CAREER awards to foster quantum material research program
2023-05-19
Physicist Jin Hu has been awarded a second Faculty Early Career Development (CAREER) award, this time from the National Science Foundation. The new award of $579,527 comes two years after Hu received a $750,000 CAREER Award from the U.S. Department of Energy.
NSF and DOE CAREER awards are considered the most competitive and prestigious awards to honor faculty members in the early stages of their careers. The awards support research and education activities. It is rare for an investigator to receive two CAREER awards.
Hu, an assistant professor of physics in the Fulbright College of Arts and Sciences, leads the Quantum Materials group at ...
UH researchers develop sensors that operate at high temperatures and in extreme environments
2023-05-19
Extreme environments in several critical industries – aerospace, energy, transportation and defense – require sensors to measure and monitor numerous factors under harsh conditions to ensure human safety and integrity of mechanical systems.
In the petrochemical industry, for example, pipeline pressures must be monitored at climates ranging from hot desert heat to near arctic cold. Various nuclear reactors operate at a range of 300-1000 degrees Celsius, while deep geothermal wells hold temperatures up to 600 degrees Celsius.
Now a team of University of Houston researchers has developed ...
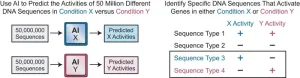
Artificial intelligence catalyzes gene activation research and uncovers rare DNA sequences
2023-05-19
Artificial intelligence has exploded across our news feeds, with ChatGPT and related AI technologies becoming the focus of broad public scrutiny. Beyond popular chatbots, biologists are finding ways to leverage AI to probe the core functions of our genes.
Previously, University of California San Diego researchers who investigate DNA sequences that switch genes on used artificial intelligence to identify an enigmatic puzzle piece tied to gene activation, a fundamental process involved in growth, ...
Promoting lower-calorie options on delivery apps could help users select healthier options, randomized trials find
2023-05-19
Simple initiatives to help people select lower-calorie options when ordering takeaways in delivery apps could help tackle the obesity epidemic, suggest three randomised trials being presented at this year’s European Congress on Obesity (ECO) in Dublin, Ireland (17-20 May).
The research, which involved using a simulated food delivery app, found that interventions which positioned lower-calorie foods and restaurants more prominently, pre-selected smaller portions by default, and displayed calorie labels, all significantly reduced the ...
Individuals who feel safe where they live lose more weight, Dutch study finds
2023-05-19
Feeling safe where you live may be key to weight loss, the European Congress on Obesity (ECO) in Dublin, Ireland (17-20 May) will hear.
Preliminary Dutch research has shown that the feeling of safety in one's neighbourhood is linked to greater weight loss when taking part in lifestyle interventions.
The term “neighbourhood safety” covered four dimensions: not feeling afraid of crime or harassment while walking through the neighbourhood, feeling safe while walking or cycling due to heavy traffic, adequate street lighting during ...
New analysis shows improved body composition with tirzepatide is consistent across adult age groups with overweight or obesity
2023-05-19
A new analysis of SURMOUNT-1, the first Phase 3 study of tirzepatide in adults for chronic weight management shows that tirzepatide improves body composition across a range of adult age groups. The analysis is presented by Dr Louis Aronne, Comprehensive Weight Control Center, Division of Endocrinology, Diabetes, and Metabolism, Weill Cornell Medicine, New York, USA, and colleagues.
The efficacy and safety of tirzepatide, a glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) and glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) ...
Whole body cryostimulation may be a useful extra treatment for obesity
2023-05-19
Whole body cryostimulation is a useful “add-on” treatment for obesity, research being presented at the European Congress on Obesity (ECO) in Dublin, Ireland (17-20 May) suggests.
Levels of cholesterol and other blood fats improved twice as much in individuals living with obesity who were exposed to extreme cold for a short period of time, compared with individuals given a sham treatment.
Those who had whole body cryostimulation (WBC) also experienced a greater reduction in waist circumference and in blood sugar levels.
Dr Jacopo Fontana, of the Istituto Auxologico ...
Boys need ‘lessons in bromance’ to tackle mental health crisis in schools
2023-05-19
Teenage boys are twice as likely as girls to die by suicide, and, when boys become men, they are three times more likely than women to die by suicide.
After years on the frontline of teaching and observing, first-hand, a decline in teenage mental health, a teacher has warned that we need to deal better with male anger, friendships, and attitudes towards sex in order to combat the male suicide crisis.
Official statistics for England, Scotland, and Wales show that in 2020, 264 people aged 10–19 died by suicide – 72% of these were boys. In England, suicide is the single biggest killer of men under ...
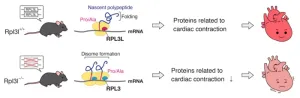
A ribosomal traffic jam that breaks the heart
2023-05-19
Fukuoka, Japan—A team of researchers have discovered that a mutation in a ribosomal protein found specifically in heart and skeletal muscle leads to impaired cardiac contractility in mice.
The mutation was found to delay the rate of translating mRNA, leading to ribosomes colliding and causing protein folding abnormalities. The abnormal proteins would then be targeted and degraded by the cell's quality control system. Moreover, while the deficiency in the ribosomal protein, known as RPL3L, altered translation dynamics for the entire tissue, ...
Illinois Tech project receives $1.6 million contract to develop system for authorship attribution and anonymization
2023-05-18
CHICAGO—May 18, 2023—Researchers at Illinois Institute of Technology have secured a $1.6 million contract to develop a groundbreaking system for authentic authorship attribution and anonymization. Using natural language processing and machine learning, the program, known as AUTHOR, promises to create “stylistic fingerprints” for reliable identification, while also providing robust solutions for anonymization. With broad applications including counterintelligence, combating misinformation, and even investigating the origins of ancient religious texts, the project marks a significant leap in computational analysis.
The project—a collaboration ...
Wayne State University receives grant to address health care and costs in state prisons
2023-05-18
DETROIT – Wayne State University faculty member Rodlescia Sneed, Ph.D. has been awarded a five-year Career Development grant from the National Institute on Aging of the National Institutes of Health. Sneed joined the Institute of Gerontology at WSU in 2022 as an assistant professor jointly appointed with the Department of Psychology in the College of Liberal Arts and Sciences. The nearly $600,000 award, Maximizing the Scalability of the Chronic Disease Self-Management Program (CDSMP) Among Older Adults in State Correctional Settings, is aimed to deepen her training ...
Catching foodborne illness early
2023-05-18
Produce such as lettuce and spinach is routinely tested for foodborne pathogenic bacteria like salmonella, listeria monocytogenes and pathogenic types of E. coli in an effort to protect consumers from getting sick.
Rapid testing of foods may occur, but it still takes time to figure out who is sick and from where the contaminated product originated. That’s far too late for the many Americans who already ate the produce. The current solution, often a multi-state recall, then becomes damage control.
University of Delaware researchers want to spot these bacteria before anyone ever falls ill. As detailed in an article published ...
NASA releases new solar eclipse educational materials
2023-05-18
To help learners of all ages understand how to safely observe the Oct. 14, 2023, annular solar eclipse and the April 8, 2024, total solar eclipse, NASA has released a new set of resources for educators.
My NASA Data, in collaboration with the NASA Heliophysics Education Activation Team (NASA HEAT), has released a new set of resources for educators centered around solar eclipses. My NASA Data allows students in grades 3 through 12 and their teachers to analyze and interpret NASA mission data. It also supports educators in the integration of authentic Earth systems data into their instruction.
The My NASA Data solar eclipse ...
Study reveals novel action mechanism of corticosteroids in combating inflammation caused by COVID-19
2023-05-18
Since the start of the COVID-19 pandemic, a class of corticosteroids called glucocorticoids (GCs) have become established as one of the main treatment options, especially for severe cases, thanks to their anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressant action. Brazilian researchers recently discovered new ways in which these drugs influence the organism’s inflammatory response during an infection: they raise levels of endocannabinoids (eCBs), molecules produced by the organism itself and that bind to the same receptor as cannabidiol; and they lower blood levels of platelet-activating factor (PAF), a lipidic mediator of inflammation and clotting.
The ...
Study: Wildfire spread risk increases where trees, shrubs replace grasses
2023-05-18
Across the United States over the past decade, an average of over 61,000 wildfires have burned some 7.2 million acres per year. Once a wildfire starts spreading, the firefighting task is exacerbated by issues like spot fires, where winds carry lofted sparks and start new fires outside of the original fire perimeter. The greater the potential spot fire distance, the more difficult wildfires are to monitor, control and suppress.
A new study, led by University of Florida forest management researcher Victoria Donovan, found that as woody ...
Novel virtual coronary roadmap tool reduces volume of iodinated contrast needed during percutaneous coronary interventions
2023-05-18
Phoenix, AZ (May 18, 2023)- Results from Dynamic Coronary Roadmap for Contrast Reduction (DCR4Contrast), a multi-center prospective, unblinded, randomized controlled trial were presented today as late-breaking clinical research at the Society for Cardiovascular Angiography & Interventions (SCAI) 2023 Scientific Sessions. The trial found that Dynamic Coronary Roadmap (DCR), a percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) navigation support tool developed by health technology company Philips, effectively reduces iodinated contrast during PCI.
Iodinated contrast is used to enhance the ability ...
First-of-its-kind study confirms safety of distal radial artery access for cardiac catheterization
2023-05-18
Phoenix, AZ (May 18, 2023)- One-year findings from the Distal versus Proximal Radial Artery Access for Cardiac Catheterization and Intervention (DIPRA) study were presented today as late-breaking clinical research at the Society for Cardiovascular Angiography & Interventions (SCAI) 2023 Scientific Sessions. The single-center, randomized-controlled trial evaluated outcomes of hand function and effectiveness of conventional proximal radial artery (PRA) access compared to distal radial artery (DRA) access for cardiac catheterization.
Current guidelines for patients undergoing percutaneous intervention recommend PRA access. A complication of PRA is radial artery occlusion, ...
Historical memories have long reach in consumer preferences, study finds
2023-05-18
Toronto - Zachary Zhong had heard his grandparents’ stories about the Japanese invasion in 1944 of neighbouring counties in his hometown in China. As the Japanese army continued their advance civilians were killed and injured, while others fled the invaders’ path, some taking shelter in his family’s ancestral home.
Those events lodged deep into locals’ memory. Curious about the impact of a re-ignited territorial dispute between Japan and China in 2012, Zhong, now an assistant professor of marketing at the University of Toronto’s Rotman School of Management looked at what happened to car sales in the province of Guangxi around ...
Forgetfulness, even fatal cases, can happen to anyone, study shows
2023-05-18
Since 1998, approximately 496 children have died of pediatric vehicular heatstroke in the United States because their caregiver forgot they were in the car, according to recent data from NoHeatStroke.org.
Advocacy groups have been lobbying Congress to enact laws to help protect against this particular forgetfulness by requiring certain safety mechanisms be installed into automobiles. Researchers at the University of Notre Dame set out to understand how and why this kind of forgetfulness is even possible.
Nathan Rose, the William P. and Hazel ...
FSU researchers analyze carbon sequestration in California Current Ecosystem
2023-05-18
Florida State University researchers have analyzed the carbon exported from surface waters of the California Current Ecosystem — the first-ever study to quantify the total carbon sequestration for a region of the ocean.
The study, published in Nature Communications, serves as a framework for assessing how the processes that sequester carbon might change in a warmer world, while also creating a blueprint for similar budgets in other ocean regions.
Understanding the carbon cycle — the sources and reservoirs of carbon — is an important focus of Earth sciences. Many studies have examined the carbon sequestered ...
Smart material prototype challenges Newton’s laws of motion
2023-05-18
COLUMBIA, Mo. – For more than 10 years, Guoliang Huang, the Huber and Helen Croft Chair in Engineering at the University of Missouri, has been investigating the unconventional properties of “metamaterials” — an artificial material that exhibits properties not commonly found in nature as defined by Newton’s laws of motion — in his long-term pursuit of designing an ideal metamaterial.
Huang’s goal is to help control the “elastic” energy waves traveling through larger structures — such as an aircraft — without light and small “metastructures.”
“For ...
MSU researchers uncover the hidden complexity of the Montmorency tart cherry genome
2023-05-18
Highlights:
Michigan State University researchers sequenced the Montmorency tart cherry genome for the first time.
This will have a major impact on all future tart cherry research and breeding efforts worldwide.
Michigan is the nation’s leading producer of tart cherries.
EAST LANSING, Mich. – Since Michigan is the nation's leading producer of tart cherries, Michigan State University researchers were searching for the genes associated with tart cherry trees that bloom later in the season to meet the needs of a changing climate. They started by comparing DNA sequences from late-blooming ...
Historical fiction: a guarantee of critical success or a trap?
2023-05-18
For 21st century authors, the odds of writing a critical hit are much higher if the novel takes place in the past, not the present or future. Between 2000 and 2020, about three quarters of the novels shortlisted for the National Book Award, the Pulitzer Prize, and the National Book Critics Circle Award took place in the historical past.
“As a reader, you may not have even noticed the growing infatuation with history in literature because the historical novel has become such a diversely practiced form by such a wide array of writers, it's almost become invisible to us as a genre in itself,” ...
Using 3D printing to improve implantable biomedical devices, touchscreens and more
2023-05-18
McGill researchers are exploring a new technique that uses 3D printing and hydrogels. It has the potential not only to improve biomedical implants but could also be useful in the development of human-machine interfaces such as touch screens and neural implants. Biomedical devices like pacemakers or blood pressure sensors that are implanted into the human body need to be fabricated in such a way that they conform and adhere to the body – and then dissolve at the right time.
Using 3D printing and hydrogel technology, researchers in McGill University’s Department of Engineering ...
Amputees feel warmth in their missing hand
2023-05-18
“When I touch the stump with my hand, I feel tingling in my missing hand, my phantom hand. But feeling the temperature variation is a different thing, something important... something beautiful,” says Francesca Rossi.
Rossi is an amputee from Bologna, Italy. She recently participated in a study to test the effects of temperature feedback directly to the skin on her residual arm. She is one of 17 patients to have felt her phantom, missing hand, change in temperature thanks to new EPFL technology. More importantly, she reports feeling reconnected to her missing hand.
“Temperature feedback is a nice ...
[1] ... [1903]
[1904]
[1905]
[1906]
[1907]
[1908]
[1909]
[1910]
1911
[1912]
[1913]
[1914]
[1915]
[1916]
[1917]
[1918]
[1919]
... [8818]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.