If the right hand is hypersensitive due to an injury to the left
2021-06-23
The results of the study were published in the journal "Neurology" on 19 May 2021 under the leadership of Professor Elena Enax-Krumova, holder of the endowed professorship of the German Social Accident Insurance (DGUV).
Nerve injuries: frequent complication after occupational accidents
Peripheral nerves refer to nerves that lie outside of the brain and spinal cord. They run throughout the entire body. These bundles of nerve fibres can be damaged in the event of blunt or sharp force trauma due to accidents, as well as during surgery. Injuries to the peripheral nerves are a frequent complication, particularly after occupational accidents. Patients often suffer from motor and sensory disorders in the affected area of the body. These can lead to persistent complaints and ...
Junk food relief in lockdown
2021-06-23
Beware of those snack attacks. A new study in Appetite has confirmed the small luxuries, from sweets and chocolate to salty treats, have helped to lift our spirits - and kilojoule intake - during COVID-19 lockdowns.
Researchers in England and Australia have gathered evidence about similar experiences in the UK and Victoria, Australia to warn about the effect of extended pandemic lockdowns on our eating behaviours.
While time at home provides more time for healthy food preparation, intake of high-energy density foods (HED) has risen for some - presenting at-risk adults with the prospect of managing weight gain, the psychology researchers warn.
"The ...
Kit clashes affect performance in football matches, new study shows
2021-06-23
The response times of footballers is slowed down when part of the kit worn by both teams is of the same colour, a new study shows.
The research from the University of York revealed that when players have any kit colour clash - either shirt or shorts - it takes them twice as long to find a fellow player on the pitch.
Study authors are calling for a change in the laws of the game or for clearer guidance.
Researchers used two experiments to investigate how kit variations affect the visual search for teammates. Their first experiment confirmed that a ...
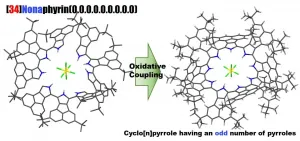
Synthesis of a near-infrared light absorbing macrocyclic aromatic compound
2021-06-23
Profs. Okujima and Uno at Ehime University, in collaboration with Prof. Kobayashi at Shinshu University, reported the selective synthesis, the molecular structure, optical properties and electronic structure of cyclo[9]pyrrole, a ring-expanded porphyrin consisting of directly connected pyrrole rings.
Porphyrins, which are well-known natural porphyrin molecules, e.g. heme and chlorophyll, are attractive for use in practical materials because of the easy optimization of their optical and physical properties by conjugation expansion and functionalization. In 2002, Sessler reported the first synthesis of cyclo[n]pyrrole (n: ...
Earth-like biospheres on other planets may be rare
2021-06-23
A new analysis of known exoplanets has revealed that Earth-like conditions on potentially habitable planets may be much rarer than previously thought. The work focuses on the conditions required for oxygen-based photosynthesis to develop on a planet, which would enable complex biospheres of the type found on Earth. The study is published today in Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society.
The number of confirmed planets in our own Milky Way galaxy now numbers into the thousands. However planets that are both Earth-like and in the habitable zone - the region around a star where the temperature is just right for liquid water to exist on the surface - are much less common.
At the moment, only a handful of such rocky and potentially habitable exoplanets ...
Influence of land use on soil erosion in European Russia for the last 30 years
2021-06-23
Research Associate Artyom Gusarov studied a vast array of erosion data to make a general takeaway that soil erosion and river sediment load in the aforementioned region has significantly decreased throughout the post-Soviet period.
"The decrease has been especially profound in the forest steppe, a part of which covers the Republic of Tatarstan, because of the combined influence of climate change and land cultivation," explains Gusarov. "To the north of the forest steppe, in the southern part of the boreal zone, the anthropogenic factor was the primary influence on the changes in soil erosion, at least in the east of the East European Plain. ...
10 keys to integrating health into urban and transport planning
2021-06-23
As much as 20% of premature mortality can be attributed to poor urban and transport planning. Nevertheless, quantitative indicators to guide the integration of health components into urban design have been lacking. To address this gap, a team from the Barcelona Institute for Global Health (ISGlobal), a centre supported by the "la Caixa" Foundation, has identified 10 principles--and corresponding indicators--to help urban planners incorporate public health into their work.
The new study, published in the International Journal of Hygiene and Environmental Health, was undertaken at the request of the Directorate-General for Environmental Policies and the Natural Environment, which forms ...
Outstanding organic solar cells' performance achieved by using new technology
2021-06-23
Organic solar elements with the self-assembling molecular-thin layer (SAM) of hole-transporting material, the technology, which was used in producing a record-breaking tandem solar cell, achieved 18.4 power conversion efficiency. The invention of Lithuanian chemists working at Kaunas University of Technology (KTU), commercialized by several global companies proved versatile and applicable to different solar technologies.
Organic solar cells are made of common organic elements such as carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, fluorine, oxygen, and sulphur. Their raw materials are cheap, abundant, and can ...
China's EarthLab begins trials as country's first facility exploring Earth system interactions
2021-06-23
The Earth is a sphere, and it comprises spheres: atmosphere, hydrosphere, cryosphere, lithosphere and biosphere -- in short, all of the cycles that interact to influence Earth's weather and climate. Now, to better research how the spheres interact and impact the planet, China is launching EarthLab in Beijing. On June 23, after EarthLab's opening ceremony, researchers will begin trials to demonstrate the facility's ability to integrate simulations and observations to more accurately project outcomes and provide a scientific foundation to predict and mitigate such things as natural weather disasters.
EarthLab's ...
The origins of farming insects
2021-06-23
A beetle bores a tree trunk to build a gallery in the wood in order to protect its lay. As it digs the tunnel, it spreads ambrosia fungal spores that will feed the larvae. When these bore another tree, the adult beetles will be the transmission vectors of the fungal spores in another habitat. This mutualism among insects and ambrosia fungi could be more than 100 years old --more than what was thought to date-- according to an article published in the journal Biological Reviews.
The study analyses for the first time the symbiotic associations and the coevolution between ambrosia fungi and beetles from a paleontological perspective using the Cretaceous ...
Asian elephants do more than just trumpet -- they buzz their lips to squeak
2021-06-23
Everybody from a child knows that elephants trumpet. Over the past decades research in general and at the University of Vienna has mainly studied the elephants low-frequency rumble. Its fundamental frequency reaches into the infrasonic range below the human hearing threshold. This call is produced by the elephant´s massive vocal folds. Much less was known about how elephants produce their higher pitched sounds, trumpets and squeaks.
The following rule generally applies to sound production in mammals: the larger the vocal fold, the lower the calls fundamental frequency. Conversely the size of the vocal folds sets an upper limit to the fundamental frequencies that can be reached. The high-pitched squeak only Asian but not African elephants ...
First clear view of a boiling cauldron where stars are born
2021-06-23
University of Maryland researchers created the first high-resolution image of an expanding bubble of hot plasma and ionized gas where stars are born. Previous low-resolution images did not clearly show the bubble or reveal how it expanded into the surrounding gas.
The researchers used data collected by the Stratospheric Observatory for Infrared Astronomy (SOFIA) telescope to analyze one of the brightest, most massive star-forming regions in the Milky Way galaxy. Their analysis showed that a single, expanding bubble of warm gas surrounds the Westerlund 2 star cluster and disproved earlier studies suggesting there may be two bubbles surrounding Westerlund 2. The researchers also identified the source of the bubble ...
Language trade-off? No, bilingual children reliably acquire English by age 5
2021-06-23
In the United States, more than 12 million children hear a minority language at home from birth. More than two-thirds hear English as well, and they reach school age with varying levels of proficiency in two languages. Parents and teachers often worry that acquiring Spanish will interfere with children's acquisition of English.
A first-of-its kind study in U.S.-born children from Spanish-speaking families led by researchers at Florida Atlantic University finds that minority language exposure does not threaten the acquisition of English by children in the U.S. and that there is no trade-off ...
Use of tobacco pipes by Native groups tells story of regional diversity
2021-06-23
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. -- Nineteenth- and 20th-century archaeologists often made sweeping claims about Native cultures, suggesting that everyone who lived in a particular region at a given time shared the same attitudes and practices. A new study of pipes recovered from Hopewell sites in Illinois and Ohio challenges this assumption, revealing that the manufacture, import, export and use of pipestone pipes for smoking varied significantly between the groups, even though they engaged in trade with one another.
The Hopewell era ran from about 50 B.C. to A.D. 250. The new findings are reported in the journal American Antiquity.
The Havana and Scioto Hopewell people, who lived in what is now Illinois ...
Bourneville's tuberous sclerosis: everything unfolds in the brain shortly after birth
2021-06-23
A Canadian research team has uncovered a new mechanism involved in Bourneville tuberous sclerosis (BTS), a genetic disease of childhood. The team hypothesizes that a mutation in the TSC1 gene causes neurodevelopmental disorders that develop in conjunction with the disease.
Seen in one in 6,000 children, tuberous sclerosis causes benign tumours or lesions that can affect various organs such as the brain, kidneys, eyes, heart and skin. While some patients lead healthy lives, others have significant comorbidities, such as epilepsy, autism and learning disabilities.
Although the role that the TSC1 gene plays in the disease is already known, Montreal scientists have only now identified a critical period in the postnatal development ...
Declining treatment during maternity care can foster tension between patients and providers
2021-06-23
When a pregnant person declines a recommended treatment such as prenatal testing or an epidural, tension and strife may ensue between the patient and provider, according to a new analysis by researchers at NYU Rory Meyers College of Nursing and the University of British Columbia.
"People should feel safe, respected, and engaged in their maternity care, but our findings suggest that when providers do not listen to patients, it can foster mistrust and avoidance," said P. Mimi Niles, PhD, MPH, CNM, assistant professor at NYU Rory Meyers College of Nursing and the lead author of the study, which is published in the journal PLOS ONE. ...
Virtual training helps underserved middle schoolers hone social skills
2021-06-23
Middle school, a time when children's brains are undergoing significant development, is often also a time of new challenges in navigating the social world. Recent research from the Center for BrainHealth at UT Dallas demonstrates the power of combining a virtual platform with live coaching to help students enhance their social skills and confidence in a low-risk environment.
In this study, BrainHealth researchers partnered with low-income public middle schools in Dallas. Teachers recommended 90 students to participate in virtual training sessions via ...
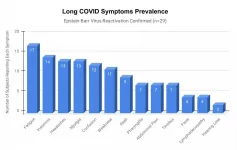
Long COVID symptoms likely caused by Epstein-Barr virus reactivation
2021-06-23
Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) reactivation resulting from the inflammatory response to coronavirus infection may be the cause of previously unexplained long COVID symptoms -- such as fatigue, brain fog, and rashes -- that occur in approximately 30% of patients after recovery from initial COVID-19 infection. The first evidence linking EBV reactivation to long COVID, as well as an analysis of long COVID prevalence, is outlined in a new long COVID study published in the journal Pathogens.
"We ran EBV antibody tests on recovered COVID-19 patients, comparing EBV reactivation rates of those with long COVID symptoms to those without ...
Systolic blood pressure above 120 mmHg increases rate of cardiovascular disease
2021-06-23
Niigata, Japan - An estimated 1.13 billion people worldwide have hypertension or high blood pressure, and two-thirds of these individuals are living in low- and middle-income countries. Blood pressure is the force manifested by circulating blood against the walls of the body's arteries, the major blood vessels in the body. Hypertension is when blood pressure is too high.
Blood pressure is written as two numbers. The first (systolic) number represents the pressure in blood vessels when the heart contracts or beats. The second (diastolic) number represents the pressure in the vessels when the heart rests between beats. Hypertension is diagnosed if, when it is measured on two different days, the systolic blood pressure (SBP) readings on both days is ≥140 mmHg and/or the diastolic ...
Machine learning for solar energy is supercomputer kryptonite
2021-06-23
Supercomputers could find themselves out of a job thanks to a suite of new machine learning models that produce rapid, accurate results using a normal laptop.
Researchers at the ARC Centre of Excellence in Exciton Science, based at RMIT University, have written a program that predicts the band gap of materials, including for solar energy applications, via freely available and easy-to-use software. Band gap is a crucial indication of how efficient a material will be when designing new solar cells.
Band gap predictions involve quantum and atomic-scale chemical calculations ...
Tuckered out: Early Antarctic explorers underfed their dogs
2021-06-23
It's one of the iconic images of early Antarctic exploration: the heroic explorer sledging across the icy wastes towed by his trusty team of canine companions.
But new research analysing a century-old dog biscuit suggests the animals in this picture were probably marching on half-empty stomachs: early British Antarctic expeditions underfed their dogs.
In a paper just published in Polar Record, researchers from Canterbury Museum, Lincoln University and University of Otago in New Zealand analysed the history and contents of Spratt's dog cakes, the chow of choice for the canine members of early Antarctic expeditions.
Lead author, ...
Had COVID-19? One vaccine dose enough; boosters for all, study says
2021-06-23
Two mRNA vaccines against COVID-19 have proven safe and effective in clinical trials, as well as in the millions of people who have been vaccinated so far. But how prior SARS-CoV-2 infection affects vaccine response, and how long that response lasts, are still uncertain. Now, a new study in ACS Nano supports increasing evidence that people who had COVID-19 need only one vaccine dose, and that boosters could be necessary for everyone in the future.
In clinical trials, the Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna COVID-19 vaccines were about 95% effective in protecting against symptomatic infections. Both mRNA vaccines trigger the immune system to produce antibodies against the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein receptor binding domain (RBD), and two doses are necessary to provide immunity in people ...
Combining three techniques boosts brain-imaging precision
2021-06-23
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. -- Researchers report that they have developed a method to combine three brain-imaging techniques to more precisely capture the timing and location of brain responses to a stimulus. Their study is the first to combine the three widely used technologies for simultaneous imaging of brain activity. The work is reported in the journal Human Brain Mapping.
The new "trimodal" approach combines functional MRI, electroencephalography and a third technique, called EROS, that tracks the activity of neurons near the surface of the brain using near-infrared light.
"We know that fMRI is very good at telling us where in the brain things are happening, but the signal is quite slow," said postdoctoral researcher Matthew Moore, the first ...
Mapping methane sources in Paris
2021-06-23
A potent greenhouse gas, methane is released by many sources, both human and natural. Large cities emit significant amounts of methane, but in many cases the exact emission sources are unknown. Now, researchers reporting in ACS' Environmental Science & Technology have conducted mobile measurements of methane and its sources throughout Paris. Their findings suggest that the natural gas distribution network, the sewage system and furnaces of buildings are ideal targets for methane reduction efforts.
In cities, major sources of atmospheric methane include heating systems, landfills, wastewater ...
Mining precious rare-earth elements from coal fly ash with a reusable ionic liquid
2021-06-23
Rare-earth elements are in many everyday products, such as smart phones, LED lights and batteries. However, only a few locations have large enough deposits worth mining, resulting in global supply chain tensions. So, there's a push toward recycling them from non-traditional sources, such as waste from burning coal -- fly ash. Now, researchers in ACS' Environmental Science & Technology report a simple method for recovering these elements from coal fly ash using an ionic liquid.
While rare-earth elements aren't as scarce as their name implies, major reserves are either in politically ...
[1] ... [2201]
[2202]
[2203]
[2204]
[2205]
[2206]
[2207]
[2208]
2209
[2210]
[2211]
[2212]
[2213]
[2214]
[2215]
[2216]
[2217]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.