading the journal’s transition to open access.
“EJSS is one of the preeminent multidisciplinary sport science journals,” said Allyn Molina, Vice President for Life Sciences at Wiley. “As a publisher at the forefront ...
A potential breakthrough treatment for cystic fibrosis enters clinical trial led by CI Med and U of Iowa researchers
2023-06-26
URBANA, Ill. – Clinical testing is underway for a potentially groundbreaking new treatment for cystic fibrosis. Pioneered by scientists at Carle Illinois College of Medicine at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign and the Carver College of Medicine at the University of Iowa in partnership with the spin-out biotechnology company, cystetic Medicines, this promising inhalable molecular prosthetic is intended to improve lung function in people with CF who cannot benefit from current therapies.
The launch of this clinical trial is an important ...
Ataxias: International Award for Bonn Patient Care and Research
2023-06-26
The Ataxia Center at the University Hospital Bonn (UKB) and DZNE have been awarded the title “Ataxia Center of Excellence” by the US National Ataxia Foundation (NAF) for their patient care and research – as the only organization in Europe. The foundation represents patient interests and is one of the world’s major non-governmental funders of ataxia research. These rare brain diseases are characterized by progressive loss of balance and coordination, accompanied by slurred speech. It is estimated that this condition affects around 16,000 women and men in Germany.
The NAF awarded the title “Ataxia ...
[1] ... [1847]
[1848]
[1849]
[1850]
[1851]
[1852]
[1853]
[1854]
1855
[1856]
[1857]
[1858]
[1859]
[1860]
[1861]
[1862]
[1863]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.