Better mental health supports for nurses needed, study finds
2021-06-24
Working in the highly charged environment of COVID-19 has had a huge impact on the mental health of nurses, according to a new survey by researchers at the University of British Columbia and the Institute for Work & Health in Toronto.
The findings, described recently in the Annals of Epidemiology, is the first to compare Canadian nurses' mental health prior to and during the pandemic.
"Whether they worked in acute care settings, in community care or in long-term care homes, nurses experienced high rates of depression and anxiety as the pandemic accelerated," says lead researcher Dr. Farinaz Havaei, a professor of nursing at UBC who studies health systems and workplace psychological health and safety.
Prior to the pandemic, two out of 10 nurses reported that they ...
COVID-19 monoclonal antibody therapy can reduce hospitalizations, healthcare system stress
2021-06-24
TAMPA, Fla. (June 24, 2021) -- A newly published study by the END ...
Researchers call for improvements to working culture and conditions for junior doctors
2021-06-24
Researchers are calling for changes to working culture and conditions for junior doctors in the UK after their new research has highlighted a lack of access to clinical and emotional support.
The call comes as a University of Birmingham-led team of researchers, including experts from Keele University, University College London, Oxford University Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust, the London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine, and the Universities of Leeds and Manchester, carried out a qualitative study using in-depth interviews with 21 NHS junior doctors.
All participants, 16 of whom were women ...
Dutch study finds antibiotic-resistant bacteria common in veterinary staff
2021-06-24
**Note this is a special early release from the European Congress of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases (ECCMID 2021). Please credit the conference if you use this story**
New research being presented at the European Congress of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases (ECCMID) held online this year (9-12 July), suggests that one in 10 veterinary workers in the Netherlands carries strains of extended spectrum beta-lactamase (ESBL)-producing bacteria compared to around one in 20 of the general Dutch population.
This higher prevalence could not be explained by known risk factors such as antibiotic use or recent travel, and it seems highly likely that occupational contact with animals in the animal healthcare setting may result in shedding and transmission ...
Delayed infection after injected buttock fillers in a 29-year-old woman
2021-06-24
**Note this is a special early release from the European Congress of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases (ECCMID 2021). Please credit the conference if you use this story*
Irish doctors highlight potential complications following buttock augmentation that can result in hospitalisation in a case report being presented at the European Congress of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases (ECCMID) held online this year (9-12 July). Dr Siobhan Quirke and colleagues from the St James Hospital in Dublin detail the case of a 29-year-old woman who was admitted to hospital with sepsis 14 months after a dermal filler injection.*
The exact ingredients of fillers vary by brand, but they all work to enlarge the buttocks, ...
Single dose of Pfizer or Astra Zeneca COVID-19 vaccine offers substantial protection to
2021-06-24
A new study to be presented at this year's European Congress of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases (ECCMID) (9-12 July) and published this week in The Lancet Infectious Diseases shows that, for residents of long-term care homes for adults aged 65 years and over, a single dose of either the Pfizer or Astra Zeneca COVID-19 vaccine offers around 60% protection against infection from SARS-CoV-2. The study is by Dr Madhumita Shrotri and Dr Laura Shallcross, UCL Institute of Health Informatics, University College London, UK, and colleagues.
The greatest effects of SARS-CoV-2 have been in residents of long-term care facilities, who represent a small fraction of the general population but account for ...
New research uncovers how cancers with common mutation develop resistance to targeted drugs
2021-06-24
A new study by Dana-Farber Cancer Institute researchers has given scientists their first look at the genomic landscape of tumors that have grown resistant to drugs targeting the abnormal KRASG12C protein. Their work shows that, far from adopting a common route to becoming resistant, the cells take a strikingly diverse set of avenues, often several at a time.
The findings, reported online today in the END ...
New class of compounds found to block coronavirus reproduction
2021-06-24
A human genetic mechanism hijacked by SARS-CoV-2, the coronavirus behind the COVID-19 pandemic, to help it spread also makes it vulnerable to a new class of drug candidates, a new study finds.
Led by researchers at NYU Grossman School of Medicine, a research team showed that coronavirus reproduction in infected human cells requires chemical changes made by the human protein METTL3 to RNA, a key form of genetic material. Additional human proteins involved in the recognition of modified RNA, YTHDF1 and YTHDF3, were also found to be important to the process.
Published online in Genes and Development on June 24, the study showed for the first time that ...
Firearm injuries in children, teens costly for US health care system, study finds
2021-06-23
Hospitalizations to treat pediatric gun injuries are expensive, and U.S. taxpayers and the poor are bearing the price, according to a new study from the Stanford University School of Medicine.
The study, which published online June 23 in PLOS ONE, found that the average cost of an initial hospitalization for a pediatric firearm injury is around $13,000. A total of about $109 million is spent on such hospitalizations in the country each year. The figures do not capture the total costs of rehabilitating young gunshot victims, which can be much higher.
Research into the financial, health and social costs of firearm injuries in the United States has focused mostly on adults, said the study's senior author, Stephanie Chao, ...
Research provides a roadmap to HIV eradication via stem cell therapy
2021-06-23
In a groundbreaking study, a team of UC Davis researchers has discovered a special type of stem cell that can reduce the amount of the virus causing AIDS, boosting the body's antiviral immunity and repairing and restoring the gut's lymphoid follicles damaged by the simian immunodeficiency virus (SIV), the equivalent of the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) in non-human primates. ...
Coral offspring physiology impacted by parental exposure to intense environmental stresses
2021-06-23
Adult corals that survive high-intensity environmental stresses, such as bleaching events, can produce offspring that are better suited to survive in new environments. These results from a series of experiments conducted at the Bermuda Institute of Ocean Sciences (BIOS) in 2017 and 2018 are deepening scientists' understanding of how the gradual increase of sea surface temperatures and other environmental disturbances may influence future coral generations.
Researchers on the project included BIOS marine ecologists Samantha de Putron and Gretchen Goodbody-Gringley (now with the Central Caribbean Marine Institute), ecophysiologist Hollie Putnam at the University of Rhode Island (URI), and Kevin Wong, then ...
Increased organizational support for employees' adoption efforts yields positive benefits
2021-06-23
WACO, Texas (June 23, 2021) - When an organization supports its employees who choose to adopt children, the employees, their families, the adopted children and the organization itself experience positive benefits and outcomes, according to new research from Baylor University.
The study, "It Takes a Village: How Organizational Support for Adoption Positively Affects Employees and Their Families," is published in the Journal of Occupational and Organizational Psychology. Researchers from Baylor's Hankamer School of Business include Matthew J. Quade, Ph.D., associate professor of management; ...
Smoother silicone breast implants may reduce severity of immune system reactions
2021-06-23
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE
STUDY SUGGESTS THAT SMOOTHER SILICONE BREAST IMPLANTS REDUCE SEVERITY OF IMMUNE SYSTEM REACTIONS
According to researchers at Johns Hopkins Medicine, the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) and Rice University in Houston, silicone breast implants with a smoother surface design have less risk of producing inflammation and other immune system reactions than those with more roughly textured coatings. Results of the experiments using mice, rabbits and samples of human breast tissue advance knowledge of how the body responds to such implants, providing new information to physicians and affirming ...
Food protein can eliminate pungency and bitterness of extra virgin olive oil
2021-06-23
PHILADELPHIA - Researchers have been investigating the potential health-promoting qualities of extra virgin olive oil (EVOO) for decades, including its possible medicinal value for preventing cancer, Alzheimer's, and cardiovascular disease, as part of the well-known Mediterranean diet. However, consumers in the U.S. have been slow to embrace it as a staple in their diet. This reluctance, say scientists, might be in part due to EVOO's bitter taste and pungency, which is caused by the presence of substances known as phenolic compounds, the very ones believed to contribute to EVOO health benefits. In 2005, researchers from the Monell Chemical ...
High-resolution microscope built from LEGO and bits of phone
2021-06-23
Microscopy is an essential tool in many fields of science and medicine. However, many groups have limited access to this technology due to its cost and fragility. Now, researchers from the Universities of Göttingen and Münster have succeeded in building a high-resolution microscope using nothing more than children's plastic building bricks and affordable parts from a mobile phone. They then went on to show that children aged 9-13 had significantly increased understanding of microscopy after constructing and working with the LEGO® microscope. Their results were published in The Biophysicist.
The researchers designed ...
Microspheres quiver when shocked
2021-06-23
New York, NY--June 23, 2021--A challenging frontier in science and engineering is controlling matter outside of thermodynamic equilibrium to build material systems with capabilities that rival those of living organisms. Research on active colloids aims to create micro- and nanoscale "particles" that swim through viscous fluids like primitive microorganisms. When these self-propelled particles come together, they can organize and move like schools of fish to perform robotic functions, such as navigating complex environments and delivering "cargo" to targeted locations.
A Columbia Engineering team led by Kyle Bishop, professor of chemical engineering, is at the forefront of studying and designing the dynamics of active colloids powered by chemical reactions ...
Shifting sands, creeping soils, and a new understanding of landscape evolution
2021-06-23
A new study published in Nature Communications finds that piles of sand grains, even when undisturbed, are in constant motion. Using highly-sensitive optical interference data, researchers from the University of Pennsylvania and Vanderbilt University present results that challenge existing theories in both geology and physics about how soils and other types of disordered materials behave.
Most people only become aware of soil movement on hillsides when soil suddenly loses its rigidity, a phenomenon known as yield. "Say that you have soil on a hillside. Then, if there's an earthquake or it rains, this material that's apparently ...
NIH scientists describe 'multi-kingdom dialogue' between internal, external microbiota
2021-06-23
WHAT:
National Institutes of Health scientists and their collaborators have identified an internal communication network in mammals that may regulate tissue repair and inflammation, providing new insights on how diseases such as obesity and inflammatory skin disorders develop. The new research is published in Cell.
The billions of organisms living on body surfaces such as the skin of mammals--collectively called microbiota--communicate with each other and the host immune system in a sophisticated network. According to the study, viruses integrated in the host genome, remnants of previous infections called endogenous retroviruses, can control how the host immune system and the microbiota ...
US beekeepers continue to report high colony loss rates, no clear improvement
2021-06-23
Beekeepers across the United States lost 45.5% of their managed honey bee colonies from April 2020 to April 2021, according to preliminary results of the 15th annual nationwide survey conducted by the nonprofit Bee Informed Partnership (BIP). These losses mark the second highest loss rate the survey has recorded since it began in 2006 (6.1 percentage points higher than the average annual loss rate of 39.4%). The survey results highlight the continuing high rates of honey bee colony turnover. The high loss rate was driven by both elevated summer and winter losses this year, with no clear progression toward improvement ...
Powerful people are less likely to be understanding when mistakes are made
2021-06-23
Those with power, such as the wealthy are more likely to blame others for having shortcomings and they are also less troubled by reports of inequality, according to recent research from the University of California San Diego's Rady School of Management.
The study published in END ...
'On/off' switches for self-assembling hydrogels could advance wound healing and more
2021-06-23
BROOKLYN, New York, Wednesday, June 23, 2021 -- Owing to their tunable properties, hydrogels comprising stimuli-sensitive polymers are among the most appealing molecular scaffolds because their versatility allows for applications in tissue engineering, drug delivery and other biomedical fields.
Peptides and proteins are increasingly popular as building blocks because they can be stimulated to self-assemble into nanostructures such as nanoparticles or nanofibers, which enables gelation -- the formation of supramolecular hydrogels that can trap water and small molecules. Engineers, to generate such smart biomaterials, are developing systems that can respond to a multitude of stimuli including heat. Although thermosensitive hydrogels are among widely ...
Study finds abnormal response to cellular stress is associated with Huntington's disease
2021-06-23
Irvine, CA - June 23, 2021 - A new University of California, Irvine-led study finds that the persistence of a marker of chronic cellular stress, previously associated with neurodegenerative diseases such as amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) and frontotemporal dementia (FTD), also takes place in the brains of Huntington's disease (HD) patients.
Chronic cellular stress results in the abnormal accumulation of stress granules (SGs), which are clumps of protein and RNAs that gather in the cell. Prior to this study, published in the Journal of Clinical ...
COVID-19 disruptions in sub-Saharan Africa will have substantial health consequences
2021-06-23
Boston, MA--Early in the COVID-19 pandemic, many African leaders implemented prevention measures such as lockdowns, travel bans, border closures, and school closures. While these efforts may have helped slow the spread of the virus on the continent and continue to be important for its containment, they inadvertently disrupted livelihoods and food systems and curtailed access to critical nutrition, health, and education services. A new series of studies by researchers from Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health and colleagues from the Africa Research, Implementation Science and Education (ARISE) Network finds that these disruptions may have serious ...
Study: Environmental risks exacerbated for vulnerable populations in small towns
2021-06-23
AMES, Iowa -- A new study of small Iowa towns found that vulnerable populations within those communities face significantly more public health risks than statewide averages.
The study, published this week in PLOS ONE, a peer-reviewed open access journal, was led by Benjamin Shirtcliff, associate professor of landscape architecture at Iowa State University.
He focused on three Iowa towns - Marshalltown, Ottumwa and Perry - as a proxy for studying shifting populations in rural small towns, in particular how vulnerable populations in these towns ...
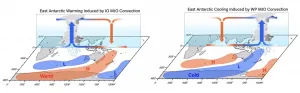
East Antarctic summer cooling trends caused by tropical rainfall clusters
2021-06-23
Our planet is warming due to anthropogenic greenhouse gas emissions; but the warming differs from region to region, and it can also vary seasonally. Over the last four decades scientists have observed a persistent austral summer cooling on the eastern side of Antarctica. This puzzling feature has received world-wide attention, because it is not far away from one of the well-known global warming hotspots - the Antarctic Peninsula.
A new study published in the journal Science Advances by a team of scientists from the IBS Center for Climate Physics at Pusan National University in South Korea, Nanjing University of Information Science and Technology, NOAA Geophysical Fluid Dynamics Laboratory, University Corporation for Atmospheric Research, Ewha Womans University, and National Taiwan ...
[1] ... [2197]
[2198]
[2199]
[2200]
[2201]
[2202]
[2203]
[2204]
2205
[2206]
[2207]
[2208]
[2209]
[2210]
[2211]
[2212]
[2213]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.