New state-of-the-art robotics lab to be created at Maynooth University
2023-06-14
The Maynooth University Foundation is delighted to announce a significant donation from Intel Ireland to support the creation of a state-of-the-art robotics lab. The lab will provide MU students with invaluable hands-on learning experiences using cutting-edge robotic technologies.
The establishment of the robotics lab at a total cost of €150,000 will equip Maynooth University students with access to innovative robotic technologies and equipment used by engineers from Intel and other companies. This hands-on experience will enable them to bridge the gap between classroom learning and real-world application, empowering them to develop and refine their skills in robotics.
The ...
Inhaled beta-2 agonists are not associated with a lower risk of Parkinson’s disease
2023-06-14
Beta-2 agonists are bronchodilators commonly used in the treatment of asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Although beta-2 agonists have been associated with a reduced risk of Parkinson’s disease in some previous epidemiological studies, this association was not found in a recent register-based study from the University of Eastern Finland. The findings were published in Clinical Epidemiology.
Accumulation of the alpha-synuclein protein in the brain plays a central role in Parkinson’s ...
Slightly lost bumblebees use scent to find their way home
2023-06-14
Put yourself in the exoskeleton of a bumblebee for a moment: your world would be a riot of colors and scents, both essential to guide your search for pollen and nectar. Bumblebees have excellent vision: they have a pair of compound eyes that can distinguish UV and most colors except red, plus three additional simple eyes specialized in detecting polarized light. Their sense of smell dwarfs ours: approximately 100 times more sensitive, and capable of sniffing out illegal drugs or explosives at airports, confirming pregnancy in women, or detecting cancers and diabetes in early-stage patients.
Now, ...
New way of identifying proteins supports drug development
2023-06-14
All living cells contains proteins with different functions, depending on the type of cell. Researchers at the University of Gothenburg have discovered a way to identify proteins even without looking at their structure. Their method is faster, easier and more reliable than previous methods.
Currently, the general view is that each protein’s structure is what controls its function in cells. The atomic sequences, meaning how the atoms are arranged in the proteins, create the protein’s structure and shape. But there are many proteins that lack a well-defined structure.
Researcher Gergely Katona ...
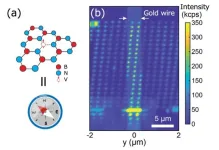
Researchers succeed in arranging nanoscale quantum sensors on desired targets
2023-06-14
Summary: The University of Tokyo scientists achieve the delicate task of arranging quantum sensors at a nanoscale, allowing them to detect extremely small variations in magnetic fields. The high-resolution quantum sensors will have potential uses in quantum materials and electronic device research. For example, the sensors can help develop hard disks that use nano-magnetic materials as storage elements. This is the world’s first successful high-resolution magnetic field imaging using a nanoscale arrangement of quantum sensors.
Sensors surround us in our daily life, from garage lights ...
Community-wide program to support teen parents serves as a model for engagement
2023-06-14
WASHINGTON (June 14, 2023) – More than 500 adolescent mothers, caregivers and community members benefitted from a coordinated “collective impact” model to provide support aimed at addressing the litany of strains faced by teen parents, according to a case study published Wednesday in the journal Pediatrics.
Known as the District of Columbia Network for Parenting and Expectant Teens (DC NEXT), the model used well-tested pillars of community organization to provide services and care that bolstered the well-being of pregnant ...
New imaging technique captures COVID-19’s impact on the brain
2023-06-14
A University of Waterloo engineer’s MRI invention reveals better than many existing imaging technologies how COVID-19 can change the human brain.
The new imaging technique known as correlated diffusion imaging (CDI) was developed by systems design engineering professor Alexander Wong and recently used in a groundbreaking study by scientists at Baycrest’s Rotman Research Institute and Sunnybrook Hospital in Toronto.
“Some may think COVID-19 affects just the lungs,” Dr. Wong said. “What was found is that this new MRI technique that we created ...
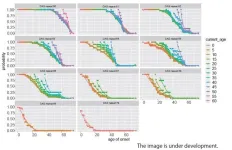
Prediction of age of onset of SCA3 and DRPLA by survival analysis using machine learning
2023-06-14
Niigata, Japan – Using machine learning, the Department of Neurology at Niigata University has developed a model to predict the asymptomatic probability at each age from the current age and number of CAG repeats in carriers of spinocerebellar degeneration. Polyglutamine diseases such as DRPLA and SCA3 are caused by an expansion of CAG repeats in the causative gene. In polyglutamine diseases, the number of CAG repeats is known to be inversely related to age of onset. Parametric survival analysis has traditionally been used to predict age of onset, but a more accurate prediction method has been desired. We ...
Remission rates of 1 in 100 people with type 2 diabetes in real world data
2023-06-14
Niigata, Japan - The phenomenon of improvement of glucose to levels in a normal range and cessation of the need for medication can occur in some patients diagnosed with type 2 diabetes who are provided with lifestyle therapy, temporary pharmacotherapy, bariatric surgery, or combinations of these treatments. However, this phenomenon is not yet fully understood in routine care settings, and many factors remain to be clarified. Moreover, since there are differences in insulin secretion and resistance between East Asian and Western populations, the natural history of diabetes seems to differ widely between Western populations and East Asians.
Therefore, ...
Sharpening Occam’s Razor
2023-06-14
In science, the explanation with the fewest assumptions is most likely to be true. Called “Occam’s Razor,” this principle has guided theory and experiment for centuries. But how do you compare between abstract concepts?
In a new paper, philosophers from UC Santa Barbara and UC Irvine discuss how to weigh the complexity of scientific theories by comparing their underlying mathematics. They aim to characterize the amount of structure a theory has using symmetry — or the aspects of an object that remain the same when other changes are made.
After much ...
C-Path’s PSTC receives positive FDA response for drug-induced pancreatic injury biomarkers
2023-06-14
Safety biomarkers aim to provide an additional tool for detecting acute drug-induced pancreatic injury (DIPI) in phase 1 clinical trials
TUCSON, Ariz., June 13, 2023 — Critical Path Institute (C-Path) today announced that the Biomarker Qualification Program (BQP) at the Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER) in the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) issued a Biomarker Letter of Support (LOS) for four pancreatic injury safety biomarkers identified and evaluated by C-Path’s Predictive Safety Testing Consortium's (PSTC) Pancreatic Injury Working Group (PIWG).
This set of biomarkers will help increase the ability ...
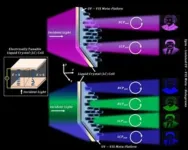
Breaking barriers: Advancements in meta-holographic display enable ultraviolet domain holograms
2023-06-14
The term meta means a concept of transcendence or surpassing, and when applied to materials, metamaterials encompass artificially engineered substances that exhibit properties not naturally found in the environment. Metasurfaces, characterized by their thinness and lightness, have garnered considerable interest as a potential component for incorporation into portable augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) devices to facilitate holographic generation. Nonetheless, it is important to note that metasurfaces have inherent limitations, such ...
Bhopal explosion may have heightened risk of disability and cancer among future generations
2023-06-14
The Bhopal gas explosion in 1984—one of India’s worst industrial disasters—may have heightened the risk of disability and cancer in later life among future generations, curbed their educational attainment, and prompted a fall in the proportion of male births the following year, suggests research in the open access journal BMJ Open.
The disaster is likely to have affected people across a substantially more extensive area than previous evidence suggested, say the researchers.
During the incident, toxic ...
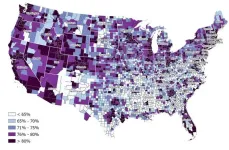
NHS “flying blind” in attempt to tackle ethnic inequalities in care, warns expert
2023-06-14
The NHS will be “flying blind” in its attempts to meet its legal, and moral, obligation to eliminate ethnic inequalities in health and care until longstanding problems with the quality of ethnicity data are resolved, warns an expert in The BMJ today.
Inequalities in health and care between ethnic groups have been documented for decades, explains Sarah Scobie at the Nuffield Trust. But she argues that analysis by broad ethnic groups (white, Asian, black, and mixed) can mask substantial variation within them.
An accompanying infographic presents some of these disparities across a range ...
Timing of childhood adversity is associated with unique epigenetic patterns in adolescents
2023-06-14
BOSTON—Childhood adversity—circumstances that threaten to a child’s physical or psychological well-being--has long been associated with poorer physical and mental health throughout life, such as greater risks of developing cardiac disease, cancer, or depression. It remains unclear, however, when and how the effects of childhood adversity become biologically embedded to influence health outcomes in children, adolescents, and adults.
A team of researchers at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH), a founding member of Mass General Brigham (MGB), previously showed that exposure to adversity between ages 3 to 5 has a ...
Lockdown children played on, study finds, despite being stuck at home
2023-06-14
Children displayed a resilient capacity to continue playing during peak COVID-19, a study has found, even though their options to do so became more limited while under stay-at-home orders.
The research, by academics at the University of Cambridge, interviewed children themselves about their playing habits during the pandemic. Without disputing the consensus that COVID-19 impeded children’s healthy development, it does suggest that they were able to adapt their play habits to their changed circumstances.
Children largely expressed ...
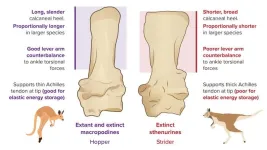
Skipping evolution: some kangaroos didn’t hop, scientists explain
2023-06-14
Extinct kangaroos used alternative methods to their famous hop according to comprehensive analysis from University of Bristol and the University of Uppsala scientists.
Although hopping is regarded as a pinnacle of kangaroo evolution, the researchers highlight that other kinds of large kangaroos, in the not too distant past, likely moved in different ways such as striding on two legs or traversing on all fours.
In the review, published in Alcheringa: An Australasian Journal of Palaeontology, the team shows that there are other ways to be an evolutionary ...
Light pollution confuses coastal woodlouse
2023-06-14
Artificial night-time light confuses a colour-changing coastal woodlouse, new research shows.
The sea slater is an inch-long woodlouse that lives around the high-tide line and is common in the UK and Europe.
Sea slaters forage at night and can change colour to blend in and conceal themselves from predators.
The new study, by the University of Exeter, tested the effects of a single-point light source (which casts clear shadows) and “diffuse” light (similar to “skyglow” found near towns and cities).
While the single light did not interfere with the sea slaters’ camouflage, diffuse light caused them to turn ...
Giving birth outside of working hours in England is safe, suggests study
2023-06-14
A new study suggests that between 2005 and 2014, for almost all births in England, being born outside of working hours did not carry a significantly higher risk of death to the baby from anoxia (lack of oxygen) or trauma, when compared to births during working hours.
The finding runs contrary to an assumed, wider ‘weekend effect,’ with previously reported research suggesting a significantly higher risk of death for births outside of working hours or at weekends.
The current study from City, University of London ...
Brighter nights risk extinguishing glow-worm twinkle
2023-06-14
The bright lights of big cities are wonders of the modern world; intended to help us work, stay safe and enjoy the world around us long after the sun has set. While artificial light has been great for increasing human productivity, some nocturnal animals, and even people, pay a price for this illumination. From increasing the amount of time that predators are active to disrupting migrations, light pollution affects many animals; but how do animals that use their own luminescence to lure food or attract mates fair against this new, brighter background? Female common glow-worms (Lampyris noctiluca) emit a green glow from their abdomen to ...
Meat processing plants: What factors are critical for survival?
2023-06-13
URBANA, Ill. — Meat processing plants in the U.S. have garnered considerable public attention in recent years, often focusing on production and labor issues. The COVID-19 pandemic underscored the vulnerability of large, concentrated plants, as major shutdowns led to reduced output and higher meat prices for consumers.
Policy makers have launched initiatives at the state and federal levels to increase meat processing capacity and industry resilience, often favoring small and medium-sized plants. But little research exists to determine what factors make plants more likely to succeed. A new study from the University of ...
CHOP researchers develop universal MHC molecules that can be produced rapidly at scale
2023-06-13
Philadelphia, June 13, 2023— Class I major histocompatibility complex (MHC-I) proteins play an essential role in the immune system of all jawed vertebrates. The MHC-I displays peptide fragments of proteins from within the cell on the cell surface, “presenting” them to the immune system, which is constantly scanning the body for foreign or toxic antigens. When foreign peptides are identified, they trigger a cascade that allows cytotoxic T cells to eliminate intruders. This process has been exploited in the development of both vaccines ...
Peptide from venomous fish toxin controls lung inflammation in mice
2023-06-13
A molecule found in the venomous toadfish Thalassophryne nattereri has proved capable of controlling lung inflammation and could be the basis for a more effective asthma drug. The research was supported by FAPESP and conducted by scientists at Butantan Institute in São Paulo, Brazil. An article describing the results is published in the journal Cells.
A welter of fish species live in freshwater, seawater and a mixture of the two, and some of them are venomous. They have spines or stingers connected to venom glands, which ...
Residents in 'digital deserts' have fewer health care options
2023-06-13
Residents in rural counties with limited access to high-speed internet cannot take advantage of increasingly popular online health services.
A new study by the University of Cincinnati highlighted disparities in access to digital technology that could widen the gap in access to health care. The study found that socially vulnerable communities in the United States face more barriers to adequate health care, live in areas with fewer health care resources and have less access to high-speed internet.
The study was published in the journal Mayo Clinic Proceedings: Digital Health.
The Biden Administration announced this year it will invest $73 million in outreach ...
Different genes are expressed at different stages during pregnancy, according to scientists
2023-06-13
We have a good understanding of how a woman’s external features can change during pregnancy, but scientists know surprisingly little about what biological changes occur internally.
A new Northwestern Medicine study, published June 5 in the journal Frontiers in Immunology, provides data about immune cells and biological changes (gene expression) in pregnant people at multiple timepoints before and during pregnancy. Using RNA sequencing and computational methods to estimate proportions of different activated types of immune cells in blood the team of scientists showed how pregnancy induces progressive changes in the maternal ...
[1] ... [1858]
[1859]
[1860]
[1861]
[1862]
[1863]
[1864]
[1865]
1866
[1867]
[1868]
[1869]
[1870]
[1871]
[1872]
[1873]
[1874]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.