Transformation toughening of ceramics made crystal clear
2021-06-09
Tsukuba, Japan - Ceramic materials that are resistant to cracking are used in a variety of industries from aerospace engineering to dentistry. Toughening them to improve their efficiency and safety is therefore an important area of investigation. Researchers from the University of Tsukuba have used time-resolved X-ray diffraction to observe transformation toughening in zirconia ceramics during dynamic fracture. Their findings are published in Applied Physics Letters.
Current methods of observation allow the formation of cracks in materials to be observed in situ while loads are applied. These close-up analyses ...
Rice fish model of a rare metabolic disorder
2021-06-09
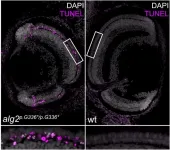
Human cells are kept healthy by the activity of millions of proteins. These proteins are modified in different ways, such as by adding sugar molecules to them, which can be crucial for them to function properly. Given this importance, defects in the sugar-adding process are often lethal at the very early stages of development. In rare cases, however, patients can develop sugar-adding deficiencies that result in a range of metabolic diseases, known collectively as 'congenital disorders of glycosylation' (CDG). These disorders are caused by defects in the enzymes involved in the sugar-adding process. For example, ALG2-CDG (or CDG-Ii) is a disorder caused by mutations in the ALG2 enzyme, ...
Personalized soundscape could help people with dementia with time, place recognition
2021-06-09
MELVILLE, N.Y., June 9, 2021 -- Designing a soundscape to improve the quality of life for an individual is centered on putting their perception at the heart of the process. It becomes trickier for people who have diminished cognitive capacities.
During the 180th Meeting of the Acoustical Society of America, which will be held virtually June 8-10, Arezoo Talebzadeh, from Ghent University, will show how a personalized soundscape can help those with dementia by providing clues regarding time of day and place. The session, "Soundscape design for people with dementia; the correlation between psychoacoustic parameter and human perception," will take place Wednesday, June 9, ...
Physicists achieve significant improvement in spotting neutrinos in a cosmic haystack
2021-06-09
UPTON, NY--How do you spot a subatomic neutrino in a "haystack" of particles streaming from space? That's the daunting prospect facing physicists studying neutrinos with detectors near Earth's surface. With little to no shielding in such non-subterranean locations, surface-based neutrino detectors, usually searching for neutrinos produced by particle accelerators, are bombarded by cosmic rays--relentless showers of subatomic and nuclear particles produced in Earth's atmosphere by interactions with particles streaming from more-distant cosmic locations. These abundant travelers, mostly muons, create a web of crisscrossing particle tracks that can easily obscure a ...
Soil microbes metabolize the same polyphenols found in chocolate, wine
2021-06-09
Fruits, vegetables, red wine and chocolate are all rich in polyphenols, natural plant compounds that double as cancer-fighting antioxidants. We can access these foods' health benefits because the microbes in our guts happily feast on them, breaking them down into smaller chemical components.
Microbiome scientists at Colorado State University wanted to know if microbes can also break down those same polyphenols in systems outside the human body, including the microbial wild west of soils.
A research team led by Kelly Wrighton, associate professor in the College of Agricultural Sciences' Department of Soil and Crop Sciences, has uncovered new insights into the role of polyphenols in the soil microbiome, known as a black box for its complexity. They proffer an updated theory that soils ...
Study finds COVID-19 vaccines safe for IBD patients
2021-06-09
Los Angeles (June 8, 2021) --
IBDs, including Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis, are chronic conditions that occur when the intestinal immune system becomes overreactive, causing chronic diarrhea and other digestive symptoms. In a published survey at the beginning of COVID-19 vaccine distribution, 70% of IBD patients reported concern about side effects from the vaccines.
"What we've learned is that if you have IBD, the side effects you're likely to experience after a vaccine are no different than they would be for anyone else," said Gil Melmed, MD, corresponding author of the study and director of Inflammatory Bowel Disease Clinical Research at Cedars-Sinai. "If ...
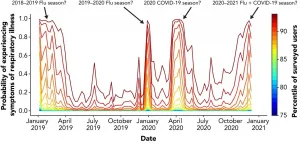
Sleep Number presents new data from its 360® Smart Beds at SLEEP 2021 Annual Meeting
2021-06-09
Real-world data from Sleep Number® smart bed sleepers shows a potential model for predicting and tracking COVID-19 infection using sleep and biometric measures.
Analysis of 18.2 million 360 smart bed sleep sessions finds heart rate variability differs with age, gender and day of the week.
MINNEAPOLIS, MN -- June 9, 2021 -- Today, END ...
Alarming rising trends in suicide by firearms in young Americans
2021-06-09
Deaths from suicide are rising in the United States. These rising trends are especially alarming because global trends in suicide are on a downward trajectory. Moreover, in the U.S., the major mode of suicide among young Americans is by firearms.
Researchers from Florida Atlantic University's Schmidt College of Medicine and collaborators explored trends in suicide by firearms in young white and black Americans (ages 5 to 24 years) from 1999 to 2018. Results, published in the journal Annals of Public Health and Research, showed that between 2008 and 2018, rates of suicide by firearms quadrupled in young Americans ages 5 to 14 ...
Novel compound reveals fundamental properties of smallest carbon nanotubes
2021-06-09
Chemical rings of carbon and hydrogen atoms curve to form relatively stable structures capable of conducting electricity and more -- but how do these curved systems change when new components are introduced? Researchers based in Japan found that, with just a few sub-atomic additions, the properties can pivot to vary system states and behaviors, as demonstrated through a new synthesized chemical compound.
The results were published on April 26 in the Journal of the American Chemical Society.
"In the past decade, open-shell molecules have attracted considerable attention not only in the field of reactive intermediates, but also in materials science," said paper author Manabu Abe, ...
Laptops, cell phones, e-games defied slump as COVID-19 dented 2020's electronics sales: UN
2021-06-09
In the first three quarters of 2020, the COVID-19 pandemic caused a 30% fall in electronic and electrical equipment sales in low- and middle-income countries but only a 5% decline in high-income countries, highlighting and intensifying the digital divide between north and south, according to a new UN report.
Worldwide, sales of heavy electric appliances like refrigerators, washing machines and ovens fell the hardest -- 6-8% -- while small IT and telecommunications equipment decreased by only 1.4%. Within the latter category, sales of laptops, cell phones and gaming equipment rose in high-income countries and on a global basis, but fell in low- and middle-income ...
As novel sights become familiar, different brain rhythms, neurons take over
2021-06-09
To focus on what's new, we disregard what's not. A new study by researchers at MIT's Picower Institute for Learning and Memory substantially advances understanding of how a mammalian brain enables this "visual recognition memory."
Dismissing the things in a scene that have proven to be of no consequence is an essential function because it allows animals and people to quickly recognize the new things that need to be assessed, said Mark Bear, Picower Professor in the Department of Brain and Cognitive Sciences and senior author of the study in the Journal of Neuroscience.
"Everyone's appropriate behavioral response to an unexpected stimulus is to devote attentional resources to that," Bear said. "Maybe it means danger. Maybe it means food. But if you learn that this once-novel ...
New defence against superbugs
2021-06-09
For the first time, Australian scientists have confirmed a link between the role of regular fish oil to break down the ability of 'superbugs' to become resistant to antibiotics.
The discovery, led by Flinders University and just published in international journal mBio, found that the antimicrobial powers of fish oil fatty acids could prove a simple and safe dietary supplement for people to take with antibiotics to make their fight against infection more effective.
"Importantly, our studies indicate that a major antibiotic resistance mechanism in cells can be negatively impacted by the uptake of omega-3 dietary lipids," says microbiologist Dr Bart Eijkelkamp, who leads the Bacterial Host Adaptation Research Lab at ...
Poll finds risky drinking patterns in older adults during pandemic
2021-06-09
As many older adults get back to normal life across the United States thanks to high rates of vaccination and lower COVID-19 activity, a new poll suggests many should watch their alcohol intake.
In all, 23% of adults over 50 who drink alcohol reported that they routinely had three or more drinks in one sitting, according to END ...
Many adults with cardiovascular disease know the risks, yet still don't stop smoking
2021-06-09
DALLAS, June 9, 2021 -- Many adults with a history of cardiovascular disease (CVD) continue to smoke cigarettes and/or use other tobacco products, despite knowing it increases their risk of having another cardiovascular event, according to new research published today in the Journal of the American Heart Association, an open access journal of the American Heart Association.
To understand how many adults with CVD continue to use tobacco products, investigators reviewed survey responses from the large, national Population Assessment of Tobacco and Health Study (PATH) to compare tobacco use rates over time. The participants of the current study included 2,615 adults (ages 18 or older) with a self-reported history of heart attack, heart failure, stroke or other heart disease, ...
Achieving UV nonlinearity with a wide bandgap semiconductor waveguide
2021-06-09
The field of ultrafast nonlinear photonics has now become the focus of numerous studies, as it enables a host of applications in advanced on-chip spectroscopy and information processing. The latter in particular requires a strongly intensity-dependent optical refractive index that can modulate optical pulses faster than even picosecond timescales and on sub-millimeter scales suitable for integrated photonics.
Despite the tremendous progress made in this field, there is currently no platform providing such features for the ultraviolet (UV) spectral range, which is where broadband spectra generated by nonlinear modulation can be used for new on-chip ultrafast chemical and biochemical spectroscopy devices.
Now, an ...
Scientists discover new exoplanet with an atmosphere ripe for study
2021-06-09
An international group of collaborators, including scientists from NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory and The University of New Mexico, have discovered a new, temperate sub-Neptune sized exoplanet with a 24-day orbital period orbiting a nearby M dwarf star. The recent discovery offers exciting research opportunities thanks to the planet's substantial atmosphere, small star, and how fast the system is moving away from the Earth.
The research, titled TOI-1231 b: A Temperate, Neptune-Sized Planet Transiting the Nearby M3 Dwarf NLTT 24399, will be published in a future issue of The Astronomical Journal. The exoplanet, TOI-1231 b, was detected ...
Localized the gene for blue plum skin
2021-06-09
The presence and accumulation of the antioxidant pigment anthocyanin dictates fruit hue in plums, and the synthesis of this compound is known to be regulated by the MYB10 genes. Now, researchers from the Centre for Research in Agricultural Genomics (CRAG) and the Institute of Agrifood Research and Technology (IRTA) have found the gene that determines Japanese plum skin colour. In a END ...
Preliminary genetic link to developmental coordination disorder, dyspraxia identified
2021-06-09
New research by scientists at Oxford Brookes University has identified specific genes which could provide vital information about the biology of developmental coordination disorder (DCD), also known as dyspraxia. Dyspraxia is a common motor coordination condition which is estimated to affect at least one child in every classroom.
DCD can impact a child's handwriting and coordination skills such as tying a shoelace or catching a ball. The condition can limit school achievement, impact cognitive development, constrain career opportunities and increase children's risk of developing mental health issues.
Despite the condition affecting five per cent of children, as common as dyslexia or autism, very little is known about why some children struggle ...
Nintendo® wii may help improve balance in children with cerebral palsy
2021-06-09
Therapy based on the Nintendo® Wii Balance Board can help improve balance in children with cerebral palsy, according to an analysis published in END ...
New analysis examines survival of older patients who undergo heart transplantation
2021-06-09
Advanced age is often considered a contraindication for heart transplantation, but a new study published in the END ...
A new bacteria, made in Belgium (and UCLouvain)
2021-06-09
It all started, when Patrice Cani, FNRS researcher at University of Louvain (UCLouvain), and his team repeatedly observed that a bacterium (called Subdoligranulum) is almost absent in obese and diabetic people, while it is systematically present in healthy people. So, they decided to take a closer look at this "family" of bacteria.
There is as yet only one cultivated strain of this family available in the world (the only known member of a large family) and, no luck, it is not the strain that was observed to be decreased in sick people. This is not unusual: nearly 70% of bacteria in the intestine have not yet been identified (this is called the dark matter of the ...
How should counselors broach topics of race, ethnicity, and culture?
2021-06-09
It's incumbent upon counselors to initiate or respond to clients' concerns about racial, ethnic, and cultural issues, but guidelines lack specific instructions. An article published in the Journal of Counseling & Development provides counselors with strategies for broaching and discussing topics of race, ethnicity, and culture with clients.
The article describes a model for broaching these issues and explains a series of steps--joining, assessment, preparation, and delivery--involved in using it.
"This and other articles serve as the foundation for the next phase in our research on counselor implementation of broaching and its impact on client mental health outcomes," the authors wrote.
INFORMATION: ...
How different beliefs and attitudes affect college students' career aspirations
2021-06-09
A study published in Career Development Quarterly has looked at whether beliefs and attitudes influence career aspirations of college students with different genders and sexual orientations.
Among 1,129 college students at a midwestern urban university, stronger self-efficacy beliefs--or perceptions about whether a person has the ability to achieve a desired outcome--led both male and lesbian, gay, bisexual, queer, intersex, and questioning (LGBQIQ) students to seek out leadership positions within their chosen career field. Stronger feminist attitudes were associated with an increase in achievement efforts for LGBQIQ college students, but not for heterosexual students.
"The results of the study not only demonstrate that beliefs and attitudes influence ...
Study examines care received by patients with knee osteoarthritis
2021-06-09
New research reveals that only a minority of U.S. Medicare beneficiaries with knee osteoarthritis in 2005-2010 used non-surgical care such as physical therapy and knee injections, and few were treated by rheumatologists, physiatrists, or pain specialists. The study, which is published in END ...
Filipino-Americans: Vitamin D binding protein in thyroid cancer health disparities
2021-06-09
Oncotarget published "Differential expression of Vitamin D binding protein in thyroid cancer health disparities" which reported that thyroid cancer incidence, recurrence, and death rates are higher among Filipino Americans than European Americans.
In this study, the authors determined the correlation between differential DBP expression in tumor tissues and cancer staging in Filipino Americans versus European Americans.
The majority of Filipino Americans presented with advanced tumor staging. In contrast, European Americans showed early staging and very few advanced tumors.
On the contrary, in the tumor tissues derived from European Americans, moderate to strong DBP staining was detected ...
[1] ... [2238]
[2239]
[2240]
[2241]
[2242]
[2243]
[2244]
[2245]
2246
[2247]
[2248]
[2249]
[2250]
[2251]
[2252]
[2253]
[2254]
... [8824]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.