Study of harvey flooding aids in quantifying climate change
2021-06-10
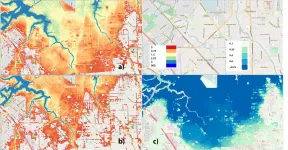
How much do the effects of climate change contribute to extreme weather events? It's hard to say--the variables involved are plentiful, each event is unique, and we can only do so much to investigate what didn't happen. But a new paper from Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab) climate scientist Michael Wehner investigates the question for one particular element of one significant storm and makes the results available to those who lived through it.
In the paper, "Attributable human-induced changes in the magnitude of flooding in the Houston, Texas region during Hurricane Harvey," published May 19 in Climatic Change, Wehner and Christopher Sampson from Fathom Bristol used a hydraulic ...
Trapping DNA damage
2021-06-10
Even on a good day, DNA is constantly getting damaged.
Nicks, scratches, breaks: the delicate strands that carry life's genetic code take a beating as they jumble about in the course of their work. If left untreated, errors accumulate, with fatal consequences -- such as cancerous tumors -- for the cell and the organism.
This is where two key proteins come to the rescue: PARP -- or poly ADP ribose polymerase -- acts as a marker for a trouble spot, allowing XRCC1 -- or X-ray repair cross-complementing protein 1 -- to zoom in and begin a repair.
This much has been known for some time and was even recognized in the 2015 Nobel prizes ...
Sealed, signed and delivered
2021-06-10
A team of archaeologists from the Hebrew University of Jerusalem (HU) made a rare discovery when they unearthed a small clay seal impression dating back some 7000 years. The impression, with two different geometric stamps imprinted on it, was discovered in Tel Tsaf, a prehistoric village located in Israel's Beit She'an Valley up north.
The discovery was made as part of a dig that took place between 2004 and 2007 and was led by HU's Professor Yosef Garfinkel along with two of his students, Professor David Ben Shlomo and Dr. Michael Freikman, both of whom are now researchers at Ariel University. One hundred and fifty clay sealings were originally found at the site, with one being particularly rare and of distinct, historic importance. The object ...
'Bad fat' suppresses killer T cells from attacking cancer
2021-06-10
LA JOLLA--(June 10, 2021) In order for cancer to grow and spread, it has to evade detection by our immune cells, particularly specialized "killer" T cells. Salk researchers led by Professor Susan Kaech have found that the environment inside tumors (the tumor microenvironment) contains an abundance of oxidized fat molecules, which, when ingested by the killer T cells, suppresses their ability to kill cancer cells. In a vicious cycle, those T cells, in need of energy, increase the level of a cellular fat transporter, CD36, that unfortunately saturates them with even more oxidized fat and further curtails their anti-tumor functions.
The discovery, published online in Immunity on June 7, 2021, suggests new pathways for safeguarding the immune system's ...
Decoded genome of little-known disease offers hope for citrus
2021-06-10
Scientists are hoping the RNA of an obscure infection can one day be used like a Trojan horse to deliver life-saving treatments to citrus trees.
The infection, citrus yellow vein disease, was discovered 64 years ago in Riverside and has never been seen elsewhere in the world. Decades later, UC Riverside researchers have finally unraveled the associated pathogen's genetic codes -- a significant step toward harnessing its unique properties.
A paper describing this work was published recently in the journal Frontiers in Microbiology. It opens the door to testing whether this apparently ...
ACS Nano: CNIC scientists describe a possible disease-causing mechanism in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
2021-06-10
Scientists at the Centro Nacional de Investigaciones Cardiovasculares (CNIC) have described a potential disease-causing mechanism in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM), the most frequent hereditary disease of the heart. The study, published in the journal ACS Nano, provides the first description of an association between this disease and mechanical alterations to a component of the contractile machinery of the heart.
The heart muscle is under constant mechanical stress throughout life as it contracts to pump blood to the body. The laboratory led by Dr. Jorge Alegre-Cebollada investigates how the mechanical properties of the cardiac proteins determine the physiological behavior of this muscle and how alterations to these properties lead to the appearance of diseases like ...
Bacteria hijack latent phage of competitor
2021-06-10
This targeted control of phages provides entirely new biotechnological and therapeutic approaches, e.g. for phage therapies. The results produced in the context of an ERC grant have been published in the Journal of the American Chemical Society.
The human body and its microbiota harbour a large amount of phages. These infect bacteria as virus particles to ensure their own survival. One of their strategies is to integrate into the bacterial genome and multiply via bacterial cell division. However, external signal molecules can trigger the phages' sudden awakening from their dormant ...
Latest tests on 6G return surprising results
2021-06-10
Imagine you're a fisherman living by a lake with a rowboat. Every day, you row out on the calm waters and life is good. But then your family grows, and you need more fish, so you go to the nearby river. Then, you realize you go farther and faster on the river. You can't take your little rowboat out there - it's not built for those currents. So, you learn everything you can about how rivers work and build a better boat. Life is good again...until you realize you need to go farther still, out on the ocean. But ocean rules are nothing like river rules. Now you have to learn how ocean currents work, and then ...
Treating sleep apnea with CPAP therapy is associated with lower risk of heart problems
2021-06-10
DARIEN, IL - Findings from a recent study show that patients with untreated, moderate to severe obstructive sleep apnea had a higher risk of experiencing a cardiovascular event, but the risk of incident heart problems was decreased in those who used CPAP therapy.
Results show that people with moderate to severe sleep apnea and no record of CPAP use were 71% more likely than those without sleep apnea to experience incident myocardial infarction, stroke, unstable angina, heart failure or cardiovascular death. Compared with the risk of heart problems in people with untreated sleep apnea, the risk of experiencing a cardiovascular event was 32% lower ...
Researchers link ancient wooden structure to water ritual
2021-06-10
ITHACA, N.Y. - The Noceto Vasca Votiva is a unique wood structure that was unearthed on a small hill in northern Italy in 2005. Built primarily of oak and slightly larger than a backyard swimming pool, the exact purpose of the in-ground structure has remained a mystery, as has the date of its construction. Italian researchers estimated its origins go back to the late Middle Bronze Age, sometime between 1600 and 1300 B.C.
While that gap might not seem huge, in archeological terms it's like comparing the culture that invented the steam engine with the one that produced the iPad.
A Cornell University team led by Sturt Manning, Distinguished ...
Over 500 new FRBs detected in single year due to CHIME telescope
2021-06-10
Fast radio bursts, or FRBs, blaze for a few milliseconds before vanishing without a trace. Their origins are unknown, and their appearance is unpredictable. In the decade following their discovery in 2007, only 140 FRBs had been seen. Now, thanks to the launch of a large stationary telescope in the interior of British Columbia in 2018, the number of new FRBs detected has almost quadrupled - for a total of 535. Moreover, the Canadian Hydrogen Intensity Mapping Experiment (CHIME/FRB), a McGill-led inter-university collaboration, has put together the first CHIME/FRB catalogue, which will be presented this week at the American Astronomical Society Meeting.
CHIME is unique in that ...
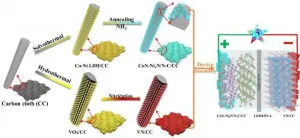
Scientists develop integrated electrodes for high-energy-density flexible supercapacitors
2021-06-10
Recently, a research team led by Prof. ZHAO Bangchuan from the Institute of Solid Materials of the Hefei Institutes of Physical Science (HFIPS) synthesized 3D porous honeycomb-like CoN-Ni3N/N-C nanosheets and vanadium nitride (VN) nanobelt arrays via in-situ growth method, respectively, and constructed a high-energy-density flexible supercapacitor device. The result has been published in Advanced Functional Materials.
Transition metal nitrides (TMNs) are potential electrode materials for high-performance energy storage devices, but the structural instability severely hinders their application. Therefore ...
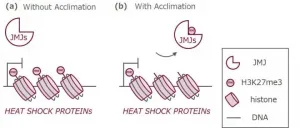
How to beat the heat: Memory mechanism allows plants to adapt to heat stress
2021-06-10
Ikoma, Japan - "If you can't stand the heat, get out of the kitchen," as the old saying goes. But for organisms that can't leave the proverbial kitchen when things get too hot, there's another way: researchers from Japan have discovered that plants can gain heat tolerance to better adapt to future heat stress, thanks to a particular mechanism for heat stress 'memory'.
In a study published in Nature Communications, researchers from Nara Institute of Science and Technology have revealed that a family of proteins that control small heat shock genes enables plants to 'remember' how to deal with heat stress.
Climate change, especially global warming, is a growing threat to agriculture ...
Prostate cancer linked to obesity
2021-06-10
Prostate cancer is the most common form of cancer among Canadian men and the third leading cause of cancer death. Abdominal obesity appears to be associated with a greater risk of developing aggressive prostate cancer. This link was demonstrated in a END ...
When physics meets financial networks
2021-06-10
Generally, physics and financial systems are not easily associated in people's minds. Yet, principles and techniques originating from physics can be very effective in describing the processes taking place on financial markets. Modeling financial systems as networks can greatly enhance our understanding of phenomena that are relevant not only to researchers in economics and other disciplines, but also to ordinary citizens, public agencies and governments. And the theory of Complex Networks represents a powerful framework for studying how shocks propagate in financial systems, identifying early-warning signals of forthcoming crises, and reconstructing ...
Climate protection: Deep decarbonization by 2050 currently not plausible
2021-06-10
Today the Hamburg-based Cluster of Excellence "Climate, Climatic Change, and Society" (CLICCS) publishes a new, essential study on climate futures. The study represents the first systematic attempt to investigate whether a climate future with net-zero carbon emissions is not only possible but also plausible. The authors examine plausibility from a technical-economic perspective, but also with regard to the societal changes necessary for such a future. They conclude that deep decarbonization by 2050 is currently not plausible - the current efforts to bring about societal transformation need to be far more ambitious.
The European Union is now increasing the ambition of its climate goals, and the German Federal Constitutional Court has recently committed Germany ...
'Vegan spider silk' provides sustainable alternative to single-use plastics
2021-06-10
Researchers have created a plant-based, sustainable, scalable material that could replace single-use plastics in many consumer products.
The researchers, from the University of Cambridge, created a polymer film by mimicking the properties of spider silk, one of the strongest materials in nature. The new material is as strong as many common plastics in use today and could replace plastic in many common household products.
The material was created using a new approach for assembling plant proteins into materials which mimic silk on a molecular level. The energy-efficient method, which uses sustainable ingredients, results in a plastic-like free-standing film, which can be made at industrial ...
New twist on DNA data storage lets users preview stored files
2021-06-10
Researchers from North Carolina State University have turned a longstanding challenge in DNA data storage into a tool, using it to offer users previews of stored data files - such as thumbnail versions of image files.
DNA data storage is an attractive technology because it has the potential to store a tremendous amount of data in a small package, it can store that data for a long time, and it does so in an energy-efficient way. However, until now, it wasn't possible to preview the data in a file stored as DNA - if you wanted to know what a file was, you had to "open" the entire file.
"The advantage to our technique is that it is more efficient ...
Rural residents, American Indians travel farthest for certified stroke care
2021-06-10
DALLAS, June 10, 2021 -- The distance a stroke patient must travel to receive care at a certified stroke center differs by race, age, income and insurance status, with the largest disparities found among rural residents and American Indians, according to a combined analysis of U.S. census data and road maps published today in Stroke, a journal of the American Stroke Association, a division of the American Heart Association.
Treatment for ischemic stroke, a blockage in an artery that supplies blood to the brain, restores blood flow to the brain. Rapid treatment is essential to reduce disability. Blood flow may be reestablished by administering intravenous clot-busting medication within 4.5 hours after the onset of stroke ...
Lodgers on manganese nodules: Sponges promote a high diversity
2021-06-10
Polymetallic nodules and crusts cover many thousands of square kilometres of the world's deep-sea floor. They contain valuable metals and rare earth elements and are therefore of great economic interest. To date, there is no market-ready technology for deep-seabed mining. But it is already clear that interventions in the seabed have a massive and lasting impact on the areas affected. This is also confirmed by a study now published by Tanja Stratmann from the Max Planck Institute for Marine Microbiology in Bremen, Germany, and researchers from the Senckenberg am Meer Institute in Wilhelmshaven, Germany, and the Dutch research institute NIOZ.
In their study, Stratmann and her colleagues used data from ...
Losing nature impacts Black, Hispanic, and low-income Americans most
2021-06-10
When nature vanishes, people of color and low-income Americans disproportionally lose critical environmental and health benefits--including air quality, crop productivity and natural disease control--a new study in Nature Communications finds.
The University of Vermont research is the first national study to explore the unequal impacts on American society--by race, income and other demographics--of projected declines in nature, and its many benefits, across the United States.
Focusing on three vital ecosystem services--air quality, crop pollination, and control of insect-borne disease (West Nile virus), researchers project that these benefits of nature will decrease for non-white people by an average of 224%, ...
Say goodbye to your camera bump: uOttawa researchers miniaturize optics by discovering counterpart to lens
2021-06-10
Can you imagine one day using a telescope as thin as a sheet of paper, or a much smaller and lighter high-performance camera? Or no longer having that camera bump behind your smartphone?
In a paper published in Nature Communications, researchers from the University of Ottawa have proposed a new optical element that could turn these ideas into reality by dramatically miniaturizing optical devices, potentially impacting many of the applications in our lives.
To learn more about this project, we talked to lead author Dr. Orad Reshef, a senior postdoctoral fellow in the Robert Boyd Group, and research lead Dr. Jeff Lundeen, who is the Canada Research Chair in Quantum Photonics, Associate Professor in the ...
Drug commonly used as antidepressant helps fight cancer in mice
2021-06-10
A class of drug called monoamine oxidase inhibitors is commonly prescribed to treat depression; the medications work by boosting levels of serotonin, the brain's "happiness hormone."
A new study by UCLA researchers suggests that those drugs, commonly known as MAOIs, might have another health benefit: helping the immune system attack cancer. Their findings are reported in two papers, which are published in the journals Science Immunology and Nature Communications.
"MAOIs had not been linked to the immune system's response to cancer before," said Lili Yang, senior author of the study and a member of the Eli and Edythe Broad Center of Regenerative Medicine and Stem Cell Research at UCLA. "What's especially exciting is that this is a very well-studied and ...
Largescale brain epigenetics study provides new insights into dementia
2021-06-10
The largest study of its kind has unveiled new insights into how genes are regulated in dementia, including discovering 84 new genes linked to the disease.
Led by the University of Exeter, the international collaboration combined and analysed data from more than 1,400 people across six different studies, in a meta-analysis published in Nature Communications. These studies had used brain samples from people who had died with Alzheimer's disease. The project, funded by Alzheimer's Society and supported by the Medical Research Council and the National Institutes for ...
Beyond Remission: From Alcohol Dependence to Optimal Mental Health
2021-06-10
UNIVERSITY OF TORONTO & CARLETON UNIVERSITY
New research published online in the journal Substance Use & Misuse is good news for those struggling with alcohol dependence: the possibility of ending this dependency gets easier with age. Moreover, more than half of individuals who have been dependent on alcohol are free of any addictions or mental illness, and nearly 40% are in excellent mental health.
Using data drawn from Statistics Canada's Canadian Community Health Survey-Mental Health, researchers examined a nationally representative sample of 820 adult Canadians with a history of alcohol dependence to 19,945 who had never been addicted to alcohol.
They found that in the past year, 71% of ...
[1] ... [2223]
[2224]
[2225]
[2226]
[2227]
[2228]
[2229]
[2230]
2231
[2232]
[2233]
[2234]
[2235]
[2236]
[2237]
[2238]
[2239]
... [8815]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.