New health benefits of red seaweeds unveiled
2021-06-14
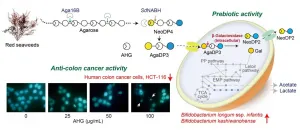
Red seaweeds have been prevalent in the diets of Asian communities for thousands of years. In a new study, published in Marine Drugs, researchers have shown how these algae confer health benefits.
"In the past, people have wondered why the number of colon cancer patients in Japan is the lowest in the world," said Yong-Su Jin (CABBI/BSD/MME), a professor of food microbiology. "Many assumed that it was due to some aspect of the Japanese diet or lifestyle. We wanted to ask whether their seaweed diet was connected to the lower frequency of colon cancer."
Although several studies have shown that Asians who eat seaweed regularly have lower risk of colon, ...
Microbes in ocean play important role in moderating Earth's temperature
2021-06-14
Methane is a strong greenhouse gas that plays a key role in Earth's climate. Anytime we use natural gas, whether we light up our kitchen stove or barbeque, we are using methane.
Only three sources on Earth produce methane naturally: volcanoes, subsurface water-rock interactions, and microbes. Between these three sources, most is generated by microbes, which have deposited hundreds of gigatons of methane into the deep seafloor. At seafloor methane seeps, it percolates upwards toward the open ocean, and microbial communities consume the majority of this methane before it reaches the atmosphere. Over the years, researchers are finding more and more methane beneath the seafloor, yet very little ever leaves the oceans and gets into the atmosphere. Where ...
Reference genome comparison finds exome variant discrepancies in 206 genes
2021-06-14
HOUSTON - (June 14, 2021) - In the two decades since the Human Genome Project mapped the entire human genome, improvements in technology have helped in developing updated reference genomes used for sequencing. But while the GRCh38 (hg38) human reference genome was released more than seven years ago, the older GRCh37 (hg19) reference remains widely used by most research and clinical laboratories. In a new study published in the American Journal of Human Genetics, researchers at the Human Genome Sequencing Center at Baylor College of Medicine identify ...
Understanding the cause of joint and tendon dysfunction in osteogenesis imperfecta
2021-06-14
HOUSTON - (June 14, 2021) - Osteogenesis imperfecta (OI) is the most common genetic form of brittle bone disease and results in defects of both bone and connective tissue. OI patients can have significant problems with mobility due to joint dysfunction due in part to tendinopathy. In a new study published in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, researchers at Baylor College of Medicine identify a protein signaling mechanism driving this dysfunction and find that inhibiting this signaling pathway can prevent onset of tendinopathy problems in mouse models.
The ...
Fitbit user data show slight increase in sleep duration in US during COVID-19 pandemic
2021-06-14
DARIEN, IL - According to a study of data from more than 163,000 Fitbit users, sleep duration increased slightly in 2020 during the COVID-19 pandemic compared with a similar timeframe in 2019.
Results show that mean sleep duration increased in nearly all groups by 5 to 11 minutes, compared with a mean decrease of 5 to 8 minutes seen over the same period in 2019. Sleep timing shifted later for nearly all groups. Sleep duration and bedtime variability decreased, largely due to fewer differences between weekday and weekend sleep.
"The most surprising thing we found was that, overall, sleep duration increased slightly, and sleep variability decreased slightly, during the most ...
Understanding the impact of patient empowerment and remote management in rheumatoid arthritis
2021-06-14
The World Health Organization describes empowerment as a process in which people can take control and make informed decisions about their life and health. Empowerment is important for people with RA since most care is provided by patients themselves.
Andersson and colleagues studied levels of empowerment and associated variables in people with RA, and investigated longitudinal clinical data in those with low and high levels of empowerment. The study involved 2837 people with RA from the BARFOT (Better Anti-Rheumatic PharmacO Therapy) cohort. Everyone was assessed according to a structured protocol at ...
Study links COVID-19 public health efforts to dramatic drop in COPD hospitalizations
2021-06-14
BALTIMORE (June 14, 2021) - Researchers at the University of Maryland School of Medicine (UMSOM) analyzed data at the 13-hospital University of Maryland Medical System (UMMS) and found public health measures designed to reduce the spread of the COVID-19 virus may have fostered a substantial side benefit: Hospital admissions for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) were reduced by 53 percent, according to a new study published in The American Journal of Medicine. This is likely due to a drop in circulating seasonal respiratory viruses such as influenza.
Hospitalizations for COPD, a group of lung diseases that make it hard to breathe and get worse over time, are commonly driven by flare-ups where symptoms are triggered by such factors ...
As climates change, prepare for more mosquitoes in winter, new study shows
2021-06-14
In many parts of the world, mosquitoes are a common summertime nuisance.
But in places on the front lines of climate change, these disease-spreading insects may one day be a year-round problem, according to new research from the University of Florida.
"In tropical regions, mosquitoes are active all year, but that isn't the case for the rest of the world. Outside of the tropics, winter temperatures cause mosquitoes to go into a kind of hibernation called diapause. We call these mosquitoes 'cold bounded' because their activity is limited by these lower temperatures," said Brett Scheffers, senior author of the study and an assistant professor in the UF/IFAS wildlife ecology and conservation department.
"However, ...
Climate change leads to unprecedented Rocky Mountain wildfires
2021-06-14
June 14, 2021 - Last fall, the Mullen fire west of Laramie raged for the better part of two months, burning more than 176,000 acres and 70 structures in Wyoming's Carbon and Albany counties, and in Jackson County, Colo.
Unfortunately, this scenario was typical during the intense 2020 fire season in the Rocky Mountain region, an area of Colorado and southern Wyoming where high-elevation forests are burning more than at any point in the past 2,000 years, according to a study in which a University of Wyoming faculty member was instrumental.
"Global warming is causing larger fires in Rocky Mountain forests than have burned for thousands of years," says Bryan Shuman, a professor in the UW Department of Geology and Geophysics. "The last time anything ...
More than a bumpy ride: turbulence offers boost to birds
2021-06-14
ITHACA, N.Y. - Most sensible air travelers dread turbulence. A little atmospheric hiccup can shake airplanes, rattle nerves and spill beverages. A Cornell University-led study found that birds don't mind at all.
By combining wind speed data with the measured accelerations of a golden eagle outfitted with GPS tracking instruments, the researchers suggest that, rather than hindering flight, turbulence is a source of energy that birds may use to their advantage.
This counterintuitive discovery could revise what we know about avian flight, and help the aerospace industry develop faster, more efficient ways to fly in turbulent environments.
The paper, ...
Targeted drug found effective in thwarting pancreatic tumors
2021-06-14
Pancreatic cancer is an aggressive disease in which malignant cells form in the tissues of the pancreas, a long and flat gland located behind the stomach that helps with digestion and blood sugar regulation. Because pancreatic cancer is difficult to detect early, it is associated with a low survival rate, accounting for just over 3% of all new cancer cases in the U.S., but leading to nearly 8% of all cancer deaths, according to the National Cancer Institute.
Through a pre-clinical study conducted in his former role at Moffitt Cancer Center and published in Clinical Cancer Research, Said Sebti, Ph.D., associate director for basic research at VCU Massey Cancer Center, identified a novel drug that effectively thwarts pancreatic tumors that are addicted ...
New app tracks human mobility and COVID-19
2021-06-14
Analyzing how people move about in their daily lives has long been important to urban planners, traffic engineers, and others developing new infrastructure projects.
But amid the social restrictions and quarantine policies imposed during the global spread of COVID-19--which is directly linked to the movement of people--human mobility patterns changed dramatically.
To understand just how COVID-19 affected human movement on a global scale, Shouraseni Sen Roy, a professor in the College of Arts and Sciences Department of Geography and Sustainable Development, and graduate student Christopher Chapin developed COVID-19 vs. Human Mobility, an innovative and interactive web application that, shared in a new ...
A 'pump' gene's surprising role in early brain formation
2021-06-14
In polymicrogyria, the cortex of the brain has many irregular, small folds (gyria) and disorganization of its layers. Many affected children have severe developmental delay, intellectual disabilities, and epilepsy, and many need to use a wheelchair. Mutations in several different genes can cause this "overfolding of the brain" condition.
Studying four patients with polymicrogyria, Richard Smith, PhD, identified mutations in a gene that caused him to do a double-take. His curiosity drove him to investigate the role of this gene, called ATP1A3, in the developing brain.
"ATP1A3 is critical to many cell biological processes," says Smith, an investigator the Division of Genetics and Genomics at Boston Children's Hospital. ...
How do social media influence ethnic polarization?
2021-06-14
Those who deactivated their Facebook profiles report a lower regard for other ethnic groups, and this effect was more prevalent among people living in more ethnically homogenous areas, shows a new study of users in Bosnia and Herzegovina (BiH). The findings run counter to a commonly held view that social media usage exacerbates societal polarization.
The work, conducted by researchers at New York University's Center for Social Media and Politics (CSMaP), appears in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS).
"For all our attention to the online drivers of polarization, we should not forget about the importance of offline factors as well," ...
UM research: Rocky mountain forests now burning more than any point in past 2,000 years
2021-06-14
MISSOULA - Following 2020's extreme fire season, high-elevation forests in the central Rocky Mountains now are burning more than at any point in the past 2,000 years, according to a new University of Montana study set to publish in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
Researchers from UM and the University of Wyoming analyzed a unique network of fire-history records to understand how 21st-century fire activity compares to wildfires in the past. The findings highlight that burning in recent decades in high-elevation forests of northern Colorado and southern Wyoming is unprecedented over the past several millennia.
As fire paleoecologists - scientists who study historical ecosystems - the team uses charcoal found in lake sediments to piece together the fire ...
Toxin-adapted fish pass down epigenetic mutations to freshwater offspring
2021-06-14
PULLMAN, Wash. - You can take a fish out of toxic water, but its epigenetic mutations will remain for at least two generations.
A research team led by Washington State University scientists analyzed the epigenetics--molecular factors and processes that determine whether genes are turned on or off--of a group of Poecilia mexicana fish, or Atlantic molly, that live in springs naturally high in hydrogen sulfide, which is normally toxic to most organisms.
The researchers removed a sample of fish from the toxic water and bred them in freshwater. They found that the grandchildren of the sulfidic-adapted fish had more epigenetic marks ...
Human microbiome could shed light on higher morbidity rate in minoritized populations
2021-06-14
EVANSTON, Ill. --- The human gut is more than a source of instinct.
A new Northwestern University study is the first to explicitly address the gut microbiome as a pathway to understanding how environmental inequities could lead to health disparities.
Biological anthropologist Katherine Amato, assistant professor of anthropology at the Weinberg College of Arts and Sciences at Northwestern, is the study's lead author.
Amato says, despite a rich body of literature documenting environmental impacts on the microbiome, and the microbiome's impact on human health, ...
Early migrations of Siberians to America tracked using bacterial population structures
2021-06-14
International team used the stomach bacteria Helicobacter pylori as a biomarker for ancient human migrations
DNA sequences catalogued at University of Warwick in EnteroBase, a public genomes database, demonstrate that a migration of Siberians to the Americas occurred approximately 12,000 years ago
Project began in 2000s but new statistical techniques allowed researchers to reconstruct and date the migrations of Siberian Helicobacter pylori
Early migrations of humans to the Americas from Siberia around 12,000 years ago have been traced using the bacteria they carried by an international team including scientists at the University of ...
Model suggests surgery should precede chemotherapy for select patients with ovarian cancer
2021-06-14
Certain patients with an aggressive form of ovarian cancer have a better chance of a cure through surgical removal of their tumor before chemotherapy instead of the reverse, a new study shows.
Led by researchers at NYU Grossman School of Medicine, Perlmutter Cancer Center, and Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, the study used a mathematical tool to examine how doctors should coordinate available treatments for high-grade serous ovarian cancer (HGSC).
Ovarian cancer is the 8th most common cancer and cancer death in women worldwide, and HGSC constitutes roughly 70 percent of ovarian malignancies and has the worst prognosis. Patients with the condition typically undergo surgery and chemotherapy, but there has been long-standing controversy over the best order of treatment.
Published ...
Biodiversity 'hotspots' imperiled along California's streams
2021-06-14
A study of woodland ecosystems that provide habitat for rare and endangered species along streams and rivers throughout California reveals that some of these ecologically important areas are inadvertently benefitting from water that humans are diverting for their own needs. Though it seems a short-term boon to these ecosystems, the artificial supply creates an unintended dependence on its bounty, threatens the long-term survival of natural communities and spotlights the need for changes in the way water is managed across the state.
"We need to be more intentional in incorporating ecosystem water needs when we manage water--both for aquatic organisms and species on land," said Melissa Rohde, the lead author of a study published June ...
Pollutant concentration increases in the franciscana dolphin
2021-06-14
The concentration of potentially toxic metals is increasing in the population of the franciscana dolphin --a small cetacean, endemic from the Rio de la Plata and an endangered species-- according to a study led by a team of the Faculty of Biology and the Biodiversity Research Institute (IRBio), published in the journal Science of The Total Environment.
The impact of human activity in the region could be the cause for the increase of trace elements such as chromium, copper, iron and nickel in the dolphins' biological tissues, as stated in the study. The paper counts on the participation of members from the National History Museum of Uruguay, and is subsidized through a project of ...
Women leaving jail have high vaccine hesitancy; app drops resistance, boosts literacy
2021-06-14
LAWRENCE -- The United States has the highest population of incarcerated citizens among developed nations. Every year, roughly 2 million women, the majority held in jails, leave incarceration. The COVID-19 pandemic hit jails and correctional facilities harder than almost any other societal setting. Many of the people leaving incarceration are returning to communities that were also disproportionately affected by the pandemic, yet many people in that population have expressed hesitancy to receive a COVID-19 vaccine.
New research from the University of Kansas found high rates of vaccine hesitancy among women transitioning from incarceration, due to a multitude ...
Study reveals COVID-19 risk factors for those with IDD
2021-06-14
Syracuse, N.Y. - A study of nearly 550 adults with intellectual and developmental disabilities receiving residential services in New York City found that age, larger residential settings, Down syndrome and chronic kidney disease were the most common risk factors for COVID-19 diagnosis, and heart disease was most associated with COVID-19 deaths.
The study, "Risk Factors Associated With COVID-19 Outcomes Among People With Intellectual and Developmental Disabilities Receiving Residential Services," was published June 8 by JAMA Network Open and provided the first evidence of the risk factors leading to COVID-19 diagnosis and death among people with IDD who receive residential services.
The study's findings suggest that ...
COVID-19 creates conditions for emergence of 'superfungus' in Brazil
2021-06-14
Fully occupied intensive care units (ICUs). Physically and mentally exhausted health workers. Chaotically overcrowded hospitals. These and similar problems posed by the COVID-19 pandemic in Brazil have created ideal conditions for the emergence of Candida auris, a microorganism some are calling a "superfungus" because of the speed with which it has developed drug resistance.
The first two cases were confirmed in December 2020 at a hospital in Salvador (state of Bahia, Northeast Brazil), and are described in the Journal of Fungi by a group of researchers led by Arnaldo Colombo, head of the Special Mycology Laboratory at the Federal University of São Paulo (UNIFESP). The study was supported by São Paulo Research Foundation - FAPESP.
"Nine other C. auris patients ...
New combination of materials provides progress toward quantum computing
2021-06-14
TROY, N.Y. -- The future of quantum computing may depend on the further development and understanding of semiconductor materials known as transition metal dichalcogenides (TMDCs). These atomically thin materials develop unique and useful electrical, mechanical, and optical properties when they are manipulated by pressure, light, or temperature.
In research published today in Nature Communications, engineers from Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute demonstrated how, when the TMDC materials they make are stacked in a particular geometry, the interaction that occurs between particles gives researchers more control over the devices' properties. Specifically, the interaction between ...
[1] ... [2233]
[2234]
[2235]
[2236]
[2237]
[2238]
[2239]
[2240]
2241
[2242]
[2243]
[2244]
[2245]
[2246]
[2247]
[2248]
[2249]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.