Researchers discover potential new approach to treating psoriatic joint inflammation
2021-06-03
(SACRAMENTO, Calif.) - An international team of researchers, led by END ...
COVID-19: Seroprevalence and vaccine responses in UK dental care professionals
2021-06-03
Alexandria, Va., USA -- Dental care professionals are thought to be at enhanced risk of occupational exposure to SARS-CoV-2, but robust data to support this is lacking. The study "COVID-19: Seroprevalence and Vaccine Responses in UK Dental Care Professionals," published in the Journal of Dental Research (JDR), provides a longitudinal analysis of antibodies to SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoprotein, including early analysis of the impact of vaccination on the immune response.
In June 2020, I,507 West Midlands dental care professionals were recruited to test for baseline seroprevalence, or the proportion of the population that have circulating antibodies to SARS-CoV-2, indicating prior ...
Filter membrane renders viruses harmless
2021-06-03
Viruses can spread not only via droplets or aerosols like the new coronavirus, but in water, too. In fact, some potentially dangerous pathogens of gastrointestinal diseases are water-borne viruses.
To date, such viruses have been removed from water using nanofiltration or reverse osmosis, but at high cost and severe impact on the environment. For example, nanofilters for viruses are made of petroleum-based raw materials, while reverse osmosis requires a relatively large amount of energy.
Environmentally friendly membrane developed
Now an international team of researchers led by Raffaele ...
You're more likely to fight misinformation if you think others are being duped
2021-06-03
People in both the United States and China who think others are being duped by online misinformation about COVID-19 are also more likely to support corporate and political efforts to address that misinformation, according to a new study. The study suggests negative emotions may also play a role in the U.S. - but not in China.
"A lot of misinformation has been shared online over the course of the COVID-19 pandemic, and we had a range of questions about how people are responding to this misinformation," says Yang Cheng, co-lead author of the study and an assistant professor of communication at North Carolina State University.
"How do different emotions influence ...
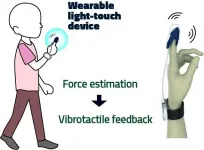
Wearable accelerometer and vibrator 'thimble' could reduce falls amongst seniors
2021-06-03
Japanese researchers have developed and tested a prototype device -- wearable on the fingertips -- that incorporates the concept of 'light touch' to enhance the sense of balance. If widely implemented, the device should significantly reduce incidence of falls amongst seniors.
The findings are published in the journal Scientific Reports on April 1.
As we age, our sense of balance can become impaired. The resulting increase in postural sway in turn increases the risk of falls and consequent injuries. Meanwhile, older people make up a large and increasing proportion of the population in highly developed countries. ...
The DNA of three aurochs found next to the Elba shepherdess opens up a new enigma for palaeontology
2021-06-03
Research involving scientists from the University of A Coruña has succeeded in sequencing the oldest mitochondrial genome of the immediate ancestor of modern cows that has been analysed to date. The remains, some 9,000 years old, were found next to a woman. Why were they with her if cattle had not yet been domesticated? Do they belong to ancestors of today's Iberian cows?
Humans have maintained a very close relationship with aurochs (Bos primigenius) since their beginnings, first by hunting them and then by breeding and selecting them.
This extinct species of mammal is little known in the Peninsula because its skeletal remains are difficult to distinguish from bison. In fact, there have been references to the presence of "large bovids" in many sites because ...
Tipping elements can destabilize each other, leading to climate domino effects
2021-06-03
Interactions in the network can lower the critical temperature thresholds beyond which individual tipping elements begin destabilizing on the long-run, according to the study - the risk already increases significantly for warming of 1.5°C to 2°C, hence within the temperature range of the Paris Agreement.
"We provide a risk analysis, not a prediction, yet our findings still raise concern," says Ricarda Winkelmann, Lead of FutureLab on Earth Resilience in the Anthropocene at the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research (PIK). "We find that the interaction of these four tipping elements can make them overall more vulnerable due to mutual destabilization on the long-run. The feedbacks between them tend to lower the critical temperature ...
Role of women highlighted in study focused on the benefits of good farmer seed production
2021-06-03
A new study looking at the benefits of good farmer seed production suggests women need more support to participate in contract farming - to the same extent as their male counterparts - and have more equality along the whole food value chain.
The CABI-led research - which sought to assess the benefits of good farmer seed production through a case study of the Good Seed Initiative in Tanzania - reveals that while around 70% of the labour to grow African Indigenous Vegetables (AIVs) is provided by women only 10 to 30% are contract farmers who own the fields, make decisions on sales and control revenues.
The paper, led by Dr Monica Kansiime ...
Big data helps assess seizure burden, improve outcomes in pediatric epilepsy patients
2021-06-03
Philadelphia, June 3, 2021 - Researchers at Children's Hospital of Philadelphia (CHOP) have demonstrated how to use standardized reporting of clinical data for seizures caused by a variety of neurological disorders, providing fundamental baseline information that can determine what methods work best for keeping seizures under control. The findings were published today in the journal Epilepsia.
In order to make improvements in epilepsy care, clinicians need a reliable and efficient method to measure outcomes. While Electronic Medical Records (EMR) are being used more frequently for research and quality improvement, important epilepsy outcome measures such ...
Aging impairs anti-tumor T-cell response via mitochondria dysfunction
2021-06-03
MUSC Hollings Cancer Center researchers are finding solutions to the aging-related changes that reduce anti-cancer immunity. Besim Ogretmen, Ph.D., and colleagues found a novel link between aging, metabolism and anti-cancer T-cell function. Their work, published in Cell Reports, sheds light on an important pathway that cannot be ignored during cancer treatment.
Two broad questions in cancer research are: How can cancer treatments be improved, and what is the link between cancer and aging?
"We know that the protective T-cell response deteriorates with age. Mitochondrial function is now thought to be one of the central regulators of the aging process. Our experiments connected the dots with what was previously shown and highlighted some ...
Study shows obesity may increase risk of long-term complications of COVID-19
2021-06-03
Thursday, June 3, 2021, CLEVELAND: A Cleveland Clinic study shows that survivors of COVID-19 who have moderate or severe obesity may have a greater risk of experiencing long-term consequences of the disease, compared with patients who do not have obesity. The study was recently published online in the journal of Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.
Multiple studies have identified obesity as a risk factor for developing a severe form of COVID-19 that may require hospital admission, intensive care, and ventilator support in the early phase of the disease. Obesity, which is a complex disease caused by multiple factors, is associated with an increased risk for cardiovascular ...
UNH research: Black bears may play important role in protecting gray fox
2021-06-03
DURHAM, N.H.-- Bears are known for being devoted and protective of their baby cubs, but research from the University of New Hampshire shows that they may also play a significant role in shielding gray fox from predators like coyotes, who compete with the fox for food and space. The research is one of the first studies to show how black bears provide a buffer to allow other, smaller carnivores to safely co-exist.
"Even though black bears and coyotes are the two most common carnivores in North America, we're still learning how they affect the ecosystems around them," said Rem Moll, assistant professor of wildlife ecology and lead author ...
The biodegradable battery
2021-06-03
The fabrication device for the battery revolution looks quite unconspicuous: It is a modified, commercially available 3D printer, located in a room in the Empa laboratory building. But the real innovation lies within the recipe for the gelatinous inks this printer can dispense onto a surface. The mixture in question consists of cellulose nanofibers and cellulose nanocrystallites, plus carbon in the form of carbon black, graphite and activated carbon. To liquefy all this, the researchers use glycerin, water and two different types of alcohol. Plus a pinch of table salt for ionic conductivity.
A sandwich of four layers
To build a functioning supercapacitor from these ingredients, four layers are needed, all flowing out of the 3D printer one after the ...
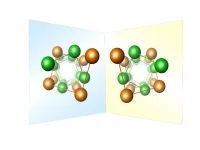
Enantiomorph distribution maps for metals and metallic alloys
2021-06-03
Left- or right-handedness is a symmetry property that many macroscopic objects also exhibit and which is of immense importance, particularly for the bioactivity of organic molecules. Chirality is also relevant for physical or chemical properties such as optical activity or enantioselectivity of crystalline solids or their surfaces. In the case of chiral metallic phases, unconventional superconductivity and unusual magnetic ordered states are linked to the chirality of the underly-ing crystal structure. Despite this connection between chirality and the properties of a material, detection is often difficult because left-handed and righthanded ...
Are wind farms slowing each other down?
2021-06-03
The expansion of wind energy in the German Bight and the Baltic Sea has accelerated enormously in recent years. The first systems went into operation in 2008. Today, wind turbines with an output of around 8,000 megawatts rotate in German waters, which corresponds to around eight nuclear power plants. But space is limited. For this reason, wind farms are sometimes built very close to one another. A team led by Dr. Naveed Akhtar from Helmholtz Zentrum Hereon has found that wind speeds at the downstream windfarm are significantly slowed down. As the researchers now write in the journal Nature Scientific Reports, this braking effect results in astonishingly large-scale low wind pattern noticeable in mean ...
Alzheimer's disease raises the risk of severe COVID-19 and death from this viral disease
2021-06-03
Neurodegenerative disorders that cause dementia increase the risk of contracting severe COVID-19 and dying from the disease. For people with Alzheimer's the risk is three times greater. It can be six times greater if they are over 80, according to a study conducted in Brazil by researchers at the University of São Paulo (USP) and Butantan Institute in partnership with colleagues at the Federal University of Rio de Janeiro (UFRJ).
An article on the study, which was supported by FAPESP, is published in Alzheimer's & Dementia: The Journal of the Alzheimer's Association.
"We found that all causes of dementia are risk factors for severity and death in COVID-19 and that these ...
Nanoscale sensors measure elusive water levels in leaves
2021-06-03
ITHACA, N.Y. - Water regulation in leaves is vital to a plant's health, affecting its growth and yield, disease susceptibility and drought resistance.
A breakthrough technology developed by Cornell University researchers uses nanoscale sensors and fiber optics to measure water status just inside a leaf's surface, where water in plants is most actively managed.
The engineering feat provides a minimally invasive research tool that will greatly advance the understanding of basic plant biology, and opens the door for breeding more drought-resistant crops. The technology could eventually be adapted for use as an agronomic tool for measuring water status in crops in real time.
The study in maize plants, "A Minimally Disruptive Method for Measuring Water Potential In-Planta ...
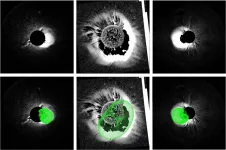
Using advanced imaging to study sickle cell disease
2021-06-03
Sickle Cell Disease (SCD) is a genetically inherited group of red blood cell disorders. END ...
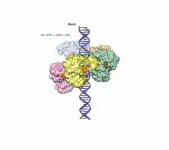
Researchers reveal the inner workings of a viral DNA-packaging motor
2021-06-03
DURHAM, N.C. - A group of researchers have discovered the detailed inner workings of the molecular motor that packages genetic material into double-stranded DNA viruses. The advance provides insight into a critical step in the reproduction cycle of viruses such as pox- herpes- and adeno-viruses. It could also give inspiration to researchers creating microscopic machines based on naturally occurring biomotors.
The research was conducted by scientists from Duke University, the University of Minnesota, the University of Massachusetts and the University of Texas Medical Branch (UTMB). The results appear online in a trilogy of papers published in Science Advances, ...
Fifty years of progress in women's health
2021-06-03
WHO: JoAnn Manson, MD, DrPH, Physician and Epidemiologist, Division of Preventive Medicine, Brigham and Women's Hospital; co-author of a new Perspective piece published in The New England Journal of Medicine (pdf attached)
WHAT: Less than 50 years ago, a U.S. Supreme Court decision paved the way for women's use of contraception irrespective of marital status, and a year later, in 1973, the Court ruled in Roe v. Wade that women have a right to legalized abortion. In recent decades, clinical researchers and policymakers alike have made important strides ...
Let's talk about the elephant in the data
2021-06-03
You would not be surprised to see an elephant in the savanna or a plate in your kitchen. Based on your prior experiences and knowledge, you know that is where elephants and plates are often to be found. If you saw a mysterious object in your kitchen, how would you figure out what it was? You would rely on your expectations or prior knowledge. Should a computer approach the problem in the same way? The answer may surprise you. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Professor Partha Mitra described how he views problems like these in a "Perspective" in Nature Machine Intelligence. He hopes his insights will help researchers teach computers how to analyze complex systems more effectively.
Mitra thinks it helps to understand the nature of knowledge. Mathematically speaking, many data scientists ...
Which way does the solar wind blow?
2021-06-03
The surface of the sun churns with energy and frequently ejects masses of highly-magnetized plasma towards Earth. Sometimes these ejections are strong enough to crash through the magnetosphere -- the natural magnetic shield that protects the Earth -- damaging satellites or electrical grids. Such space weather events can be catastrophic.
Astronomers have studied the sun's activity for centuries with greater and greater understanding. Today, computers are central to the quest to understand the sun's behavior and its role in space weather events.
The ...
Polar vortex, winter heat may change bird populations
2021-06-03
MADISON, Wis. -- For birds and other wildlife, winter is a time of resource scarcity. Extreme winter weather events such as a polar vortex can push some species to the edge of survival. Yet winter tends to get short shrift in climate change research, according to UW-Madison forest and wildlife ecology Professor Ben Zuckerberg.
"When we think about the impact of climate change, winter tends to be overlooked as a time of year that could have significant ecological and biological implications," says Zuckerberg. "It makes me, and my colleagues, think quite deeply about the impacts of these extreme events during this time when species are particularly vulnerable."
Zuckerberg, ...
Water droplets become hydrobots by adding magnetic beads
2021-06-03
Using a piece of magnet, researchers have designed a simple system that can control the movement of a small puddle of water, even when it's upside down. The new liquid manipulation strategy, described in the journal Cell Reports Physical Science on June 3, can have a wide range of applications including cleaning hard-to-reach environments or delivering small objects.
Previous attempts to control the movement of fluids often relied on special platforms. For example, on a surface that has one section more hydrophobic than another, water will spontaneously ...
Puppies are born ready to communicate with people, study shows
2021-06-03
Anyone that's ever interacted with a dog knows that they often have an amazing capacity to interact with people. Now researchers reporting in the journal Current Biology on June 3 have found that this ability is present in dogs from a very young age and doesn't require much, if any, prior experience or training. But, some of them start off better at it than others based on their genetics.
"We show that puppies will reciprocate human social gaze and successfully use information given by a human in a social context from a very young age and prior to extensive experience with humans," said Emily E. Bray of the University of Arizona, Tucson. "For example, even before puppies have left their littermates to live ...
[1] ... [2250]
[2251]
[2252]
[2253]
[2254]
[2255]
[2256]
[2257]
2258
[2259]
[2260]
[2261]
[2262]
[2263]
[2264]
[2265]
[2266]
... [8818]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.