IMDEA Software and IMDEA Networks work to deploy in the Community of Madrid "MadQCI": Europe's largest quantum network
2023-05-31
IMDEA Software and IMDEA Networks Institutes participate together with six other partners (Instituto Nacional de Técnica Aeroespacial, Centro Español de Metrología, Fundación Vithas, Universidad Autónoma de Madrid, Universidad Politécnica de Madrid and Universidad Complutense de Madrid) in the MADQuantum-CM project, funded by the Community of Madrid, the Spanish State through the Plan for Recovery, Transformation and Resilience, and the European Union through the NextGeneration EU funds. The objective ...
1 in 3 adults with Type 2 diabetes may have undetected cardiovascular disease
2023-05-31
Research Highlights:
One-third of adults in the U.S. with Type 2 diabetes may have symptomless or undetected cardiovascular disease.
Adults with Type 2 diabetes who do not have any signs or symptoms of cardiovascular disease are more likely to have elevated levels of two proteins linked to heart disease than peers without Type 2 diabetes. These cardiac biomarkers are associated with an increased risk of death from cardiovascular disease and any cause.
The findings suggest that routine screening for these two cardiac biomarkers and more tailored interventions may help to reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease ...
Heart health is sub-optimal among American Indian/Alaska Native women, supports needed
2023-05-31
Statement Highlights:
In its first scientific statement addressing cardiovascular health in American Indian/Alaska Native (AI/AN) women of childbearing age, the American Heart Association reports that more than 60% of AI/AN women already have suboptimal heart health when they enter pregnancy, which is strongly related to the development of heart disease later in life.
In addition, more than 4 in 5 AI/AN women reported they have experienced violence, and they are disproportionately likely to have also experienced a high number of adverse childhood experiences, which contribute to higher heart disease risk.
Type 2 diabetes is the predominant, traditional cardiovascular ...
New health indicator can revolutionize how we measure and achieve well-being
2023-05-31
The term ‘well-being’ entered popular vocabulary during the Covid-19 pandemic soon after ‘lockdown’ and ‘quarantine’. We quickly discovered that without the ability to take walks, socialize, and work, our well-being suffered. Health was suddenly more than just the state of our bodies – it also depended on our ability to engage in activities that matter to us.
Though this was a revelation to many, the World Health Organization (WHO) had already begun this rethinking of health. It created a new concept and assessment ...
Research calls for changes to state law requiring child protective services to be notified when medications for opioid use disorder are used during pregnancy
2023-05-31
BOSTON—In the United States, federal legislation mandates that all states track data on all newborns who have been exposed to substances during pregnancy and ensure that a plan of Safe Care is created for each family. Yet each state manages those regulations differently.
In Massachusetts, the Department of Children and Families (DCF) has issued guidance that any prenatal substance exposure—including exposure to medications for opioid use disorder (MOUD)—is an indication to file a report for alleged child abuse/neglect upon the birth of the child.
MOUD ...
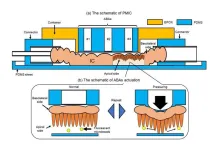
Actively reducing noise by ionizing air
2023-05-31
Did you know that wires can be used to ionize air to make a loudspeaker? Simply put, it’s possible to generate sound by creating an electric field in a set of parallel wires, aka a plasma transducer, strong enough to ionize the air particles. The charged ions are then accelerated along the magnetic field lines, pushing the residual non-ionized air in a way to produce sound.
If a loudspeaker can generate sound, it can also absorb it.
While this plasma loudspeaker concept is not new, EPFL scientists went ahead and built a demonstration of the plasma transducer, with the aim to study noise reduction. They came up with a new concept, ...
Can phrases like ‘isn’t it?’ or ‘right?’ compromise classroom learning? New study answers
2023-05-31
Classroom education, in an ideal sense, must engage all students in a constructive discussion with the teacher, making it the latter’s responsibility to utilize different inclusive strategies. To bring the attention of distracted students back to the classroom discussion, teachers often have to use different methods to remind them that they are an equal and important part of this shared activity. This task can be tricky since most teachers attend to multiple students in a classroom. What strategies do teachers use to draw the attention of all the students to the ...
Reduced emissions during the pandemic led to increased climate warming
2023-05-31
The Covid pandemic shutdowns in South Asia greatly reduced the concentration of short-lived cooling particles in the air, while the concentration of long-lived greenhouse gases was barely affected. Researchers were thus able to see how reduced emissions of air pollution leads to cleaner air but also stronger climate warming.
It is well known that emissions of sulfur and nitrogen oxides and other air pollutants lead to the formation of aerosols (particles) in the air that can offset, or mask, the full climate warming caused by greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide and methane. But there has been a lack of knowledge about this ‘masking effect’. ...
1 in 5 teachers feel carrying gun to class would make schools safer; More than half think armed teachers would make students less safe
2023-05-31
U.S. teachers are divided on whether arming themselves would make schools safer, with one in five saying they would be interested in carrying a gun to school, according to a nationally representative survey conducted by the RAND Corporation.
The survey found that 54% of teachers believe teachers carrying firearms would make schools less safe, 20% believe teacher-carry would make schools safer, and 26% feel it would make schools neither more nor less safe.
Yet even more concerning to teachers than guns is bullying, which teachers listed as their top safety concern.
The survey, conducted in October and November 2022, focused on how K-12 teachers view safety ...
Four ways to advance equity and justice goals in climate action planning
2023-05-31
Municipal climate action plans often identify equity and justice as goals, but engagement with these concepts is mostly rhetorical. A new study from the University of Waterloo details how planners can bridge the gap and challenge the current state of climate change and social inequity.
The study asserts that developing participatory approaches to public consultation and community engagement that actively and intentionally involve vulnerable populations who are most affected by climate change is critical. Expanding the sphere of knowledge we ...
Biological cleanup discovered for certain “forever chemicals”
2023-05-31
University of California, Riverside, chemical and environmental engineering scientists have identified two species of bacteria found in soil that break down a class of stubborn “forever chemicals,” giving hope for low-cost biological cleanup of industrial pollutants.
These bacteria destroy a subgroup of per- and poly-fluoroalkyl substances, or PFAS, that have one or more chlorine atoms within their chemical structure, Yujie Men, an assistant professor in the Bourns College of Engineering, and her UCR colleagues, reported in the journal Natural Water.
Unhealthful forever chemicals persist in the environment ...
Cancer survivors who quit smoking have 36% lower cardiovascular risk than continuers
2023-05-31
Sophia Antipolis, 31 May 2023: Cancer patients who continue smoking after their diagnosis have a nearly doubled risk of heart attack, stroke or death due to cardiovascular disease compared with non-smokers, according to research published on World No Tobacco Day in European Heart Journal, a journal of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC).1
According to the World Health Organization, there were more than 50.5 million cancer survivors worldwide in 2020.2 Study author Dr. Hyeok-Hee Lee of Yonsei University College ...
More depressed patients than previously estimated could have increased activation of their immune system
2023-05-31
New research from the Institute of Psychiatry, Psychology & Neuroscience (IoPPN) at King’s College London has used an assessment of gene expression involved in the immune response to show that there could be more patients with MDD with activated immune systems than research has previously estimated.
By identifying the molecular mechanisms involved in this association, the research could pave the way to better identify those patients with an immune component to their depression which would potentially help to provide more personalised approaches to treatment ...
Shedding light on the complex flow dynamics within the small intestine
2023-05-31
Science is well aware of the important role that gut bacteria and their interactions with the gastrointestinal tract play in our overall health. Villi, tiny finger-like structures that line the inside of the small intestine (SI), are known to interact with the gut bacteria and trigger a protective immune response. Despite researching into the molecular mechanisms underlying these interactions, however, not much is known about the dynamics of liquid flow around the villi.
While computer simulations have aided such observations, ...
UK cardiology societies issue joint policy statement to stamp out bullying, harassment, and discrimination in the specialty
2023-05-31
The British Junior Cardiologists’ Association (BJCA) and the British Cardiovascular Society (BCS) have issued a joint position statement in a bid to stamp out bullying, harassment, discrimination and other “unacceptable” and “unprofessional” behaviours in the specialty.
The statement, published online in the journal Heart, urges every cardiology team member to call out these behaviours to drive culture change.
Endorsed by 19 organisations affiliated with the BCS, the statement represents a specialty-wide response to the issue.
It comes in the wake of evidence suggesting ...
Predominance of young Asian men among large UK case series of laughing gas users
2023-05-31
The largest clinical case series to date of recreational users of nitrous oxide, popularly known as laughing gas, has found a predominance of young men of Asian ethnicity among those with neurological side effects who were seen at hospitals in 3 major cities in England.
This may indicate genetic susceptibility to the nerve damage caused by exposure to the gas, or other, as yet unidentified, social factors, suggest the researchers by way of an explanation for the finding, published online in the Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery & Psychiatry.
Nitrous oxide is widely used as an anaesthetic in people and animals, ...
Ketamine nasal spray may prove safe and effective treatment for refractory migraine
2023-05-31
Ketamine taken in the form of a nasal spray may prove a safe and effective treatment for refractory chronic migraine, suggests a single centre study, published in the open access journal Regional Anesthesia & Pain Medicine.
It’s a more convenient alternative to intravenous infusion—the usual method of administration for these patients—but the potential for overuse means that it should be reserved for those in whom other treatment approaches have failed, caution the researchers.
Several clinical trials have shown ...
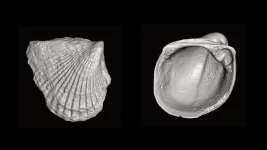
The clams that fell behind, and what they can tell us about evolution and extinction
2023-05-31
Every so often, life on Earth steps onto a nearly empty playing field and faces a spectacular opportunity. Something major changes—in the atmosphere or in the oceans, or in the organisms themselves —and the existing species begin to branch out into a brand-new world. Scientists are fascinated by this process, because it’s a unique look into evolution at pivotal moments in the history of life.
A new study led by scientists with the University of Chicago examined how bivalves—the group that includes clams, mussels, scallops, and oysters—evolved among many others in the period of rapid evolution known as the Cambrian Explosion. The team found ...
Medical school does not equip new doctors for the real working world, junior doctor warns
2023-05-31
Clinician burnout and overwork are known to adversely affect patient safety and junior doctors may be particularly vulnerable, research suggests.
The UK is facing a crisis in recruitment and retention in medicine, with a recent survey by the British Medical Association reporting that 4 in 10 junior doctors will quit their roles as soon as they find another job.
Considering the immense pressure doctors are under, with their decisions having the potential to shape the course of patients’ illnesses and even their lives, is a balanced and happy life as a doctor still possible?
In a new book released today titled The Bleep Test, junior doctor Luke Austen has combined ...
Unique “bawdy bard” act discovered, revealing 15th-century roots of British comedy
2023-05-31
University of Cambridge media release
UNDER STRICT EMBARGO UNTIL 00:01AM (UK TIME) ON WEDNESDAY 31ST MAY 2023
An unprecedented record of medieval live comedy performance has been identified in a 15th-century manuscript. Raucous texts – mocking kings, priests and peasants; encouraging audiences to get drunk; and shocking them with slapstick – shed new light on Britain’s famous sense of humour and the role played by minstrels in medieval society.
The texts contain the earliest recorded use of ‘red herring’ in English, extremely rare forms of medieval literature, as well as a ...
Saved from extinction, Southern California’s Channel Island Foxes now face new threat to survival
2023-05-31
Tiny foxes — each no bigger than a five-pound housecat — inhabiting the Channel Islands off the coast of Southern California were saved from extinction in 2016. However, new research reveals that the foxes now face a different threat to their survival.
Suzanne Edmands, professor of biological sciences at USC Dornsife College of Letters, Arts and Sciences, and Nicole Adams, who earned her PhD from USC Dornsife in 2019, found that the foxes’ genetic diversity has decreased over time, possibly jeopardizing their survival ...
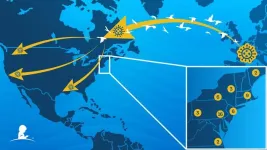
Genetic change increased bird flu severity during U.S. spread
2023-05-31
(MEMPHIS, Tenn. – May 29, 2023) St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital scientists discovered how the current epizootic H5N1 avian influenza virus (bird flu) gained new genes and greater virulence as it spread west. Researchers showed that the avian virus could severely infect the brains of mammalian research models, a notable departure from previous related strains of the virus. The researchers genetically traced the virus’ expansion across the continent and its establishment in wild waterfowl populations to understand what makes it so different. The study was recently published in Nature Communications.
“We ...
New Jersey Health Foundation awards grants to Kessler Foundation to advance research in brain and spinal cord stimulation methods
2023-05-30
East Hanover, NJ – May 30, 2023 – Annually, New Jersey Health Foundation (NJHF) invites researchers to submit applications for grants aimed at supporting pilot research projects that exhibit promising potential. These grants serve as opportunities for scientists to utilize their initial findings to secure further funding and progress their research. This year, NJHF granted awards to two Kessler Foundation scientists to conduct studies that expand research in upper extremity exercise after stroke ...
Extracting a clean fuel from water
2023-05-30
A plentiful supply of clean energy is lurking in plain sight. It is the hydrogen we can extract from water (H2O) using renewable energy. Scientists are seeking low-cost methods for producing clean hydrogen from water to replace fossil fuels, as part of the quest to combat climate change.
Hydrogen can power vehicles while emitting nothing but water. Hydrogen is also an important chemical for many industrial processes, most notably in steel making and ammonia production. Using cleaner hydrogen is highly desirable in those industries.
“By using ...
NJIT researchers awarded $4.6m to unlock mysteries of solar eruptions
2023-05-30
A New Jersey Institute of Technology research team led by physics professor Wenda Cao at the university’s Center for Solar Terrestrial Research (CSTR) has been awarded a $4.64 million National Science Foundation grant to continue leading explorations of the Sun’s explosive activity at Big Bear Solar Observatory (BBSO).
The grant marks the largest project that the Solar-Terrestrial Research Program under NSF’s Division of Atmospheric and Geospace Sciences (AGS) supports, extending five more years of baseline funding for all science, instrumentation and education activities at BBSO, located at California’s Big Bear Lake.
The ...
[1] ... [1899]
[1900]
[1901]
[1902]
[1903]
[1904]
[1905]
[1906]
1907
[1908]
[1909]
[1910]
[1911]
[1912]
[1913]
[1914]
[1915]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.