Genetic variants may affect treatment response to commonly prescribed type 2 diabetes medication
2023-06-02
BOSTON – Various medications can be prescribed to lower blood sugar levels in individuals at high risk for developing type 2 diabetes, but it’s often unclear which patients will benefit most from which drugs.
In a study published in Diabetologia, investigators at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH), founding member of Mass General Brigham (MGB), identified genetic variants associated with response to two such drugs: metformin and glipizide. The findings may help personalize ...
UC Davis C-STEM trains Redlands teachers on bringing computer science into math
2023-06-02
Twenty-five teachers from Redlands Unified School District in southern California recently completed training in integrating computer science into math education through a joint program offered by the University of California, Davis, and UC Riverside Extension. The Joint Computer Science Supplementary Teaching Credential Authorization Program has helped Redlands address gaps in student opportunity and achievement, and teachers’ skills.
“Improving math instruction for student success is the most challenging task in education. Redlands partnered with UC Davis to make math instruction with ...
Changes in RECIST tumor measures correlate linearly with survival in patients treated with checkpoint inhibitors
2023-06-02
The Response Evaluation Criteria In Solid Tumors (RECIST), used in many clinical trials to evaluate changes in tumor burden over time, classify objective tumor response into one of four categories (complete or partial response, or stable or progressive disease) based on the percent of change in the sum of the longest diameters of a set of target lesions.
An analysis of data from the SWOG S1609 trial conducted by the NCI-funded National Clinical Trials Network (NCTN) finds that in patients treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors, survival times correlate linearly with that change, rather than exhibiting threshold effects ...
Bench-to-field study identifies pesticides that could influence Parkinson's disease
2023-06-02
A new study from researchers in the Khurana lab at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, a founding member of the Mass General Brigham healthcare system, in close collaboration with researchers from the Ritz lab at UCLA and the Rubin lab at Harvard University, identified pesticides that could be relevant to the development of Parkinson’s disease. The study was led by Richard Krolewski, MD, PhD, a neurologist in the Brigham’s Division of Movement Disorders and Ann Romney Center for Neurologic Diseases, and Kimberly ...
Results of SWOG S1929 trial show patients with small-cell lung cancer with SLFN11 expression can benefit from PARP inhibitor added to immune checkpoint blockade
2023-06-02
Among patients with extensive stage small-cell lung cancer (SCLC) that is positive for expression of the Schlafen-11 gene (SLFN11), those who received maintenance atezolizumab immunotherapy plus the PARP inhibitor talazoparib had significantly longer progression-free survival (PFS) times than those who received atezolizumab alone (median PFS 4.2 months versus 2.8 months).
These results from the phase II S1929 trial conducted by the SWOG Cancer Research Network, a clinical trials group funded by the National Cancer Institute (NCI), will be reported ...
UCSF Health Cancer experts featured at premier cancer meeting
2023-06-02
Oncology specialists from around the globe will gather for the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) Annual Meeting to discuss the latest cancer therapies, technologies, research and education.
The theme this year is Partnering With Patients: The Cornerstone of Cancer Care and Research. More than 30,000 people are expected to attend the meeting taking place in Chicago and online June 2-6, 2023.
“As the world’s leading clinical cancer meeting, ASCO is an important event for oncology professionals to share information on the latest ...
Multiple sclerosis more prevalent in Black Americans than previously thought
2023-06-02
Multiple sclerosis has traditionally been considered a condition that predominantly affects white people of European ancestry. However, a new analysis conducted by a North American team led by University of Maryland School of Medicine (UMSOM) researchers suggests that the debilitating neurological condition is more prevalent in Black Americans than once thought. It is also far more prevalent in Northern regions of the country including New England, the Dakotas, and the Pacific Northwest.
Findings from the new study were recently published in the journal JAMA Neurology.
“We found a much higher prevalence of multiple sclerosis in Black Americans than previously ...
Sensory adapted dental rooms significantly reduce autistic children’s physiological and behavioral stress during teeth cleanings
2023-06-02
New results from a study led by USC researchers at Children’s Hospital Los Angeles show that a sensory adapted dental clinic environment creates less distressing oral care experiences for autistic children. The open-access article is available today in JAMA Network Open.
“We’ve shown that the combination of curated visual, auditory and tactile adaptations — all of which are easily implemented, relatively inexpensive and don’t require training to safely use — led to statistically significant decreases in autistic children’s behavioral ...
Couples’ social networks took long-lasting hit during COVID
2023-06-02
Key takeaways:
A UCLA study shows that a the outset of the COVID-19 pandemic, social interactions, both virtual and in person, declined significantly for married couples.
The decline was found to be greater and more long-lasting for Black and Latino couples and lower-income couples than for white couples and wealthier couples.
The researchers suggest exploring new ways of protecting public health during crises that also help more vulnerable populations sustain meaningful relationships.
Following the lockdowns and restrictions on public gatherings in the early days of COVID-19, the social networks of white, ...
AI software can provide ‘roadmap’ for biological discoveries
2023-06-02
Predicting a protein’s location within a cell can help researchers unlock a plethora of biological information that’s critical for developing future scientific discoveries related to drug development and treating diseases like epilepsy. That’s because proteins are the body’s “workhorses,” largely responsible for most cellular functions.
Recently, Dong Xu, Curators Distinguished Professor in the Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science at the University of Missouri, and colleagues updated their protein localization prediction model, MULocDeep, ...
Study helps explain what drives psoriasis severity and offers clues as to how disease may spread to other body parts
2023-06-02
Beneath and beyond the reddish, flaky lesions that form in the skin of those with psoriasis, mild and severe forms of the disease can be told apart by the activity of key cells and signaling pathways, a new study shows.
Led by researchers at NYU Grossman School of Medicine, the study mapped hidden features of inflammation and how they compared in cases of increasing severity of psoriatic disease. The team’s findings may help explain how small areas of skin inflammation can have wide-ranging effects in other parts of the body. Up to one-fifth of those with the skin disease, the researchers note, ...
New study finds strengthening protection of existing parks is crucial for biodiversity conservation
2023-06-02
-With pictures-
In a new study, bioscientists argue that strengthening the protection given to areas already protected under law or by local communities is as critical for safeguarding biodiversity as creating new protected areas.
The research team, which included scientists from Durham University, National University of Singapore (NUS) and Princeton University, found that about 70 per cent of the roughly 5000 species analysed either have no apparent representation in protected areas, occur in protected areas that have been downgraded, downsized or degazetted, ...
Scientists reveal new details of cellular process which prevents spread of cancer
2023-06-02
Researchers have for the first time characterised a unique molecular mechanism of the early stages of programmed cell death or apoptosis, a process which plays a crucial role in prevention of cancer.
The study, which is published today (Friday 2nd June 2023) in Science Advances, was led by Dr Luke Clifton at the STFC ISIS Neutron and Muon Source (ISIS) in Oxfordshire, alongside co-lead Professor Gerhard Gröbner at the University of Umeå and partners at the European Spallation Source in Sweden. It is ...
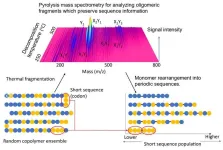
Development of an AI-based mass spectrometric technique capable of determining the monomeric sequence of a polymer
2023-06-02
1. The National Institute for Materials Science (NIMS) has developed an AI-based mass spectrometric technique capable of determining the monomeric sequence of a polymer. This technique may be useful in gaining a deeper understanding of basic polymeric structures, facilitating the development of new materials and helping solve plastic recycling problems.
2. A polymer is a very large molecule composed of a chain of many (ranging from hundreds to hundreds of thousands) small molecules called monomers that are bonded together. Many common polymers (e.g., plastics and resins) are copolymers, consisting of several different types of monomers. During the copolymerization process, the monomers ...
Non-invasive treatment of uterine fibroids research project secures grant at Baton Rouge Health-Tech Catalyst Pitch Night
2023-06-02
BATON ROUGE – A collaboration among Dr. Frank Greenway of Pennington Biomedical Research Center, Dr. Beverly Ogden of Woman’s Hospital in partnership with LSU, and the University of Louisiana at Lafayette, was named as one of three award recipients at the Baton Rouge Health-Tech Catalyst Pitch Night. The team will investigate non-invasive treatment of uterine fibroids, or benign growths, such as leiomyomas or myomas, that development from the muscle tissue of the uterus.
“Fibroids are non-cancerous tumors in the wall of the uterus that are common, and can cause bleeding, pain, and infertility,” ...
nTIDE May 2023 Jobs Report: Job numbers rebound bringing people with disabilities close to previous high in employment
2023-06-02
East Hanover, NJ – June 2, 2023 – In a sharp reversal, employment indicators rebounded for people with disabilities in May, according to today’s National Trends in Disability Employment – semi-monthly update (nTIDE), issued by Kessler Foundation and the University of New Hampshire’s Institute on Disability (UNH-IOD). Employment appears to be remaining strong despite the threats to the labor market posed by the debt ceiling crisis and ongoing efforts to control inflation.
Month-to-Month nTIDE Numbers (comparing April 2023 to May 2023)
Based ...
American Tinnitus Association elects Wayne State researcher as new chair
2023-06-02
DETROIT – The American Tinnitus Association (ATA) has elected Jinsheng Zhang, Ph.D., professor and chair of the Department of Communication Sciences and Disorders in Wayne State University’s College of Liberal Arts and Sciences, as the new chair of its board of directors. With decades of experience in tinnitus research and work with the ATA, Zhang aims to assist with proactive recruitment of scientists to the field of tinnitus and engage more researchers in ATA grant opportunities that will spur progress toward more effective treatments and cures.
Tinnitus ...
Media Alert: American College of Cardiology to host Sports Cardiology Conference
2023-06-02
The American College of Cardiology will host the annual Care of the Athletic Heart course on June 8-10, 2023, in Washington, including poster abstracts and educational sessions. The course is designed for all clinicians who provide cardiovascular care for the professional, occupational, tactical or recreational athlete. As the athletic population expands to all demographic groups, it is critical that there is a larger contingent of clinicians who understand the latest care and practice management for athletes at every level.
Dermot Phelan, BAO, MBBCh, PhD, FACC, and Megan Wasfy, ...
Immunotherapy for brain cancer metastases shows clinical benefit
2023-06-02
In a phase 2 clinical trial of the immune checkpoint inhibitor pembrolizumab, investigators found that 42 percent of patients with metastatic brain cancer benefited from the therapy, with seven patients in the trial surviving longer than two years. The authors caution that these benefits must be weighed against risk of toxicity, but, overall, the study shows promising results that warrant larger studies and efforts to identify patients most likely to benefit from this treatment. Their findings are published in Nature Medicine and presented simultaneously at the 2023 ASCO Annual Meeting on June 2.
“There ...
Commentary calls for equal access to healthcare for DACA recipients and all immigrants
2023-06-02
The paper, published April 17 in The Lancet Regional Health – Americas, was co-authored by Dr. Gunisha Kaur, an associate professor of anesthesiology at Weill Cornell Medicine and medical director of the Weill Cornell Center for Human Rights; Stephen Yale-Loehr, a professor of immigration law practice at Cornell Law School; and Jin K. Park, a medical student at the Harvard School of Medicine and the first DACA recipient awarded a Rhodes Scholarship.
“The erratic enforcement of the DACA program since its inception has led many immigrants and their families to disengage completely from the healthcare system to avoid risking deportation,” said ...
Taming a frenzied immune system
2023-06-02
Researchers at the University of Louisville have received $5.8 million in two grants from the National Institutes of Health to expand their work to better understand and prevent immune system dysregulation responsible for acute respiratory distress, the condition responsible for serious illness and death in some COVID-19 patients. A separate $306,000 NIH Small Business Innovation Research grant supports early testing of a compound developed at UofL as a potential treatment.
The three grants combined total $6.1 million.
During the pandemic, health care providers worked tirelessly to treat patients ...
Veterans exposed to Agent Orange may be at increased risk of developing progressive blood cancers
2023-06-02
WASHINGTON --- Research conducted at Georgetown University’s Lombardi Comprehensive Cancer Center and the Washington DC VA Medical Center on a database of veterans exposed to Agent Orange found an association for an increased risk of developing myeloproliferative neoplasms (MPNs), which are acquired stem cell disorders that can lead to overproduction of mature blood cells complicated by an increased risk of blood clots in arteries and veins. When MPNs progress, they can become deadly leukemias.
The findings will be presented at the American Society of Clinical Oncology 2023 annual meeting in Chicago in June.
Agent Orange is an herbicide that was utilized by the United States military ...
Hispanic women still at higher risk for births with neural tube defects after voluntary folic acid fortification of corn masa flour
2023-06-02
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) mandated folic acid fortification of all enriched cereal grains in 1996, and this regulation resulted in a reduction of neural tube defect (NTD)–affected pregnancies for the population in the United States. While this mandatory food fortification strategy is an example of a public health success, Hispanic women in the US continued to be twice as likely to give birth to a child affected by NTD compared to non-Hispanic women. It was not until the year 2016 that the FDA approved voluntary, but not mandatory, folic acid fortification for corn masa flour products in the US to focus on the Hispanic diet staples, such ...
Buckle up! A new class of materials is here
2023-06-02
Usually, the two characterizations of a material are mutually exclusive: something is either stiff, or it can absorb vibrations well – but rarely both. However, if we could make materials that are both stiff and good at absorbing vibrations, there would be a whole host of potential applications, from design at the nano-scale to aerospace engineering.
Buckling does the trick
A team of researchers from the University of Amsterdam has now found a way to create materials that are stiff, but still good at absorbing vibrations – and equally importantly, that can be kept very light-weight. David Dykstra, lead author of the ...
Lupus Therapeutics partners to evaluate potential treatment for SLE and lupus nephritis through North American trial network
2023-06-02
NEW YORK, N.Y. — June 2. Lupus Therapeutics announced the start of a collaboration to conduct three Phase 3 clinical trials testing an investigational therapeutic ianalumab for systemic lupus erythematosus and lupus nephritis. Lupus Therapeutics, the clinical research affiliate of the Lupus Research Alliance, will help Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation (Novartis) conduct the trials through the Lupus Clinical Investigators Network (LuCIN) at top academic centers throughout North America.
Lupus is a devastating heterogeneous autoimmune disease affecting millions worldwide with symptoms that can range from debilitating fatigue to ...
[1] ... [1891]
[1892]
[1893]
[1894]
[1895]
[1896]
[1897]
[1898]
1899
[1900]
[1901]
[1902]
[1903]
[1904]
[1905]
[1906]
[1907]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.