Study: Removing 'bad apples' from police forces unlikely to significantly reduce use-of-force complaints
2021-06-21
The idea that a small number of "bad apples" are responsible for an outsized share of complaints against police officers has gained considerable traction over the last four decades. A new study considered the extent to which police misconduct is likely to be reduced by removing police officers identified early in their careers as being at risk for misconduct. The study concluded that replacing the top 10 percent of police identified as being the most likely to generate use-of-force complaints with officers who have not or are less likely to do so would reduce use-of-force complaints by just 6 percent over a 10 year period.
Conducted by researchers at the University of Pennsylvania and Princeton University, the study appears in Criminology & Public Policy, ...
Creating cooler cities
2021-06-21
If you've ever been in a city's central core in the middle of summer, you know the heat can be brutal--and much hotter than in the surrounding region.
Temperatures in cities tend to be several degrees warmer than in its rural areas, a phenomenon called the Urban Heat Island (UHI) effect. Many cities have been observed to be 2-4ºC warmer than the countryside in virtually every inhabited continent. This phenomenon occurs because urban infrastructure, especially pavements, absorbs a lot of heat as compared to natural vegetated surfaces. This heat pollution causes higher air conditioning and water costs, while also posing a public health hazard.
One mitigation strategy called gray infrastructure involves the ...
'Background' adverse event study will inform global COVID vaccine safety monitoring
2021-06-21
NEW YORK, NY--COVID vaccine surveillance efforts are a global priority, but safety monitoring for vaccines should not reflect a single population. The largest, most extensive international study of the background rates of adverse events of special interest (AESI) that are being tracked in vaccine surveillance efforts show that adverse event rates vary substantially by age, sex, and method of data capture.
Led by researchers at Oxford University, Columbia University, Erasmus MC, UCLA, and Janssen, an international team of collaborators from the Observational Health Data Sciences and Informatics (OHDSI) network provided a timely reference of the background rates of AESIs in a new study published ...
Researchers trace dust grain's journey through newborn solar system
2021-06-21
A research team led by the University of Arizona has reconstructed in unprecedented detail the history of a dust grain that formed during the birth of the solar system more than 4.5 billion years ago. The findings provide insights into the fundamental processes underlying the formation of planetary systems, many of which are still shrouded in mystery.
For the study, the team developed a new type of framework, which combines quantum mechanics and thermodynamics, to simulate the conditions to which the grain was exposed during its formation, when the solar system was a swirling disk of gas ...
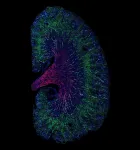
The same cell type can help or hinder kidney repair after acute injury
2021-06-21
The USC Stem Cell laboratory of Andy McMahon has identified a type of injured cell that might contribute to the transition from an acute kidney injury to chronic kidney disease, as described in a new study published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS). The same issue of PNAS also features an accompanying Q&A with McMahon to mark his recent election as a member of the National Academy of Sciences.
"Acute kidney injury can be a common side effect of surgery, sepsis or certain prescription drugs, and there is no effective treatment," said McMahon, who is the W.M. Keck Provost and University Professor of Stem Cell Biology and Regenerative Medicine, and Biological Sciences at USC. "Even a mild or moderate injury can progress into chronic ...
Women who lose close elections are just as likely to run again as men
2021-06-21
CAMBRIDGE, Mass. - Women who lose local or state elections are just as likely to run for office again as men, suggesting the recent surge in women running for office may have a long-term impact on women's political representation, according to a new study by researchers from Harvard and the University of California, Davis.
Pundits and scholars have argued that women are more likely to abandon politics after a losing campaign than men, citing evidence that women are more risk-averse and more likely to avoid competition than men.
Political scientists Rachel Bernhard, assistant professor at UC-Davis, and Justin de Benedictis-Kessner, assistant professor of public policy at Harvard Kennedy School, ...
Changes in farming practices could reduce greenhouse gas emissions by 70% by 2036
2021-06-21
Team used Argonne's GREET model to simulate changes, predict outcomes.
Scientists from the U.S. Department of Energy's Argonne National Laboratory participated in a study that shows innovation in technologies and agricultural practices could reduce greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions from grain production by up to 70% within the next 15 years.
Published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States, the study identifies a combination of readily adoptable technological innovations that can significantly reduce emissions and fit within current production systems and established grain markets.
The study, "Novel ...
Butterflies cross the Sahara in longest-known insect migration
2021-06-21
A species of butterfly found in Sub-Saharan Africa is able to migrate thousands of miles to Europe, crossing the Saharan Desert, in years when weather conditions are favourable, scientists have found.
The striking Painted Lady (Vanessa cardui) butterfly has been shown for the first time to be capable of making the 12,000-14,000km round trip - the longest insect migration known so far - in greater numbers, when wetter conditions in the desert help the plants on which it lays eggs.
The international research team's findings increase understanding of how insects, including pollinators, pests and the diseases they carry could spread between continents in ...
Lead from leaded petrol persists in London air despite '90s ban
2021-06-21
Lead levels in London's atmosphere have dropped drastically since lead additives in petrol were phased out, and currently meet UK air quality targets. However despite this drop, airborne particles in London are still highly lead-enriched compared to natural background levels, according to new Imperial research published today in PNAS.
The study found that up to 40 per cent of lead in airborne particles today comes from the legacy of leaded petrol. The researchers say this highlights the long-term persistence of contaminants introduced by human activities in the environment.
Lead author of the study Dr Eléonore Resongles, who carried out the work at Imperial's Department of Earth Science and Engineering, said: "Petrol-derived lead deposited decades ago remains an important ...
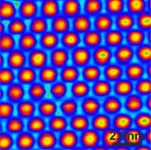
New method for molecular functionalization of surfaces
2021-06-21
One vision that is currently driving material scientists is to combine organic molecules (and their diverse functionalities) with the technological possibilities offered by extremely sophisticated semiconductor electronics. Thanks to modern methods of micro- and nanotechnology, the latter designs ever more efficient electronic components for a wide variety of applications. However, it is also increasingly reaching its physical limits: Ever smaller structures for functionalizing semiconductor materials such as silicon cannot be produced using the approaches of classical technology. Scientists ...
Modeling a circular economy for electronic waste
2021-06-21
Think about how many different pieces of technology the average household has purchased in the last decade. Phones, TVs, computers, tablets, and game consoles don't last forever, and repairing them is difficult and often as expensive as simply buying a replacement.
Electronics are integral to modern society, but electronic waste (e-waste) presents a complex and growing challenge in the path toward a circular economy--a more sustainable economic system that focuses on recycling materials and minimizing waste. Adding to the global waste challenge is the prevalence of dishonest recycling practices by companies who claim to be recycling electronics but actually dispose of them by other means, such as in ...
Ben-Gurion U. scientists invent an artificial nose for continuous bacterial monitoring
2021-06-21
BEER-SHEVA, Israel, June 21, 2021 - A team of scientists at Ben-Gurion University of the Negev (BGU) have invented an artificial nose that is capable of continuous bacterial monitoring, which has never been previously achieved and could be useful in multiple medical, environmental and food applications.
The study was published in Nano-Micro Letters.
"We invented an artificial nose based on unique carbon nanoparticles ("carbon dots") capable of sensing gas molecules and detecting bacteria through the volatile metabolites the emit into the air," says lead researcher Prof. Raz Jelinek, BGU vice president ...
Study: Electronic monitoring failed to reduce recidivism for girls in juvenile justice system
2021-06-21
In recent years, many juvenile courts have adopted in-home detention with electronic monitoring tethers as an alternative to institutional incarceration. A new study examined whether this approach reduces recidivism among girls involved in the juvenile justice system. The study found that tethers failed to reduce reoffending among the girls; in fact, they may be harmful because in-home detention limits girls' access to treatment programs.
The study, by researchers at the University of Cincinnati (UC) and Michigan State University, appears in Justice Evaluation Journal, a publication of the Academy of Criminal Justice Sciences.
"We believe this ...
Study examines how breast implant surfaces affect immune response
2021-06-21
HOUSTON - (June 21, 2021) - Rice University bioengineers collaborated on a six-year study that systematically analyzed how the surface architecture of breast implants influences the development of adverse effects, including an unusual type of lymphoma.
Every year, about 400,000 people receive silicone breast implants in the United States. According to FDA data, most of those implants need to be replaced within 10 years due to the buildup of scar tissue and other complications.
A team including researchers from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT), Rice, the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center and Baylor College of Medicine published its findings online ...
Landmark field trials show potential of gene-editing
2021-06-21
Field trials investigating healthy compounds in agronomically important brassica crops have underlined the "immense potential" of gene editing technology, say researchers.
The trials are the first field application of the technology in the UK since the reclassification of gene-edited crops as genetically modified organisms by the Court of Justice of the European Union (CJEU) in 2018.
The results come as the UK Government is determining whether to allow gene-editing approaches for the purpose of food production, following a DEFRA-led public consultation.
"Our results demonstrate the immense potential for gene-editing to facilitate crop improvement by translating discoveries in fundamental biological processes," ...
AGS publishes updated AGS Minimum Geriatrics Competencies for Graduating Medical Students
2021-06-21
New York (June 21, 2021)--The American Geriatrics Society (AGS) has published an updated version of the AGS Minimum Geriatrics Competencies for Graduating Medical Students, which were created to ensure that medical school graduates across the U.S. are prepared to provide high-quality care for us all as we age. A refresh of the original set first published more than a decade ago, the 27 competencies integrate new concepts that have emerged more recently in the field of geriatrics, including frailty and person-centered care, and are framed around five key areas of focus for all geriatrics healthcare professionals.
"The updated competencies reflect an evolution in how we frame the work of geriatrics health professionals, a greater understanding of frailty, and a greater focus ...
How do developing spinal cords choose 'heads' or 'tails'?
2021-06-21
SAN FRANCISCO, CA--June 21, 2021--The progression from a round ball of cells to an embryo with a head and a tail is one of the most critical steps in an organism's development. But just how cells first start organizing themselves with directionality along this head-to-tail axis is hard to study because it happens in the earliest days of embryonic development, in the confines of a mammal's uterus.
Now, scientists at Gladstone Institutes have created an organoid--a three-dimensional cluster of cells grown in the lab--that mimics the earliest developmental steps of the nervous system in embryos. The organoid is the first to show how human spinal cord cells ...
Poaching affects behavior of endangered capuchin monkeys in Brazilian biological reserve
2021-06-21
A study conducted in the Una Biological Reserve in the state of Bahia, Brazil, shows that in a habitat with high hunting pressure the risk of predation has such a significant impact on the behavior of the Yellow-breasted capuchin monkey Sapajus xanthosternos that it even avoids areas offering an abundant supply of plant biomass and invertebrates, its main sources of food.
An article reporting the findings of the study is published in the American Journal of Primatology.
"Many theories in the field of primatology assume that pressure to find food is more important that predation pressure. In this study we were able ...
Childhood BMI may influence poorer health outcomes in adulthood
2021-06-21
A high body mass index (BMI) during adolescence is a significant risk factor for Type 2 diabetes, early heart attack and overall poorer health for young adults, regardless of BMI in adulthood, according to a research letter published today in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
BMI is calculated based on weight and height. According to the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, BMI categories are defined as: less than 18.5 kg/m2 is underweight; 18.5 to 24.9 is normal weight; 25 to 29.9 is overweight; and 30 or greater is obese.
Researchers analyzed the BMI z-scores, which is relative weight adjusted for a child's age and sex, of 12,300 adolescents ...
Study shows registry data could support clinical trials
2021-06-21
Data captured in NCDR registries is similar in quality, depth and granularity when compared to data captured through clinical trials, according to research in JACC: Cardiovascular Interventions that compared data from the DAPT Study to NCDR CathPCI Registry data. This is good news for streamlining data collection and supports recent efforts to standardize data elements and definitions used in clinical trials and registries.
"We found an overall high level of similarity in data between these two sources. This suggests that registries may also be suitable to support baseline data collection for many clinical studies," said senior study author Robert W. Yeh, MD, MSc, director of the Richard A. and Susan F. Smith Center for Outcomes Research in Cardiology ...
Statin therapy not associated with cognitive decline, dementia in older adults, study says
2021-06-21
The use of statin therapy in adults 65 years old or older is not associated with incident dementia, mild cognitive impairment (MCI) or decline in individual cognition domains, according to a study published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology (JACC).
Cognitive decline and dementia are major health concerns in older individuals, affecting about 10% of people over 60 years old. Statins are used to reduce low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, or bad cholesterol, thus they are a fundamental treatment for prevention of primary and secondary cardiovascular disease (CVD) events. The Food and Drug Administration released a warning in 2012 about cases of apparent short-term ...
Vegetation of planet Earth: Researchers publish unique database as Open Access
2021-06-21
It's a treasure trove of data: the global geodatabase of vegetation plots "sPlotOpen" is now freely accessible. It contains data on vegetation from 114 countries and from all climate zones on Earth. The database was compiled by an international team of researchers led by Martin Luther University Halle-Wittenberg (MLU), the German Centre for Integrative Biodiversity Research (iDiv) and the French National Centre for Scientific Research (CNRS). Researchers around the world finally have a balanced, representative dataset of the Earth's vegetation at their disposal, as the team reports in the journal Global Ecology & Biogeography.
Global issues and questions require global answers. "If we want to understand or predict how climate ...
Potato nutrients can help reduce sodium retention, may help reduce risk of hypertension
2021-06-21
June 21, 2021 -- A new study published in Nutrients investigated the effect of increased dietary potassium from a whole food source--baked/boiled potatoes and baked French fries--or a potassium supplement on blood pressure and other cardiovascular disease risk factors compared to a 'typical American' control diet (lower potassium intake) among 30 pre-hypertensive to hypertensive men and women. Results showed that including baked/boiled potato consumption as part of a typical American diet had the greatest benefit on reducing sodium retention, even more than the supplement, and resulted ...
COVID-19 dual-antibody therapies effective against variants in animal study
2021-06-21
COVID-19 therapies made from antibodies often are given to patients who are at high risk of severe illness and hospitalization. However, there have been nagging questions about whether such antibody therapies retain their effectiveness as worrisome new virus variants arise.
New research at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis suggests that many, but not all, therapies made from combinations of two antibodies are effective against a wide range of variants of the virus. Further, combination therapies appear to prevent the emergence of drug resistance.
The study, in mice and hamsters, tested all single and combination antibody-based therapies authorized for emergency use ...
'Flashed' nanodiamonds are just a phase
2021-06-21
HOUSTON - (June 21, 2021) - Diamond may be just a phase carbon goes through when exposed to a flash of heat, but that makes it far easier to obtain.
The Rice University lab of chemist James Tour is now able to "evolve" carbon through phases that include valuable nanodiamond by tightly controlling the flash Joule heating process they developed 18 months ago.
Best of all, they can stop the process at will to get product they want.
In the American Chemical Society journal ACS Nano, the researchers led by Tour and graduate student and lead author Weiyin Chen show that adding organic fluorine compounds and ...
[1] ... [2208]
[2209]
[2210]
[2211]
[2212]
[2213]
[2214]
[2215]
2216
[2217]
[2218]
[2219]
[2220]
[2221]
[2222]
[2223]
[2224]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.