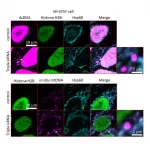
AMP recommends minimum set of pharmacogenetic alleles to guide clinical CYP2D6 genotype testing, pro
2021-06-10
ROCKVILLE, Md. - June 10, 2021 - The Association for Molecular Pathology (AMP), the premier global, molecular diagnostic professional society, today published consensus recommendations to aid in the design and validation of clinical CYP2D6 assays, promote standardization of testing across different laboratories and improve patient care. The manuscript, "Recommendations for Clinical CYP2D6 Genotyping Allele Selection: A Joint Consensus Recommendation of the Association for Molecular Pathology, College of American Pathologists, Dutch Pharmacogenetics Working Group of the Royal Dutch Pharmacists Association, and European Society for Pharmacogenomics and Personalized Therapy," was released online ahead of publication in The Journal ...
New method to measure milk components has potential to improve dairy sustainability
2021-06-10
Champaign, IL, June 10, 2021 - Present in blood, urine, and milk, the chemical compound urea is the primary form of nitrogen excretion in mammals. Testing for urea levels in dairy cows helps scientists and farmers understand how effectively nitrogen from feed is used in cows' bodies, with important economic implications for farmers in terms of feed costs, physiological effects for cows such as reproductive performance, and environmental impacts from excretion of nitrogen in dairy cow waste. Thus, accuracy in testing dairy cow urea levels is essential.
Since the 1990s, mid-infrared testing of milk urea nitrogen (MUN) has been the most efficient and least invasive way to measure nitrogen use by dairy cows in large numbers. In a recent ...
Combating maritime litter
2021-06-10
Plastic bottles drifting in the sea; bags in the stomachs of turtles; Covid-19 masks dancing in the surf: few images are as unpleasant to look at as those that show the contamination of our oceans. And few environmental issues are as urgent and as present in the public awareness. "Most people have an emotional connection to the sea. They think of ocean pollution as an attack on a place they long for," said Nikoleta Bellou, marine scientist at Hereon's Institute of Coastal System - Analysis and Modeling. Between 1990 and 2015 alone, an estimated 100 million metric tons of mostly plastic waste entered the oceans. For that instance the study fits to the UN Decade of Ocean Science for Sustainable Development, which started this year to emphasize a sustainable use of ...
BU researchers create novel curriculum assessment tool to improve medical education about sexual and gender minority (LGBTQI) populations
2021-06-10
(Boston)--Medical education aspires to mitigate bias in future professionals by providing a robust curriculum that includes perspectives and practices for caring for sexual and gender minority (SGM) populations, including lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender and intersex (LGBTQI) persons. To provide medical schools with a more systematic, uniform approach to teaching these topics in their curriculum, the Association of American Medical Colleges (AAMC) in 2014 published 30 SGM competencies and topics that curricula should address. However, implementation of these ideals remains challenging.
Building off the AAMC's comprehensive ...
Researchers turned transparent calcite into artificial gold
2021-06-10
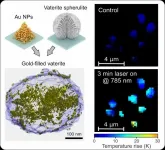
Breakthrough in metamaterials: for the first time in the world, researchers at Tel Aviv University developed an innovative nanotechnology that transforms a transparent calcite nanoparticle into a sparkling gold-like particle. In other words, they turned the transparent particle into a particle that is visible despite its very small dimensions. According to the researchers the new material can serve as a platform for innovative cancer treatments.
In a new paper published in Advanced Materials, an international team of scientists, coordinated by Dr. Roman Noskov and Dr. Pavel Ginzburg from the Iby and Aladar Fleischman Faculty of Engineering at Tel Aviv University, Prof. Dmitry Gorin from the Center ...
Binding of a second CO molecule observed
2021-06-10
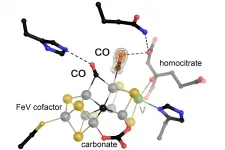
Through the biological fixation of the element nitrogen by the enzyme nitrogenase, organisms gain access to molecular nitrogen (N2) in the Earth's atmosphere, which is essential for building cellular structures. In addition, a vanadium-dependent variant of nitrogenase can reduce the toxic gas carbon monoxide (CO) to hydrocarbons. These reductions of N2 and CO are among the most important processes in industrial chemistry, as they are used to produce both fertilizers and synthetic fuels. However, researchers have not yet been able to decipher the different pathways of the two reactions. Dr. Michael Rohde from Prof. Dr. Oliver Einsle's team at the Institute of Biochemistry at the ...
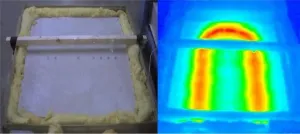
More sustainable mortars and concrete with optimal thermal and mechanical efficiency
2021-06-10
The consumption of raw materials has increased notably in industry in general, and in the construction industry in particular, amidst growing concerns over sustainability issues. Concrete and mortar are the most commonly used materials in construction, and many studies are currently under way to try and reduce the harmful effects of their manufacture. Concrete and mortar are made by mixing water, sand, cement and aggregates.
"The main problem is the amount of cement used to produce this type of material; cement manufacturing uses a huge amount of energy and natural resources, which implies a high level of CO2 emissions. Diverse studies are under way aimed at reducing the quantity of cement required. We are working to replace cement and aggregates ...
University of Minnesota Medical School identifies placental protein as possible birthweight regulator
2021-06-10
MINNEAPOLIS/ST.PAUL (06/10/2021) -- New findings from the University of Minnesota Medical School are helping uncover why some people are more likely to be overweight and develop Type 2 diabetes -- and it starts in the womb.
Previous association studies have shown that low birthweight among infants is a strong determinant for eventual obesity and Type 2 diabetes. The placenta of infants with a low birthweight have reduced levels of mTOR (mechanistic target of rapamycin), and the placenta of bigger infants have increased levels of mTOR. Building off of that research, a U of M Medical ...
Children cannot understand sadness and happiness in people wearing facemasks
2021-06-10
Genova (Italy) 10 June, 2021 - The U-Vip (Unit for Visually Impaired People) research team led by Monica Gori at the IIT- Istituto Italiano di Tecnologia (Italian Institute of Technology) has recently published a study which shows for the first time how children aged from 3 to 5 years old have problems in recognising the emotions of people wearing surgical masks. This collateral effect of the preventive measures linked to the Covid-19 health emergency could influence the correct development of children's capabilities of social interaction. The research paper has been published in Frontiers in Psychology.
The use of facemasks for children ...
For bay oysters, protection plus restoration creates healthiest reefs
2021-06-10
Actively restoring oyster reefs--beyond simply protecting them from harvest--can create big payoffs for habitat quality and the other species that flock to them. A new study from the Smithsonian Environmental Research Center (SERC), published June 3 in the journal Marine Ecology Progress Series, compared restored, protected and harvested areas using photos and video footage from roughly 200 sites.
Roughly a quarter of Maryland's oyster habitat lies protected in oyster sanctuaries. But only a small fraction of those sanctuaries have undergone full-scale restorations, with reconstructed reefs and new live oyster plantings. ...
Noise and light pollution can change which birds visit our backyards
2021-06-10
A new study reports that birds across the continental U.S. tend to avoid backyard feeders in louder areas. When light and noise pollution were both present, even more species stayed away.
The study, published in Global Change Biology, used data from the community science program Program FeederWatch. The research team analyzed more than 3.4 million observations of 140 different bird species across the continental U.S.
"Broadly speaking, we are just starting to dive into the consequences of light and noise for animals," said Ashley Wilson, a graduate student at California Polytechnic State University who led the study. "Most studies focus on a single species' responses to noise or light pollution. As such, our study involving 140 species provides the most comprehensive assessment ...
LIM domain only 1: One gene, many roles in cancer
2021-06-10
Humans have been plagued by a myriad of deadly cancers since ages. Parallelly, they have also been attempting different permutations and combinations of treatments to cure the disease. Part of these attempts involving biomolecular targets have come to the fore in recent years. Like a broad-spectrum antibiotic that can attack and eliminate several microbes at a time, some of these biomolecular targets, when manipulated appropriately, can alleviate different cancers. One such biomolecular target of interest is LIM domain only 1 gene (LMO1).
LMO1 codes for a protein 'connector' that helps in the assembly ...
Memory biomarkers confirm aerobic exercise helps cognitive function in older adults
2021-06-10
Increasing evidence shows that physical activity and exercise training may delay or prevent the onset of Alzheimer's disease (AD). In aging humans, aerobic exercise training increases gray and white matter volume, enhances blood flow, and improves memory function. The ability to measure the effects of exercise on systemic biomarkers associated with risk for AD and relating them to key metabolomic alterations may further prevention, monitoring, and treatment efforts. However, systemic biomarkers that can measure exercise effects on brain function and that link to relevant metabolic responses are lacking.
To address this issue, Henriette van Praag, Ph.D., from Florida Atlantic University's ...
Active platinum species
2021-06-10
Highly dispersed platinum catalysts provide new possibilities for industrial processes, such as the flameless combustion of methane, propane, or carbon monoxide, which has fewer emissions and is more resource efficient and consistent than conventional combustion. In the journal Angewandte Chemie, a team of researchers reports on which platinum species are active in high-temperature oxidations and what changes they can undergo in the course of the process--important prerequisites for the optimization of catalysts.
Individual metal atoms and clusters consisting of only a few metal atoms have interesting catalytic properties determined by the exact nature of the active metal species. Usually, these are highly dispersed and deposited on ...
Screening uptake may contribute to higher risk of colon cancer for black people
2021-06-10
Black people have a higher risk of colorectal cancer than white people, but this risk is likely not due to genetics. Data from a recent study by researchers from the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs, Regenstrief Institute and Indiana University School of Medicine adds more data to the existing evidence.
"The next step is determining what is behind this increased risk," said lead author Thomas Imperiale, M.D., Regenstrief Institute research scientist, VA investigator and professor of gastroenterology and hepatology at IU School of Medicine. "Lifestyle and healthcare-related behaviors may explain some of the difference." ...
Pfizer COVID-19 vaccine protective against SARS-CoV-2 variants
2021-06-10
Washington, D.C. - June 9, 2021 - The Pfizer COVID-19 vaccine is protective against several SARS-CoV-2 variants that have emerged, according to new research presented in the journal mBio, an open-access journal of the American Society for Microbiology. While this is good news, the study also found that the only approved monoclonal antibody therapy for SARS-CoV-2 might be less effective against SARS-CoV-2 variants in laboratory experiments.
"The vaccines provide very strong protection against the earlier forms of the virus as well as the newer variants. This is an important point because I have heard people say that they don't think there is a reason to get vaccinated, because the vaccine isn't going to ...
Could naked mole rats hold key to curing cancer and dementia?
2021-06-10
Scientists say naked mole rats - a rodent native to West Africa - may hold the key to new treatments for degenerative diseases such as cancer and dementia.
The reclusive animals have a lifespan far in excess of other rodents - for example, mice and rats live about two years, whereas naked mole rats can live for 40 or 50 years.
Researchers at the University of Bradford say the animals have a unique DNA repair mechanism that enables them to prevent cancers and other degenerative conditions, including dementia.
Cancer resistant
Professor Sherif El-Khamisy, Director of the Institute of Cancer Therapeutics at the University, said: "Naked mole rats are fascinating ...
New study gives clue to the cause, and possible treatment of Parkinson's Disease
2021-06-10
Niigata, Japan - Researchers from Brain Research Institute, Niigata University, Japan may have unraveled a new approach that could revolutionize the treatment, prevention, and possibly reversal of the damages that could lead to Parkinson's Disease (PD). This novel finding utilizing the cellular and zebrafish models, demonstrated how the leakage of mitochondrial dsDNA into the cytosol environment of the cell can contribute to the impairment of brain tissue of patients with PD.
Parkinson's disease is the second most common neurodegenerative disease, and its prevalence ...
Many surgery patients get opioid prescriptions, but many don't need to, study suggests
2021-06-10
Surgeons can ease their patients' pain from common operations without prescribing opioids, and avoid the possibility of starting someone on a path to long-term use, a pair of new studies suggests.
Treating post-surgery pain with non-opioid pain medications such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen didn't lead to higher pain levels or more serious issues during recovery, and didn't dampen patients' satisfaction with their care, according to new results from a study of more than 22,000 patients who had one of seven common operations at 70 hospitals.
The team behind the study has also produced a free, evidence-based guide for surgeons and other acute care providers, ...
Cloud computing expands brain sciences
2021-06-10
People often think about human behavior in terms of what is happening in the present--reading a newspaper, driving a car, or catching a football. But other dimensions of behavior extend over weeks, months, and years.
Examples include a child learning how to read; an athlete recovering from a concussion; or a person turning 50 and wondering where all the time has gone. These are not changes that people perceive on a day-to-day basis. They just suddenly realize they're older, healed, or have a new development skill.
"The field of neuroscience looks at the brain in multiple ways," says Franco Pestilli, a neuroscientist at The University of Texas at Austin (UT Austin). "For ...
Bacteria serves tasty solution to global plastic crisis
2021-06-10
Researchers have discovered that the common bacteria E. coli can be deployed as a sustainable way to convert post-consumer plastic into vanillin, a new study reveals.
Vanillin is the primary component of extracted vanilla beans and is responsible for the characteristic taste and smell of vanilla.
The transformation could boost the circular economy, which aims to eliminate waste, keep products and materials in use and have positive impacts for synthetic biology, experts say.
The world's plastic crisis has seen an urgent need to develop new methods to recycle polyethylene terephthalate (PET) - the strong, lightweight plastic derived from non-renewable materials such as oil and gas and widely used for ...
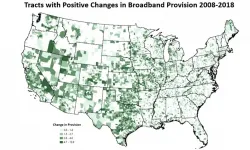
Research uncovers broadband gaps in US to help close digital divide
2021-06-10
High-speed internet access has gone from an amenity to a necessity for working and learning from home, and the COVID-19 pandemic has more clearly revealed the disadvantages for American households that lack a broadband connection.
To tackle this problem, Michigan State University researchers have developed a new tool to smooth the collection of federal broadband access data that helps pinpoint coverage gaps across the U.S. The research was published May 26 In the journal PLOS ONE.
"Nearly 21% of students in urban areas are without at-home broadband, while 25% and 37% lack at-home broadband in suburban ...
Study shows when people with cerebral palsy are most likely to break bones
2021-06-10
Researchers at Michigan Medicine found a subset of middle-aged men with cerebral palsy are up to 5.6 times more likely to suffer fractures than men without the disorder.
"We are not really sure why this happens," said Edward A. Hurvitz, M.D., professor and chair of the Michigan Medicine Department of Physical Therapy and Rehabilitation. "It may be related to structural differences that occur during adolescent growth, or to greater bone mineral loss at earlier age for people with cerebral palsy compared to peers."
For a study published in BONE, the team examined the timing and site of bone fractures for around ...
Ludwig Cancer Research study shows how certain macrophages dampen anti-tumor immunity
2021-06-10
JUNE 10, 2021, NEW YORK - A Ludwig Cancer Research study adds to growing evidence that immune cells known as macrophages inhabiting the body cavities that house our vital organs can aid tumor growth by distracting the immune system's cancer-killing CD8+ T cells.
Reported in the current issue of Cancer Cell and led by Ludwig investigators Taha Merghoub and Jedd Wolchok at Memorial Sloan Kettering (MSK) and Charles Rudin of MSK, the study shows that cavity-resident macrophages express high levels of Tim-4, a receptor for phosphatidylserine (PS), a molecule that they surprisingly ...
In Cell commentary, NIH outlines commitment to addressing structural racism in biomedicine
2021-06-10
Earlier this year, the US National Institutes of Health (NIH) acknowledged the impact of structural racism on biomedical science and committed to doing more to dismantle it. Now, in a commentary appearing June 10 in the journal Cell, NIH Director Francis Collins (@NIHDirector) and colleagues describe the NIH's UNITE initiative and how it differs from the agency's previous diversity, equity, and inclusion efforts.
The UNITE initiative was launched on February 26, 2021 and, for the first time, brings together all 27 NIH institutes to focus on structural racism. It is made up of five committees with members from across the agency and aims to accelerate efforts to address racism ...
[1] ... [2220]
[2221]
[2222]
[2223]
[2224]
[2225]
[2226]
[2227]
2228
[2229]
[2230]
[2231]
[2232]
[2233]
[2234]
[2235]
[2236]
... [8815]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.