Scientists make highly maneuverable miniature robots controlled by magnetic fields
2021-06-15
A team of scientists at Nanyang Technological University, Singapore (NTU Singapore) has developed millimetre-sized robots that can be controlled using magnetic fields to perform highly manoeuvrable and dexterous manipulations. This could pave the way to possible future applications in biomedicine and manufacturing.
The research team created the miniature robots by embedding magnetic microparticles into biocompatible polymers -- non-toxic materials that are harmless to humans. The robots are 'programmed' to execute their desired functionalities when magnetic fields are applied.
The made-in-NTU robots improve on many existing small-scale robots by optimizing their ability to move ...
Is artificial intelligence the key to preventing relapse of severe mental illness?
2021-06-15
Is artificial intelligence the key to preventing relapse of severe mental illness?
New AI software developed by researchers at Flinders University shows promise for enabling timely support ahead of relapse in patients with severe mental illness.
The AI2 (Actionable Intime Insights) software, developed by a team of digital health researchers at Flinders University, has undergone an eight-month trial with psychiatric patients from the Inner North Community Health Service, located in Gawler, South Australia.
The digital tool is tipped to revolutionise consumer-centric timely mental health treatment provision outside hospital, with researchers labelling it as readily available and scalable.
In the trial of 304 ...
Common cold combats COVID-19
2021-06-15
Exposure to the rhinovirus, the most frequent cause of the common cold, can protect against infection by the virus which causes COVID-19, Yale researchers have found.
In a new study, the researchers found that the common respiratory virus jump-starts the activity of interferon-stimulated genes, early-response molecules in the immune system which can halt replication of the SARS-CoV-2 virus within airway tissues infected with the cold.
Triggering these defenses early in the course of COVID-19 infection holds promise to prevent or treat the infection, ...
Let there be light! New tech to revolutionize night vision
2021-06-15
Researchers from The Australian National University (ANU) have developed new technology that allows people to see clearly in the dark, revolutionising night-vision.
The first-of-its-kind thin film, described in a new article published in Advanced Photonics, is ultra-compact and one day could work on standard glasses.
The researchers say the new prototype tech, based on nanoscale crystals, could be used for defence, as well as making it safer to drive at night and walking home after dark.
The team also say the work of police and security guards - who regularly employ night vision - will be easier and safer, reducing chronic neck injuries from currently bulk night-vision devices.
"We have made the invisible visible," lead researcher Dr Rocio Camacho Morales said. ...
Baltic herring larvae appear earlier and grow faster due to climate change
2021-06-15
Data collected for over two decades shows that rising Baltic Sea water temperature is one of the main factors in the increasingly earlier appearance and faster growth of Baltic herring larvae.
Baltic herring (Clupea harengus membras) is commercially the most important fish species in Finland, and an important part of the Baltic marine ecosystem. Conditions during herring spawning may have cascading effects on the whole Baltic ecosystem.
According to a recent research, both developmental stages in Baltic herring larvae, small and large, have shifted their timing to earlier dates.
"This suggests that herring spawn earlier and larvae grow faster, by about 7.7 days per decade. Water ...
Liver cancer call for help
2021-06-15
Rising numbers of liver cancer in Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander communities has led experts at Flinders University to call for more programs, including mobile liver clinics and ultrasound in rural and remote Australia.
The Australian study just published in international Lancet journal EClinicalMedicine reveals the survival difference was largely accounted for by factors other than Indigenous status - including rurality, comorbidity burden and lack of curative therapy.
The study of liver cancer, or Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), included 229 Indigenous and 3587 non-Indigenous HCC cases in South Australia, Queensland and the ...
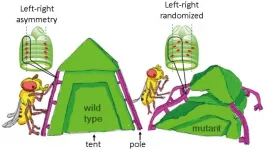
From symmetry to asymmetry: The two sides of life
2021-06-15
Osaka, Japan - On the outside, animals often appear bilaterally symmetrical with mirror-image left and right features. However, this balance is not always reflected internally, as several organs such as the lungs and intestines are left-right (LR) asymmetrical. Researchers at Osaka University, using an innovative technique for imaging movement of cell nuclei in living tissue, have determined the patterns of nuclear alignment responsible for LR-asymmetrical shaping of internal organs in the developing embryo.
Embryogenesis involves complex genetic and molecular processes that transform a single-celled zygote into a complete, living individual with multiple functional axes, including the LR axis. A long-standing conundrum of Developmental ...
Cancer cells fight for their footing by using an ageing gene
2021-06-15
Researchers at the University of Helsinki and the Beatson Institute for Cancer Research in Glasgow have discovered how mutated cells promote their chances to form cancer. Typically, the accumulation of harmful cells is prevented by active competition between multiple stem cells in intestinal glands, called crypts.
"The functioning of intestinal stem cells relies on growth factors, named Wnts, produced by the surrounding environment. Intestinal cancers typically originate from stem cells where mutations allow growth independent of these factors. When we removed a gene called Notum, which renders Wnts inactive, from mutated stem cells, the number of precancerous adenomas in the intestine was greatly reduced. We found that ...
Fungal spores from 250-year-old collections given new lease of life
2021-06-15
Echoing through history by reviving fungal specimens originally preserved and described a flabbergasting quarter of a millenium ago by the "Father of Modern Taxonomy" Carl Linnaeus, this study highlights the untapped potential of museum collections in modern research programmes. The results have just been published in the renowned Cell Press journal iScience.
The "desert coprinus" fungus Podaxis has fascinated scientists and explorers for centuries, still the genus has been subjected to relatively little research. These large mushrooms thrive in hostile and mostly species-free environments and while they occur seasonally ...
Obesity and hypertension: Researchers discover novel mechanisms
2021-06-15
Hypertension is a widespread comorbidity of patients with obesity that greatly increases the risk of mortality and disability. In recent years, researchers have found that a high-calorie diet increases the density of blood vessels (hypervascularization) in the hypothalamus - an important "eating control" area in our brain. Researchers hypothesized that elevated hormone levels of leptin are associated with a higher risk of developing hypertension. However, the exact mechanisms that contribute to the condensed growth of blood vessels in the hypothalamus were unknown.
New research conducted by Cristina García-Cáceres' research group at Helmholtz Zentrum ...
Cosmic rays: Coronal mass ejections and cosmic ray observations at Syowa Station in the Antarctic
2021-06-15
Solar activities, such as CME(Coronal Mass Ejection), cause geomagnetic storm that is a temporary disturbance of the Earth's magnetosphere. Geomagnetic storms can affect GPS positioning, radio communication, and power transmission system. Solar explosions also emit radiation, which can affect satellite failures, radiation exposure to aircraft crew, and space activity. Therefore, it is important to understand space weather phenomena and their impact on the Earth.
Space weather research by continuous observation of cosmic rays on the ground is mainly conducted using observation data from neutron monitors and multi-directional muon detectors. Since the phenomenon of space weather is on a short-term, days-long scale, it is effective to investigate changes in the flow ...
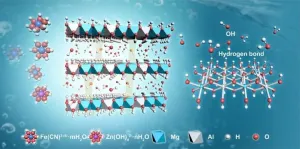
Newly developed ion-conducting membrane improves performance of alkaline-zinc iron flow battery
2021-06-15
Alkaline zinc-iron flow battery (AZIFB) is well suitable for stationary energy storage applications due to its advantages of high open-cell voltage, low cost, and environmental friendliness. However, it surfers from zinc dendrite/accumulation and relatively low operation current density.
Recently, a research group led by Prof. LI Xianfeng from the Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics (DICP) of the Chinese Academy of Science (CAS) developed layered double hydroxide (LDH) membrane with high hydroxide conductivity and ion selectivity for alkaline-zinc iron flow battery.
The ...
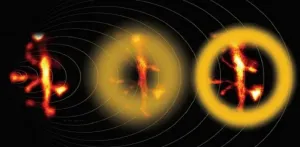
Novel calibration procedure for super-resolution brain imaging
2021-06-15
Light--and all waves--can bend around the corners of obstacles found along its path. Because of this phenomenon, called diffraction, it is impossible to focus light onto a spot that is smaller than half its wavelength. In other words, the highest resolution one can theoretically achieve using an optical microscope is approximately 250 nm, a barrier called the diffraction limit. Unfortunately, this resolution is not enough for observing fine cellular structures, such as those found in neurons.
Over more than a century, microscopists were hamstrung by this classic barrier until the invention of super-resolution fluorescence microscopy. One particularly powerful ...
Teenagers at greatest risk of self-harming could be identified almost a decade earlier
2021-06-15
Researchers have identified two subgroups of adolescents who self-harm and have shown that it is possible to predict those individuals at greatest risk almost a decade before they begin self-harming.
The team, based at the MRC Cognition and Brain Sciences Unit, University of Cambridge, found that while sleep problems and low self-esteem were common risk factors, there were two distinct profiles of young people who self-harm - one with emotional and behavioural difficulties and a second group without those difficulties, but with different risk factors.
Between one in five and one in seven adolescents in England self-harms, for example by deliberately cutting themselves. While self-harm is a significant risk factor for subsequent suicide attempts, many do not intend suicide but face ...
Study reveals bycatch risk for dolphins and porpoises in global small-scale fisheries
2021-06-15
A new study by Newcastle University shows that the risk of dolphins and porpoises being caught in small-scale (artisanal) fisheries is highest in low- and middle-income regions around the tropics and sub-tropics.
Marine scientists assessed the risk posed by small-scale fisheries to all 72 species of toothed whales found throughout the world's oceans. They found that this risk was highest in the Central Indo-Pacific, Temperate Northern Pacific, Temperate South America and the Western Indo-Pacific.
Publishing their findings in the journal Fish and Fisheries, the authors ...
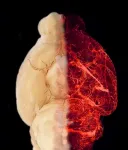
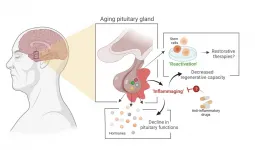
Main gland in hormonal system ages due to process that can potentially be slowed down
2021-06-15
Stem cell biologist Hugo Vankelecom (KU Leuven) and his colleagues have discovered that the pituitary gland in mice ages as the result of an age-related form of chronic inflammation. It may be possible to slow down this process or even partially repair it. The researchers have published their findings in PNAS.
The pituitary gland is a small, globular gland located underneath the brain that plays a major role in the hormonal system, explains Professor Hugo Vankelecom from the Department of Development and Regeneration at KU Leuven. "My research group discovered that the pituitary gland ages as a result of a form of chronic inflammation that affects tissue and even the organism as a whole. This natural process usually goes unnoticed ...
Predicting the evolution of a pandemic
2021-06-15
The inclusion of biological uncertainty and the latest case data can significantly improve the prediction accuracy of standard epidemiological models of virus transmission, new research led by KAUST and the Kuwait College of Science and Technology (KCST) has shown.
Modern mathematical epidemic models have been tested like never before during the COVID-19 pandemic. These models use mathematics to describe the various biological and transmission processes involved in an epidemic. However, when such factors are highly uncertain, such as during the emergence of a new virus like COVID-19, the predictions ...
Untapped rice varieties could sustain crop supplies in face of climate change
2021-06-15
Local rice varieties in Vietnam could be used to help breed improved crops with higher resilience to climate change, according to a new study published in Rice.
Earlham Institute researchers are part of an international collaboration with genebanks and rice breeders in Vietnam - championed by the International Rice Research Institute (IRRI) to help abolish world poverty and hunger - are aiming to identify varieties that can survive an increasingly unpredictable climate.
The new genomic data they have generated will significantly support efforts to ...
Small streams in agricultural ecosystems are heavily polluted with pesticides
2021-06-15
Pesticides safeguard agricultural yields by controlling harmful insects, fungi, and weeds. However, they also enter neighbouring streams and damage the aquatic communities, which are crucial for maintaining biodiversity, are part of the food web and support the self-purification of water. In a nationwide monitoring programme, a consortium of scientists led by the Helmholtz Centre for Environmental Research (UFZ) has shown that the governmental thresholds for pesticides are generally too high and that even these excessively high levels are still exceeded in over 80% of water bodies. As they published in the scientific journal Water Research the loss of biodiversity can only be halted if the environmental risk assessment ...
Bed sharing does not lead to stronger infant-mother attachment or maternal bonding
2021-06-15
New research led by the University of Kent has found that there is no link between bed sharing, infant-mother attachment, and infant behavioural outcomes.
Contrary to previous beliefs that bed sharing is beneficial (or even required) for babies to develop a secure attachment style and for mothers to develop a strong bond to their baby, researchers have found that it is neither associated with positive or negative outcomes related to infant attachment and maternal bonding.
There is a lot of controversial debate about bed sharing by parents and the infant sleep literature, in particular. Notably, researchers and practitioners recommend against bed sharing, particularly before four months of age due to the increased risk of Sudden Infant Death Syndrome (SIDS).
In reality, ...
Heat from below: How the ocean is wearing down the Arctic sea ice
2021-06-15
The influx of warmer water masses from the North Atlantic into the European marginal seas plays a significant role in the marked decrease in sea-ice growth, especially in winter. Sea-ice physicists from the Alfred Wegener Institute, Helmholtz Centre for Polar and Marine Research (AWI) together with researchers from the US and Russia, now present evidence for this in two new studies, which show that heat from the Atlantic has hindered ice growth in the Barents and Kara Seas for years. Furthermore, they demonstrate that the invasion of warm Atlantic water masses further east, ...
Research suggests ways to tackle water security challenges in world's drylands
2021-06-15
The research - published ahead of World Day to Combat Desertification and Drought on 17 June 2021 - examines recent and projected climate change impacts on water security across the world's drylands up to the year 2100.
It concludes that more efficient water management, technology and infrastructure, and better demand and supply management can offer more equitable access to water resources and help to achieve development goals.
Lead author, Professor Lindsay Stringer from the Department of Environment and Geography at the University of York said "People in dryland areas are already adapting to climate changes, but they need to be supported with coherent system-oriented policies and institutions that put water security at their core."
Globally, water scarcity already affects ...
New COVID-19 content from Annals of Internal Medicine
2021-06-15
Below please find link(s) to new coronavirus-related content published today in Annals of Internal Medicine. All coronavirus-related content published in Annals of Internal Medicine is free to the public. A complete collection is available at https://annals.org/aim/pages/coronavirus-content.
1. NFL employee and player surveillance program enabled early detection of COVID-19, even among those who were asymptomatic
Free full text: https://www.acpjournals.org/doi/10.7326/M21-0319
Frequent, routine testing within the National Football League (NFL) enabled early detection of COVID-19 infection among players and ...
For transplant recipients, third time may be the charm for better COVID vaccine protection
2021-06-15
In a study published today in the Annals of Internal Medicine, Johns Hopkins Medicine researchers say they believe that, for the first time, there is evidence to show that three doses of vaccine increase antibody levels against SARS-CoV-2 -- the virus that causes COVID 19 -- more than the standard two-dose regimen for people who have received solid organ transplants.
"Our findings suggest clinical trials are warranted to determine if transplant recipients should receive COVID-19 vaccine booster doses as standard clinical practice, similar to what ...
University of Washington researchers can turn a single photo into a video
2021-06-15
Sometimes photos cannot truly capture a scene. How much more epic would that vacation photo of Niagara Falls be if the water were moving?
Researchers at the University of Washington have developed a deep learning method that can do just that: If given a single photo of a waterfall, the system creates a video showing that water cascading down. All that's missing is the roar of the water and the feeling of the spray on your face.
The team's method can animate any flowing material, including smoke and clouds. This technique produces a short video that loops seamlessly, giving the impression of endless movement. The researchers will present this approach June 22 at the Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.
"A ...
[1] ... [2213]
[2214]
[2215]
[2216]
[2217]
[2218]
[2219]
[2220]
2221
[2222]
[2223]
[2224]
[2225]
[2226]
[2227]
[2228]
[2229]
... [8818]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.