Are zoos inadvertently complicit in wildlife trade? The case of a rare Borneo lizard
2021-06-16
Should zoos display legally protected species that have been smuggled out of their range countries? A new study suggests that a pause and rethink may be needed, as it reports that accredited zoos have acquired a rare and legally protected reptile, the earless monitor lizard endemic to Borneo, without any evidence that the animals were legally exported.
The earless monitor lizard occurs only on the island of Borneo and has been described as a "miniature Godzilla" and "the Holy Grail of Herpetology." Discovered by western scientists almost 150 years ago, for most of this period the species was known largely from pickled specimens in natural history collections, and wasn't recorded from ...
New in Ethics & Human Research, May-June 2021
2021-06-16
American Indian and Alaska Native Enrollment in Clinical Studies in the National Institutes of Health's Intramural Research Program
Dejonna Vigil, Ninet Sinaji, and Barbara Karp
This is the first study to provide data about the inclusion of American Indians and Alaska Natives in the National Institutes of Health's Intramural Research Program (NIH-IRP), which provides eligible individuals with access to innovative research treatments that may not otherwise be available. The program's mission is to include all Americans. This study analyzed data from more than 1,800 NIH-IRP protocols active in 2014 and 2017. While the number of American ...
Bruisable artificial skin could help prosthetics, robots sense injuries
2021-06-16
When someone bumps their elbow against a wall, they not only feel pain but also might experience bruising. Robots and prosthetic limbs don't have these warning signs, which could lead to further injury. Now, researchers reporting in ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces have developed an artificial skin that senses force through ionic signals and also changes color from yellow to a bruise-like purple, providing a visual cue that damage has occurred.
Scientists have developed many different types of electronic skins, or e-skins, that can sense stimuli through electron transmission. However, these electrical conductors are not always biocompatible, which could limit their use in some types of prosthetics. In contrast, ionic skins, or I-skins, ...
Several persistent chemicals were found in fetal organs
2021-06-16
Researchers at Karolinska Institutet in Sweden found industrial chemicals in the organs of fetuses conceived decades after many countries had banned the substances. In a study published in the journal Chemosphere, the researchers urge decision makers to consider the combined impact of the mix of chemicals that accumulate in people and nature.
"These are important findings that call for regulators to consider the collective impact of exposure to multiple chemicals rather than evaluating just one chemical at a time," says first author Richelle Duque Björvang, PhD student at the Department of Clinical ...
Can biodegradable polymers live up to the hype?
2021-06-16
As consumers and corporations alike become more environmentally conscious, the chemical industry is working to find solutions to the plastic waste crisis. One idea is to use biodegradable polymers known as polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA) as replacements for traditional plastic packaging and other materials. A feature article in Chemical & Engineering News, the weekly newsmagazine of the American Chemical Society, explores the possibilities and pitfalls of PHA.
PHA is not a new human invention; this class of polymers can be found in nature and is used to store cellular energy, writes Senior Editor Alex Tullo. Commercially, it is manufactured through the industrial fermentation of sugars or lipids. As cities ...
Using microorganisms to monitor water quality within minutes
2021-06-16
Researchers from the Singapore University of Technology and Design (SUTD) have demonstrated a technology that rapidly detects pollutants in water by measuring their impacts on swimming microorganisms.
Their proof-of-concept, published in Scientific Reports, does not require any chemicals, reagents or laboratory equipment. Instead, it leverages the regular camera of a smartphone as well as microorganisms called Paramecia that are ubiquitous in water bodies--making it especially suitable for assessing water drinkability in underdeveloped regions.
Typically, levels of environmental pollutants are measured by assessing their impact on a given population. Though such impacts may be visible after several days for microorganisms, it takes several years for the true scale to be ...
Online mental health therapy significantly aids the isolated, immunosuppressed in pandemic
2021-06-16
People with a rare autoimmune disease, who likely experience more serious isolation during a global pandemic, saw their anxiety and depression improve after receiving online mental health intervention through an international study involving investigators from Michigan Medicine.
The paper, END ...
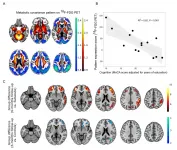
SNMMI Image of the Year: PET imaging measures cognitive impairment in COVID-19 patients
2021-06-16
Reston, VA--The effects of COVID-19 on the brain can be accurately measured with positron emission tomography (PET), according to research presented at the Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging (SNMMI) 2021 Annual Meeting. In the study, newly diagnosed COVID-19 patients, who required inpatient treatment and underwent PET brain scans, were found to have deficits in neuronal function and accompanying cognitive impairment, and in some, this impairment continued six months after their diagnosis. The detailed depiction of areas of cognitive impairment, neurological symptoms and comparison of impairment over a six-month time frame has been selected as SNMMI's 2021 Image of the Year.
Each year, SNMMI chooses an image that best exemplifies the most promising ...
Intestinal cancers: The 14-3-3sigma gene acts as a tumor suppressor
2021-06-16
LMU researchers have identified the 14-3-3sigma gene as an important suppressor of carcinogenesis in the gastrointestinal tract.
Intestinal cancers, also known as colorectal cancer, are among the most prevalent forms of malignancy worldwide. If detected early enough, tumors can be surgically excised. However, as cancer growth progresses, cells may escape from the primary tumor, which can then establish metastatic tumors in other organs. Once such satellite tumors have formed, survival rates fall significantly. Formation of the initial tumor can be triggered by mutations in any of a number of genes. Together with postdocs ...
Model helps analyze decision-making on adopting Type 2 diabetes medical guidelines
2021-06-16
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. -- Health care workers often don't adopt new guidelines for best practices in medical care until well after those guidelines are established. A team of researchers led by Eunice E. Santos, the dean of the School of Information Sciences at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign, has developed a new computational modeling and simulation framework to analyze decision-making and identify effective dissemination strategies for medical guidelines.
The research team examined guidelines for Type 2 diabetes that were established in 2012 and were still not adopted years later. The researchers found that health ...
What factors put Philippine birds at risk of extinction?
2021-06-16
The lush forests and more than 7,000 islands of the Philippines hold a rich diversity of life, with 258 bird species who live nowhere but the Philippine archipelago. A new study from University of Utah researchers suggests that, due to deforestation and habitat degradation, more bird species may be endangered that previously thought - including species that may not have been discovered yet. The study is published in Frontiers in Ecology and Evolution.
"Our study provides a roadmap for not only which species may warrant heightened conservation attention," says Kyle Kittelberger, a doctoral student in the University of Utah School of Biological Sciences, "but which traits ...
Algorithm reveals the mysterious foraging habits of narwhals
2021-06-16
An algorithm can predict when narwhals hunt - a task once nearly impossible to gain insight into. Mathematicians and computer scientists at the University of Copenhagen, together with marine biologists in Greenland, have made progress in gathering knowledge about this enigmatic Arctic whale at a time when climate change is pressuring them.
The small whale, known for its distinctively spiraled tusk, is under mounting pressure due to warming waters and the subsequent increase in Arctic shipping traffic. To better care for narwhals, we need to learn more about their foraging behaviour - and how these may change as a result of human disturbances and global warming. Biologists know almost nothing about this. Because narwhals live in isolated Arctic regions and ...
Smartphone bans in the workplace
2021-06-16
For many of us, our smartphone has become our ever-present companion and is usually far more than just a phone. Thanks to the constant availability of online content as well as our reachability through messenger services and social networks via our smartphone, this everyday object's potential to distract us is high - at work too. This is why many employers view the use of smartphones during work time with suspicion, and countermeasures taken range from asking staff to refrain voluntarily from using them to banning smartphones in the workplace through an internal agreement. But do such measures actually work and, if so, how?
This is the ...
Sweeping analysis concludes there's no cheating old age
2021-06-16
DURHAM, N.C. - Special diets, exercise programs, supplements and vitamins -- everywhere we look there is something supposed to help us live longer. Maybe those work: human average life expectancy has gone from a meager 40-ish years to a whopping 70-something since 1850. Does this mean we are slowing down death?
A new study comparing data from nine human populations and 30 populations of non-human primates says that we are probably not cheating the reaper. The researchers say the increase in human life expectancy is more likely the statistical outcome of improved survival for children and young adults, not slowing the aging clock.
"Populations get older mostly because more individuals get through those early stages of life," ...
Stoneflies: Youth influences adulthood
2021-06-16
In the majority of insects, metamorphosis fosters completely different looking larval and adult stages. For example, adult butterflies are completely different from their larval counterparts, termed caterpillars. This "decoupling" of life stages is thought to allow for adaptation to different environments. Researchers of the University of Bonn now falsified this text book knowledge of evolutionary theory for stoneflies. They found that the ecology of the larvae largely determines the morphology of the adults by investigating 219 earwig and stonefly species at high-resolution particle accelerators. The study has ...
Osteoporosis: New approach to understanding bone strength pays dividends
2021-06-16
Osteoporosis researchers at the UVA School of Medicine have taken a new approach to understanding how our genes determine the strength of our bones, allowing them to identify several genes not previously known to influence bone density and, ultimately, our risk of fracture.
The work offers important insights into osteoporosis, a condition that affects 10 million Americans, and it provides scientists potential new targets in their battle against the brittle-bone disease.
Importantly, the approach uses a newly created population of laboratory mice that allows researchers to identify relevant genes and overcome limitations of human studies. Identifying such genes has been very difficult but is key to using genetic discoveries to improve ...
Icebergs drifting from Canada to southern Florida
2021-06-16
Woods Hole, MA (June 16, 2021) -- Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) climate modeler Dr. Alan Condron and United States Geological Survey (USGS) research geologist Dr. Jenna Hill have found evidence that massive icebergs from roughly 31,000 years ago drifted more than 5000km (> 3,000 miles) along the eastern United States coast from Northeast Canada all the way to southern Florida. These findings were published today in Nature Communications.
Using high resolution seafloor mapping, radiocarbon dating and a new iceberg model, the team analyzed about 700 iceberg scours ("plow marks" on the seafloor left behind by the bottom parts of icebergs dragging through marine sediment ) from Cape Hatteras, North Carolina to the Florida Keys. ...
Yeast mating -- more than meets the eye
2021-06-16
Researchers from the Max-Planck Institute for Terrestrial Microbiology have discovered a surprising asymmetry in the mating behavior of unicellular yeast that emerges solely from molecular differences in pheromone signaling. Their results, published in the current issue of "Science Advances", might shed new light on the evolutionary origins of sexual dimorphism in higher eukaryotes.
Resemblant of higher organisms, yeast gametes communicate during the mating process by secreting and sensing sexual pheromones. However, in contrast to higher eukaryotes, budding yeast is isogamous: seen through a microscope, gametes of both mating types ("sexes"), MATa and MATα, look exactly the same. Since anisogamy -- difference in size between male and female gametes --was ...
MD Anderson research highlights for June 16, 2021
2021-06-16
HOUSTON ? The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center's Research Highlights provides a glimpse into recently published studies in basic, translational and clinical cancer research from MD Anderson experts. Current advances include a new combination therapy for acute myeloid leukemia (AML), a greater understanding of persistent conditions after AML remission, the discovery of a universal biomarker for exosomes, the identification of a tumor suppressor gene in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and characterization of a new target to treat Clostridioides difficile (C. difficile) infections.
Utilizing combination therapy for AML
While a majority of patients with acute myeloid leukemia (AML) respond favorably ...
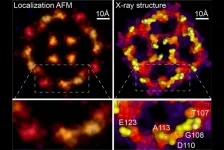
New super-resolution microscopy method approaches the atomic scale
2021-06-16
Scientists at Weill Cornell Medicine have developed a computational technique that greatly increases the resolution of atomic force microscopy, a specialized type of microscope that "feels" the atoms at a surface. The method reveals atomic-level details on proteins and other biological structures under normal physiological conditions, opening a new window on cell biology, virology and other microscopic processes.
In a study, published June 16 in Nature, the investigators describe the new technique, which is based on a strategy used to improve resolution in light microscopy.
To study proteins and other biomolecules at high resolution, investigators have long relied on two techniques: X-ray crystallography ...
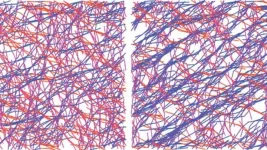
UChicago scientists identify properties that allow proteins to strengthen under pressure
2021-06-16
A new rubber band stretches, but then snaps back into its original shape and size. Stretched again, it does the same. But what if the rubber band was made of a material that remembered how it had been stretched? Just as our bones strengthen in response to impact, medical implants or prosthetics composed of such a material could adjust to environmental pressures such as those encountered in strenuous exercise.
A research team at the University of Chicago is now exploring the properties of a material found in cells which allows cells to remember and respond to environmental pressure. In a paper published on May 14, 2021 in Soft Matter, they teased ...
A distinctive inflammatory signature found in a genetic form of ALS
2021-06-16
PHILADELPHIA - Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), also known as Lou Gehrig's disease, is a neurodegenerative disease that strikes nearly 5,000 people in the U.S. every year. About 10% of ALS cases are inherited or familial, often caused by an error in the C9orf72 gene. Compared to sporadic or non-familial ALS, C90rf72 patients are considered to have a more aggressive disease course. Evidence points to the immune system in disease progression in C90rf72 patients, but we know little of what players are involved. New research from the Jefferson Weinberg ALS Center identified an increased ...
Machine learning can now reduce worry about nanoparticles in food
2021-06-16
While crop yield has achieved a substantial boost from nanotechnology in recent years, alarms over the health risks posed by nanoparticles within fresh produce and grains have also increased. In particular, nanoparticles entering the soil through irrigation, fertilizers and other sources have raised concerns about whether plants absorb these minute particles enough to cause toxicity.
In a new study published online in the journal END ...
When small epigenomic signals matter
2021-06-16
Although each organism has a unique genome, a single gene sequence, each individual has many epigenomes. An epigenome consists of chemical compounds and proteins that can bind to DNA and regulate gene action, either by activating or deactivating them or producing organ- or tissue-specific proteins. As it is a highly dynamic material, it can provide a large amount of information to shed light on the evolution of the various tissues and organs that make up the body.
Now, a team from the Institute of Evolutionary Biology (IBE), a joint centre of the Spanish National Research Council (CSIC) and Pompeu Fabra University, has carried out the largest study to date on the regulatory ...
Sticky transparent wall coating can capture aerosols and droplets from the air
2021-06-16
By repurposing common ingredients in hair conditioner, scientists have designed an inexpensive, transparent coating that can turn surfaces like windows and ceilings into glue pads to trap airborne aerosol droplets. This new strategy is described June 16 in the journal Chem.
"Facing a pandemic, we need to proactively leverage all of the different layers of defense mechanisms, including the physical barriers," says corresponding author Jiaxing Huang, a professor of materials science and engineering at Northwestern University. "After all, these viruses must travel through physical space before reaching and eventually infecting people."
The ...
[1] ... [2225]
[2226]
[2227]
[2228]
[2229]
[2230]
[2231]
[2232]
2233
[2234]
[2235]
[2236]
[2237]
[2238]
[2239]
[2240]
[2241]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.