Religious participation makes both old and young more likely to trust their neighbors and donate to charity
2021-06-17
"Boomers" and "millennials" who go to church are more likely to trust their neighbours and donate to charity, according to a new study.
Religious beliefs and participation help close the gaps in civic participation between millennials and their elders, researchers have found.
Experts have measured the social "capital" religion gives people of all ages. They found those in their 20s and 30s were less likely to join groups and associations, and less likely to be religious, but being involved with the church gave them more "religious capital" than older people who also attended services.
The study shows boomers often have more social capital than millennials and are more likely to be religious. Religious ...
'Mosquito smoothie' innovation boosts future malaria vaccine potential
2021-06-17
A faster method for collecting pure malaria parasites from infected mosquitos could accelerate the development of new, more potent malaria vaccines.
The new method, developed by a team of researchers led by Imperial College London, enables more parasites to be isolated rapidly with fewer contaminants, which could simultaneously increase both the scalability and efficacy of malaria vaccines.
The parasite that causes malaria is becoming increasingly resistant to antimalarial drugs, with the mosquitoes that transmit the disease also increasingly resistant to pesticides. This has created an urgent need for new ways to fight malaria, which is the world's third-most deadly disease in under-fives, with a child dying from malaria every two minutes.
Existing ...
Innovative mouse model pumps new blood into study of pediatric heart disease
2021-06-17
Ibaraki, Japan - Severe childhood restrictive cardiomyopathy is a condition that causes the muscles in the walls of the heart to become stiff, so that the heart is unable to fill properly with blood. A mutation in a protein called BAG3 is known to result in restrictive cardiomyopathy, muscle weakness, difficulty taking in enough oxygen, and damage to multiple peripheral nerves, often shortening the patient's lifespan significantly. Until now there has been no successful model for the disease, making it extremely difficult to study.
However, researchers in Japan and Germany have now created a mouse model that mimics the human pathology, allowing the disease to be studied more easily. The team's data suggest ...
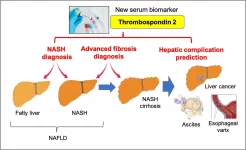
A simple blood test to identify patients at risk of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
2021-06-17
Osaka, Japan - Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is the most common liver disease worldwide and can progress to liver cirrhosis, liver failure or cancer. Currently, nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) diagnosis requires an invasive liver biopsy which can lead to procedural complications. Now, researchers at Osaka University working with international collaborators have identified a noninvasive biomarker that can identify patients at risk of NAFLD complications using a simple blood test.
Owing to the increasing prevalence of obesity worldwide, ...
Hydrophobic copper catalyst to mitigate electrolyte flooding
2021-06-17
The electroreduction of carbon dioxide (CO2) to produce value-added multicarbon compounds is an effective way to cut down CO2 emission. However, the low solubility of CO2 largely limits the application of related technology.
Although gas diffusion electrode (GDE) can accelerate the reaction rate, the instability of the catalysts caused by electrolyte flooding hinders further reaction.
Recently, inspired by setaria's hydrophobic leaves, Prof. GAO Minrui's team from University of Science and Technology of China developed Cu catalyst composed of sharp needles which possesses high level ...
Heat spells doom for Aussie marsupials
2021-06-17
When animals are hot, they eat less. This potentially fatal phenomenon has been largely overlooked in wild animals, explain researchers from The Australian National University (ANU).
According to lead author Dr Kara Youngentob, it means climate change could be contributing to more deaths among Australia's iconic marsupials, like the greater glider, than previously thought.
"Hot weather puts all animals off their food. Humans can deal with it fairly well; we usually have plenty of fat reserves and lots of different ...
'Unshackled' palm-destroying beetles could soon invade Australia
2021-06-17
A destructive pest beetle is edging closer to Australia as biological controls fail, destroying home gardens, plantations and biodiversity as they surge through nearby Pacific islands.
University of Queensland researcher Dr Kayvan Etebari has been studying how palm-loving coconut rhinoceros beetles have been accelerating their invasion.
"We thought we'd outsmarted them," Dr Etebari said.
"In the 1970s, scientists from Australia and elsewhere found that coconut rhinoceros beetles could be controlled with a beetle virus from Malaysia.
"This virus stopped the beetle in its tracks and, for the last 50 years or so, it more-or-less stayed put ...
After the big storm: How to supply emergency power
2021-06-17
As demand for electricity rises and climate change brings more frequent and extreme storms, residents in rural and suburban communities must have access to the minimal electricity they need to survive a large, long-duration (LLD) power outage.
A new study in the journal Risk Analysis compared strategies for providing emergency power to residents in two hypothetical New England communities during such an event. The results suggest that cooperative strategies like sharing a higher capacity generator among multiple homes cost 10 to 40 times less than if each household used its own generator.
"Our findings provide impetus for utilities, regulators, ...
Passing the COVID test in just five minutes
2021-06-17
Osaka, Japan - A team of scientists headed by SANKEN (The Institute of Scientific and Industrial Research) at Osaka University demonstrated that single virus particles passing through a nanopore could be accurately identified using machine learning. The test platform they created was so sensitive that the coronaviruses responsible for the common cold, SARS, MERS, and COVID could be distinguished from each other. This work may lead to rapid, portable, and accurate screening tests for COVID and other viral diseases.
The global coronavirus pandemic has revealed the ...
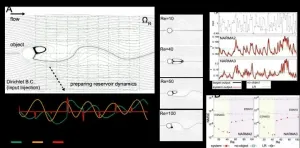
Vortex, the key to information processing capability: Virtual physical reservoir computing
2021-06-17
[Background]
In recent years, physical reservoir computing*1), one of the new information processing technologies, has attracted much attention. This is a physical implementation version of reservoir computing, which is a learning method derived from recurrent neural network (RNN)*2) theory. It implements computation by regarding the physical system as a huge RNN, outsourcing the main operations to the dynamics of the physical system that forms the physical reservoir. It has the advantage of obtaining optimization instantaneously with limited computational resources by adjusting linear and static readout weightings between the output and a physical reservoir without requiring optimization of the weightings by back propagation. However, since the information processing capability depends ...
Close-up look at brain uptake of omega-3
2021-06-17
SINGAPORE, 17 June 2021 - New details on the structure and function of a transport protein could help researchers develop drugs for neurological diseases that are better able to cross the blood-brain barrier. The findings were published in the journal Nature by researchers at Columbia University Vagelos College of Physicians and Surgeons, Duke-NUS Medical School, Weill Cornell Medicine and colleagues.
Omega-3 fatty acids, like docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), are important for brain and eye development. They are derived mainly from dietary sources and converted ...
Bronze Age Scandinavia's trading networks for copper settled
2021-06-17
New research presents over 300 new analyses of bronze objects, raising the total number to 550 in 'the archaeological fingerprint project'. This is roughly two thirds of the entire metal inventory of the early Bronze Age in southern Scandinavia. For the first time, it was possible to map the trade networks for metals and to identify changes in the supply routes, coinciding with other socio-economic changes detectable in the rich metal-dependent societies of Bronze Age southern Scandinavia.
The magnificent Bronze Age in southern Scandinavia rose from copper traded from the British Isles and Slovakia 4000 years ago. 500 ...
Sensitive and specific detecting biomarker of radiation-resistant nasopharyngeal carcinoma
2021-06-17
In a paper published in NANO, a team of researchers from Jiangnan University, China have prepared a convenient sensing platform which can detect microRNA-205 (MiR-205) with high sensitivity and excellent selectivity using TpTta-COF nanosheet and fluorescent oligonucleotide probes.
Nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) is a kind of malignant cancer derived from the epithelial cells, which shows an apparent regional aggregation with a high prevalence in Southern China and Southeast Asia. With the ongoing improvement of radiotherapy technology, the therapeutic effect of NPC patients has been increased significantly. However, the easy recurrence and metastasis still cause the poor prognosis of NPC patients. Many researches indicated that ...
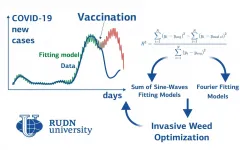
RUDN mathematician builds a COVID-19 spread model -- it shows how vaccination affects pandemic
2021-06-17
RUDN University mathematicians built a model of COVID-19 spreading based on two regression models. The mathematicians divided the countries into three groups, depending on the spreading rate and on the climatic conditions, and found a suitable mathematical approximation for each of them. Based on the model, the mathematicians predicted the subsequent waves. The forecast was accurate in countries where mass vaccination was not introduced. The results are published in Mathematics.
The epidemy spreading rate within the country depends, among other things, on the climatic ...
State of the art and future directions in the clinical application of HR-pQCT in adults
2021-06-17
In recent years, significant progress has been made towards the use of high-resolution peripheral computed tomography (HR-pQCT) imaging in research, and new potential for applications in the clinic have emerged, particularly with the advent of second generation devices.
A newly published state-of-the-art publication on the use and future directions of HR-PQCT provides a concise overview of current clinical applications as well as valuable guidance on the interpretation of results.
Specifically, it gives an overview of:
differences and reference data for HR-pQCT variables by age, sex, body composition and race/ethnicity;
fracture risk prediction using HR-pQCT, specifically in regard to bone microarchitecture in individuals ...
Foresight diagnostics to show vision of the new standard of lymphoma MRD detection at ICML
2021-06-17
AURORA, COLORADO, June 16, 2021 -- Foresight Diagnostics, the emerging leader in blood-based lymphoma disease monitoring, announced today that clinical performance of its minimal residual disease (MRD) detection platform in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) will be presented at the 16th International Conference on Malignant Lymphoma (ICML) on June 18-22, 2021. The oral presentation demonstrates the utility of Foresight Diagnostics' proprietary PhasED-Seq technology to improve MRD detection rates in DLBCL patients in low-disease burden settings.
"Foresight's MRD testing platform can detect relapsing disease 200 ...
Predicting resistance to anticancer drugs
2021-06-17
Cancer cells can develop resistance to therapy through both genetic and non-genetic mechanisms. But it is unclear how and why one of these routes to resistance prevails. Understanding this 'choice' by the cancer cells may help us devise better therapeutic strategies. Now, the team of Prof. Jean-Christophe Marine (VIB-KU Leuven Center for Cancer Biology) shows that the presence of certain stem cells correlates with the development of nongenetic resistance mechanisms. Their study is published in the prestigious journal Cancer Cell.
Two routes to resistance
Even though cancer therapy has made great strides in the ...
Racism and racial trauma as barriers to breastfeeding
2021-06-17
African American mothers continue to have the lowest breastfeeding rates, even as the breastfeeding rates have risen in the U.S. over the past 25 years. Racism is an important barrier to breastfeeding, as examined in Part 2 of a special issue on "Breastfeeding and the Black/African American Experience: Cultural, Sociological, and Health Dimensions Through an Equity Lens," published in the peer-reviewed journal Breastfeeding Medicine. Click here to read the issue now.
The special issue is led by Guest Editor Sahira Long, MD, a pediatrician and lactation consultant.
Exploring how racism creates barriers to breastfeeding for Black mothers and how Black women resist racism during their quest to breastfeed are Catasha Davis, PhD and Aubrey Van Kirk Villalobos, DrPH, Milken Institute School ...
Induced hypothermia after cardiac arrest did not improve survival
2021-06-17
Since 2005, the guidelines for the care of unconscious cardiac arrest patients have been to cool the body temperature down to 33 degrees Celsius. A large, randomised clinical trial led by Lund University and Region Skåne in Sweden has shown that this treatment does not improve survival. The study is published in the New England Journal of Medicine.
"These results will affect the current guidelines", says Niklas Nielsen, researcher at Lund University and consultant in anaesthesiology and intensive care at Helsingborg Hospital, who led the study.
In the early 2000s, two studies in the New England Journal of Medicine showed that induced hypothermia in unconscious cardiac arrest patients ...
UBCO researchers identify best strategy to reduce human-bear conflict
2021-06-17
Conservationists have long warned of the dangers associated with bears becoming habituated to life in urban areas. Yet, it appears the message hasn't gotten through to everyone.
News reports continue to cover seemingly similar situations -- a foraging bear enters a neighbourhood, easily finds high-value food and refuses to leave. The story often ends with conservation officers being forced to euthanize the animal for public safety purposes.
Now, a new study by sustainability researchers in the Irving K. Barber Faculty of Science uses computer modelling to look at the best strategies to reduce human-bear conflict.
"It happens all the time, and unfortunately, humans are almost ...
Cell death discovery could lead to new treatment for COPD
2021-06-17
Research shows that inhibiting necroptosis, a form of cell death, could be a novel therapeutic approach for treating chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), an inflammatory lung condition, also known as emphysema, that makes it difficult to breathe.
Published in the prestigious American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine, the study by a team of Australian and Belgian researchers, revealed elevated levels of necroptosis in patients with COPD.
By inhibiting necroptosis activity, both in the lung tissue of COPD patients as well as ...
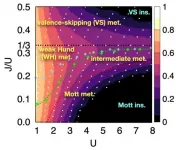
Defining the Hund physics landscape of two-orbital systems
2021-06-17
Electrons are ubiquitous among atoms, subatomic tokens of energy that can independently change how a system behaves--but they also can change each other. An international research collaboration found that collectively measuring electrons revealed unique and unanticipated findings. The researchers published their results on May 17 in Physical Review Letters.
"It is not feasible to obtain the solution just by tracing the behavior of each individual electron," said paper author Myung Joon Han, professor of physics at KAIST. "Instead, one should describe or track all the entangled electrons at once. This requires a clever way of treating this entanglement."
Professor Han and the researchers used a recently developed "many-particle" theory to account for the ...
When tyrannosaurs dominated, medium-sized predators disappeared
2021-06-17
New UMD study suggests that everywhere tyrannosaurs rose to dominance, their juveniles took over the ecological role of medium-sized carnivores
A new study shows that medium-sized predators all but disappeared late in dinosaur history wherever Tyrannosaurus rex and its close relatives rose to dominance. In those areas--lands that eventually became central Asia and Western North America--juvenile tyrannosaurs stepped in to fill the missing ecological niche previously held by other carnivores.
The research conducted by Thomas Holtz, a principal lecturer in ...
Alpine plant spins its own flavonoid wool
2021-06-17
Like the movie version of Spider-Man who shoots spider webs from holes in his wrists, a little alpine plant has been found to eject cobweb-like threads from tiny holes in specialised cells on its leaves. It's these tiny holes that have taken plant scientists by surprise because puncturing the surface of a plant cell would normally cause it to explode like a water balloon.
The small perennial cushion-shaped plant with bright yellow flowers, Dionysia tapetodes, is in the primula family and naturally occurs in Turkmenistan and north-eastern Iran, and through the mountains of Afghanistan to the border of Pakistan. What makes it unusual is its leaves, which are covered in long silky fibres that ...
Study of young chaotic star system reveals planet formation secrets
2021-06-17
A team of scientists using the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA) to study the young star Elias 2-27 have confirmed that gravitational instabilities play a key role in planet formation, and have for the first time directly measured the mass of protoplanetary disks using gas velocity data, potentially unlocking one of the mysteries of planet formation. The results of the research are published today in two papers in The Astrophysical Journal.
Protoplanetary disks--planet-forming disks made of gas and dust that surround newly formed young stars--are ...
[1] ... [2209]
[2210]
[2211]
[2212]
[2213]
[2214]
[2215]
[2216]
2217
[2218]
[2219]
[2220]
[2221]
[2222]
[2223]
[2224]
[2225]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.