Virtual ward for atrial fibrillation patients could prevent thousands of hospital admissions per year
2023-06-07
A new virtual ward to safely treat atrial fibrillation patients could prevent thousands of hospital admissions per year, easing NHS pressure, according to new research from the University of Leicester presented at the British Cardiovascular Society (BCS) conference in Manchester.
In the year-long study, patients with a fast heart rate due to atrial fibrillation or atrial flutter that met the necessary safety criteria(1) were sent home with the heart rate-lowering medication they would usually get in hospital, and told to submit daily information using a smartphone app.
Their data, including ECG recordings, blood pressure, oxygen ...
Daily beetroot juice reduces rate of repeat procedures and heart attacks in angina patients with stents
2023-06-07
Drinking beetroot juice every day for six months after having a stent fitted reduced the chance of angina patients having a heart attack or needing a repeat procedure, according to new research presented at the British Cardiovascular Society conference.
The finding on the benefits of the vegetable juice comes from a trial funded by the National Institute for Health and Care Research and the British Heart Foundation (BHF), presented at the conference in Manchester.
The researchers, based at St Bartholomew’s Hospital and Queen Mary University ...
Knowledge coproduction: Working together to solve a complex conservation problem
2023-06-07
A new publication from a team of scientists at USGS, Point Blue Conservation Science, and Conservation Biology Institute shows how knowledge coproduction - the collaborative creation of actionable information by scientists, resource managers, and policy makers - can help identify viable conservation options for a dynamic ecosystem with a complex web of stressors.
The wetland habitats of California’s Central Valley support millions of migratory birds each year and are an important part of the Pacific Flyway, a bird migration route that ...
UW research shows real-world value of strategy courses for MBA students
2023-06-07
More than 100,000 Master of Business Administration students graduate each year in the United States, and all of them take at least one strategy course. Even so, little is known about the effects of the degree’s most popular course offering.
Strategy courses typically focus on frameworks and cases that develop decision-making abilities for eventual MBA graduates, who make up most associates and partners at leading consulting firms, as well as 40% of the chief executive officers of publicly traded firms in the U.S. A new University of Washington study, published online June 5 ...
Measuring greenhouse gas from ponds improves climate predictions
2023-06-06
ITHACA, N.Y. – Shallow lakes and ponds emit significant amounts of greenhouse gases into the atmosphere, but emissions from these systems vary considerably and are not well understood.
Now, a new Cornell University-led study measures methane and carbon dioxide emissions from 30 small lakes and ponds (one acre or less) in temperate areas of Europe and North America, revealing that the smallest and shallowest bodies of water exhibit the greatest variability over time.
The paper marks an important step toward calibrating climate models so they better predict emissions from inland waterbodies, and it points to the need to study small waterbodies more closely.
“This ...
Cobalt mineralogy at the Iron Creek deposit, Idaho cobalt belt, USA: Implications for domestic critical mineral production
2023-06-06
Contributed by Laura Fattaruso, GSA Science Communication Fellow
Boulder, Colo., USA: A new study published in Geology evaluates the potential for cobalt extraction from the Idaho Cobalt Belt (ICB) of east-central Idaho, using a detailed study of the Iron Creek deposit. The ICB hosts the second largest known domestic resource of the critical mineral cobalt, one of the key ingredients in many rechargeable batteries needed for the green energy transition. Demand for cobalt is projected to increase more than 500% by 2050. Roughly 70% of the cobalt mined globally is from the Democratic Republic of the Congo, where mining practices have been criticized for human rights violations including ...
Predictive models show wildlife managers where to find destructive feral swine
2023-06-06
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — Feral swine are considered one of the top invasive species of concern in North America because of the damage they do to agricultural and natural systems. To best manage them, resource management agencies need to know more precisely where and when to implement control methods. A new study by a Penn State-led research team developed a method to help guide control efforts in the Great Smoky Mountains National Park.
Descended from wild European boars imported centuries ago that bred with escaped domestic pigs, feral swine cause widespread damage to ecosystems by wallowing ...
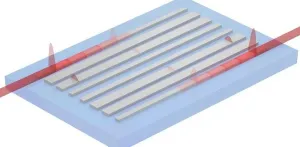
Revolutionizing optical control with topological edge states
2023-06-06
Nanophotonics and topology have gained significant interest due to the unique properties they offer. One area of focus is the investigation of topological edge states (TESs). These states have captured widespread attention because they are very resistant to errors and imperfections. Arising from topologically nontrivial phases, TESs provide a powerful toolkit for the architectural design of photonic integrated circuits. TES transport has led to the discovery of various intriguing optical effects and applications, including directional couplers, one-way waveguides, mode-locked waveguides, ...
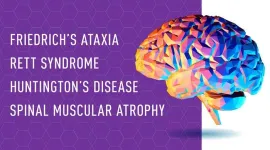
Research to develop new rare disease therapies underway at The Jackson Laboratory
2023-06-06
Researchers led by Cathleen Lutz, Ph.D., are using an exciting new method, preclinical genomic editing, to develop safe, effective therapies for rare diseases and bring them to the clinic.
Unfortunately, the translation of the accumulated knowledge to safe and effective therapies has lagged. There are many reasons to predict that the situation is changing for the better, however, as powerful new gene-based therapies succeed in clinical trials and receive FDA approval.
Therapeutic strategies such as gene replacement and gene modulation (e.g., blocking protein production with anti-sense oligonucleotides) are at the forefront of the recent progress. ...
Elizabeth Anderson and Alondra Nelson win 2023 Sage-CASBS Award
2023-06-06
Sage and the Center for Advanced Study in the Behavioral Sciences (CASBS) at Stanford University are pleased to announce Elizabeth Anderson and Alondra Nelson as winners of the 2023 Sage-CASBS Award.
Established in 2013, the Sage-CASBS Award recognizes outstanding achievement in the behavioral and social sciences that advances our understanding of pressing social issues. It underscores the role of the social and behavioral sciences in enriching and enhancing public discourse and good governance. Past winners of the award include Daniel Kahneman, psychologist and Nobel laureate in economic sciences; Pedro ...
Study: Doing good for others is good for children’s and teens’ mental, physical health
2023-06-06
Children and teenagers who volunteer tend to flourish mentally and physically, according to a new study from UTHealth Houston.
The study, led by Kevin Lanza, PhD, assistant professor of epidemiology, human genetics, and environmental sciences at UTHealth Houston School of Public Health, was published recently in JAMA Network Open.
Overall, the research team found that youths who had volunteered in the past year were in better physical health, had a more positive outlook on life, and were less likely to have anxiety, depression, or behavioral problems compared to their peers who did not volunteer.
“These study results bring optimism that youth volunteering could be ...
Health equity is the focus of LBGTQ+ Pride Month celebrations across the country
2023-06-06
DALLAS, June 6, 2023 — According to a study recently published in the Journal of the American Heart Association, lesbian and bisexual women in France had poorer heart health than heterosexual women, a finding that could be attributed to discrimination and other stressors faced by the LGBTQ+ community. In support of Pride Month, the American Heart Association, a global force for longer, healthier lives for all, is promoting awareness and health education for all people across the spectrum of diversity, including those who identify as LGBTQ+.
For more than 50 years, the LGBTQ+ community has spent the month of June ...
Order in chaos: Atmosphere’s Antarctic oscillation has natural cycle
2023-06-06
HOUSTON – (June 6, 2023) – Climate scientists at Rice University have discovered an “internally generated periodicity” — a natural cycle that repeats every 150 days — in the north-south oscillation of atmospheric pressure patterns that drive the movement of the Southern Hemisphere’s prevailing westerly winds and the Antarctic jet stream.
“This is something that arises from the internal dynamics of the atmosphere,” said Pedram Hassanzadeh, co-author of a study about the discovery in the open-access journal AGU Advances. “We were playing with some new equations that we had derived ...
Recent papers in ACS Measurement Science Au
2023-06-06
ACS Measurement Science Au is a member of the ACS Au family of journals. These publications are open access, and each one focuses on a specific field relevant to chemistry. Here, we take a look at a few recent papers from ACS Measurement Science Au, which publishes experimental, computational or theoretical research in all areas of chemical measurement science. The journal welcomes papers on any phase of analytical operations, such as sampling, measurement and data analysis.
“Colorimetric Signal Readout for the Detection of Volatile Organic Compounds Using a Printable Glass-Based ...
Two brain mechanisms for picking speech out of a crowd
2023-06-06
Researchers led by Dr. Nima Mesgarani at Columbia University, US, report that the brain treats speech in a crowded room differently depending on how easy it is to hear, and whether we are focusing on it. Publishing June 6th in the open access journal PLOS Biology, the study uses a combination of neural recordings and computer modeling to show that when we follow speech that is being drowned out by louder voices, phonetic information is encoded differently than in the opposite situation. The findings could help improve hearing aids that work by isolating attended speech.
Focusing on speech in a crowded room can be difficult, especially ...
Does multimorbidity impact chronic disease treatment?
2023-06-06
Treatment efficacy for a broad range of chronic diseases does not differ depending on patients’ comorbidities, according to a new study publishing June 6th in the open access journal PLOS Medicine by David McAllister of the University of Glasgow, UK, and colleagues.
There is often uncertainty about how treatments for single conditions should be applied to people who have multiple chronic conditions (multimorbidity). This confusion stems, in part, from the fact that people with multimorbidity are under-represented in randomized controlled trials, and trials rarely report whether the efficacy of treatment ...
Finding clues about the process of cell plasticity
2023-06-06
Researchers have long thought that once a cell starts down its path of differentiation, growing into a skin cell or a liver cell or a neuron, that path could not be changed.
But over the past two decades, scientists have realized this pathway is more complex. Now, using zebrafish as a model, a University of Michigan research team has discovered that a loop in the body's mitochondria—organelles within cells that produce energy for the body—may allow cells to retreat up the path of differentiation. Their results are published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
"Cell fate and differentiation ...
Tectonics matter: USU geoscientists probe geochemistry, microbial diversity of Peruvian hot springs
2023-06-06
LOGAN, UTAH, USA -- South America’s Andes Mountains, the world’s longest mountain range and home to some of the planet’s highest peaks, feature thousands of hot springs. Driven by plate tectonics and fueled by hot rock and fluids, these thermal discharges vary widely in geochemistry and microbial diversity.
Utah State University geoscientists, along with colleagues from Montana State University, examined 14 hot springs within the southern Andes in Peru and discovered microbial community composition is distinctly different in two tectonic settings. Dennis Newell, associate professor in USU’s Department of Geosciences, and recent USU graduate Heather Upin, ...
To prevent future pandemics, leave bats alone
2023-06-06
A new paper in the journal The Lancet Planetary Health makes the case that pandemic prevention requires a global taboo whereby humanity agrees to leave bats alone—to let them have the habitats they need, undisturbed.
Like the SARS coronavirus outbreak of 2003, the COVID-19 pandemic can be traced back to a bat virus. Whether someone handled or ate an infected bat or was exposed to a bat’s bodily fluids in a cave or some other way, or was exposed to another animal that had been infected by a bat, we will quite likely never know. Even a virus released via a lab accident would still have originally come from ...
Investments advance brain research, name MRI for longtime BrainHealth couple
2023-06-06
The Laurie and Todd Platt BrainHealth Project MRI Scanner will help researchers identify neural markers of improved brain health
Center for BrainHealth® celebrates major contributions reaching more than $1 million to support discoveries of brain improvement biomarkers. This investment in advancing the science of brain health is made possible by Sarah and Ross Perot, Jr., Laurie and Todd Platt and many of their friends.
The Sammons BrainHealth Imaging Center is dedicated to discovering a scalable panel of brain measurements correlating physical changes in the brain with changes in a holistic composite metric of brain ...
Nebraska scientists closing in on long-lasting swine flu vaccine
2023-06-06
A successful long-term experiment with live hogs indicates Nebraska scientists may be another step closer to achieving a safe, long-lasting and potentially universal vaccine against swine flu.
The results are not only important to the pork industry, they hold significant implications for human health. That’s because pigs act as “mixing vessels,” where various swine and bird influenza strains can reconfigure and become transmissible to humans. In fact, the 2009 swine flu pandemic, involving ...
Bubble, bubble, more earthquake trouble? Geoscientists study Alaska's Denali fault
2023-06-06
LOGAN, UTAH, USA -- The 1,200-mile-long Denali Fault stretches in an upward arc from southwestern Alaska and the Bering Sea eastward to western Canada’s Yukon Territory and British Columbia. The long-lived and active strike-slip fault system, which slices through Denali National Park and Preserve, is responsible for the formation of the Alaska Range.
“It’s a big, sweeping fault and the source of a magnitude 7.9 earthquake in 2002, that ruptured more than 200 miles of the Denali Fault, along with the Totschunda Fault to the east, causing significant damage to remote villages and central Alaska’s infrastructure,” says Utah State University ...
Movement symptoms in dystonia are caused by spinal cord dysfunction
2023-06-06
Many neurological conditions that involve involuntary muscle contractions have long been considered as diseases of the brain. However, both the brain and the spinal cord contain many nerve cells associated with movement.
The research, published in Science Translational Medicine, used state-of-the-art mouse genetics to distinguish whether the brain or spinal cord was responsible for the disorganisation of movement experienced by dystonia patients.
Focusing on the most common inherited form of dystonia called DYT1, UCL scientists confined a genetic mutation to the spinal cord of the ...
Why are dog breeds with innate diseases popular?
2023-06-06
Flat-faced dogs, such as French and English Bulldogs, are extremely popular despite suffering from severe innate diseases. Hungarian researchers have attempted to uncover the explanation for this paradox. In the end, they concluded that although enthusiasts of flat-faced dogs are aware of the health issues and strive to provide the best for their dogs, they are likely to normalize health problems.
The French and English Bulldogs are among the most popular breeds in both the United States and Europe, but Pugs ...
Nursing home dementia residents’ care linked to majority presence, UC Irvine-led study finds
2023-06-06
Irvine, Calif., June 6, 2023 — The quality of care for nursing home residents with Alzheimer’s disease and related dementias is best when they are in the majority, but most facilities also accommodate a heterogeneous population, where specialized staff training is limited, according to a study led by the University of California, Irvine.
“Recognizing and managing the complex medical conditions and behavioral symptoms of residents with ADRD require enhanced knowledge among staff. These findings raise significant concerns regarding the level of care and quality of life for the majority of these people, highlighting ...
[1] ... [1873]
[1874]
[1875]
[1876]
[1877]
[1878]
[1879]
[1880]
1881
[1882]
[1883]
[1884]
[1885]
[1886]
[1887]
[1888]
[1889]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.