A randomised trial comparing imaging-guided PCI with Orsiro vs Xience
A randomised clinical trial comparing the imaging-guided implantation of the Ultrathin strut biodegradable polymer sirolimus-eluting stent (Orsiro) and durable polymer everolimus-eluting stents (Xience)
2021-05-18
(Press-News.org) Previous clinical trials suggested that ultra-thin strut biodegradable polymer sirolimus-eluting stent (BP-SES) may be associated with lower target lesion failure (TLF) when compared to durable polymer everolimus-eluting stents (DP-EES). However, the possible underlying mechanisms remain unclear. Therefore, the all-comers CASTLE study was designed to assess the role of imaging-guided percutaneous cardiac intervention (PCI) in the clinical outcomes difference between BP-SES vs DP-EES.
BP-SES has ultra-thin struts (60μm) and a biodegradable polymer that may provide potential advantages such as reduced vessel inflammation and thrombogenicity. Randomised clinical trials have provided mixed results. The BIOFLOW-V and BIOSTEMI trial showed a lower risk of TLF with BP-SES when compared to DP-EES. Meanwhile, the BIOSCIENCE trial showed neutral results. One of the possible explanations of these contradictory findings is the use of intracoronary imaging. The CASTLE investigator hypothesised that under imaging-guidance PCI, the actual difference in clinical outcomes between BP-SES and DP-EES might be clarified.
The CASTLE study is an investigator-initiated, multicentre, single-blinded, randomised, non-inferiority clinical trial executed in 69 centres in Japan. The population was composed of patients with acute and chronic coronary syndromes. Patients were randomised in a 1:1 ratio to image-guided PCI (intravascular ultrasound or optical coherence tomography) with BP-SES (intervention group) or DP-EES (control group). The primary outcome was TLF (cardiovascular death, target vessel myocardial infarction, and clinically driven target lesion revascularisation) at 12-month follow-up. An independent clinical event committee evaluated angiographies and clinical events. The prespecified margin for non-inferiority was 3.3%.
The investigator reported an interim analysis with ~70% of the follow-up. Between May 2019 and March 2020, 1440 patients were randomised; 722 were allocated to BP-SES and 718 to DP-EES. The 12-month follow-up was completed in 69.1% in the BP-SES group and 68.6% in the DP-EES. There were no significant differences between groups in terms of clinical and procedural characteristics. The trial included mainly chronic coronary syndromes (85%), stent diameter ? 3mm (66%), and imaging-guidance was performed in at least 97.5% of the patients. At 30-day follow-up, there was no difference in TLF between DP-SES vs DP-EES (5.0% vs 4.9%) or its components. In the primary endpoint, at 12-month follow-up, there was no difference in TLF between DP-SES vs DP-EES (HR 0.59 [95%CI 0.26 to 1.36]).
At least in this interim analysis, the data suggest that BP-SES and DP-EES may have similar clinical outcomes when PCI is performed under intracoronary imaging guidance. However, we should cautiously wait until the complete follow-up is performed to assess any potential difference between these two devices.
INFORMATION:
NOTES TO EDITORS
Key information
A randomised study comparing imaging guided implantation of Orsiro and Xience - CASTLE study - Masato Nakamura
Embargo will be lifted on Tuesday 18 May - 9:00 - Paris time
Available on the Video on Demand Section - http://www.europcr.com
Livestream presentation on 20 May - 11:40 - Coronary Channel
About EuroPCR 2021
The World-Leading Course in interventional cardiovascular medicine and the official annual meeting of the European Association of Percutaneous Cardiovascular Interventions (EAPCI) will take place from 18 to 20 May 2021 online, http://www.europcr.com and in different hubs (depending on the sanitary situation).
The detailed Course Programme is available on: https://www.pcronline.com/Courses/EuroPCR.
About PCR
The mission of PCR is to serve the needs of each individual patient by helping the cardiovascular community to share knowledge, experience and practice. PCR offers a large range of many other educational meetings and resources for the continuing education of the interventional cardiovascular community. These include major annual Courses across the globe, e-Learning with high-profile PCR Webinars, Courses specifically dedicated to valvular heart disease, tailor-made PCR Seminars on specific topics, online resources and medical publications such as EuroIntervention, the official journal of the EAPCI.
Gateways to all PCR activities are available on http://www.pcronline.com.
For further information, please contact Ce?lia Vila?: cvila@europa-group.com.
HELP FOR JOURNALISTS TO COVER EUROPCR 2021
Register and attend EuroPCR 2021 as a journalist
Open to accredited journalists, free of charge. Journalists must hold a valid press card and/or provide a letter of assignment from a recognised publication. To register as press, go to https://www.pcronline.com/Courses/EuroPCR/Press.
EuroPCR press releases can be found at
https://www.pcronline.com/News/PCR-Press-Releases.
For any press-related enquiries, please contact
EuroPCR Press Coordinator, Isabelle Uzielli: iuzielli@europcr.com.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-05-18
The European Bifurcation Club Left Main (EBC MAIN) trial addressed the issue of provisional single stent versus upfront double stenting in 467 patients with true bifurcation distal left main disease.
So far, only one other randomized trial, DKCRUSH-V (n=482), has addressed the same research question, showing better outcomes with an upfront two-stent strategy, more specifically the double-kissing crush (DK CRUSH) technique.
In terms of methodology, two aspects need to be considered for the correct interpretation of the EBC MAIN trial results. First, both LAD and CX ostia were affected by significant disease on angiography ...
2021-05-18
Results of the interim analyses performed after 12 months in the first 111 patients enrolled in phase II Cool AMI trial evaluating safety and effectiveness of systemic therapeutic hypothermia as an adjunctive therapy in anterior STEMI undergoing PCI as compared to PCI only. Analyses showed significant differences among treatment groups, including longer randomization-to-balloon time and total ischemic time in treatment arm, justifying premature trial discontinuation.
Therapeutic mild systemic hypothermia, when achieved before reperfusion of the infarct related vessel, has shown to limit infarct size in experimental animal models. Despite ...
2021-05-18
The ISCHEMIA trial found no significant difference between an invasive vs. a conservative strategy in patients with chronic coronary syndromes and moderate to severe ischemia at a mean of 3.2 years. However, the cumulative difference in the estimates of cardiac death between the invasive and conservative strategies tended to increase numerically over time (e.g., 0.3% in favor of the invasive strategy at 2 years and 1.3% at 5 years). Because the ISCHEMIA trial was not powered for cardiac mortality and did not focus on long-term follow-up, the rationale for a meta-analysis emerged.
At EuroPCR 2021, Navarese and colleagues present the results of a new meta-analysis of revascularization plus medical therapy versus medical therapy alone. A total of 19,806 patients with chronic coronary syndromes ...
2021-05-18
Imagine an entire twenty storey concrete building which can store energy like a giant battery. Thanks to unique research from Chalmers University of Technology, Sweden, such a vision could someday be a reality. Researchers from the Department of Architecture and Civil Engineering recently published an article outlining a new concept for rechargeable batteries - made of cement.
The ever-growing need for sustainable building materials poses great challenges for researchers. Doctor Emma Zhang, formerly of Chalmers University of Technology, Sweden, joined Professor Luping Tang's research group several years ago to search for the building materials of the future. Together they have now succeeded in developing a world-first ...
2021-05-18
Researchers have developed a tool to help governments and other organizations with limited budgets spend money on building repairs more wisely.
The new tool uses artificial intelligence (AI) and text mining techniques to analyze written inspection reports and determine which work is most urgently needed.
"Those assessments are now largely subjective, the opinions of people based on experience and training," said Kareem Mostafa, an engineering PhD student at the University of Waterloo who led the project. "We're using actual data on buildings to make spending decisions more objective."
Researchers looked at inspection reports on the roofs of 400 schools managed by the Toronto District School Board. A computer ...
2021-05-18
MUSC Hollings Cancer Center lung cancer researcher Gerard Silvestri, M.D., found that a lack of insurance leads to worse cancer survival than for those with Medicare, in a paper published in the May issue of Health Affairs. This work, a joint effort between Silvestri and researchers at the American Cancer Society, highlights the current dire barrier in medical care: Many people cannot take advantage of the newer potentially lifesaving treatments due to the high costs.
Silvestri said the research began last year, inspired by the hotly debated topic of expanding Medicare ...
2021-05-17
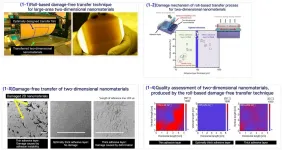
The Korea Institute of Machinery and Materials (KIMM) under the Ministry of Science and ICT developed a roll-based damage-free transfer technique that allows two-dimensional (2D) nanomaterials to be transferred into wafer scale without damage. The proposed technique has a variety of applications from transparent displays and semiconductors to displays for self-driving cars, and is expected to accelerate the commercialization of 2D nanomaterial-based high-performance devices.
Dr. Kwang-Seop Kim, principal researcher of the Department of Nano-Mechanics at KIMM, succeeded in developing a technique of transferring 2D nanomaterials, as thin as 1/50,000 of a strand of hair, to a substrate of at least 4 inches (approx. 10 cm) without damage.
The roll-based transfer is a process in ...
2021-05-17
On the evening of May 6, 1937, the largest aircraft ever built by mankind, a towering example of technological prowess, slipped through the stormy skies of New Jersey and prepared to land. The airship Hindenburg was nearing the end of a three-day voyage across the Atlantic Ocean from Frankfurt, Germany. It was a spectacle and a news event. Onlookers and news crews gathered to watch the 800-foot-long behemoth touch down.
And then, in one horrifying half minute, it was all over. Flames erupted from the airship's skin, fed by the flammable hydrogen gas that ...
2021-05-17
One of the especially dangerous health risks of being extremely overweight occurs when an obese person begins to accumulate fat in their liver.
This condition--non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD)--is the world's most common chronic liver disease and is the primary underlying cause for liver transplants in children and adults. Without such transplants, which are available to only a small percentage of patients, NAFLD over time can be fatal. In fact, (excluding alcohol-related liver damage) more than 30,000 people a year die from NAFLD.
For years, the primary way to treat NAFLD has ...
2021-05-17
Early preterm births may be dramatically decreased with docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) supplements, with a dose of 1000 mg more effective for pregnant women with low DHA levels than the 200 mg found in some prenatal supplements, according to a study led by researchers from the University of Kansas and the University of Cincinnati and published today in EClinicalMedicine, a clinical journal of The Lancet. Early preterm birth, defined as birth before 34 weeks gestation, is a serious public health issue because these births result in the highest risk of infant mortality and child disability.
"This study tells us that pregnant women should be taking DHA," said Susan E. Carlson, Ph.D., professor of nutrition in the Department ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] A randomised trial comparing imaging-guided PCI with Orsiro vs Xience
A randomised clinical trial comparing the imaging-guided implantation of the Ultrathin strut biodegradable polymer sirolimus-eluting stent (Orsiro) and durable polymer everolimus-eluting stents (Xience)