Early warning system for COVID-19 gets faster through wastewater detection and tracing
2021-06-04
Toronto -- Math continues to be a powerful force against COVID-19.
Its latest contribution is a sophisticated algorithm, using municipal wastewater systems, for determining key locations in the detection and tracing of COVID-19 back to its human source, which may be a newly infected person or a hot spot of infected people. Timing is key, say the researchers who created the algorithm, especially when COVID-19 is getting better at transmitting itself, thanks to emerging variants.
"Being quick is what we want because in the meantime, a newly-infected person can infect others," said Oded Berman, a professor of operations management and statistics at the University of Toronto's Rotman School of Management.
This latest ...
Remote patient monitoring may reduce need to hospitalize cancer patients
2021-06-04
ROCHESTER, Minn. -- A study by researchers at Mayo Clinic Cancer Center has found that cancer patients diagnosed with COVID-19 who received care at home via remote patient monitoring were significantly less likely to require hospitalization for their illness, compared to cancer patients with COVID-19 who did not participate in the program. Results of the study were presented Friday, June 4, at the American Society of Clinical Oncology Annual Meeting and published in the Journal of Clinical Oncology.
"For our study, we evaluated 224 Mayo Clinic patients with cancer who were found to have COVID-19 through standardized screening prior to receiving cancer treatment, or due to symptoms or close exposure," says Tufia Haddad, ...
Vitamin D may not protect against COVID, as previously suggested
2021-06-04
While previous research early in the pandemic suggested that the vitamin D cuts the risk of contracting COVID-19, a new study from McGill University finds there is no genetic evidence that the vitamin works as a protective measure against the coronavirus.
"Vitamin D supplementation as a public health measure to improve outcomes is not supported by this study. Most importantly, our results suggest that investment in other therapeutic or preventative avenues should be prioritized for COVID-19 randomized clinical trials," say the authors.
To assess the relationship between vitamin D levels and COVID-19 ...
Collaboration controls killers
2021-06-04
Effector and killer T cells are types of immune cells. Their job is to attack pathogens and cancers. These cells can also go after normal cells causing autoimmune diseases. But, if harnessed properly, they can destroy cancer cells that resist treatment.
Scientists at St. Jude wanted to understand how these T cells are controlled. They looked at enhancers, sequences of DNA that when bound to certain proteins determine how genes are turned on or off.
The scientists found that enhancers of a gene named Foxp3 work as a pair to keep effector and killer T cells in check. The enhancers working together is essential.
"These ...
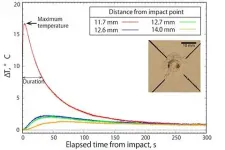
Did heat from impacts on asteroids provide the ingredients for life on Earth?
2021-06-04
A research group from Kobe University has demonstrated that the heat generated by the impact of a small astronomical body could enable aqueous alteration (*1) and organic solid formation to occur on the surface of an asteroid. They achieved this by first conducting high-velocity impact cratering experiments using an asteroid-like target material and measuring the post-impact heat distribution around the resulting crater. From these results, they then established a rule-of-thumb for maximum temperature and the duration of the heating, and developed a heat ...
Songbirds can control single vocal muscle fibers when singing
2021-06-04
The melodic and diverse songs of birds frequently inspire pop songs and poems, and have been for centuries, all the way back to Shakespeare's "Romeo and Juliet" or "The Nightingale" by H.C. Andersen.
Despite our fascination with birdsong, we are only beginning to figure out how this complicated behavior is being produced and which extraordinary specializations enabled songbirds to develop the diverse sound scape we can listen to every morning.
Songbirds produce their beautiful songs using a special vocal organ unique to birds, the syrinx. It is surrounded by muscles that contract with superfast speed, two orders of magnitude faster than e.g. human leg muscles.
"We found that songbirds have incredible fine control of their song, including frequency ...
ADHD medications associated with reduced risk of suicidality in certain children
2021-06-04
Philadelphia, June 4, 2021--ADHD medications may lower suicide risk in children with hyperactivity, oppositional defiance and other behavioral disorders, according to new research from the Lifespan Brain Institute (LiBI) of Children's Hospital of Philadelphia (CHOP) and the University of Pennsylvania. The findings, published today in JAMA Network Open, address a significant knowledge gap in childhood suicide risk and could inform suicide prevention strategies at a time when suicide among children is on the rise.
"This study is an important step in the much-needed effort of childhood suicide prevention, ...
Public awareness, willingness to use gun violence restraining orders
2021-06-04
What The Study Did: This survey study in California assesses what the public knows about extreme risk protection orders and if people are willing to use them to prevent firearm-related harm, both in general and when a family member is at risk, and if not, why not. The orders temporarily suspend firearm and ammunition access by individuals a judge has deemed to be at substantial risk of harming themselves or others.
Authors: Nicole Kravitz-Wirtz, Ph.D., M.P.H., of the University of California Davis School of Medicine in Sacramento, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamahealthforum.2021.0975)
Editor's Note: The article includes funding/support disclosures. Please ...
Most Californians unaware of law to prevent gun violence but would support using it
2021-06-04
(SACRAMENTO, Calif.) -- Extreme risk protection orders, also known as END ...
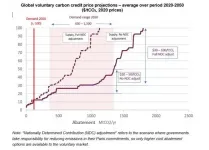
Ten-fold increase in carbon offset cost predicted
2021-06-04
The cost of offsetting corporate carbon emissions needs to increase ten-fold to drive meaningful climate action, says a landmark report by Trove Research and UCL.
Current prices of carbon offsets are unsustainably low and need to increase significantly to encourage greater investment in new projects that remove carbon from the atmosphere.
If prices stay low companies could be accused of greenwashing their emissions, as real emissions reduction and carbon removals are more costly than today's prices.
Prices of carbon credits used by companies to offset their emissions are currently low, due to an excess of supply built up over several years, together with issues over whether payments for credits really result in additional reductions ...
Multisensory facilitation near the body in all directions
2021-06-04
Details:
Peripersonal space (PPS) is defined as the space near the body within which we can reach external objects and be reached by others. It has the special function of multisensory facilitation. A research team at Toyohashi University of Technology, in collaboration with researchers at Keio University and the University of Tokyo, investigated PPS representation in the front, rear, left, and right directions by audio-tactile multisensory integration using tactile detection with task-irrelevant approaching and receding sounds. They found that the tactile stimulus was detected faster near the body space than far from it when sound approached from any direction, but not when it receded. Thus, peripersonal representations exist with approaching sound, irrespective ...
Self-excising designer proteins report isoform expression
2021-06-04
Proteins are the key players in our cellular processes. Their generation follows principles called transcription and translation. First, DNA copies its genetic information to messenger RNA (mRNA), which then determines the sequence in a chain of amino acids, which finally fold into a protein. The reality, however, is more complex: More than 90 per cent of our genes do not result in only one mRNA and then one protein, but a process called alternative splicing produces several mRNA variants, only some of which are then translated into a specific protein isoform in a specific cell at a given time. Conventional techniques to detect alternative splicing are mostly single time-point measurements that are work-intense and cannot reliably ...
Geostationary Earth Orbit Hyperspectral Infrared Radiance data improve local severe storm forecasts proofed by using a new Hybrid OSSE method
2021-06-04
Since the era of meteorological satellites began in the 1950s, continuous remote sensing instrument improvements have elevated Earth science and have significantly increased available atmospheric observations. Likewise, scientists have made considerable advancements in understanding Earth's atmosphere, climate, and environment. Furthering growth of atmospheric science within the last 20 years, satellite-based infrared (IR) sounders onboard low Earth orbiting (LEO) satellites have provided high spectral (or hyperspectral) IR radiances. These sounders can determine ...
Gene protection for COVID-19 identified
2021-06-04
The first evidence of a genetic link explaining why some people who catch Covid-19 don't become sick has been discovered
A scientific and medical team led by Newcastle University, UK, has demonstrated that the gene, HLA-DRB1*04:01, is found three times as often in people who are asymptomatic. This suggests that people with this gene have some level of protection from severe Covid.
The study, funded by Innovate UK, the UK's innovation agency, compared asymptomatic people to patients from the same community who developed severe Covid but had no underlying illnesses, and is published in the HLA journal.
The study team believe this is the first clear evidence of genetic ...
How to retard time for cells
2021-06-04
They recently published their findings in the renowned journal "Advanced Materials". Cells are not only our biological building blocks, but also highly dynamic, active systems. The research group led by Professor Käs has succeeded in significantly reducing these dynamics with heavy water, without damaging the cells.
"Generally, a lot of people know heavy water for its important technical use in nuclear power plants. We took a different approach here and were able to show that for cells, time - or, more specifically, their dynamics - can be significantly slowed down in the presence of heavy ...
Using HPC and experiment, researchers continue to refine graphene production
2021-06-04
Graphene may be among the most exciting scientific discoveries of the last century. While it is strikingly familiar to us--graphene is considered an allotrope of carbon, meaning that it essentially the same substance as graphite but in a different atomic structure--graphene also opened up a new world of possibilities for designing and building new technologies.
The material is two-dimensional, meaning that each "sheet" of graphene is only 1 atom thick, but its bonds make it as strong as some of the world's hardest metal alloys while remaining lightweight and flexible. This valuable, unique mix of properties have piqued the interest of scientists from a wide range of fields, leading to research in using graphene for next-generation ...
Attentive listening helps teens open up, study finds
2021-06-04
Engaged listening techniques such as eye contact, nodding and using key words to praise openness helps teenagers when they admit bad behaviour and share hurt feelings with their parents, a new study has shown.
University of Reading and Haifa researchers asked 1001 13 to 16-year-olds to watch a staged conversation between a parent and teenager about a difficult situation, with the parent adopting different body language and listening behaviour in different versions.
The participants who watched the versions where the parent was visibly attentive stated that they would have felt better about themselves as the teenager and would be more likely to open up about their ...
What we know about water may have just changed dramatically
2021-06-04
Water is weird - and yet so important. In fact, it is one of the most unusual molecules on Earth. It boils at a temperature it shouldn't. It expands and floats when it is in the solid-state. Its surface tension is higher than it should be. Now, new research published in the journal Nature has added one other equally strange property to water's list of oddities. The implications of this new revelation could have a remarkable impact on all water-related processes from water purification to drug manufacturing.
Stephen Cronin, professor of electrical and computer engineering at USC Viterbi School of Engineering, ...
Targeted 'radioligand' improves survival in advanced prostate cancer
2021-06-04
Cancer researchers say they have established a new, life-extending treatment option for men with prostate cancer that has spread and become resistant to hormone therapy. The injected treatment combines a targeting compound with a radioactive isotope to irradiate and kill cancer cells.
An international clinical trial sponsored by Endocyte, Inc., a Novartis company tested the targeted radioligand therapy in study participants with advanced prostate cancer. All subjects had cancers that had spread to other organs and continued to progress after previous treatment with two kinds of drugs, androgen axis inhibitors and taxanes. The experimental treatment significantly extended survival, delayed ...
MLB 'FEVER' -- improved elbow MRI view for Major League Baseball pitchers
2021-06-04
Leesburg, VA, June 4, 2021--According to a pilot study published in ARRS' American Journal of Roentgenology (AJR), the flexed elbow valgus external rotation (FEVER) view can improve MRI evaluation of the ulnar collateral ligament (UCL) in Major League Baseball (MLB) pitchers.
"The increased joint space width confirms elbow valgus stress with FEVER view," wrote corresponding author Thomas Knoblauch at the University of Nevada Las Vegas. "Diagnostic confidence increased, and additional UCLs were identified as abnormal."
Due to repetitive extreme valgus stress during overhead throwing maneuvers, UCL injuries remain common in throwing athletes. Because standard positioning for elbow MRI ...
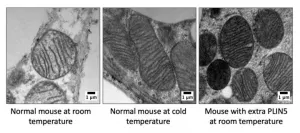
Giving brown fat a boost to fight type 2 diabetes
2021-06-04
DALLAS - June 4, 2021 - Increasing a protein concentrated in brown fat appears to lower blood sugar, promote insulin sensitivity, and protect against fatty liver disease by remodeling white fat to a healthier state, a new study led by UT Southwestern scientists suggests. The END ...
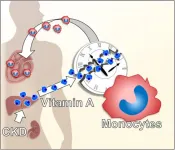
How do bad kidneys lead to heart disease? Broken cellular clocks provide new clues
2021-06-04
Fukuoka, Japan--According to the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017, close to nine percent of the global population lives with some form of chronic kidney disease, or CKD. Not only does the condition affect renal function, CKD has long been associated with increased risk of cardiovascular disease.
Now, in a new study that could aid the development of therapeutic drugs to reduce these cardiac complications, researchers led by Kyushu University have found an underlying molecular pathway that can explain how chronic kidney disease induces heart failure.
Studying mice, the researchers found that a key driver is the dysfunction of a type of white blood cell called a ...
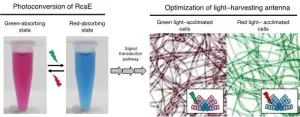
Structural uniqueness of the green- and red-light sensing photosensor in cyanobacteria
2021-06-04
Overview:
Certain cyanobacteria can change the absorbing light colors for photosynthesis using a green- and red-light sensing photosensor protein. A Japanese research group elucidated the molecular structure of RcaE, a representative member of the photosensors. They revealed the unique conformation of the bilin chromophore and the unique protein structure that potentially functions as a proton transfer route to bilin. They also demonstrated that RcaE undergoes protonation and deprotonation of the bilin chromophore during the green and red photoconversion. These results provide insights into how cyanobacteria evolved photosensors with diverse spectral sensitivities and contribute to the development of new photoswitches of ...
Corals tell Arabian Sea story of global warming
2021-06-04
Coral insights into 1,000 years of seasonal changes in the Arabian Sea warn of significant impacts caused by global warming.
Every year, the southwesterly winds of the summer monsoon sweep down the Arabian Peninsula, pushing the surface waters of the Arabian Sea away from the coast and driving an upwelling of deep waters to the surface. This rising seawater is colder and less saline than the surface water and is rich in nutrients, providing energy for the various organisms living in the Arabian Sea and Indian Ocean.
Scientists from Japan, Taiwan and Germany, including coral reef scientist Dr. Tsuyoshi Watanabe of Hokkaido University, have uncovered evidence from corals off the coast of Oman suggesting that global warming is causing changes to the Arabian Sea that could impact the ...
Don't like your greens? Blame it on Brassica domestication
2021-06-04
Delicious to some, but a bitter bane to others' taste buds, vegetables like broccoli rabe, bok choy and turnips are a dinner staple ---and picky eater conflict --- around the world.
It all likely started in the mountains near present-day Afghanistan, where humans first domesticated turnips 3,500 to 6,000 years ago, according to a new study recently published in the journal Molecular Biology and Evolution. University of Wisconsin-Madison Professor of Botany Eve Emshwiller and her former graduate student Alex McAlvay (now an assistant curator assistant ...
[1] ... [2247]
[2248]
[2249]
[2250]
[2251]
[2252]
[2253]
[2254]
2255
[2256]
[2257]
[2258]
[2259]
[2260]
[2261]
[2262]
[2263]
... [8818]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.