New approach opens avenue to investigate element distribution and transport pathways in plants
2023-06-13
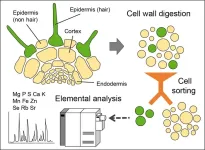
Plant roots play a critical role in taking up, selecting, enriching and retaining a range of different mineral elements thereby supplying distant plant tissues with nutrients while sequestering excessive amounts of metals. To execute such element-specific functions, a range of ion transporters present at roots mediate the uptake, efflux and intracellular compartmentalization of different mineral elements. Most ion transporters show characteristic tissue and cell type-specific localization patterns, which can be altered in response to internal signalling or external cues. To fully ...
The best drug combos to prevent COVID recurrence
2023-06-13
A groundbreaking machine-learning study has unmasked the best drug combinations to prevent COVID-19 from coming back after an initial infection. It turns out these combos are not the same for every patient.
Using real-world data from a hospital in China, the UC Riverside-led study found that individual characteristics, including age, weight, and additional illness determine which drug combinations most effectively reduce recurrence rates. This finding has been published in the journal Frontiers in Artificial Intelligence.
That the data came from China is significant for two reasons. First, when patients are treated for COVID-19 in the U.S, it is ...
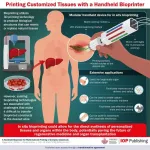
Bioprinting personalized tissues and organs within the body: A breakthrough in regenerative medicine
2023-06-13
In situ bioprinting, which involves 3D printing biocompatible structures and tissues directly within the body, has seen steady progress over the past few years. In a recent study, a team of researchers developed a handheld bioprinter that addresses key limitations of previous designs, i.e., the ability to print multiple materials and control the physicochemical properties of printed tissues. This device will pave the way for a wide variety of applications in regenerative medicine, drug development and testing, and custom orthotics and prosthetics.
The emergence of regenerative medicine has resulted ...
Why women with multiple sclerosis get better when pregnant
2023-06-13
Women suffering from the autoimmune disease multiple sclerosis temporarily get much better when pregnant. Researchers have now identified the beneficial changes naturally occurring in the immune system during pregnancy. The findings, published in Journal of Neuroinflammation, can show the way to new treatments.
Pregnancy is a very special condition from an immunological point of view. The immune system serves to defend us against foreign substances. However, although half of the genetic material of the foetus ...
Adhering to global health recommendations reduces cancer risk
2023-06-13
People who adhere to global Cancer Prevention Recommendations are putting themselves at lower risk of developing the disease, new research confirms.
Experts at Newcastle University have reviewed evidence of following the 2018 World Cancer Research Fund (WCRF) and American Institute for Cancer Research (AICR) lifestyle-based recommendations.
The findings, published today in Cancer, revealed that adhering to a healthier lifestyle, including maintaining a healthy body weight and eating little red meat and processed meats such as bacon, helps ...
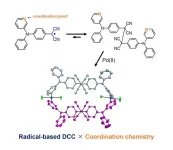
Creation of a new molecule through innovative combination of two reactions
2023-06-13
A research group led by Professor Hideki Fujiwara and Associate Professor Daisuke Sakamaki from the Graduate School of Science at Osaka Metropolitan University succeeded, for the first time, in synthesizing a new molecule using a novel combination of dynamic covalent chemistry, in which organic radicals couple and dissociate reversibly, and coordination chemistry, which binds radicals to metal ligands. The study shows that the two types of reactions work without inhibiting each other.
“This research was based on a very simple idea of combining two types of reactions,” stated Professor Sakamaki. “However, it was not clear ...
Elevated Lipoprotein(a) is the latest variant of ‘bad cholesterol’ found to increase the risk of recurrent coronary heart disease
2023-06-13
Increased levels of Lipoprotein(a), a variant of ‘bad cholesterol’, in the bloodstream are a risk factor for recurrent coronary heart disease (CHD) in people aged 60 or over, according to the results of a new study which tracked the issue over the course of 16 years.
The results, published today in Current Medical Research & Opinion, suggest that current cholesterol-lowering medications may not be effective at reducing the risk of recurrent CHD – such as a heart attack – due to elevated Lp(a).
“This finding adds to growing evidence of a relationship between increased Lp(a) and the risk of recurrent CHD,” says lead author Associate Professor ...
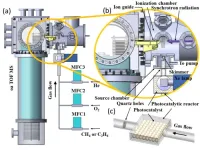
USTC achieves breakthrough in in-situ detection of gas-phase active intermediates in photocatalysis
2023-06-13
Prof. PAN Yang and Associate Researcher LIU Chengyuan, researchers from the University of Science and Technology of China (USTC) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), have achieved significant progress in detecting intermediates in methane photocatalytic reactions. Their technique, Synchronous Radiation Photoionization Mass Spectrometry (SR-PIMS), allows for in-situ detection of active intermediates. The findings were published in the prestigious chemistry journal Angewandte Chemie International ...
USTC provides comprehensive review of quantum teleportation in Nature Review Physics
2023-06-13
A team led by Academician Prof. GUO Guangcan from the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) provides a comprehensive overview of the progress achieved in the field of quantum teleportation. The team, which includes Prof. HU Xiaomin, Prof. GUO Yu, Prof. LIU Biheng, and Prof. LI Chuanfeng from the University of Science and Technology of China (USTC),CAS, was invited to publish a review paper on quantum teleportation in Nature Review Physics. The paper was officially released online on May 24.
As one of the most important protocols in the field ...
USTC achieves thousand-kilometer quantum key distribution
2023-06-13
A point-to-point long-distance quantum key distribution (QKD) over a distance of 1,002 km has been achieved by scientists from the University of Science and Technology of China (USTC) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), and their collaborators from Tsinghua University, Jinan Institute of Quantum Technology, and Shanghai Institute of Microsystem and Information Technology (SIMIT), CAS. This milestone not only sets a new world record for non-relay QKD but also provides a solution for high-speed intercity quantum communication. The ...
ASHP Summer Meeting Tip Sheet
2023-06-13
Posters
All poster presentations will take place on Monday, June 12, 2023, from 12:15 to 1:30 p.m. EDT, or Tuesday, June 13, 2023, from 12:15 to 1:30 p.m. EDT at the Baltimore Convention Center, Exhibit Hall E, Level 100.
Abstract 4-M (Monday)
Avoiding Clinical Inertia: Comparing Time to Intensification of Glucagon-like
peptide-1 (GLP-1) Receptor Agonists in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Among Clinical Pharmacists versus Providers
Clinical pharmacists have a significant impact on medication optimization and reduction ...
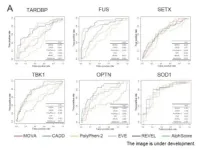
MOVA: new method for evaluating the pathogenicity of missense variants using AlphaFold2
2023-06-13
Niigata, Japan - The Department of Neurology at Niigata University has developed a new in silico method for evaluating the pathogenicity of missense variants using AlphaFold2 (MOVA). Rare variants in the causative gene of ALS are present in 10-30% of sporadic ALS cases, which highlights the need for accurate and efficient pathogenicity prediction methods. To predict the pathogenicity of the variants, in silico analysis methods are commonly used. In some ALS causal genes, the mutations are concentrated in specific regions, and the accuracy of pathogenicity prediction can be improved by considering the positional information of the variants. ...
23Na MRI technique unleashes new approach for diagnosing diabetic kidney disease
2023-06-13
Niigata, Japan - The gold standard test for predicting the onset of diabetic kidney disease is albuminuria. However, detecting albuminuria alone has limited sensitivity and specificity in end-stage renal failure with a decreased estimated glomerular filtration rate. This is supported by several reports, which state that about half of the type 2 diabetes patients who developed kidney dysfunction showed no preceding albuminuria.
In this study, the authors propose the possibility of diagnosing tubular abnormalities in diabetic kidney disease at an early stage and connecting them to treatment by combining the evaluation of sodium concentration using 23Na MRI ...
Immune cell movement worse in older females, mice study finds
2023-06-13
Older female mice had more immune cells entering areas of the body where they shouldn’t according to a new study, demonstrating that sex differences contribute to age-related inflammation that needs to be considered in future research.
In a paper published in Journal of Leukocyte Biology today (Tuesday 13 June), at team of researchers led by Dr Myriam Chimen from the University of Birmingham have found that age significantly increases the number of immune cells entering the sack that holds major organs (peritoneal cavity) in female mice, when compared to young mice or older male mice.
The findings support previous studies that suggest ...
THE LANCET: First phase 3 trial of a chikungunya vaccine candidate finds it is generally safe and provokes an immune response
2023-06-13
Peer-reviewed / Randomised Controlled Trial / People
Study of healthy US adults found that a single dose of the VLA1553 vaccine candidate was generally safe, well tolerated and provokes an immune response.
After a single vaccination, the vaccine produced neutralizing antibody levels which are thought to protect against chikungunya disease in 99% (263/266) of participants.
Antibody levels declined 28 days after vaccination, but seroprotection persisted in more than 96% (233/242) participants after six months.
Most adverse events were moderate or mild and the authors say its safety profile is similar to other licensed vaccines
The VLA1553 vaccine candidate ...
The chatbot will see you now:
2023-06-13
Glasgow, UK: The informed consent process in biomedical research is biased towards people who can meet with clinical study staff during the working day. For those who have the availability to have a consent conversation, the time burden can be off-putting. Professor Eric Vilain, from the Department of Paediatrics, University of California, Irvine, USA, will tell the European Society of Human Genetics annual conference today (Tuesday 13 June) how results from his team’s study of the use of a chatbot (GIA – ‘Genetics Information Assistant’ ...
NHS policies on patient’s weight and access to hip replacement surgery are inappropriate, study finds
2023-06-13
Weight and body mass index (BMI) policies introduced by NHS commissioning groups in England are inappropriate and worsening health inequalities, according to a new study published in BMC Medicine today [13 June] that analysed nearly 490,000 hip surgeries. With one in ten people likely to need a joint replacement in their lifetime, many thousands of patients are directly affected by these policies.
Rules implemented by NHS clinical commissioning groups (CCGs) across England to change the access to hip and knee replacement surgery for patients who are overweight or obese have been in effect for over ten years. ...
A baking soda solution for clean hydrogen storage
2023-06-13
In a world of continuously warmer temperatures, a growing consensus demands that energy sources have zero, or next-to-zero, carbon emissions. That means growing beyond coal, oil, and natural gas by getting more energy from renewable sources.
One of the most promising renewable energy carriers is clean hydrogen, which is produced without fossil fuels.
It’s a promising idea because the most abundant element in the universe is hydrogen, found in 75 percent of all matter. Moreover, a hydrogen molecule has two paired atoms—Gemini twins that are both non-toxic and highly combustible.
Hydrogen’s combustive potential ...
Can this medication reverse MS? Brain biomarker shows it can
2023-06-13
A decade after UC San Francisco scientists identified an over-the-counter antihistamine as a treatment for multiple sclerosis, researchers have developed an approach to measure the drug’s effectiveness in repairing the brain, making it possible to also assess future therapies for the devastating disorder.
The researchers, led by physician-scientist Ari Green, MD, who together with neuroscientist Jonah Chan, PhD, first identified clemastine as a potential MS therapy, used MRI scans to study the drug’s impact on the brain of 50 participants in a clinical study.
In MS, patients lose myelin, the protective insulation around ...
The advances and promise of continuous glucose monitoring in diabetes management
2023-06-13
As adoption of Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) continues to increase, there is a growing body of evidence supporting the use of this technology in improving diabetes outcomes for patients with Type 1 or Type 2 Diabetes. A new supplement in the peer-reviewed journal Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics (DTT) provides an excellent perspective of the past, present, and future of CGM. Click here to read the supplement now.
In the supplement Rickson et al. review the rapid pace in which diabetes technology has progressed and the implications for relying on rigorous and extensive timelines to publish randomized controlled trials to impact ...
Ochsner Health names new chief financial officer and treasurer
2023-06-13
NEW ORLEANS, La. – Ochsner Health has named Jim Molloy as the organization’s next Executive Vice President, Chief Financial Officer and Treasurer. A leader at Citi bringing decades of extensive experience in healthcare finance, Molloy will oversee the organization’s accounting, financial planning and analysis, reimbursement and revenue cycle functions, as well as managed care contracting and treasury. He will also play a pivotal role in the continued development and execution of ...
Low birthweight is independently linked to increased risk of type 2 diabetes, and a particular presentation including lower age at diagnosis
2023-06-13
T2D patients with lower birthweight also show higher use of diabetes drugs than those with normal birthweight, and a larger number of comorbidities including high blood pressure, at the time of diagnosis.
The first study is by Dr Rasmus Wibaek, Steno Diabetes Center Copenhagen, Herlev, Denmark, and Dr Allan Vaag, Steno Diabetes Center Copenhagen, and also Lund University, Malmö, Sweden, and colleagues.
This study included adults aged 30–60 years enrolled in the Danish Inter99 cohort in 1999–2001 (baseline examination), with information on birthweight from original birth records from 1939–1971 and without diabetes at baseline. Birth records were linked ...
Gentle cleansers kill viruses as effectively as harsh soaps, study finds
2023-06-13
Gentle cleansers are just as effective in killing viruses – including coronavirus – as harsh soaps, according to a new study from scientists at the University of Sheffield
Healthcare professionals often substitute alcohol-based hand sanitisers and harsh soaps for skin-friendly cleansers in order to treat or prevent irritant contact dermatitis, which develops when chemical or physical agents damage the skin surface faster than the skin can repair
Incidence and severity of irritant contact dermatitis increased from 20 per cent to 80 per cent amongst healthcare professionals during the Covid-19 pandemic
Researchers also found non-enveloped ...
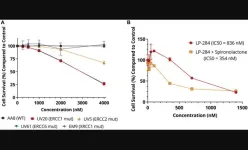
LP-284 targets non-Hodgkin's lymphoma and DNA damage repair deficiency
2023-06-12
“[...] we demonstrated the new acylfulvene compound LP-284 has anti-tumor activity including nanomolar potency in fifteen in vitro NHL cell lines and in vivo preclinical NHL models.”
BUFFALO, NY- June 12, 2023 – A new research paper was published in Oncotarget's Volume 14 on June 12, 2023, entitled, “LP-284, a small molecule acylfulvene, exerts potent antitumor activity in preclinical non-Hodgkin's lymphoma models and in cells deficient in DNA damage repair.”
Despite advances in therapies treating non-Hodgkin’s ...
Damon Runyon Cancer Research Foundation announces three recipients of 2023 Physician-Scientist Training Award
2023-06-12
Three scientists with exceptional promise and novel approaches to fighting cancer have been named the 2023 recipients of the Damon Runyon Physician-Scientist Training Award. The awardees were selected through a highly competitive and rigorous process by a scientific committee comprised of leading cancer researchers who are themselves physician-scientists.
Physician-scientists are uniquely positioned to translate scientific discoveries into therapies that improve and prolong the lives of their patients. However, ...
[1] ... [1861]
[1862]
[1863]
[1864]
[1865]
[1866]
[1867]
[1868]
1869
[1870]
[1871]
[1872]
[1873]
[1874]
[1875]
[1876]
[1877]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.