Preventing plant disease pandemics
2021-06-08
During the COVID-19 pandemic, food systems faced disruptions from staff shortages and supply chain issues. Now, a Virginia Tech researcher is assisting with efforts to help plants themselves from facing their own pandemic.
Just like human diseases, plant diseases don't have arbitrary boundaries. These diseases don't stop at a border crossing or a port of entry. That's why plant disease surveillance, improved plant disease detection systems, and predictive plant disease modeling - integrated at the global scale - are necessary to mitigate future plant disease outbreaks and protect the global food supply, according to a team of researchers in a new commentary published in "Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences."
"The ...
Discovery of circadian rhythm gene in mice could lead to breakthroughs
2021-06-08
That internal nagging feeling that drives you to seek sleep at night and wake in the morning to eat, work, and play, is, it turns out, genetic, and it's not just in people. Nearly every living organism - from animals to plants as well as several microorganisms and fungi - has an internal body clock, or a circadian rhythm.
Yet, scientists have been perplexed out how these genes operate. Now, Virginia Tech scientists have taken a step closer to an answer thanks to the DNA of a mouse, a petri dish, and much patience. In a new study published in the journal Genes & Development, Shihoko Kojima, an assistant professor in the Department of Biological Sciences, part of the
Virginia Tech College of Science, ...
Study shows how taking short breaks may help our brains learn new skills
2021-06-08
In a study of healthy volunteers, National Institutes of Health researchers have mapped out the brain activity that flows when we learn a new skill, such as playing a new song on the piano, and discovered why taking short breaks from practice is a key to learning. The researchers found that during rest the volunteers' brains rapidly and repeatedly replayed faster versions of the activity seen while they practiced typing a code. The more a volunteer replayed the activity the better they performed during subsequent practice sessions, suggesting rest ...
From burglar alarms to black hole detectors
2021-06-08
Last year, Anupam Mazumdar, a physicist from the University of Groningen, jointly proposed an experiment together with colleagues from the UK that could conclusively prove whether gravity is a quantum phenomenon. This experiment would focus on observing two relatively large, entangled quantum systems in free fall. In a new article, published on 4 June in Physical Review Research, the scientists describe in more detail how two types of noise could be reduced. They suggest that quantum interference could be applied in the production of a sensitive instrument that could detect movements of objects ranging from butterflies to burglars and black holes.
Is gravity a quantum phenomenon? That is one of the major outstanding questions ...
Peace accord in Colombia has increased deforestation of biologically-diverse rainforest
2021-06-08
CORVALLIS, Ore. - Since the end of the long-running conflict in Colombia, large areas of forest have been rapidly converted to agricultural uses, suggesting the peace agreement presents a threat to conservation the country's rainforest, a new study from Oregon State University shows.
In 2016, Colombia officially signed a peace agreement ending the country's six-decade civil war, which mainly took place within the Andes-Amazon region, an extremely biodiverse rainforest and a critical biological corridor.
Some deforestation was expected after the peace accord was reached, but an analysis of 30 years of land transfers - a term used to describe changes in control and use of a parcel of land - showed a 40% increase in conversion from ...
Mapping a successful recovery
2021-06-08
Mining involves moving a lot of rock, so some mess is expected. However, mining operations can continue to affect ecosystems long after activity has ended. Heavy metals and corrosive substances leach into the environment, preventing wildlife and vegetation from returning to the area.
Fortunately, this damage can be reversed. A team of scientists, including UC Santa Barbara's Dave Herbst, investigated how river ecosystems respond to remediation efforts. The team combined decades of data from four watersheds polluted by abandoned mines. It took creative thinking to simplify ...
UIC research paves way for next-generation of crystalline material screening devices
2021-06-08
Researchers at the University of Illinois Chicago have developed a novel continuous-flow microfluidic device that may help scientists and pharmaceutical companies more effectively study drug compounds and their crystalline shapes and structures, which are key components for drug stability.
The device consists of a series of wells in which a drug solution - made up of an active pharmaceutical ingredient, or API, dissolved in solvent, such as water - can be mixed with an anti-solvent in a highly controlled manner. When mixed together, the two solutions allow for the API crystals to form a nucleus and grow. ...
Oral health needs among youth with a history of foster care
2021-06-08
According to estimates from the Children's Bureau, an agency within the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, there were 673,000 children in or entering foster care in the United States in 2019.
Data from the Minnesota Department of Human Services say that approximately 15,300 children experienced foster care in 2019. Minnesotan children of color were overrepresented compared to the general population, with Native American children 18 times more likely and Black children three times more likely to experience foster care than white children.
Most children in the foster care system have medical and dental coverage through Medicaid. However, despite ...
Pandemic teaching transitions back to classroom with lessons learned
2021-06-08
MELVILLE, N.Y., June 8, 2021 -- The COVID-19 pandemic created numerous changes and challenges for many people. In the education field, teachers were asked to re-create lesson plans and student interactivity in a virtual realm, something many had never experienced.
During the 180th Meeting of the Acoustical Society of America, which will be held virtually June 8-10, Andrew Morrison, from Joliet Junior College, will reveal lessons learned by educators during remote teaching caused by the pandemic and what techniques they can use in the return to classroom instruction. The session, "Lessons learned teaching through a pandemic and looking forward to a post-COVID-19 classroom," will take place Tuesday, June 8, at 1:45 p.m. Eastern U.S.
Morrison ...
Noisy homes during pandemic drive future design choices
2021-06-08
MELVILLE, N.Y., June 8, 2021 -- Due to strict lockdown measures around the globe during the coronavirus pandemic, many of us have seen and heard our family members and neighbors much more than ever before. Accordingly, many of us have been more annoyed by the sounds of our household than ever before.
During the 180th Meeting of the Acoustical Society of America, which will be held virtually June 8-10, Ayca Sentop Dümen and Konca Saher, from the Turkish Acoustical Society, will discuss the effects of pandemic-related noise on people's satisfaction with their homes and how this information can help inform future design choices. Their presentation, "Noise annoyance in dwellings during the first wave of Covid-19," will take place Tuesday, June ...
Optimizing immunization with Sanaria® PfSPZ-CVac malaria vaccine
2021-06-08
ROCKVILLE, MD, USA - June 8, 2021 - The PfSPZ malaria vaccines of Sanaria Inc. are unique in vaccine development as they are composed of weakened (attenuated) forms of the live parasite cells that cause malaria. These parasite cells are called eukaryotic cells and there are no vaccines against any infectious disease composed of such cells. Furthermore, there are no licensed vaccines against any infectious disease caused by a eukaryotic pathogen. Thus, Sanaria and its collaborators have had to take a step by step empirical approach to optimizing immunization with PfSPZ vaccines to achieve a safe, effective, durable, and broadly protective malaria vaccine.
Two recent landmark malaria vaccine studies ...
Study identifies major barriers to financing a sustainable ocean economy
2021-06-08
Financing a sustainable global ocean economy may require a Paris Agreement type effort, according to a new report from an international team of researchers led by the University of British Columbia.
That's because a significant increase in sustainable ocean finance will be required to ensure a sustainable ocean economy that benefits society and businesses in both developing and developed countries.
The report, published today - on World Ocean Day - identifies major barriers to financing such a sustainable ocean economy. This includes all ocean-based industries, like seafood production, shipping and renewable energy, and ecosystem goods and services, ...
Monarchs raised in captivity can orient themselves for migration, U of G study reveals
2021-06-08
Monarch butterflies raised indoors still know how to fly south if given enough time to orient themselves, according to new University of Guelph research.
The finding is good news for the many nature lovers and school students who raise monarchs and then set them free to help boost struggling numbers.
Monarchs are the only butterfly known to make a long-distance migration to warmer wintering grounds. While those born in the spring and early summer live only from two to six weeks, those that emerge in the late summer sense environmental signals that tell them to fly thousands of kilometres south, to central Mexico.
Recent ...
Machine learning reduces microscope data processing time from months to just seconds
2021-06-08
Ever since the world's first ever microscope was invented in 1590 by Hans and Zacharias Janssen --a Dutch father and son-- our curiosity for what goes on at the tiniest scales has led to development of increasingly powerful devices. Fast forward to 2021, we not only have optical microscopy methods that allow us to see tiny particles in higher resolution than ever before, we also have non-optical techniques, such as scanning force microscopes, with which researchers can construct detailed maps of a range of physical and chemical properties. IBEC's Nanoscale bioelectrical characterization group, led by UB Professor Gabriel Gomila, in collaboration with members of the IBEC's Nanoscopy for nanomedicine group, have been ...
AI could soon tell you, how often to see the eye doctor
2021-06-08
Age-related macular degeneration (AMD) is the most common cause of vision loss in people over 50. Up to 12 percent of those over 80 have the chronic disease. An estimated 16.4 million adults are affected by retinal vein occlusion (RVO) worldwide, a condition caused by a thrombosis of a retinal vein. It is the second most common cause of blindness from retinal vascular disease after diabetic retinopathy (DR). DR in turn is the leading cause of blindness in developed countries and affects up to 80 percent of people with more than 20 years of diabetes. It can lead ...
Scientists develop the 'evotype' to unlock power of evolution for better engineering biology
2021-06-08
A defining characteristic of all life is its ability to evolve. However, the fact that biologically engineered systems will evolve when used has, to date, mostly been ignored. This has resulted in biotechnologies with a limited functional shelf-life that fail to make use of the powerful evolutionary capabilities inherent to all biology.
Sim Castle, first author of the research, published in Nature Communications, and a PhD student in the School of Biological Sciences at Bristol, explained the motivation for the work: "The thing that has always fascinated me about biology is that it changes, it is chaotic, it adapts, it evolves. Bioengineers therefore do not just design static artefacts - they design living populations that ...
Mechanochemical peptide bond formation behind the origins of life
2021-06-08
The presence of amino acids on the prebiotic Earth is widely accepted, either coming from endogenous chemical processes or being delivered by extraterrestrial material. On the other hand, plausibly prebiotic pathways to peptides often rely on different aqueous approaches where condensation of amino acids is thermodynamically unfavorable. Now, chemists from the Ruđer Bošković Institute (RBI), in collaboration with colleagues from Xellia Pharmaceuticals, have shown that solid-state mechanochemical activation of glycine and alanine in combination with mineral surfaces leads to the formation of peptides. ...
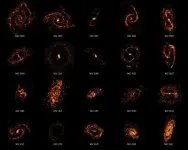
Cosmic cartographers map nearby Universe revealing the diversity of star-forming galaxies
2021-06-08
A team of astronomers using the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA) has completed the first census of molecular clouds in the nearby Universe, revealing that contrary to previous scientific opinion, these stellar nurseries do not all look and act the same. In fact, they're as diverse as the people, homes, neighborhoods, and regions that make up our own world.
Stars are formed out of clouds of dust and gas called molecular clouds, or stellar nurseries. Each stellar nursery in the Universe can form thousands or even tens of thousands of new stars during its lifetime. Between 2013 and 2019, astronomers on the PHANGS-- Physics at High Angular Resolution in Nearby GalaxieS-- project conducted the first systematic survey of 100,000 stellar nurseries ...
An unprecedented survey of the 'nurseries' where stars are born
2021-06-08
COLUMBUS, Ohio - Astronomers have taken a big step forward in understanding the dark and violent places where stars are born.
Over the past five years, an international team of researchers has conducted the first systematic survey of "stellar nurseries" across our part of the universe, charting the more than 100,000 of these nurseries across more than 90 nearby galaxies and providing new insights into the origins of stars.
"Every star in the sky, including our own sun, was born in one of these stellar nurseries," said Adam Leroy, associate professor of astronomy at The Ohio State University and one of ...
Organic molecules reveal clues about dying stars and outskirts of Milky Way
2021-06-08
Researchers from the University of Arizona will present findings from radio-astronomical observations of organic molecules at the 238th Meeting of the American Astronomical Society, or AAS, during a press conference titled "Molecules in Strange Places" at the 238th AAS Meeting on Tuesday, June 8, at 12:15 p.m. EDT.
A team led by Lucy Ziurys at the University of Arizona reports observations of organic molecules in planetary nebulae in unprecedented detail and spatial resolution. Using the Atacama Large Millimeter Array, or ALMA, Ziurys and her team observed radio emissions from hydrogen cyanide (HCN), formyl ion (HCO+) and carbon monoxide (CO) in five planetary nebulae: M2-48, M1-7, M3-28, K3-45 and K3-58.
The ...
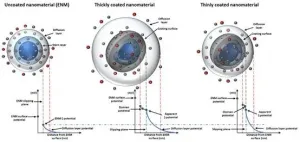
Online 'library of properties' helps to create safer nanomaterials
2021-06-08
Researchers have developed a 'library of properties' to help identify the environmental impact of nanomaterials faster and more cost effectively.
Whilst nanomaterials have benefited a wide range of industries and revolutionised everyday life, there are concerns over potential adverse effects - including toxic effects following accumulation in different organs and indirect effects from transport of co-pollutants.
The European Union H2020-funded NanoSolveIT project is developing a ground-breaking computer-based Integrated Approach to Testing and Assessment (IATA) for the environmental health and safety of nanomaterials.
Over ...
Food systems offer huge opportunities to cut emissions, study finds
2021-06-08
A new global analysis says that greenhouse-gas emissions from food systems have long been systematically underestimated--and points to major opportunities to cut them. The authors estimate that activities connected to food production and consumption produced the equivalent of 16 billion metric tons of carbon dioxide in 2018--one third of the human-produced total, and an 8 percent increase since 1990. A companion policy paper highlights the need to integrate research with efforts to reduce emissions. The papers, developed jointly by the UN Food and Agriculture Organization, NASA, New York University and experts at Columbia University, are part of a special issue of Environmental Research Letters on sustainable food systems.
The Center on Global Energy ...
Science and performing arts against stereotypes
2021-06-08
Stereotypes are knowledge structures integrated in our world representation, which have an influence on our decisions and which are hard to change. A team from the Faculty of Psychology of the University of Barcelona (UB) and the Bellvitge Biomedical Research Institute (IDIBELL), in collaboration with the Èpica Foundation - La Fura dels Baus analysed how a performing experience could have a positive impact in reducing the population's bias against physical illnesses. This performing experience is a pioneer one for it combines scientific training and theatre performance in the same working platform.
The study, published in the journal Frontiers in Psychology, shows that the participation ...
'Camouflage breakers' can find a target in less than a second
2021-06-08
After looking for just one-twentieth of a second, experts in camouflage breaking can accurately detect not only that something is hidden in a scene, but precisely identify the camouflaged target, a skill set that can mean the difference between life and death in warfare and the wild, investigators report.
They can actually identify a camouflaged target as fast and as well as individuals identifying far more obvious "pop-out" targets, similar to the concept used at a shooting range, but in this case using easy-to-spot scenarios like a black O-shaped target among a crowd of black C shapes.
In fact, the relatively rapid method for training civilian novices to become expert camouflage breakers developed by Medical College of Georgia neuroscientist ...
'Significant reduction' in GP trainee burnout following mindfulness programme
2021-06-08
Medics training to be GPs reported positive improvement in burnout and resilience after completing a mindfulness course specially designed for doctors
The participants in the study by Warwick Medical School also saw improvements in their wellbeing and stress
By improving the mental wellbeing of trainees the researchers hope to better prepare them for the challenges of general practice and the impact of Covid-19 on the profession
Supports the wider adoption of mindfulness in medical training and the need for larger studies
Medics training to become general practitioners reported a significant positive improvement in their mental wellbeing after participating in a specially-designed mindfulness programme, a study from University of Warwick researchers ...
[1] ... [2231]
[2232]
[2233]
[2234]
[2235]
[2236]
[2237]
[2238]
2239
[2240]
[2241]
[2242]
[2243]
[2244]
[2245]
[2246]
[2247]
... [8815]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.