Infrared imaging leaves invasive pythons nowhere to hide
2021-06-07
WASHINGTON -- For more than 25 years, Burmese pythons have been living and breeding in the Florida Everglades where they prey on native wildlife and disrupt the region's delicate ecosystems. A new study shows that infrared cameras could make it easier to spot these invasive snakes in the Florida foliage, providing a new tool in the effort to remove them.
In the Optical Society (OSA) journal Applied Optics, researchers led by Dr. Kyle Renshaw from the University of Central Florida College of Optics and Photonics report that a near infrared camera helped people detect Burmese pythons at distances up to 1.3 times farther away than was possible using a traditional visible-wavelength ...
Sensing what plants sense: Integrated framework helps scientists explain biology and predict crop performance
2021-06-07
AMES, Iowa - Scientists have invested great time and effort into making connections between a plant's genotype, or its genetic makeup, and its phenotype, or the plant's observable traits. Understanding a plant's genome helps plant biologists predict how that plant will perform in the real world, which can be useful for breeding crop varieties that will produce high yields or resist stress.
But environmental conditions play a role as well. Plants with the same genotype will perform differently when grown in different environments. A new study led by an Iowa State University scientist uses advanced data analytics to help scientists understand ...
Study helps to deeper understanding of brain dysfunctions in patients with schizophrenia
2021-06-07
A study conducted by a group of Brazilian researchers contributes to a deeper understanding of the molecular basis for schizophrenia, and potentially to the development of more specific and effective treatments for the disease. The medications currently available on the market act generically on the brain and can have severe adverse side effects.
Treatment of post-mortem samples from the hippocampus of schizophrenic patients with an NMDA receptor antagonist pointed to biological processes associated with the disease that are specific to neurons and oligodendrocytes. NMDA receptors are neurotransmitter receptors located in the postsynaptic ...
New potential therapy for fatty liver disease
2021-06-07
In those with fatty liver disease, a person's fat goes to their liver instead of their fat tissue, either because of an absence of fat depots, which is seen in the rare genetic disease lipodystrophy, or because the depots are too full, which is seen in people with obesity.
One third of these people will go on to develop nonalcoholic steatohepatitis, or NASH - an advanced form of fatty liver disease brought on by progressive inflammation and scarring in the organ.
In 2002, Michigan Medicine endocrinologist Elif Oral, M.D., who had just moved from the National Institutes of Health at the time, published her discovery that patients with severe lipodystrophy lack leptin, a hormone that helps curb appetite and control weight gain. When given ...
Feedback on cafeteria purchases helps employees make healthier food choices
2021-06-07
BOSTON - Automated emails and letters that provide personalized feedback related to cafeteria purchases at work may help employees make healthier food choices. That's the conclusion of a new study that was led by investigators at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) and is published in END ...
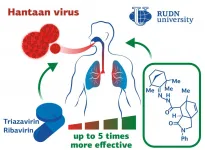
RUDN University chemists created anti-hantavirus drugs 5 times more efficient than existing drugs
2021-06-07
RUDN University chemists and their colleagues from Novosibirsk State University, Novosibirsk Institute of Organic Chemistry and The State Research Center of Virology and Biotechnology VECTOR have obtained a new class of compounds that inhibit the replication of the deadly Hantaan virus that affects blood vessels and internal organs of humans. The resulting substances were 5 times more effective than existing antiviral drugs. The results have been published Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters.
The Hantaan virus causes acute haemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome (HFRS). The disease ...
Space travel weakens our immune systems: Now scientists may know why
2021-06-07
Microgravity in space perturbs human physiology and is detrimental for astronaut health, a fact first realized during early Apollo missions when astronauts experienced inner ear disturbances, heart arrhythmia, low blood pressure, dehydration, and loss of calcium from their bones after their missions.
One of the most striking observations from Apollo missions was that just over half of astronauts became sick with colds or other infections within a week of returning to Earth. Some astronauts have even experienced re-activation of dormant viruses, such as the chickenpox virus. These findings stimulated studies on the effects of weak gravity, or ...
Drop in convalescent plasma use at US hospitals linked to higher COVID-19 mortality rate
2021-06-07
A new study from researchers at Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health and colleagues suggests a slowdown in the use of convalescent plasma to treat hospitalized COVID-19 patients led to a higher COVID-19 mortality during a critical period during this past winter's surge.
U.S. hospitals began treating COVID-19 patients with convalescent plasma therapy--which uses antibody-rich blood from recovered COVID-19 patients--in the summer of 2020 when doctors were looking to identify treatments for the emerging disease. By the spring of 2021, doctors in the United States had treated over 500,000 COVID-19 patients with convalescent plasma. The use ...
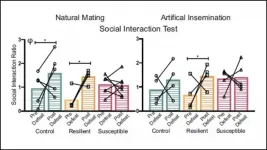
Mice fathers pass down stress responses to offspring via sperm
2021-06-07
Male mice more susceptible to stress can pass down their behaviors to offspring via changes in their sperm's genetic code, according to new research published in JNeurosci.
Stressful experiences alter gene expression, which parents can pass down to their offspring. But it was unclear if sperm itself transmits this information, or if behavioral cues between the parents play a larger role.
Cunningham et al. tracked the stress response of male mice after ten days of chronic stress and sorted them into resilient and susceptible groups, based on the severity of their response. The offspring of resilient and control mice showed decreased stress behaviors ...
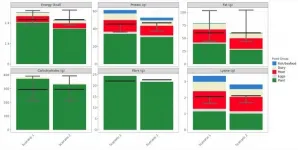
Health benefits of low protein-high carbohydrate diets depend on carb type
2021-06-07
Researchers at the University of Sydney's Charles Perkins Centre conducted the largest ever study of nutrient interactions by examining the health of mice on 33 different diets containing various combinations of protein to carbs, and different sources of carbohydrate.
They found that a low-protein (10% of dietary energy), high-carbohydrate (70%) diet produced either the healthiest or unhealthiest metabolic outcomes of all 33 diets, depending on the kind of carbs.
When carbs were made up mainly of resistant starch, a form of starch that is resistant to digestion and is fermented by bacteria in the gut, the low protein diet was the healthiest of all diets. When the ...
Gender bias is real for women in family-owned businesses
2021-06-07
A study examining gender bias and family-owned businesses found daughters were rarely encouraged nor received support to pursue entrepreneurship education while sons mostly did.
Professors James Combs, Peter Jaskiewicz, and Sabine Raul from the Telfer School of Management uncovered new insights about how gender bias - the preference of a gender over the other - affects the succession strategy in multi-generational family firms. Their findings are published in the Journal of Small Business Management.
When nurturing the next generation, entrepreneurial families often prepare their daughters and sons differently for their careers. The researchers noticed a common pattern in the stories shared by the next generation: Sons are often nurtured to ...
Stream of stars extends thousands of light-years across the Milky Way
2021-06-07
It's hard to see more than a handful of stars from Princeton University, because the lights from New York City, Princeton and Philadelphia prevent our sky from ever getting pitch black, but stargazers who get into more rural areas can see hundreds of naked-eye stars -- and a few smudgy objects, too.
The biggest smudge is the Milky Way itself, the billions of stars that make up our spiral galaxy, which we see edge-on. The smaller smudges don't mean that you need glasses, but that you're seeing tightly packed groups of stars. One of the best-known of these "clouds" or "clusters" -- groups of stars that travel together -- is the Pleiades, also known as the Seven Sisters. Clusters are stellar nurseries where thousands of stars are born from clouds of gas and dust and then ...
A quantum step to a heat switch with no moving parts
2021-06-07
COLUMBUS, Ohio - Researchers have discovered a new electronic property at the frontier between the thermal and quantum sciences in a specially engineered metal alloy - and in the process identified a promising material for future devices that could turn heat on and off with the application of a magnetic "switch."
In this material, electrons, which have a mass in vacuum and in most other materials, move like massless photons or light - an unexpected behavior, but a phenomenon theoretically predicted to exist here. The alloy was engineered with the elements bismuth and antimony at precise ranges based ...
CO2 sensors in two urban areas registered big drop in emissions during COVID-19 pandemic
2021-06-07
Carbon dioxide emissions in Los Angeles fell 33% in April of 2020 compared with previous years, as roads emptied and economic activity slowed due to the COVID-19 pandemic, according to a new study in Geophysical Research Letters. In the Washington, D.C./Baltimore region, emissions of carbon dioxide, or CO2, dropped by 34% during the same period.
The study was led by scientists at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL), the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) and the University of Notre Dame.
While the emissions reductions are significant, the method that scientists used to measure them may have the greater long-term impact.
In both locations, scientists had previously ...
Researchers make new charge storage mechanism discovery
2021-06-07
Research between the University of Liverpool, UK and National Tsing Hua University (NTHU), Taiwan has revealed a new charge storage mechanism that has the potential to allow rechargeability within calcium-air batteries.
In a paper published in the journal Chemical Science, Professor Laurence Hardwick from the University of Liverpool's Stephenson Institute for Renewable Energy (SIRE) and colleagues discover a distinctive form of charge storage at the electrode interface described as trapped interfacial redox. This new finding introduces a new mechanism of charge storage that could be harnessed in practical devices.
Lead author of the paper, Yi Ting (Leo) Lu, is a joint PhD student in ...
Restoring gut microbes missing in early life dysbiosis can reduce risk of colitis in mice
2021-06-07
A new study at the University of Chicago has determined that restoring a single microbial species -- Bacteroides sp. CL1-UC (Bc) -- to the gut microbiome at a key developmental timepoint can prevent antibiotic-induced colitis in a mouse model of the condition. The results, published on June 7 in END ...
New COVID-19 model reveals effectiveness of travel restrictions
2021-06-07
TROY, N.Y. -- More strategic and coordinated travel restrictions likely could have reduced the spread of COVID-19 in the early stages of the pandemic. That's according to new research published in Communications Physics. This finding stems from new modeling conducted by a multidisciplinary team of scientists and engineers at Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute.
The researchers evaluated the distance between countries in terms of air travel, a more complex measurement than simply mapping physical distance. For instance, while China and Thailand may be geographically more proximate to one another, if there are significantly ...
From meat-production to urinary tract infections
2021-06-07
In young women, Staphylococcus saprophyticus is a main cause of urinary tract infections (UTI), reaching 20% prevalence. Understanding the epidemiology of this microorganism can help identify its origin, distribution, causes, and risk factors. Now, ITQB NOVA researchers led by Maria Miragaia showed evidence that Staphylococcus saprophyticus can originate in food, namely in the meat-production chain.
Europe is the world's second-biggest producer of pork, the most favored meat type in these countries. One of the contaminants of that meat is S. saprophyticus, which is found also in the environment, ...
Two-thirds of women don't meet criteria to discontinue cervical cancer screening
2021-06-07
BOSTON - Current guidelines recommend stopping cervical cancer screening at age 65, but women over age 65 make up over one in five new cervical cancer diagnoses, and are twice as likely to die after a cervical cancer diagnosis compared to younger women. New research from Boston Medical Center found that fewer than one in three women aged 64 to 66 met the criteria to discontinue cervical cancer screening while looking at patients with both private insurance and from a safety-net hospital setting. Published in Gynecologic Oncology, researchers found that even among women with 10 years of continuous insurance coverage, ...
School lesson gone wrong leads to new, bigger megalodon size estimate
2021-06-07
GAINESVILLE, Fla. --- A more reliable way of estimating the size of megalodon shows the extinct shark may have been bigger than previously thought, measuring up to 65 feet, nearly the length of two school buses. Earlier studies had ball-parked the massive predator at about 50 to 60 feet long.
The revised estimate is the result of new equations based on the width of megalodon's teeth - and began with a high school lesson that went awry.
Victor Perez, then a doctoral student at the Florida Museum of Natural History, was guiding students through a math ...
Exploring an epidemic's meaning from the perspective of nursing
2021-06-07
PHILADELPHIA (June 7, 2021) - An article written almost 30 years ago helps frame social constructs around the COVID-19 pandemic. By reviewing the essay, an historian of nursing at the University of Pennsylvania School of Nursing (Penn Nursing) extends that construct to include nurses and patients, delivering a local and personal meaning to the epidemic experience.
In an essay in the Bulletin of the History of Medicine, Julie A. Fairman, PhD, RN, FAAN, Endowed Chair, the Nightingale Professor in Honor of Nursing Veterans, and Professor of Nursing at Penn Nursing, reviews Charles Rosenberg's 1992 article about the AIDS epidemic. Using Rosenberg's theme, she further develops the ...
Lead halide perovskites -- a horse of a different color
2021-06-07
Metal halide perovskites have been under intense investigation over the last decade due to the remarkable rise in their performance in optoelectronic devices such as solar cells or light-emitting diodes. Despite tremendous progress in this field, many fundamental aspects of the photophysics of perovskite materials remain unknown, such as a detailed understanding of their defect physics and charge recombination mechanisms. These are typically studied by measuring the photoluminescence - i.e. the emission of light upon photoexcitation - of the material in both the steady-state and transient regimes. ...
The latest science on staying healthy during pregnancy
2021-06-07
Rockville, Md. (June 7, 2021) - Healthy habits are particularly important during pregnancy. Four new studies being presented at NUTRITION 2021 LIVE ONLINE look at how supplements, eating habits and physical activity can affect various aspects of health during pregnancy.
Prenatal supplements might influence bacterial composition of breast milk
Breast milk contains a unique mix of bacteria - known as its microbiota - that plays an important role in child health. In a new study, researchers from Purdue University examined whether diet or supplements taken prenatally affected the microbiota of breast milk in 771 mothers participating in the CHILD Cohort Study. The analysis revealed that supplements, but not dietary patterns, were linked with changes in human milk microbiota ...
Most Americans are not getting enough fiber in our diets
2021-06-07
Rockville, Maryland (June 7, 2021) -- Only 5% of men and 9% of women are getting the recommended daily amount of dietary fiber, according to a study being presented at NUTRITION 2021 LIVE ONLINE. Insufficient fiber intake is associated with a higher risk of heart disease and diabetes, two of the most common diseases in the U.S.
"These findings should remind people to choose fiber-rich foods like whole grains, fruits and vegetables to reduce their risk for heart disease," said Derek Miketinas, PhD, RD, an assistant professor at Texas Woman's University, the study's ...
Cutting food waste alone won't solve world's nutritional needs
2021-06-07
Rockville, Maryland (June 7, 2021) -- Reducing food waste is crucial to our ability to feed the growing human population but will not fully solve the problem alone, according to a new study based on a computational model.
Researchers calculate that the world already produces enough protein and energy to feed 9.7 billion people--the projected population as of 2050--if food waste were cut in half. However, projections indicate global food production will still fall short in terms of micronutrients that our bodies need to stay healthy, including calcium, iron, vitamin E and others.
"Reducing food waste would give us enough protein and food energy to feed the 2050 population today--but not enough of the essential ...
[1] ... [2254]
[2255]
[2256]
[2257]
[2258]
[2259]
[2260]
[2261]
2262
[2263]
[2264]
[2265]
[2266]
[2267]
[2268]
[2269]
[2270]
... [8832]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.