Cooling LIGO's mirrors to near quantum ground state
2021-06-17
Using LIGO's suspended mirrors, researchers have demonstrated the ability to cool a large-scale object - the 10-kilogram optomechanical oscillator the suspended mirrors form - to nearly the motional quantum ground state. Upgrading LIGO (Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory) with such a modification would not only increase the device's sensitivity and range in detecting gravitational waves but could also provide new insights into large-scale quantum phenomena. For most mechanical objects to be coaxed into a quantum state, they need to be cooled to exceedingly low temperatures to overcome the thermal vibrations, or phonons, that mask the signature of quantum motion. This brings the ...
Marine ice cliff collapse limited by ice sheet thickness
2021-06-17
Marine-terminating glaciers may be less vulnerable to rapid and irreversible collapse than previously suggested, according to a new study, which finds that ice cliff collapse is limited by upstream thinning of the ice sheet and how quickly calved icebergs and sea-ice float away. The glaciers of Greenland and Antarctica slowly flow to the sea, terminating in massive vertical ice cliffs. Occasionally, these partially submerged margins can collapse under their own weight and trigger rapid disintegration of ice sheets. It's thought that this process, called marine ice cliff instability (MICI), could lead to the catastrophic retreat of some of the planet's largest ice sheets, substantially contributing to global sea level rise. However, current ...
Physicists bring human-scale object to near standstill, reaching a quantum state
2021-06-17
CAMBRIDGE, MA -- To the human eye, most stationary objects appear to be just that -- still, and completely at rest. Yet if we were handed a quantum lens, allowing us to see objects at the scale of individual atoms, what was an apple sitting idly on our desk would appear as a teeming collection of vibrating particles, very much in motion.
In the last few decades, physicists have found ways to super-cool objects so that their atoms are at a near standstill, or in their "motional ground state." To date, physicists have wrestled small objects such as clouds of millions of atoms, or nanogram-scale objects, into such pure quantum states.
Now for the first time, scientists at MIT and elsewhere have cooled a large, human-scale object to close to its motional ground state. The object ...
Anti-aging protein in red blood cells helps stave off cognitive decline
2021-06-17
Research conducted by Qiang et al has discovered a link between a protein in red blood cells and age-related decline in cognitive performance. Published in the open access journal PLOS Biology on 17th June 2021, the study shows that depleting mouse blood of the protein ADORA2B leads to faster declines in memory, delays in auditory processing, and increased inflammation in the brain.
As life expectancies around the world increase, so are the number of people who will experience age-related cognitive decline. Because the amount of oxygen in the blood also declines with age, the team hypothesized that ...
Unraveling the origin of Alzheimer's disease
2021-06-17
CLEVELAND--Case Western Reserve University researchers studying prions--misfolded proteins that cause lethal incurable diseases--have identified for the first time surface features of human prions responsible for their replication in the brain.
The ultimate goal of the research is to help design a strategy to stop prion disease in humans--and, ultimately, to translate new approaches to work on Alzheimer's and other neurodegenerative diseases.
Scientists have yet to discover the exact cause of Alzheimer's disease, but largely agree that protein issues play a role in its emergence and progression. Alzheimer's disease afflicts more than 6 million people in the U.S., and the Alzheimer's Association ...
Masonic Medical Research Institute researchers develop new imaging agent to detect activated platelets
2021-06-17
UTICA, NY -- More than 2 million coronary artery stents are implanted each year to help protect or restore normal blood flow to the heart, to treat patients suffering from angina or a heart attack due to coronary artery disease (CAD). While stents are highly effective and safe devices, scarring or clotting of unhealed stents can occur in a small percentage of subjects, leading to complications such as stent restenosis or thrombosis, which can be life-threatening. At present, approaches to understand stent healing based on their biological clotting status is unavailable in patients.
To devise a potential solution to this problem, Dr. Jason McCarthy, an Associate Professor at the Masonic Medical Research Institute (MMRI), and his team have developed a fluorescent probe that binds ...
Passive rewilding can rapidly expand UK woodland at no cost
2021-06-17
A long-term passive rewilding study has shown that natural woodland regeneration could make a significant contribution to meeting the UK's ambitious tree planting targets - potentially at no cost and within relatively short timescales.
The research, led by the UK Centre for Ecology & Hydrology (UKCEH), found natural growth due to seed dispersal by birds, mammals and wind can produce biodiverse and resilient woodland.
Woodland development can be rapid, while avoiding the cost, management and plastic tubing involved in planting schemes.
The study - published in the journal PLOS ONE - found that after just 15 years, previously bare agricultural ...
Probing the dynamics of photoemission
2021-06-17
Physicists at Ludwig-Maximilian University in Munich (LMU) and the Max Planck Institute for Quantum Optics (MPQ) have used ultrashort laser pulses to probe the dynamics of photoelectron emission in tungsten crystals.
Almost a century ago, Albert Einstein received the Nobel Prize for Physics for his explanation of the photoelectric effect. Published in 1905, Einstein's theory incorporated the idea that light is made up of particles called photons. When light impinges on matter, the electrons in the sample respond to the input of energy, and the interaction gives rise to what is known as the photoelectric effect. Light quanta (photons) are absorbed by the ...
Adding checkpoint inhibition to anti-HER2 breast cancer therapy brings no benefit
2021-06-17
Lugano, Switzerland, 17 June 2021 - Adding an immune checkpoint inhibitor to anti-HER2 treatment in breast cancer does not improve pathological complete response (pCR), according to the primary analysis of the IMpassion050 trial presented today during the ESMO Virtual Plenary. (1) The phase III trial is the first to report data comparing a neoadjuvant anti-HER2 based regimen with or without the anti-PD-L1 antibody atezolizumab in patients with high-risk, HER2-positive early breast cancer.
The standard treatment for high-risk, HER2-positive early breast cancer is dual anti-HER2 blockade plus chemotherapy. While antibody therapy may enhance innate and adaptive immunity and activate cellular cytotoxicity, there is evidence ...
Researchers identify gene responsible for increased risk of infantile fragility
2021-06-17
(Boston)--An intrauterine fracture is a rare finding during routine prenatal imaging. This condition can be due to maternal trauma, genetic disorders of the skeleton, as well as other predisposing maternal metabolic and vascular disorders. Genetic disorders that have previously been reported to cause intrauterine fracture include brittle bone disease (osteogenesis imperfecta or OI), osteopetrosis, hypophosphatasia and Ehlers-Danlos syndrome (EDS).
Now for the first time, researchers from Boston University School of Medicine (BUSM) report a new genetic cause, unrelated to OI, for the 23 fractures that occurred in-utero to a mother with EDS hypermobility type.
EDS is a disease that weakens the bones and connective tissues ...
Asymptomatic pertussis more common in infants than previously thought
2021-06-17
New study challenges long-standing assumptions about disease severity in infants, and suggests that standard qPCR interpretations underestimate the true burden of other highly contagious diseases, such as COVID-19 and influenza.
Pertussis, also known as "whooping cough," remains a significant cause of death in infants and young children around the world and, despite global vaccination programs, many countries are experiencing a resurgence of this highly contagious disease.
A new study by Boston University School of Public Health and the University of Georgia's Odum School of Ecology presents evidence that could help explain this ...
Red meat consumption may promote DNA damage-assoc. mutation in colorectal cancer patients
2021-06-17
Bottom Line: Genetic mutations indicative of DNA damage were associated with high red meat consumption and increased cancer-related mortality in patients with colorectal cancer.
Journal in Which the Study was Published: Cancer Discovery, a journal of the American Association for Cancer Research
Author: Marios Giannakis, MD, PhD, an assistant professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School and a physician at Dana-Farber Cancer Institute
Background: "We have known for some time that consumption of processed meat and red meat is a risk factor for colorectal cancer," said Giannakis. The International Agency for Research on Cancer declared that processed meat was carcinogenic and that red meat was probably carcinogenic to humans in 2015.
Experiments ...
Engineered NK cells can eliminate glioblastoma stem cells
2021-06-17
HOUSTON ? Preclinical research from The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center finds that although glioblastoma stem cells (GSCs) can be targeted by natural killer (NK) cells, they are able to evade immune attack by releasing the TFG-β signaling protein, which blocks NK cell activity. Deleting the TFG-β receptor in NK cells, however, rendered them resistant to this immune suppression and enabled their anti-tumor activity.
The findings, published today in the Journal of Clinical Investigation, suggest that engineering NK cells to resist immune suppression may be a feasible path ...
Hybrid membrane doubles the lifetime of rechargeable batteries
2021-06-17
The energy density of traditional lithium-ion batteries is approaching a saturation point that cannot meet the demands of the future - for example in electric vehicles. Lithium metal batteries can provide double the energy per unit weight when compared to lithium-ion batteries. The biggest challenge, hindering its application, is the formation of lithium dendrites, small, needle-like structures, similar to stalagmites in a dripstone cave, over the lithium metal anode. These dendrites often continue to grow until they pierce the separator membrane, causing the battery to short-circuit and ultimately destroying ...
Excess nitrogen puts butterflies at risk
2021-06-17
Nitrogen from agriculture, vehicle emissions and industry is endangering butterflies in Switzerland. The element is deposited in the soil via the air and has an impact on vegetation - to the detriment of the butterflies, as researchers at the University of Basel have discovered.
More than half of butterfly species in Switzerland are considered to be at risk or potentially at risk. Usually, the search for causes focuses on intensive agriculture, pesticide use and climate change. A research team led by Professor Valentin Amrhein from the University of Basel, however, has been investigating another factor - the depositing ...
Response to DNA damage: The dual role of extramitochondrial cytochrome C
2021-06-17
Living beings are continuously exposed to harmful agents, both exogenous (ultraviolet radiation, polluting gases, etc.) and endogenous (secondary products of cellular metabolism) that can affect DNA integrity. That's why cells are endowed with a series of molecular mechanisms whose purpose is to identify and signpost possible damage to the genetic material for speedy repair. These mechanisms are precisely regulated because they are key to cell survival. In extreme situations of massive and irreparable damage, cells enter a phase of controlled dismantling called "programmed cell death". Among the events that take place during this process is the massive delivery to the cytoplasm of a mitochondrial protein called cytochrome C. Under homeostatic conditions, this protein plays a role in energy ...
Novel chirped pulses defy 'conventional wisdom'
2021-06-17
The 2018 Nobel Prize in Physics was shared by researchers who pioneered a technique to create ultrashort, yet extremely high-energy laser pulses at the University of Rochester.
Now researchers at the University's Institute of Optics have produced those same high-powered pulses--known as chirped pulses--in a way that works even with relatively low-quality, inexpensive equipment. The new work could pave the way for:
Better high-capacity telecommunication systems
Improved astrophysical calibrations used to find exoplanets
Even more accurate atomic clocks
Precise devices for measuring chemical contaminants in the atmosphere
In a paper in Optica, the researchers describe the first demonstration ...
Historical climate effects of permafrost peatland surprise researchers
2021-06-17
Peatlands are an important ecosystem that contribute to the regulation of the atmospheric carbon cycle. A multidisciplinary group of researchers, led by the University of Helsinki, investigated the climate response of a permafrost peatland located in Russia during the past 3,000 years. Unexpectedly, the group found that a cool climate period, which resulted in the formation of permafrost in northern peatlands, had a positive, or warming, effect on the climate.
The period studied, which began 3,000 years ago, is known as a climate period of cooling temperatures. The climate-related effect of permafrost formation brought about by the cooling was investigated particularly by analysing the ancient plant communities of the peatland, using similarly analysed peatland data from elsewhere in ...
'First empirical evidence of an identity-related societal cleavage'
2021-06-17
An international survey by the University of Münster's Cluster of Excellence "Religion and Politics" provides the first empirical evidence of an identity-related political cleavage of European societies that has resulted in the emergence of two entrenched camps of substantial size. "We see two distinct groups with opposing positions, which we call 'Defenders' and 'Explorers'", says psychologist Mitja Back, spokesperson of the interdisciplinary research team that conducted the most comprehensive survey of identity conflicts in Europe to date. "Who belongs to our country, who threatens whom, who is disadvantaged? Across all such questions of identity, the initial analyses of the survey reveal a new line of conflict between the two groups, which have almost diametrically opposite ...
RUDN University medics detect alterations in amino acid profiles in children with ADHD
2021-06-17
RUDN University doctors found alterations in serum amino acid profile in children with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). The findings will help to understand the mechanism of the disorder and develop new treatment strategies. The study is published in the journal Biomedical Reports.
Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is a neurodevelopmental disorder that manifests itself in childhood. Children with ADHD find it difficult to concentrate and manage their impulsivity. It is known that ADHD is also manifested at the neurochemical level -- for example, the work of dopamine and norepinephrine is disrupted. However, there is still no definitive data ...
Wild chimpanzee orphans recover from the stress of losing their mother
2021-06-17
The death of a mother is a traumatic event for immature offspring in species in which mothers provide prolonged maternal care, such as in long-lived mammals, including humans. Orphan mammals die earlier and have less offspring compared with non-orphans, but how these losses arise remains under debate. Clinical studies on humans and captive studies on animals show that infants whose mothers die when they are young are exposed to chronic stress throughout their lives. However, such chronic stress, which has deleterious consequences on health, can be reduced or even cancelled if human orphans are placed in foster families young enough. How stressed orphans are in the wild and whether ...
Testicular cancer: Improved treatment and prognosis
2021-06-17
Testicular cancer is the most common cancer among men under 40 in Europe and the USA. National statistics from the Cancer League indicate 471 new cases and 12 deaths in Switzerland. In general, the prospects for successful treatment of testicular cancer are good over time and, especially with early diagnosis, even further improved. Even if metastases are already present, testicular cancer can be successfully treated with appropriate therapy in the majority of cases.
New classification enables even more targeted treatment
The primary treatment for testicular cancer is the removal of the affected testicle. However, the disease is often only discovered at a stage where metastases are already present and then, after the primary surgical procedure, ...
Financial networks: A new discipline to interpret crises and green transition
2021-06-17
Modelling the financial system as a network is a precondition to understanding and managing challenges of great relevance for society, including the containment of financial crises and the transition to a low-carbon economy.
Financial Networks is the scientific discipline that deals with these issues. An article published in the scientific journal Nature Review Physics carries out the first comprehensive review of this exciting interdisciplinary field. By covering over 250 studies across domains, the paper is also a call for researchers in all scientific disciplines to consider the insights from the financial network models, because of their implications for citizens, public agencies and governments. Professor Guido Caldarelli from Ca' Foscari University of Venice coordinated ...
First evidence that medieval plague victims were buried individually with 'considerable care'
2021-06-17
In the mid-14th century Europe was devastated by a major pandemic - the Black Death - which killed between 40 and 60 per cent of the population. Later waves of plague then continued to strike regularly over several centuries.
Plague kills so rapidly it leaves no visible traces on the skeleton, so archaeologists have previously been unable to identify individuals who died of plague unless they were buried in mass graves.
Whilst it has long been suspected that most plague victims received individual burial, this has been impossible to confirm until now. ...
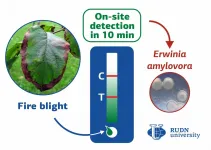
RUDN University biologists develop a rapid test for detecting the fire blight in plants
2021-06-17
RUDN University biotechnologists have created a method for detection of bacterial infection in apple, pear, hawthorn and other plants of the Rosaceae family. The test does not require laboratory equipment, the result is ready in 10 minutes. This will allow detecting the disease quickly and prevent the spread of infection. The results are published in Physiological and Molecular Pathology of Plants.
Erwinia amylovora bacteria causes a dangerous infectious disease in plants -- a fire blight. Most plants of the Rosaceae family are vulnerable to it, for example, hawthorn, apple, pear. The bacteria causes the blossom to wither, the leaves dry up and curl, the bark develop necrotic lesions. The disease can spread through infected plants, garden tools, and with the wind, which ...
[1] ... [2219]
[2220]
[2221]
[2222]
[2223]
[2224]
[2225]
[2226]
2227
[2228]
[2229]
[2230]
[2231]
[2232]
[2233]
[2234]
[2235]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.