Chill out: Advanced solar tech runs cooler and lasts longer
2021-05-10
Australian photovoltaics researchers have made a 'cool' discovery: Singlet fission and tandem solar cells - two innovative ways to generate solar power more efficiently - also help to lower operating temperatures and keep devices running for longer.
Tandem cells can be made from a combination of silicon - the most commonly used photovoltaics material - and new compounds like perovskite nanocrystals, which can have a larger bandgap than silicon and help the device to capture more of the solar spectrum for energy generation.
Singlet fission, meanwhile, is a technique that produces twice the electronic charge carriers than normal for each photon of light that's absorbed. ...
Firefighting chemical found in sea lion and fur seal pups
2021-05-10
A chemical that the NSW government has recently partially banned in firefighting has been found in the pups of endangered Australian sea lions and in Australian fur seals.
The finding represents another possible blow to Australian sea lions' survival. Hookworm and tuberculosis already threaten their small and diminishing population, which has fallen by more than 60 percent over four decades.
The new research - part of a long-term health study of seals and sea lions in Australia - identified the chemicals in animals at multiple colonies in Victoria and South Australia from 2017 to 2020.
As well as in pups, the chemicals (Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances - 'PFAS') were detected in juvenile ...
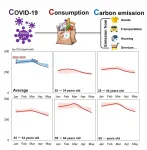
Rapid lifestyle changes during early COVID-19 pandemic had no impact on climate change
2021-05-10
Despite the rapid and significant changes in consumption patterns witnessed during the initial months of the COVID-19 pandemic, Japanese households maintained their normal levels of greenhouse gases emissions. The "anthropause" -- reduction of human activity due to the pandemic -- made headlines last summer, but factory shutdowns and broken global supply chains did not translate into the adoption of eco-friendly lifestyles for the average household.
"During the early COVID-19 period, we could witness lifestyle changes happening around us fast, so we decided to explore the environmental impacts of these lifestyle changes. Some other research at that period was showing that the production-side greenhouse gases emissions ...
Researchers in Sweden develop light emitters for quantum circuits
2021-05-10
The promise of a quantum internet depends on the complexities of harnessing light to transmit quantum information over fiber optic networks. A potential step forward was reported today by researchers in Sweden who developed integrated chips that can generate light particles on demand and without the need for extreme refrigeration.
Quantum computing today relies on states of matter, that is, electrons which carry qubits of information to perform multiple calculations simultaneously, in a fraction of the time it takes with classical computing.
The co-author of the research, Val Zwiller, Professor ...
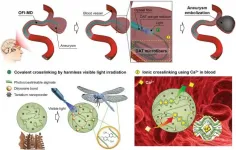
Treating cerebral aneurysms with a new filling method
2021-05-10
Cerebral aneurysms are malformations caused by abnormalities on the walls of blood vessels in the brain. When these blood vessels rupture, about 30% of the sufferers die on the spot, giving these the rightful label of 'ticking bombs in the head'. Recently, a research team at POSTECH has come up with a new treatment that can disassemble these time bombs by filling the aneurysm in blood with a new method.
In order to overcome the shortcomings of coil embolization, POSTECH's joint research team (Professor Joonwon Kim and Dr. Jongkyeong Lim of the Department of Mechanical Engineering with Professor ...
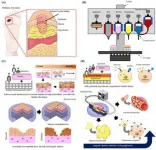
Engineering diseased human skin in vitro
2021-05-10
The skin, which covers the surface of the human body, is its largest organ. It is the first organ to show changes stemming from organ or physiological activity. It is especially common for diabetic patients to suffer from skin diseases or infections. Recently, a POSTECH research team has succeeded in creating a 3D artificial skin that enables observation of skin diseases of diabetic patients.
A research team led by Professor Dong-Woo Cho and Minjun Ahn of POSTECH's Department of Mechanical Engineering and Professor Byoung Soo Kim of School of Biomedical Convergence Engineering at Pusan National University has ...
One-year results from the FUTURE-II trial
2021-05-10
A decade already passed from the first use of bioresorbable vascular scaffold in percutaneous coronary interventions. The first studies - by using surrogate endpoints - showed some superiority of BRS vs. metallic drug-eluting stent in terms of the so-called vascular restoration therapy with recovery of vasomotion and vascular pulsatility when the scaffold was absorbed.
Nevertheless, after these first promising findings, larger and randomized clinical trials and subsequent meta-analyses, powered to hard clinical endpoints, showed that bioresorbable vascular scaffolds, made ...
3D printing lays the foundation for a new range of diagnostic tests
2021-05-10
Researchers at KU Leuven (Belgium) have developed a 3D printing technique that extends the possibilities of lateral flow testing. These tests are widespread in the form of the classic pregnancy test and the COVID-19 self-tests. With the new printing technique, advanced diagnostic tests can be produced that are quick, cheap, and easy to use.
The COVID-19 pandemic has made everyone aware of the importance of rapid diagnosis. The sale of self-tests in pharmacies has been permitted in Belgium since the end of March. This self-test is a so-called lateral flow test. Using a ...
Analysis of autopsy, toxicological and psychiatric reports of Portugal's first major forensic case
2021-05-10
Analysis of The Autopsy, Toxicological, and Psychiatric Reports of Portugal's First Major Forensic Case: Part III
https://doi.org/10.1080/20961790.2021.1898079
Announcing a new article publication for Forensic Sciences Research journal. In this review article the author Ricardo Jorge Dinis-Oliveira of the University Institute of Health Sciences (IUCS)-CESPU, Gandra, Portugal continues a three-part investigation of the "Crime of Flores Street" one of the most famous cases of poisoning which occurred in Portugal in the late 19th century. The case demonstrated the weaknesses of the Portuguese medicolegal system and attests to the importance of toxicological analysis. The first article ...
Biomarker detects severe COVID-19 early on
2021-05-10
Most people who are infected with SARS-CoV-2 develop no or only mild symptoms. However, some patients suffer severe life-threatening cases of COVID-19 and require intensive medical care and a ventilator to help them breathe. Many of these patients eventually succumb to the disease or suffer significant long-term health consequences. To identify and treat these patients at an early stage, a kind of "measuring stick" is needed - predictive biomarkers that can recognize those who are at risk of developing severe COVID-19.
First biomarker to predict severity of disease
A team led by Professor Burkhard Becher at the Institute of Experimental Immunology at the University of Zurich, working with researchers from Tübingen, Toulouse and Nantes, has now discovered such ...
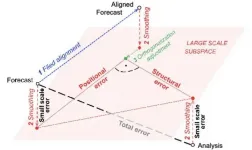
Unraveling positional and structural errors in numerical weather forecast models
2021-05-10
Due to the chaotic nature of the atmosphere, weather forecasts, even with ever improving numerical weather prediction models, eventually lose all skill. Meteorologists have a strong desire to better understand this process as they try to trace forecast error back to observational gaps and to provide a means for improvement.
Root mean square error (rms, or its square, the variance distance) is often used to measure differences between simulated and observed fields. In this case, scientists measured the distance between a model forecast field within its grid and the verifying analysis field ...
TB immune response discovery could significantly reduce disease harm
2021-05-10
A pioneering study by UCL scientists has discovered the presence of a harmful inflammatory protein in patients with symptomatic tuberculosis (TB).
Researchers say, by targeting the IL-17 cytokine, a component produced naturally by the immune system in response to infection, excessive and damaging lung inflammation caused by TB may be significantly reduced to help speed up patient recovery.
TB is an infection caused by the bacterium Mycobacterium tuberculosis and is the leading cause of death from infections worldwide. The World Health Organisation estimates that 1.4 million people died of TB disease worldwide in 2019.
Explaining the experimental study, lead author Dr Gabriele Pollara (UCL Division of Infection & Immunity), ...
Once we're past the fear stage, where do we place the blame for the COVID-19 pandemic?
2021-05-10
In a time of a global crisis such as the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic, it is easy to note how people move through different phases to buckle up for such unprecedented and arduous times.
In the very beginning of the pandemic last year, we observed "an epidemic of fear", where it was all about the calamitous nature of a totally unknown virus and its worrying contagiousness and mortality rate. A few months later, with lockdown and restrictions already in place across the world, the fear was replaced by "an epidemic of explanations", where people even in their naivety, started to seek a sense of comfort by ...
Universal equation for explosive phenomena
2021-05-10
Climate change, a pandemic or the coordinated activity of neurons in the brain: In all of these examples, a transition takes place at a certain point from the base state to a new state. Researchers at the Technical University of Munich (TUM) have discovered a universal mathematical structure at these so-called tipping points. It creates the basis for a better understanding of the behavior of networked systems.
It is an essential question for scientists in every field: How can we predict and influence changes in a networked system? "In biology, one example is the modelling of coordinated neuron activity," says Christian Kühn, professor of multiscale and stochastic dynamics ...
Why Germany's coal compromise failed to end the debate
2021-05-10
Can expert commissions develop solutions for controversial issues that will enjoy broad democratic support? A team of researchers from the Institute for Advanced Sustainability Studies (IASS) has analysed the work of Germany's "Coal Exit Commission" using a set of new criteria. While the authors view positively the Commission's success in reaching a compromise, they criticise its failure to deliver an outcome that promotes the common good, particularly with respect to the high cost of the coal exit and its unambitious contribution towards Germany's climate goals, as well as the lack of public participation.
On 29 April 2021, Germany's Federal Constitutional Court ruled that the provisions of the Climate Protection Act (2019) are incompatible ...
Errors at the start of life
2021-05-10
Only one in three fertilizations leads to a successful pregnancy. Many embryos fail to progress beyond early development. Cell biologists at the Max Planck Institute (MPI) for Biophysical Chemistry in Göttingen (Germany), together with researchers at the Institute of Farm Animal Genetics in Mariensee and other international colleagues, have now developed a new model system for studying early embryonic development. With the help of this system, they discovered that errors often occur when the genetic material from each parent combines immediately after fertilization. This is due to a remarkably inefficient process.
Human somatic cells typically have 46 chromosomes, which together carry ...
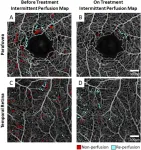
Mount Sinai ophthalmologists develop new technique to assess progression of sickle cell retinopathy
2021-05-10
Ophthalmologists at New York Eye and Ear Infirmary of Mount Sinai have created a new technique to evaluate patients with sickle cell retinopathy and assess the disease before it progresses and leads to permanent vision loss.
Using optical coherence tomography (OCT) angiography--an advanced imaging system that captures the motion of red blood cells in blood vessels non-invasively--the researchers discovered that sequential imaging of affected retinal blood flow in sickle cell patients can help assess how the disease is progressing and how effective their treatment is for reducing focal vascular strokes. Their study was published ...
Conservationists concerned about illegal hunting and exploitation of porcupines in Indonesia
2021-05-10
Porcupines are frequently traded across Asia, and Indonesia, home to five species, is no exception. They are targeted for a number of reasons: their meat as an alternative source of protein, their bezoars consumed as traditional medicine, and their quills used as talismans and for decorative purposes.
A new study examining seizure data of porcupines, their parts and derivatives in Indonesia found a total of 39 incidents from January 2013 to June 2020 involving an estimated 452 porcupines. The research was published in the open-access, peer-reviewed journal Nature Conservation.
There are no harvest quotas for any porcupine species in Indonesia, which makes all hunting and trade in porcupines illegal. Of the five species found in the country, only the Sunda porcupine (Hystrix javanica) ...
Understanding family members' grief for a living loved one
2021-05-10
COLUMBUS, Ohio - The symptoms of grief people feel for a loved one facing a life-limiting illness fluctuate over time, a new study found - suggesting that individuals can adjust to their emotional pain, but also revealing factors that can make pre-loss grief more severe.
Researchers examined changes in the severity of pre-loss grief symptoms in people whose family members had either advanced cancer or dementia.
The study is the first to document pre-loss grief at two points in time, and found that about 70% of participants' symptoms decreased over a month. However, compared to initial symptoms reported by participants, ...
Prenatal exposure to famine heightens risk for later being overweight
2021-05-10
An analysis of historical medical records found that men who were prenatally exposed during early gestation to the Dutch famine of 1944-1945 were 30 percent more likely to be overweight with a Body Mass Index of 25 or over at age 19, compared to a similar group not exposed to the famine. Professor L. H. Lumey at Columbia University Mailman School of Public Health led the study, which is published in the International Journal of Obesity. The study confirms evidence on the health risks of prenatal famine exposure, which also includes diabetes and schizophrenia.
The mechanism by which famine exposure raises the risk for later excess weight is still unknown. The researchers speculate that famine exposure could lead to changes in DNA methylation that stimulate being overweight. Or that surviving ...
Microneedle patch delivers antibiotics locally in the skin
2021-05-10
MRSA skin infections are often treated with intravenous injection of antibiotics, which can cause significant side effects and promote the development of resistant bacterial strains. To solve these problems, researchers at Karolinska Institutet in Sweden are developing a microneedle patch that delivers antibiotics directly into the affected skin area. New results published in Advanced Materials Technologies show that the microneedle patch effectively reduces MRSA bacteria in the skin.
MRSA (methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus) skin infections are potentially lethal, ...
Agents that target viral RNA could be the basis for next generation anti-viral drugs
2021-05-10
A new approach to tackling viruses by targeting the 'control centre' in viral RNA could lead to broad spectrum anti-viral drugs and provide a first line of defence against future pandemics, according to new research at the University of Birmingham.
In a new study, published in Angewandte Chemie, researchers have shown how this approach could be effective against the SARS-CoV-2 virus responsible for the COVID-19 pandemic. Earlier modelling and in vitro analysis by the team and published in Chemical Science has also shown effectiveness against the HIV virus.
Professor Mike Hannon, from the University of Birmingham's School of Chemistry, is co-lead author ...
Friendly pelicans breed better
2021-05-10
Captive pelicans that are free to choose their own friendships are more likely to breed successfully on repeated occasions, new research suggests.
Social network analysis on captive great white pelicans, led by the University of Exeter, found that providing social choice within the flock and allowing partnerships to form naturally led to improved breeding success.
The study revealed that the pelicans chose their specific social relationships, and that there was a social structure across the flock, in which sub-adults (the equivalent of teenagers) spent more time with each other than with adult birds.
Zoo-housed pelicans are common, but their breeding record is poor and they receive little ...
SARS-CoV-2 research: Second possible effective mechanism of remdesivir discovered
2021-05-10
FRANKFURT. The virostatic agent remdesivir was developed to disrupt an important step in the propagation of RNA viruses, to which SARS-CoV-2 also belongs: the reproduction of the virus's own genetic material. This is present as RNA matrices with which the host cell directly produces virus proteins. To accelerate the production of its own proteins, however, RNA viruses cause the RNA matrices to be copied. To do so, they use a specific protein of their own (an RNA polymerase), which is blocked by remdesivir. Strictly speaking, remdesivir does not do this itself, but rather a substance that is synthesized from remdesivir in five steps when remdesivir penetrates a cell.
In ...
Dartmouth-led study finds overemphasis on toy giveaways in TV ads unfairly promotes fast-food to children
2021-05-10
A new Dartmouth-led study, published this week in the journal Pediatrics, has found that the disproportionate use of premiums within child-targeted TV advertising for children's fast-food meals is deceptive. The researchers examined thousands of advertisements from 11 fast-food restaurants, but one company--McDonald's--accounted for nearly all the airtime and, as a result, the findings.
The researchers report that these ads often overemphasize premiums such as toy giveaways and games relative to the primary product being sold, the fast food itself. This marketing practice violates the industry's own guidelines--put in place to ensure that the use of premiums in ads is not deceptive or unfair--as young children lack the cognitive ability ...
[1] ... [2355]
[2356]
[2357]
[2358]
[2359]
[2360]
[2361]
[2362]
2363
[2364]
[2365]
[2366]
[2367]
[2368]
[2369]
[2370]
[2371]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.