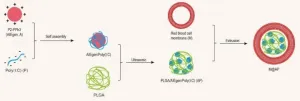
Highly efficient photodynamic-immunotherapy by combining AIEgen with Poly(I:C)
2021-04-30
Immunotherapy is a type of anti-tumor treatment and has shown great clinical success against a wide variety of malignancies in recent years. Poly(I : C), a TLR3 agonist, is the most potent type I interferon (IFN) inducer. Poly(I : C) not only directly induces tumorous apoptosis, but also stimulates tumor cells to secrete immune factors. However, the immune response rate induced by Poly(I : C) remains low in several types of malignancies and higher doses are often required to achieve the desired effect. However, poly(I : C) is highly toxic and thus only a very narrow therapeutic window is available, which greatly limits clinical application of Poly(I : C)-based treatments.
Photodynamics therapy (PDT) is a promising anti-tumor treatment ...
CO2 catalysis made more accessible
2021-04-30
Many industrial processes emit carbon dioxide into the atmosphere. Unfortunately, however, current electrochemical separation methods are expensive and consume large amounts of power. They also require expensive and rare metals as catalysts. A study in the journal Angewandte Chemie describes a new aerogel electrocatalyst formed from an inexpensive metal alloy, which enables highly efficient electrochemical conversion of carbon dioxide. The main product is formic acid, which is a nontoxic basic chemical.
Capturing and chemically fixing carbon dioxide from industrial processes would be a huge step towards carbon neutrality. To prevent the ...
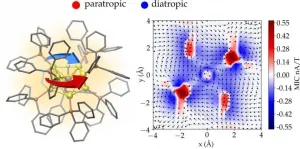
Researchers analyzed circulating currents inside gold nanoparticles
2021-04-30
Researchers in the Nanoscience Center of University of Jyvaskyla, in Finland and in the Guadalajara University in Mexico developed a method that allows for simulation and visualization of magnetic-field-induced electron currents inside gold nanoparticles. The method facilitates accurate analysis of magnetic field effects inside complex nanostructures in nuclear magnetic resonance measurements and establishes quantitative criteria for aromaticity of nanoparticles. The work was published 30.4.2021 as an Open Access article in Nature Communications.
According to the classical electromagnetism, a charged particle moving in an external magnetic field experiences a force that makes the particle's path circular. This basic law of physics is used, e.g., in designing cyclotrons ...
A milestone in muscular dystrophy therapy
2021-04-30
Muscle stem cells enable our muscle to build up and regenerate over a lifetime through exercise. But if certain muscle genes are mutated, the opposite occurs. In patients suffering from muscular dystrophy, the skeletal muscle already starts to weaken in childhood. Suddenly, these children are no longer able to run, play the piano or climb the stairs, and often they are dependent on a wheelchair by the age of 15. Currently, no therapy for this condition exists.
"Now, we are able to access these patients' gene mutations using CRISPR-Cas9 technology," explains Professor Simone Spuler, head of the Myology Lab at the Experimental and Clinical Research Center (ECRC), a joint institution of the Max Delbrück Center for Molecular Medicine in the Helmholtz Association and Charité ...
Vaccines bring us closer
2021-04-30
Effectively and safely protecting against disease--this is what makes vaccines a vital and successful public health tool that saves lives and safeguards health and well-being. Today, vaccines shield us from more than 20 life-threatening diseases.
Each year, between 2 to 3 million lives are saved by immunisation against diseases like diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis, influenza or measles [1]. However, several vaccines such as the one against measles can only reach their full potential--protecting not just those who are immunised, but also those who might not be eligible for vaccination--if ...
Latest observations by MUSER help clarify solar eruptions
2021-04-30
Prof. YAN Yihua and his research team from the National Astronomical Observatories of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (NAOC) recently released detailed results of observations by the new generation solar radio telescope--Mingantu Spectral Radio Heliograph (MUSER)--from 2014 to 2019.
The study was published in Frontiers in Astronomy and Space Sciences on March 29. It may help us better understand the basic nature of solar eruptions.
Solar radio bursts are associated with different types of powerful eruptions like solar flares, coronal mass ejections, and various thermal and nonthermal processes. They are prompt indicators of disastrous space weather events.
Solar radio observations, especially at centimeter ...
New view of species interactions offers clues to preserve threatened ecosystems
2021-04-30
As the health of ecosystems in regions around the globe declines due to a variety of rising threats, scientists continue to seek clues to help prevent future collapses.
A new analysis by scientists from around the world, led by a researcher at the University of California San Diego, is furthering science's understanding of species interactions and how diversity contributes to the preservation of ecosystem health.
A coalition of 49 researchers examined a deep well of data describing tree species in forests located across a broad range of countries, ecosystems and latitudes. Information about the 16 forest diversity plots in Panama, China, Sri Lanka, Puerto Rico and other locations--many in remote, inaccessible ...
Researchers develop chip that improves testing and tracing for COVID-19
2021-04-30
Jeremy Edwards, director of the Computational Genomics and Technology (CGaT) Laboratory at The University of New Mexico, and his colleagues at Centrillion Technologies in Palo Alto, Calif. and West Virginia University, have developed a chip that provides a simpler and more rapid method of genome sequencing for viruses like COVID-19.
Their research, titled, "Highly Accurate Chip-Based Resequencing of SARS-CoV-2 Clinical Samples" was published recently in the American Chemical Society's Langmuir. As part of the research, scientists created a tiled genome array they developed for rapid and inexpensive full viral genome resequencing and applied their SARS-CoV-2-specific genome tiling array to rapidly and accurately resequenced ...
Clinically viable blood test for donor-derived cell-free DNA
2021-04-30
Boston, MA (April 30, 2021) - A new study, presented today at the AATS 101st Annual Meeting, shows that non-invasive cell-free DNA tests can reduce the need for regular surveillance biopsies to detect early rejection in heart transplant patients. The study was the first of its kind to be performed on both adult and pediatric patients.
Pediatric and adult heart transplant recipients were recruited prospectively from eight participating sites and followed longitudinally for at least 12 months with serial plasma samples collected immediately prior to all endomyocardial biopsies. Structured biopsy results and clinical data were collected and monitored by an independent clinical research organization (CRO).
For ...
Study finds similar long-term outcomes for mechanically-ventilated COVID-19 patients
2021-04-30
Boston, MA (April 30, 2021) - A new study, presented today at the AATS 101st Annual Meeting, found that severely ill COVID-19 patients treated with ECMO did not suffer worse long-term outcomes than other mechanically-ventilated patients. The multidisciplinary team included cardio thoracic surgeons, critical care doctors, medical staff at long-term care facilities, physical therapists and other specialists, and followed patients at five academic centers: University of Colorado; University of Virginia; University of Kentucky; Johns Hopkins University; and Vanderbilt University. ...
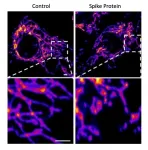
The novel coronavirus' spike protein plays additional key role in illness
2021-04-30
LA JOLLA--(April 30, 2021) Scientists have known for a while that SARS-CoV-2's distinctive "spike" proteins help the virus infect its host by latching on to healthy cells. Now, a major new study shows that they also play a key role in the disease itself.
The paper, published on April 30, 2021, in Circulation Research, also shows conclusively that COVID-19 is a vascular disease, demonstrating exactly how the SARS-CoV-2 virus damages and attacks the vascular system on a cellular level. The findings help explain COVID-19's wide variety of seemingly unconnected complications, and could ...
Move over CRISPR, the retrons are coming
2021-04-30
While the CRISPR-Cas9 gene editing system has become the poster child for innovation in synthetic biology, it has some major limitations. CRISPR-Cas9 can be programmed to find and cut specific pieces of DNA, but editing the DNA to create desired mutations requires tricking the cell into using a new piece of DNA to repair the break. This bait-and-switch can be complicated to orchestrate, and can even be toxic to cells because Cas9 often cuts unintended, off-target sites as well.
Alternative gene editing techniques called recombineering instead perform this bait-and-switch ...
Decoding the effect of body mass index on breast cancer
2021-04-30
Medical researchers at Flinders University have established a new link between high body mass index (BMI) and breast cancer survival rates - with clinical data revealing worse outcomes for early breast cancer (EBC) patients and improved survival rates in advanced breast cancer (ABC).
In a new study published in a top breast cancer journal- researchers evaluated data from 5 thousand patients with EBC and 3496 with ABC to determine associations between BMI and survival rates across both stages.
Researchers say the results present an 'obesity paradox' which will impact the survival outcomes of the 19,807 women and 167 men diagnosed with breast cancer in Australia in 2020.
Natansh Modi, a NHMRC PHD Candidate at Flinders University, says understanding the ...
Brazilian Amazon released more carbon than it stored in 2010s
2021-04-30
The Brazilian Amazon rainforest released more carbon than it stored over the last decade - with degradation a bigger cause than deforestation - according to new research.
More than 60% of the Amazon rainforest is in Brazil, and the new study used satellite monitoring to measure carbon storage from 2010-2019.
The study found that degradation (parts of the forest being damaged but not destroyed) accounted for three times more carbon loss than deforestation.
The research team - including INRAE, the University of Oklahoma and the University of Exeter - said large areas of rainforest were degraded or destroyed due to human activity and climate change, leading to carbon loss.
The findings, published in Nature Climate Change, also ...
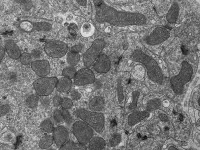
DNA building blocks regulate inflammation
2021-04-30
Mitochondria are the energy suppliers of our body cells. These tiny cell components have their own genetic material, which triggers an inflammatory response when released into the interior of the cell. The reasons for the release are not yet known, but some cardiac and neurodegenerative diseases as well as the ageing process are linked to the mitochondrial genome. Researchers at the Max Planck Institute for Biology of Ageing and the CECAD Cluster of Excellence in Ageing research have investigated the reasons for the release of mitochondrial genetic material and found a direct link to cellular metabolism: when the cell's DNA building blocks are in short supply, mitochondria release their genetic material and trigger inflammation. ...
World's first fiber-optic ultrasonic imaging probe for future nanoscale disease diagnostics
2021-04-30
Scientists at the University of Nottingham have developed an ultrasonic imaging system, which can be deployed on the tip of a hair-thin optical fibre, and will be insertable into the human body to visualise cell abnormalities in 3D.
The new technology produces microscopic and nanoscopic resolution images that will one day help clinicians to examine cells inhabiting hard-to-reach parts of the body, such as the gastrointestinal tract, and offer more effective diagnoses for diseases ranging from gastric cancer to bacterial meningitis.
The high level of performance the technology delivers is currently only possible in state-of-the-art research labs with large, scientific instruments - whereas this compact system has the potential to bring it into clinical settings to improve patient care.
The ...
Navigating the squircle
2021-04-30
Successful navigation requires the ability to separate memories in a context-dependent manner. For example, to find lost keys, one must first remember whether the keys were left in the kitchen or the office. How does the human brain retrieve the contextual memories that drive behavior? J.B. Julian of the Princeton Neuroscience Institute at Princeton University, USA, and Christian F. Doeller of the Max Planck Institute for Human Cognitive and Brain Sciences in Leipzig, Germany, found in a recent study that modulation of map-like representations in our brain's hippocampal formation can predict contextual memory retrieval in an ambiguous environment.
The researchers developed a novel virtual reality navigation task in which human participants learned object positions in two different ...
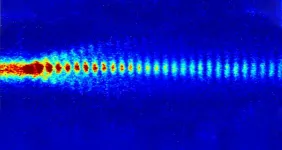
Awake brings proton bunches into sync
2021-04-30
The future of particle acceleration has begun. Awake is a promising concept for a completely new method with which particles can be accelerated even over short distances. The basis for this is a plasma wave that accelerates electrons and thus brings them to high energies. A team led by the Max Planck Institute for Physics now reports a breakthrough in this context. For the first time, they were able to precisely time the production of the proton microbunches that drive the wave in the plasma. This fulfills an important prerequisite for using the Awake technology for collision experiments.
How do you create a wave for electrons? The carrier substance for this is a plasma (i.e., an ionized gas in which positive and negative charges are separated). Directing a proton beam through ...
Important factor in the development of dendritic cells identified
2021-04-30
The human immune system comprises functionally specialised cellular defence mechanisms that protect the body against disease. These include the dendritic cells. Their main function is to present antigens to other immune cells, especially T cells, thereby activating a primary immune response. Dendritic cells are divided into Type 1 (DC1) and Type 2 (DC2) dendritic cells. Each type fulfils different functions: DC1 provide an immune response to bacteria and viruses, DC2 protect against fungal or parasitic infections. In a recent study conducted at MedUni Vienna's Institute of Cancer Research, researchers found that a particular group of proteins plays a major role in the development of Type 1 dendritic ...
NIH study identifies diverse spectrum of neurons that govern movement
2021-04-30
WHAT:
In a mouse study, National Institutes of Health researchers have identified and mapped a diverse spectrum of motor neurons along the spinal cord. These neurons, which send and receive messages throughout the body, include a subset that is susceptible to neurodegenerative diseases. Created with a genetic sequencing technique, the atlas reveals 21 subtypes of neurons in discrete areas throughout the spinal cord and offers insight into how these neurons control movement, how they contribute to the functioning of organ systems and why some are disproportionately affected in neurodegenerative diseases.
The study ...
New brain-like computing device simulates human learning
2021-04-30
Researchers have developed a brain-like computing device that is capable of learning by association.
Similar to how famed physiologist Ivan Pavlov conditioned dogs to associate a bell with food, researchers at Northwestern University and the University of Hong Kong successfully conditioned their circuit to associate light with pressure.
The research will be published April 30 in the journal Nature Communications.
The device's secret lies within its novel organic, electrochemical "synaptic transistors," which simultaneously process and store information just like the human brain. The researchers demonstrated ...
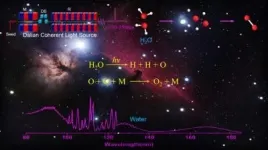
Dalian coherent light source reveals oxygen production from three-body photodissociation of water
2021-04-30
The provenance of oxygen on Earth and other solar planetary bodies is a fundamental issue. It is widely accepted that the prebiotic pathway of oxygen production in the Earth primitive atmosphere was via vacuum ultraviolet (VUV) photodissociation of CO2 and subsequent recombination of two O atoms.
In contrast, the photodissociation of H2O, one of the dominant oxygen carriers, has long been assumed to proceed mainly to produce hydroxyl (OH)- and hydrogen (H)-atom primary products, and its contribution to oxygen production is limited.
Recently, a research group ...
WIN's DDPP biomarker to guide cancer therapy and predict response duration
2021-04-30
The Worldwide Innovative Network in personalized cancer medicine consortium - WIN Consortium announces the publication of the Digital Display Precision Predictor: the prototype of a global biomarker model to guide treatments with targeted therapy and predict progression-free survival for cancer patients in NPJ Precision Oncology (10.1038/s41698-021-00171-6)
Precision oncology has led to approved, molecularly specific, biomarker-defined indications for targeted therapies. With the number of validated drug targets increasing, testing each patient's tumor for all markers related to all possible targeted therapies becomes infeasible due to limited amount of tissue usually obtained by biopsies. In addition, the current companion diagnostic approach ...
New genetic target for blood cancer treatment
2021-04-30
Targeting a pathway that is essential for the survival of certain types of acute myeloid leukaemia could provide a new therapy avenue for patients, the latest research has found.
Researchers from the Wellcome Sanger Institute found that a specific genetic mutation, which is linked with poor prognosis in blood cancer, is involved in the development of the disease when combined with other mutations in mice and human cell lines.
The study, published today (30th April) in Nature Communications, provides a greater understanding of how the loss-of-function mutation in the CUX1 gene leads to the development and survival of acute myeloid leukaemia. ...
Care teams differ for Black, white surgical patients in the same hospitals
2021-04-30
A new study finds Black patients are more likely to die after their heart bypass surgery if they're at a hospital where some care teams see mostly white patients and others see mostly Black patients. On the other hand, mortality rates are comparable between Black and white patients after heart bypass surgery when the teams of health care providers at their hospitals all care for patients of all races.
Some level of care team segregation within hospitals was very common, and the findings bring up another angle to better understand racial inequities in surgical outcomes, says co-first author John Hollingsworth, M.D., M.Sc., a professor of urology at Michigan Medicine and of health management and policy at the University of Michigan School of Public Health.
Previous studies ...
[1] ... [2360]
[2361]
[2362]
[2363]
[2364]
[2365]
[2366]
[2367]
2368
[2369]
[2370]
[2371]
[2372]
[2373]
[2374]
[2375]
[2376]
... [8813]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.