Junk food diet may boost risk of dangerous driving among truck/lorry drivers
2021-06-16
A junk food diet may increase the risk of dangerous driving among truck/lorry drivers by boosting fatigue, which is often a key factor in vehicle collisions, suggests research published online in the journal Occupational & Environmental Medicine.
Some 1.35 million people die in road traffic collisions every year, with professional drivers at greater risk because of the time they spend behind the wheel.
There are several known contributory factors, among which gender, age, experience, driving skills and attitudes seem to be important, note the researchers. But lifestyle ...
Inkjet printing show promise as new strategy for making e-textiles, study finds
2021-06-16
In a new study, North Carolina State University researchers demonstrated they could print layers of electrically conductive ink on polyester fabric to make an e-textile that could be used in the design of future wearable devices.
Since the printing method can be completed at room temperature and in normal atmospheric conditions, researchers believe inkjet printing could offer a simpler and more effective method of manufacturing electronic textiles, also known as e-textiles. In addition, researchers said the findings suggest they could extend techniques common in the flexible electronic industry to textile manufacturing. They reported their findings in the journal ACS Applied ...
How political bias impacts believing sexual assault victims
2021-06-15
New research from Syracuse University Newhouse School of Public Communications reveals a relationship between political biases and attitudes about sexual assault.
Authored by assistant professor Rebecca Ortiz and PhD student Andrea Smith, the article "A social identity threat perspective on why partisans may engage in greater victim blaming and sexual assault myth acceptance in the #MeToo era," was published in the peer-reviewed journal Violence Against Women.
Ortiz and Smith found that the stronger the partisan identity of Republicans and Democrats, the more likely they were to engage in victim blaming attitudes, which was then related to a lesser likelihood to perceive the #MeToo ...
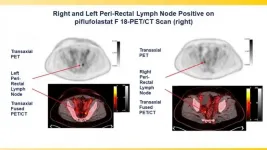
PSMA-targeted radiotracer pinpoints metastatic prostate cancer across anatomic regions
2021-06-15
Reston, VA (Embargoed until 3:00 p.m. EDT, Tuesday, June 15, 2021)--A phase III clinical trial has validated the effectiveness of the prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA)-targeted radiotracer 18F-DCFPyL in detecting and localizing recurrent prostate cancer. Approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration last month, the radiotracer identified metastatic lesions with high positive predictive values regardless of anatomic region, adding to the evidence that PSMA-targeted radiotracers are the most sensitive and accurate agents for imaging prostate cancer. This study was presented at the ...
Infrared imaging by ultrathin nanocrystal layers
2021-06-15
The demand for detecting infrared (IR) light, invisible to human eyes, is constantly growing, due to a wide variety of applications ranging from food quality control and remote sensing to night vision devices and lidar. Commercial IR cameras require the conversion of infrared light to electrons and the projection of the resultant image on a display. This display blocks the transmission of visible light, thereby disrupting normal vision. Moreover, such IR detectors require low temperature and even cryogenic cooling due to the low energies of the IR photons, making IR detectors bulky and heavy.
An all-optical alternative to traditional cameras is the use of a nonlinear optical process to convert IR light into visible. In this case, electrical signals are no ...
Analysis: Chile's transition to democracy slow, incomplete, fueled by social movements
2021-06-15
A new article analyzes Chile's transition in 1990 from dictatorship to democracy, the nature of democracy between 1990 and 2019, and the appearance of several social movements geared to expanding this democracy. The article, by researchers at Carnegie Mellon University (CMU), appears in The Latin Americanist, a publication of the Southeastern Council of Latin American Studies.
"Our goal is to locate the October 2019 protest movement in the context of Chile's very slow and incomplete transition to democracy, as well as amid social movements that have consistently challenged the economic ...
Investigating carbonate mineral chemical variations to improve oil recovery
2021-06-15
Dr. Igor Ivanishin, a postdoctoral researcher in the Harold Vance Department of Petroleum Engineering at Texas A&M University, has firsthand experience with the frustrations of oil production. He spent nine years as a hydraulic fracturing engineer with operating and service companies in Russia. A few years ago, he came to Texas A&M to get his doctoral degree while delving into a reoccurring recovery problem in carbonate reservoirs: why don't they produce oil as predicted?
Ivanishin is investigating variations in the chemical composition of dolomite and calcite ...
Two COVID-19 vaccines show safety, strong immunity in infant model
2021-06-15
CHAPEL HILL, NC - A group of scientists led by researchers at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Weill Cornell Medicine and NewYork-Presbyterian reported that the Moderna mRNA vaccine and a protein-based vaccine candidate elicited durable neutralizing antibody responses to SARS-CoV-2 in pre-clinical research. There were no adverse effects.
The research, published June 15 in Science Immunology, suggests that vaccines for young children are likely important, safe tools to curtail the pandemic.
The co-senior authors of the paper are Kristina De Paris, PhD, professor of microbiology and immunology at the UNC School ...
Quality supervision, coworker support key to child welfare caseworker retention
2021-06-15
Instead of looking at the reasons child welfare caseworkers leave their jobs, Oregon State University researchers examined the common factors among workers who stay in the field, and what makes them feel most satisfied in their work.
In their recent study, researchers found that quality supervisory support and strong relationships with coworkers helped caseworkers feel appreciated and understood, while having adequate technology and equipment helped them manage their workload effectively
They hope child welfare agencies can use this information to support ...
Data and safety review board reports how it monitored the COVID-19 vaccine trials
2021-06-15
BIRMINGHAM, Ala. - Clinical evaluation of three COVID-19 vaccine candidates in 2020-21 during a worldwide pandemic that killed or sickened millions was unprecedented in terms of urgency and scope. Responsibility for the safety, integrity and scientific validity of the trials in the United States fell to 12 experts of the federally appointed COVID-19 Vaccine Data and Safety Monitoring Board, or COVID-19 DSMB, who in turn report to an oversight group.
This COVID-19 DSMB team -- which included co-contributing author Richard Whitley, M.D., distinguished professor of pediatrics in the University of Alabama ...
Balanced rocks set design ground motion values for New Zealand dam
2021-06-15
For the first time, researchers have used precariously-balanced rocks to set the formal design earthquake motions for a major existing engineered structure--the Clyde Dam, the largest concrete dam in New Zealand.
Mark Stirling of the University of Otago and colleagues identified and assessed the ages of these gravity-defying rock formations located about 2 kilometers from the dam site, using these data to determine the peak ground accelerations that the rocks could withstand before toppling.
This in turn was used to set the Safety Evaluation Earthquake (SEE) spectrum for the dam, or ...
At underwater site, research team finds 9,000-year-old stone artifacts
2021-06-15
An underwater archaeologist from The University of Texas at Arlington is part of a research team studying 9,000-year-old stone tool artifacts discovered in Lake Huron that originated from an obsidian quarry more than 2,000 miles away in central Oregon.
The obsidian flakes from the underwater archaeological site represent the oldest and farthest east confirmed specimens of western obsidian ever found in the continental United States.
"In this case, these tiny obsidian artifacts reveal social connections across North America 9,000 years ago," said Ashley Lemke, assistant professor of sociology and anthropology at UT Arlington. "The artifacts found below the Great Lakes come from a geological source in Oregon, 4,000 kilometers away---making it one of the longest distances ...
That song is stuck in your head, but it's helping you to remember
2021-06-15
"So, no one told you life was going to be this way.
Your job's a joke, you're broke, you're love life's DOA.
It's like you're always stuck in second gear,
When it hasn't been your day, your week, your month, or even your year..."
If you have watched TV since the 1990s, the sitcom theme song, "I'll Be There for You," has likely been stuck in your head at one point or another. New research from UC Davis suggests these experiences are more than a passing nuisance -- they play an important role in helping memories form, not only for the song, but also related life events like hanging out with friends ...
Hollywood stereotypes of female journalists feed a 'vicious cycle' of sexism
2021-06-15
When a fictional female journalist appears on screen, chances are she's about to sleep with one of her sources. It's a trope that infuriates actual women in news media -- and it can have real-life consequences, says University of Florida researcher Frank Waddell, Ph.D.
In shows like "House of Cards" and movies like "Thank You for Smoking," female reporters are quick to trade sex for information. Even when sex with sources has nothing to do with ambition -- such as the hookups in "Sharp Objects," "Top Five," "Trainwreck," and the "Gilmore Girls" reboot, to name a few -- it still portrays unethical behavior.
"In the past 20 to 30 years, Hollywood has really latched on to this. ...
Alzheimer disease research results over-hyped if science papers omit mice from the title
2021-06-15
A study of media coverage of 623 scientific papers on Alzheimer disease research conducted in mice reveals that the news media are more likely to write a story about alleged breakthroughs or medical research findings if research authors omit mice from their studies' titles. On the other hand, papers that acknowledge mice in their titles result in limited media coverage.
In addition, the study titled "What's not in the news headlines or titles of Alzheimer disease articles? #In mice" conducted by Dr Marcia Triunfol of Humane Society International and Dr Fabio Gouveia of the Oswaldo Cruz Foundation in Brazil, and published in PLoS ...
A push for a shift in the value system that defines "impact" and "success"
2021-06-15
Discussions of a broken value system are ubiquitous in science, especially after the COVID-19 pandemic served to expose inequality globally. However, according to the authors of an article publishing 15th June 2021 in the open access journal PLOS Biology, science itself is not "broken," but it was built on deeply-entrenched, systemic sexist and racist values, which perpetuate biases through the continued focus on citation rates and impact factors.
The author maintain that while equity within science has advanced thanks to the tireless efforts of generations of systemically marginalized groups, the system remains outdated, colonialist, and patriarchal. ...
Financial distress similar, or greater, for patients with heart disease compared to cancer
2021-06-15
Financial toxicity, the financial strain experienced by patients accessing health care, impacts a large population of cancer patients according to prior research. A new study, published in JACC: CardioOncology, finds financial toxicity is often greater among heart disease patients compared to cancer patients, and those with both conditions suffer the highest burden.
"Heart disease and cancer are the leading causes of death in the United States, yet most research on financial toxicity has focused on cancer patients. It is important to consider that cancer patients may have short bursts of high expenditures for treatments, while heart disease patients are often incurring ...
Over half of cardiovascular disease deaths worldwide occur in Asia
2021-06-15
The number of people dying from cardiovascular disease (CVD) in Asia is increasing rapidly, with over half of all CVD deaths globally in 2019 occurring in Asian countries, according to a state-of-the-art review paper published in the inaugural issue of JACC: Asia. The data demonstrates an urgent need to understand the burdens and epidemiological features of CVD in Asian countries to develop localized CVD prevention strategies to combat the epidemic.
From 1990 to 2019, the number of CVD deaths in Asia rose from 5.6 million to 10.8 million. Nearly 39% of these CVD deaths were premature, meaning they occurred in a person less than 70 years old, which was significantly higher than premature CVD deaths in the U.S. (23%). Most ...
Research papers that omit 'mice' from titles receive misleading media coverage
2021-06-15
There is increasing scrutiny around how science is communicated to the public, but what is the relationship between how scientists report their findings and how media reports it to the public? A study published in PLOS Biology by Marcia Triunfol at Humane Society International, in Washington, DC and Fabio Gouveia at Oswaldo Cruz Foundation in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil suggests that when authors of scientific papers omit the basic fact that a study was conducted in mice (and not in humans) from the article title, journalists reporting on the paper tend to do the same.
Alzheimer's Disease is an exclusively ...
The long view
2021-06-15
What will the Earth be like for our children and grandchildren, as temperatures continue to rise? We can be fairly certain of some things: Some regions will become inhospitable, as heat drives their inhabitants away or causes massive declines and changes in their ecosystems. Many other physical, chemical and biological processes will also be affected by rising temperatures that threaten critical ecosystem services such as food production, biodiversity and energy security.
But what these changes will be and exactly how they impact the Earth -- and ultimately us humans -- are still difficult to predict. Many of them are so gradual and happen over such a long timescale that they wouldn't be noticeable ...
Drug rebates for insurers tied to higher costs for patients, especially the uninsured
2021-06-15
Federal agencies that regulate drug pricing and healthcare insurance are concerned that an industry practice of using rebates to lower drug costs for insurers has led to increases in list prices and out-of-pockets costs for patients.
To investigate whether patients with or without insurance were paying more because of rebates to insurers, researchers led by the University of Washington examined cost and price data on more than 400 branded drugs. The study found that rebates were associated with increases in out-of-pocket costs for patients by an average of $6 for those with commercial insurance, $13 for Medicare ...
New Web Tool Fights Antibacterial Resistance
2021-06-15
In 1943, two scientists named Max Delbrück and Salvador Luria conducted an experiment to show that bacteria can mutate randomly, independent of external stimulus, such as an antibiotic that threatens a bacterial cells' survival. Today the Luria-Delbrück experiment is widely used in laboratories for a different purpose--scientists use this classic experiment to determine microbial mutation rates. When performing the Luria-Delbrück experiment, scientists need efficient computer algorithms to extract reliable estimates of mutation rates from data, and they also need well-designed software tools to access these sophisticated algorithms.
Through the years, several web tools that allow researchers to more easily input and analyze data on a computer were developed to increase ...
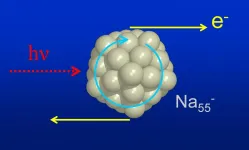
The electron merry-go-round
2021-06-15
Photoemission is a property of metals and other materials that emit electrons when struck by light. Electron emission after light absorption was already explained by Albert Einstein. But since this effect is a highly complex process, scientists have still not been able to fully elucidate its details. Prof. Dr. Bernd von Issendorff and his team at the University of Freiburg's Institute of Physics have now succeeded in detecting a previously unknown quantum effect in the angular distributions of photoelectrons from cryogenic mass-selected metal clusters. ...
Sequencing of wastewater can help monitor SARS-COV-2 variants
2021-06-15
Washington, D.C. - June 15, 2021 - Viral genome sequencing of wastewater can provide an early warning system of emerging SARS-CoV-2 variants that is independent of investigations of identified clinical cases, according to a new study published in mSystems, an open-access journal of the American Society for Microbiology. In the study, researchers describe the detection and quantification of variant B.1.1.7, first identified in southeast England, in sewage samples from London, United Kingdom before widespread transmission of this variant was obvious from clinical cases.
"Wastewater sampling and environmental surveillance ...
Soaking up the sun: Artificial photosynthesis promises clean, sustainable source of energy
2021-06-15
Humans can do lots of things that plants can't do. We can walk around, we can talk, we can hear and see and touch. But plants have one major advantage over humans: They can make energy directly from the sun.
That process of turning sunlight directly into usable energy - called photosynthesis - may soon be a feat humans are able to mimic to harness the sun's energy for clean, storable, efficient fuel. If so, it could open a whole new frontier of clean energy. Enough energy hits the earth in the form of sunlight in one hour to meet all human civilization's energy needs for an entire year.
Yulia Puskhar, a biophysicist and professor of physics in Purdue's College of Science, may have a way to harness that energy by mimicking plants.
Wind ...
[1] ... [2216]
[2217]
[2218]
[2219]
[2220]
[2221]
[2222]
[2223]
2224
[2225]
[2226]
[2227]
[2228]
[2229]
[2230]
[2231]
[2232]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.