Researchers design next-generation photodetector
The advanced photodetector could be used in night vision, optical communication, and thermal and medical imaging
2021-02-02
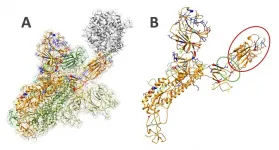
(Press-News.org) Northwestern University researchers have developed a new approach to quantum device design that has produced the first gain-based long-wavelength infrared (LWIR) photodetector using band structure engineering based on a type-II superlattice material.
This new design, which demonstrated enhanced LWIR photodetection during testing, could lead to new levels of sensitivity for next-generation LWIR photodetectors and focal plane array imagers. The work could have applications in earth science and astronomy, remote sensing, night vision, optical communication, and thermal and medical imaging.
"Our design can help meet the urgent demand for ultra-sensitive photodetectors," said Manijeh Razeghi, Walter P. Murphy Professor of Electrical and Computer Engineering, who led the study. "The architecture uses a unique type-II superlattice material that optimizes LWIR photodetectors to run with low power, higher optical gain, and excellent stability."
While recent advances in semiconductor materials and devices have led to notable progress in the development of photodetectors that can capture LWIR wavelengths, state-of-the-art LWIR detection technology still suffers from shortcomings. Many photodetectors rely on mercury cadium telluride as a semiconductor, a material that can achieve excellent sensitivity and speed, but also produces low photocurrent gain and excess spectral noise.
Razeghi, who directs Northwestern's Center for Quantum Devices (CQD), designed the photodetector using a type-II superlattice, a material system known for its outstanding growth uniformity and exceptional band structure engineering -- the ability to control the band gap in a material, the space where no electron charge is present. This made it an optimal alternative semiconductor to mercury cadmium telluride for a LWIR system. Her team then applied the new material to a heterojunction phototransistor device structure, a detection system known for its high stability, but one previously limited to short-wave and near infrared detection.
During testing, the type-II superlattice allowed each part of the photodetector to be carefully tuned to use the phototransistor to achieve high optical gain, low noise, and high detectivity.
"The material's demonstrated flexibility allows for meticulous quantum mechanics-based band structure engineering for the heterostructure design, making it a versatile candidate to push the limits of infrared detection," Razeghi said.
The research builds on CQD's long history of work developing and understanding the physics of quantum semiconductor devices for novel applications, from military and earth science to medical systems. This novel artificial quantum structure opens the door toward next-generation high-gain photodetectors with potential for high-speed applications with ultra-sensitive detection capabilities for single photon detection.
INFORMATION:
A paper outlining the work, titled "Band-structure-engineered High-gain LWIR Photodetector Based on a Type-II Superlattice," was published January 14 in the journal Light: Science and Applications.
The study was supported by the Defense Advanced Research Project Agency (DARPA), US Army Future's Command, US Army Night Vision Laboratory, US Air Force Research Laboratory, and NASA Goddard Space Flight Center.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-02-02
Oxford, February 2, 2021 - In an upcoming issue of the Journal of Medical Imaging and Radiation Sciences, published by Elsevier, undergraduate researchers from the University of Alberta's Radiation Therapy Program in the Faculty of Medicine and Dentistry describe how LGBTQ2SPIA+ patients face unique cancer risks, including fear of discrimination, higher incidence of certain cancer sites, and lower screening rates, resulting in more cancers detected at later stages.
"I understand that there are different gender pronouns, I do not understand them all."
To discover the knowledge, attitudes, and practice behaviors of the healthcare professionals treating these patients, the authors surveyed ...
2021-02-02
Beaten ballots: political participation dynamics amidst police interventions is the title of the academic article by Toni Rodon and Marc Guinjoan, lecturers of Political Sciences at UPF and the UB, respectively, which seeks to look in greater depth at the effects of police interventions regarding political participation, taking the "repression-mobilization" nexus debate as a starting point.
The study, published recently in the Cambridge University Press journal Political Science Research and Methods, focuses on the analysis of the referendum on independence held in Catalonia on 1 October 2017, when despite the police crackdown, 2,286,217 people voted, representing 44% of ...
2021-02-02
Experts predict that autonomous vehicles (AVs) will eventually make our roads safer since the majority of accidents are caused by human error. However, it may be some time before people are ready to put their trust in a self-driving car.
A new study in the journal Risk Analysis found that people are more likely to blame a vehicle's automation system and its manufacturer than its human driver when a crash occurs.
Semi-autonomous vehicles (semi-AVs), which allow humans to supervise the driving and take control of the vehicle, are already on the ...
2021-02-02
Recent global calamities - the pandemic, wildfires, floods - are spurring interdisciplinary scientists to nudge aside the fashionable First Law of Geography that dictates "everything is related to everything else, but near things are more related than distant things."
Geography, and by association, ecology, has largely followed what's known as Tobler's Law, which took hold in the early 1970s. But then came the novel coronavirus apparently has leapt from wildlife meat markets in China to the world in a matter of months. Global climate change creates conditions ripe for infernos in the North American west and Australia. ...
2021-02-02
EL PASO, Texas - An effort led by Lin Li, Ph.D., assistant professor of physics at The University of Texas at El Paso, in collaboration with students and faculty from Howard University, has identified key variants that help explain the differences between the viruses that cause COVID-19 and Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome (SARS).
A team comprised of researchers from UTEP and the historically Black research university in Washington, D.C., discovered valuable data in comparing the fundamental mechanisms of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus (SARS-CoV) and SARS-CoV-2 -- also known as COVID-19 -- to better understand how ...
2021-02-02
CORVALLIS, Ore. - Extensive sea ice covered the world's oceans during the last ice age, which prevented oxygen from penetrating into the deep ocean waters, complicating the relationship between oxygen and carbon, a new study has found.
"The sea ice is effectively like a closed window for the ocean," said Andreas Schmittner, a climate scientist at Oregon State University and co-author on the paper. "The closed window keeps fresh air out; the sea ice acted as a barrier to keep oxygen from entering the ocean, like stale air in a room full of people. If you open the window, oxygen ...
2021-02-02
Amazon's search algorithm gives preferential treatment to books that promote false claims about vaccines, according to research by UW Information School Ph.D. student Prerna Juneja and Assistant Professor Tanu Mitra.
Meanwhile, books that debunk health misinformation appear lower in Amazon's search results, where they are less likely to be seen, the researchers wrote in a paper that was recently accepted to CHI, the top annual conference on human-computer interaction.
In their paper, Juneja and Mitra noted that Amazon has faced criticism for not regulating health-related products on its platform. They conducted audits to determine how much health misinformation is present in Amazon's recommendations ...
2021-02-02
The lockdowns and reduced societal activity related to the COVID-19 pandemic affected emissions of pollutants in ways that slightly warmed the planet for several months last year, according to new research led by the National Center for Atmospheric Research (NCAR).
The counterintuitive finding highlights the influence of airborne particles, or aerosols, that block incoming sunlight. When emissions of aerosols dropped last spring, more of the Sun's warmth reached the planet, especially in heavily industrialized nations, such as the United States and Russia, that normally pump high amounts of aerosols into the atmosphere.
"There was a big decline in emissions from the most polluting industries, and that had immediate, short-term effects on temperatures," said ...
2021-02-02
Yale researchers are developing a skin cancer treatment that involves injecting nanoparticles into the tumor, killing cancer cells with a two-pronged approach, as a potential alternative to surgery.
The results are published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
"For a lot of patients, treating skin cancer is much more involved than it would be if there was a way to effectively treat them with a simple procedure like an injection," said Dr. Michael Girardi, professor and vice chair of dermatology at Yale School of Medicine and senior author of the study. "That's always been a holy grail in dermatology -- to find a simpler way to treat skin cancers such as basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma."
For the treatment, tumors are injected ...
2021-02-02
A new study from scientists of the Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Biology in Plön, Germany, and the Chinese Academy of Sciences in Beijing shows that the potential genetic burden of mutations arising from retrogenes is significantly greater than originally thought.
Genetic information is stored in DNA and transcribed as mRNA. The mRNA is usually translated into proteins. However, it has long been known that mRNA can also be reverse transcribed to DNA and integrated back into the genome. Such cases are referred to as retrogenes. In an article, a team from the Max Planck Institute for ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Researchers design next-generation photodetector
The advanced photodetector could be used in night vision, optical communication, and thermal and medical imaging