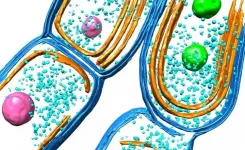
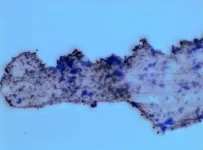
New insight into biosynthesis and architecture of photosynthetic membranes in bacteria
2021-06-10
A new study conducted by the researchers at the University of Liverpool reveals how the ancient photosynthetic organisms - cyanobacteria - evolve their photosynthetic machinery and organise their photosynthetic membrane architecture for the efficient capture of solar light and energy transduction.
Oxygenic photosynthesis, carried out by plants, algae, and cyanobacteria, produces energy and oxygen for life on Earth and is arguably the most important biological process. Cyanobacteria are among the earliest phototrophs that can perform oxygenic photosynthesis and make significant contributions to the Earth's atmosphere and primary production.
Light-dependent photosynthetic reactions are performed by a set of photosynthetic ...
Scientists create unique instrument to probe the most extreme matter on Earth
2021-06-10
Laser-produced high energy density plasmas, akin to those found in stars, nuclear explosions, and the core of giant planets, may be the most extreme state of matter created on Earth. Now scientists at the U.S. Department of Energy's (DOE) Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory (PPPL), building on nearly a decade of collaboration with the National Ignition Facility (NIF) at the DOE's Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL), have designed a novel X-ray crystal spectrometer to provide high-resolution measurements of a challenging feature of NIF-produced HED plasmas.
Most powerful lasers
The ...
New light on making two-dimensional polymers
2021-06-10
An international research team led by members from the Technical University of Munich, the Deutsches Museum, Munich, and the Swedish Linköping University has developed a method to manufacture two-dimensional polymers with the thickness of a single molecule. The polymers are formed on a surface by the action of light. The discovery paves the way to new ultrathin and functional materials.
The quest for new two-dimensional materials has rapidly intensified after the discovery of graphene - a supermaterial whose excellent properties include high conductivity and strength, making it incredibly versatile.
Two main ...
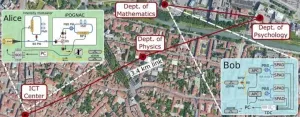
Researchers take quantum encryption out of the lab
2021-06-10
WASHINGTON -- In a new study, researchers demonstrate an automated, easy-to-operate quantum key distribution (QKD) system using the fiber network in the city of Padua, Italy. The field test represents an important step toward implementing this highly secure quantum communication technology using the type of communication networks already in place in many regions around the world.
QKD offers impenetrable encryption for data communication because it uses the quantum properties of light to generate secure random keys for encrypting and decrypting data.
"QKD can be useful in any situation where security is paramount because it offers unconditional security for the key exchange process," ...
Breast cancer risk in African-Americans tied to genetic variations
2021-06-10
Two gene variants found in African American women may explain why they are more likely to be diagnosed with triple negative breast cancer (TNBC) than white women of European ancestry, according to Weill Cornell Medicine and NewYork-Presbyterian investigators. The study findings may have implications for developing better risk assessment tools for TNBC in African American women and for understanding why they have poorer TNBC outcomes.
In a study, published April 29 in Scientific Reports, the investigators found that a version of the ANKLE1 gene that can be protective against TNBC is less likely to be found in African American women than white women of European ancestry. In addition, African American women with a mutation in the Duffy gene, which plays a role in inflammation, ...
GEM simplifies the internal structure of protons and their collisions
2021-06-10
Inside each proton or neutron there are three quarks bound by gluons. Until now, it has often been assumed that two of them form a "stable" pair known as a diquark. It seems, however, that it's the end of the road for the diquarks in physics. This is one of the conclusions of the new model of proton-proton or proton-nucleus collisions, which takes into account the interactions of gluons with the sea of virtual quarks and antiquarks.
In physics, the emergence of a new theoretical model often augurs badly for old concepts. This is also the case with the description of collisions of protons with protons or atomic nuclei, proposed by scientists from the Institute of Nuclear Physics of the Polish Academy of Sciences (IFJ PAN) ...
Ceramics provide insights into medieval Islamic cuisine
2021-06-10
Organic residues on ceramic pottery are a valuable resource for understanding medieval cuisines of Islamic-ruled Sicily, according to a study published June 9, 2021 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Jasmine Lundy of the University of York, UK and colleagues.
During the 9th to 12th century AD, Sicily was under Islamic rule. This transition is known to have profoundly impacted the region, and the capital city of Palermo thrived as an economic and cultural center of the Mediterranean Islamic world. But little is known about how the lives of people in the region were impacted during this important time period.
In this study, researchers examined organic residues of plant and animal products on ceramic pottery to gain insights ...
Engineers apply physics-informed machine learning to solar cell production
2021-06-09
Today, solar energy provides 2% of U.S. power. However, by 2050, renewables are predicted to be the most used energy source (surpassing petroleum and other liquids, natural gas, and coal) and solar will overtake wind as the leading source of renewable power. To reach that point, and to make solar power more affordable, solar technologies still require a number of breakthroughs. One is the ability to more efficiently transform photons of light from the Sun into useable energy.Organic photovoltaics max out at 15% to 20% efficiency -- substantial, but a limit on solar energy's potential. Lehigh University engineer Ganesh Balasubramanian, like many others, wondered if there were ways to improve the design of solar cells to make them more ...
Understanding gut inflammation may hold clues to mitigating Parkinson's onset
2021-06-09
GRAND RAPIDS, Mich. (JUNE 8, 2021) -- Chronic inflammation in the gut may propel processes in the body that give rise to Parkinson's disease, according to a study by scientists at Van Andel Institute and Roche.
The study, published in Free Neuropathology, is the latest in a growing list that links the gut and the immune system to Parkinson's. The researchers' findings in an experimental mouse model of gut inflammation track with several large-scale epidemiological studies that show an association between Parkinson's and inflammatory bowel diseases, such as ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease.
Epidemiological evidence from other groups indicates the risk of developing Parkinson's fades in certain people whose ...
Bacteria-sized robots take on microplastics and win by breaking them down
2021-06-09
Small pieces of plastic are everywhere, stretching from urban environments to pristine wilderness. Left to their own devices, it can take hundreds of years for them to degrade completely. Catalysts activated by sunlight could speed up the process, but getting these compounds to interact with microplastics is difficult. In a proof-of-concept study, researchers reporting in ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces developed self-propelled microrobots that can swim, attach to plastics and break them down.
While plastic products are omnipresent indoors, plastic waste and broken bits now litter the outdoors, too. The smallest of these ...
Social media use one of four factors related to higher COVID-19 spread rates early on
2021-06-09
TORONTO, June 9, 2021 - Researchers from York University and the University of British Columbia have found social media use to be one of the factors related to the spread of COVID-19 within dozens of countries during the early stages of the pandemic.
The researchers say this finding resembles other examples of social media misinformation ranging from the initial phase of vaccine rollout to the 2021 Capitol riot in the United States.
Countries with high social media use leading to off-line political action prior to the pandemic, as surveyed before the pandemic by V-Dem (a database from the University of Gothenburg), showed ...
Researchers tame silicon to interact with light for next-generation microelectronics
2021-06-09
Skoltech researchers and their colleagues from RAS Institute for Physics of Microstructures, Lobachevsky State University of Nizhny Novgorod, ITMO University, Lomonosov Moscow State University, and A.M. Prokhorov General Physics Institute have found a way to increase photoluminescence in silicon, the notoriously poor emitter and absorber of photons at the heart of all modern electronics. This discovery may pave the way to photonic integrated circuits, boosting their performance. The paper was published in the journal Laser and Photonics Reviews.
"Natural selection" in semiconductor technology ...
For early amphibians, a new lifestyle meant a new spine
2021-06-09
Vertebrate life began in the water, but around 340-360 million years ago, four-limbed creatures, or tetrapods, made the transition onto land. In the years that followed, some species adapted to terrestrial life, while others turned back to the water and readapted to an aquatic lifestyle.
A new study of these early amphibians, published in the journal PLOS ONE and led by Penn paleontologist Aja Carter, suggests that these environmental shifts left an impression--on the shape of the animals' spines.
"I'm interested in how the shapes of the vertebrae affect how animals move," she says. "Our findings suggest that, in at least one part of the vertebrae, the shape of the bones ...
Forget wearables: Future washable smart clothes powered by Wi-Fi will monitor your health
2021-06-09
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. - Purdue University engineers have developed a method to transform existing cloth items into battery-free wearables resistant to laundry. These smart clothes are powered wirelessly through a flexible, silk-based coil sewn on the textile.
In the near future, all your clothes will become smart. These smart cloths will outperform conventional passive garments, thanks to their miniaturized electronic circuits and sensors, which will allow you to seamlessly communicate with your phone, computer, car and other machines. This smart clothing will not only make you more productive but also check on your health status and even call for help if you suffer an accident. The reason why this smart clothing ...
Nearly 1 in 5 patients who die from unexplained sudden cardiac death have suspicious gene
2021-06-09
As many as 450,000 Americans die every year from a sudden, fatal heart condition, and in slightly more than one in ten cases the cause remains unexplained even after an autopsy. Researchers from the University of Maryland School of Medicine (UMSOM) and their colleagues found that nearly 20 percent of patients with unexplained sudden cardiac death - most of whom were under age 50 - carried rare genetic variants. These variants likely raised their risk of sudden cardiac death. In some cases, their deaths may have been prevented if their doctors had known about their genetic predisposition to heart disease. The study findings were published ...
Scientists identify distinctive deep infrasound rumbles of space launches
2021-06-09
WASHINGTON--After their initial blast, space rockets shoot away from the Earth with rumbles in infrasound, soundwaves too low to be heard by human ears that can travel thousands of miles.
New research used a system for monitoring nuclear tests to track the infrasound from 1,001 rocket launches. The research identified the distinctive sounds from seven different types of rockets, including the Space Shuttles, Falcon 9 rockets, various Soyuz rockets, the European Space Agency's Ariane 5, Russian Protons and several types of Chinese Long March rockets.
In some cases, like the Space Shuttle and the Falcon 9, the researchers were also able to identify the various stages of the rockets' journey.
https://youtu.be/IfMtEcNkkho
The ...
Smokers needed angioplasty and stenting a decade before non-smokers
2021-06-09
Smokers needed their blocked arteries fixed nearly a decade earlier than non-smokers, and patients with obesity underwent these procedures four years earlier than non-obese patients, according to a new statewide study.
The research included patients without a history of heart attack who were treated at hospitals across Michigan participating in BMC2, the Blue Cross Blue Shield of Michigan Cardiovascular Consortium. The patients had undergone angioplasty and/or stenting to widen or unblock their coronary arteries and restore blood flow. Almost all of them had at least one traditional ...
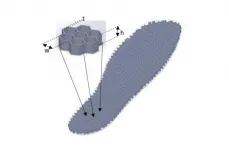
New research a 'step change' for diabetes patients
2021-06-09
Millions of people with diabetes are at risk of developing foot ulcers, which often lead to amputations and other health complications. Now, Scientists from the Centre for Biomechanics and Rehabilitation Technologies (CRBT) have developed a new method to reliably detect this risk without the need for complex electronic in-shoe sensors.
Dr Panagiotis Chatzistergos, Associate Professor in Orthopaedic Biomechanics, explained: "In the UK alone, 169 people have a toe, foot or limb amputated as a result of diabetes every week, yet importantly up to 80% of these amputations could have been prevented with correct management.
"Routine overloading ...
More 'fairness' needed in conservation
2021-06-09
New research shows what is often assumed to be 'fair' in conservation practice may not be considered so by the very people most affected by it--and a new approach is needed if protected areas are to be effective.
Lead author Dr Georgina Gurney, from the ARC Centre of Excellence for Coral Reef Studies based at James Cook University, said considering local stakeholder conceptions of fairness in conservation is critical.
"If conservation is perceived as unfair it can lead to conflict, undermining support and cooperation," Dr Gurney said.
She said it is not only an ethical matter but key to achieving good ...
Study: Maternal adult characteristics do not predict stillbirth, early neonatal death
2021-06-09
University of Illinois Chicago researchers studying birth outcomes in marmoset monkeys found there were no adult maternal characteristics like age or weight gain during pregnancy to predict stillbirth or early neonatal death, but that a mother's birth weight or litter size were associated with early neonatal death.
"Our findings of early life contributions to adult pregnancy outcomes in the common marmoset disrupt mother-blaming narratives of pregnancy outcomes in humans," the paper states.
Julienne Rutherford, associate professor at UIC's School of Nursing, is lead author of "Womb to Womb: Maternal litter size and birth weight but not adult characteristics predict early neonatal death of offspring in the common marmoset monkey" published in the journal PLOS ONE.
Marmosets ...
Study confirms safety and effectiveness of COVID-19 vaccination in people with cancer
2021-06-09
Since the early days of the COVID-19 pandemic, there were questions about how people in active cancer treatment would fare if they became infected with SARS-CoV-2. The worries were due, in large part, to the effects that cancer and its treatments can have on the immune system. Now that COVID-19 vaccines are widely available, concerns have shifted to the safety and effectiveness of vaccination in this potentially vulnerable population. A study published June 5 in the journal Cancer Cell aims to allay those fears.
In a review of 200 patients with a wide spectrum of cancer diagnoses, researchers at Montefiore Health System and Albert Einstein College of Medicine in the Bronx, NY, found that after full vaccination, 94% of patients overall demonstrated seroconversion, ...
'Transportation is a form of freedom': How to make it more equitable
2021-06-09
The routes and schedules of public transit, the presence or absence of sidewalks, the availability of different transportation options, and the design of highways that divide cities--these are examples of aspects of transportation systems that can profoundly impact underserved communities' access to basic needs like jobs, health care, education and even food.
A new study by University of Michigan researchers reveals common barriers that transportation decision-makers face in considering these issues and addressing them.
To conduct the study, a team from a multidisciplinary project involving engineering, ...
Artificial intelligence predicts brain age from EEG signals recorded during sleep studies
2021-06-09
DARIEN, IL - A study shows that a deep neural network model can accurately predict the brain age of healthy patients based on electroencephalogram data recorded during an overnight sleep study, and EEG-predicted brain age indices display unique characteristics within populations with different diseases.
The study found that the model predicted age with a mean absolute error of only 4.6 years. There was a statistically significant relationship between the Absolute Brain Age Index and: epilepsy and seizure disorders, stroke, elevated markers of sleep-disordered breathing (i.e., apnea-hypopnea index and arousal ...
Asteroid 16 Psyche might not be what scientists expected
2021-06-09
The widely studied metallic asteroid known as 16 Psyche was long thought to be the exposed iron core of a small planet that failed to form during the earliest days of the solar system. But new University of Arizona-led research suggests that the asteroid might not be as metallic or dense as once thought, and hints at a much different origin story.
Scientists are interested in 16 Psyche because if its presumed origins are true, it would provide an opportunity to study an exposed planetary core up close. NASA is scheduled to launch its Psyche mission in 2022 and arrive at the asteroid in 2026.
UArizona ...
SNAPSHOT USA: First-ever nationwide mammal survey published
2021-06-09
[RALEIGH, N.C.] - How are the squirrels doing this year? The bears? The armadillos? How would you know? A new paper published June 8 sets up the framework for answering these questions across the United States by releasing the data from the first national mammal survey made up of 1,509 motion-activated camera traps from 110 sites located across all 50 states.
Unlike birds, which have multiple large-scale monitoring programs, there has been no standard way to monitor mammal populations at a national scale. To address this challenge, scientists from the North Carolina Museum of Natural Sciences and the Smithsonian Conservation Biology Institute recently collaborated ...
[1] ... [2246]
[2247]
[2248]
[2249]
[2250]
[2251]
[2252]
[2253]
2254
[2255]
[2256]
[2257]
[2258]
[2259]
[2260]
[2261]
[2262]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.