Most mitral regurgitation patients treated with TEER will require surgery if treatment fails
2021-05-01
Boston, MA (May 1, 2021) - A new study, presented today at the AATS 101st Annual Meeting, and simultaneously published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology, finds that patients suffering from severe mitral regurgitation should be carefully screened and counselled before undergoing transcatheter edge-to-edge mitral repair (TEER). Data showed that up to 95 percent of patients who needed surgery after failed TEER could not have their valves repaired, and needed mitral valve replacement to resolve the issue. The findings highlight the need to select patients carefully ...
Low profile thoracic aortic endograft device reduces complications and expands patient pool
2021-05-01
Boston, MA (May 1, 2021) - Preliminary results of a clinical trial, presented today at the AATS 101st Annual Meeting, showed that a new, low-profile thoracic aortic endograft is safe and effective in the treatment of descending thoracic aortic aneurysm or penetrating atherosclerotic ulcer (PAU) diseases. A multi-disciplinary team, led by both cardiac and vascular surgeons as co-investigators, conducted the study in 36 centers in the United States and Japan, enrolling patients between 2016 and 2019.
The trial aimed to measure safety and efficacy of the RELAY®Pro endovascular device, a second-generation product featuring a dramatically reduced profile and a non-bare stent ...
Study finds up to 24 percent of esophagectomy patients can develop VTE post-operatively
2021-05-01
Boston, MA (May 1, 2021) - A new study presented today at the AATS 101st Annual Meeting, found that the percentage of patients undergoing esophagectomy for cancer who suffer Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) post-operatively is much higher than previously reported, with as many as 24 percent suffering from Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) or Pulmonary Embolism (PE). Six-month mortality for patients with VTE was 17.6 percent compared to 2.1 percent for those without.
Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) is a common, potentially preventable post-operative complication leading to significant morbidity and mortality. Esophagectomy patients are amongst the highest risk groups ...
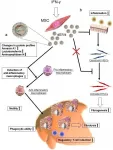
A glimmer of hope: New weapon in the fight against liver diseases
2021-05-01
Niigata, Japan--Researchers from Niigata University , the University of Tokyo, Osaka University and Tokyo Medical University, Japan have developed a new approach that could revolutionize the treatment, prevention, and possibly reversal of the damages caused by liver diseases. This novel strategy exploits small extracellular vesicles (sEVs) derived from interferon-γ (IFN-γ) pre-conditioned MSCs (γ-sEVs).
Cirrhosis and other chronic liver diseases remain a global health concern, with close to 2 million deaths reported annually, these account for approximately 3.5% of annual worldwide deaths. All these ...
Three ways to improve scholarly writing to get more citations
2021-05-01
Researchers from University of Arizona and University of Utah published a new paper in the Journal of Marketing that examines why most scholarly research is misinterpreted by the public or never escapes the ivory tower and suggests that such research gets lost in abstract, technical, and passive prose.
The study, forthcoming in the Journal of Marketing, is titled "Marketing Ideas: How to Write Research Articles that Readers Understand and Cite" and is authored by Nooshin L. Warren, Matthew Farmer, Tiany Gu, and Caleb Warren.
From developing vaccines to nudging people to eat less, scholars conduct research that could change the world, but most of their ideas either are misinterpreted by the public or never escape the ivory tower.
Why does most academic ...
Save the mother, save the child
2021-05-01
Supporting female survivors of childhood maltreatment is critical to disrupting intergenerational abuse as new research from the University of South Australia shows a clear link between parents who have suffered abuse and the likelihood of their children suffering the same fate.
The finding amplifies an acute need for far better support for victims of child maltreatment to ensure safer and more nurturing environments for all children.
Funded by the NHMRC and the Channel 7 Children's Research Foundation, and published in The Lancet Public Health today, the study found that most child maltreatment is occurring among families caught up in intergenerational cycles of child abuse and neglect - 83 per cent of ...
The Lancet: Study confirms greater risk of poor COVID outcomes in minority ethnic groups in England
2021-05-01
Largest study so far of more than 17 million adults in England confirms that minority ethnic groups had a higher risk of testing positive, hospitalisation, admission to intensive care units (ICU), and death from COVID-19 compared with white groups, even after accounting for other factors known to increase risk like deprivation, occupation, household size and underlying health conditions.
Disparities for hospitalisation and death lessened for most minority ethnic groups between pandemic waves 1 (February to September 2020) and wave 2 (September to December 2020), but increased for South Asian groups.
To tackle ethnic disparities in COVID-19 risks, the authors call for reducing structural disadvantage and inequality, improving quality of and access to healthcare, and improving uptake ...
Antiviral T cells safe and effective for treating debilitating complication common after stem cell transplants
2021-04-30
HOUSTON ? A Phase II trial led by researchers at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center found that BK virus (BKV)-specific T cells from healthy donors were safe and effective as an off-the-shelf therapy for BKV-associated hemorrhagic cystitis (BKV-HC), a painful complication common after allogeneic stem cell transplants for patients with leukemia or lymphoma. The study was published today in the Journal of Clinical Oncology.
Infusion of T cells targeting BKV resulted in rapid responses, with 67.7% of patients seeing a complete or partial improvement in symptoms after 14 days. This increased to 81.6% of patients after 28 days post-infusion. No cases of grade ...
Branching worm with dividing internal organs growing in sea sponge
2021-04-30
The marine worm Ramisyllis multicaudata, which lives within the internal canals of a sponge, is one of only two such species possessing a branching body, with one head and multiple posterior ends. An international research team led by the Universities of Göttingen and Madrid is the first to describe the internal anatomy of this intriguing animal. The researchers discovered that the complex body of this worm spreads extensively in the canals of their host sponges. In addition, they describe the anatomical details and nervous system of its unusual reproductive ...
Large collaboration creates cell atlas of COVID-19 pathology
2021-04-30
Scientists from several hospitals and research centers have shown what happens in individual cells of patients who died of COVID-19. In a study published in Nature, the researchers describe how infected cells from multiple organs exhibited a range of molecular and genomic changes. They also saw signs of multiple, unsuccessful attempts by the lungs to repair themselves in response to respiratory failure, which is the leading cause of death in COVID-19 patients.
"You really feel the tragedy of the disease when you see that result," said Aviv Regev, co-senior author of the study and a core institute member at the Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard when the study began. "The lung tries everything at its disposal, and it still can't fix itself. This was a very ...
Neural nets used to rethink material design
2021-04-30
HOUSTON - (April 30, 2021) - The microscopic structures and properties of materials are intimately linked, and customizing them is a challenge. Rice University engineers are determined to simplify the process through machine learning.
To that end, the Rice lab of materials scientist Ming Tang, in collaboration with physicist Fei Zhou at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory, introduced a technique to predict the evolution of microstructures -- structural features between 10 nanometers and 100 microns -- in materials.
Their open-access paper in the Cell Press journal Patterns shows how neural networks ...
UVA engineering computer scientists discover new vulnerability affecting computers globally
2021-04-30
CHARLOTTESVILLE, Va. - In 2018, industry and academic researchers revealed a potentially devastating hardware flaw that made computers and other devices worldwide vulnerable to attack.
Researchers named the vulnerability END ...
How much does it itch?
2021-04-30
CHICAGO --- Itch torments its sufferers and can be as debilitating as chronic pain.
But it's a hard symptom to measure -- particularly for the 10 million U.S. children with atopic dermatitis, also known as eczema. They can't always verbalize or quantify their suffering via a survey or scale.
It can also be difficult to objectively measure itch for adults with liver disease, kidney disease and certain cancers who experience its symptoms.
So, it's hard to track how well treatments and drugs are working.
But now there is a soft, wearable sensor that actually quantifies itch by measuring scratching when placed on the hand developed by Northwestern University scientists. While it was tested ...
Modifications to ERATS protocol significantly reduces post-operative opioid usage
2021-04-30
Boston, MA (April 30, 2021) - A new study, presented today at the AATS 101st Annual Meeting, shows significant reduction in post-operative use of Schedule II opioids for pain management following robotic surgery. To address the on-going issues of opioid overuse and abuse, the study aimed to examine the use of painkillers in Enhanced Recovery After Thoracic Surgery (ERATS) protocols and determine the impact of alternative pain management approaches on clinical outcomes.
An Institutional Review Board-approved retrospective analysis of a prospectively maintained ...
Panel finds 30-day course of VTE prophylaxis post-discharge improves outcomes
2021-04-30
Boston, MA (April 30, 2021) - A new set of guidelines, developed by AATS and ESTS (European Society for Thoracic Surgery) presented today at the AATS 101st Annual Meeting, recommends a 30-day course of Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) prophylaxis post-discharge for patients undergoing surgical resection for lung or esophagus cancer. The AATS and ESTS formed a multidisciplinary guideline panel that included broad membership to minimize potential bias when formulating recommendations. The McMaster University GRADE Centre supported the guideline development process, including updating or performing systematic reviews and meta-analyses. The results are endorsed by the American Society of Hematology (ASH) and the International Society ...
Antarctic ice-sheet melting to lift sea level higher than thought, Harvard study says
2021-04-30
Global sea level rise associated with the possible collapse of the West Antarctic Ice Sheet has been significantly underestimated in previous studies, meaning sea level in a warming world will be greater than anticipated, according to a new study from Harvard researchers.
The report, published in Science Advances, features new calculations for what researchers refer to as a water expulsion mechanism. This occurs when the solid bedrock the West Antarctic Ice Sheet sits on rebounds upward as the ice melts and the total weight of the ice sheet decreases. The bedrock sits below sea level so when it lifts, it pushes water from the surrounding area into the ocean, adding to global ...
Newly discovered miocene biome sheds light on rainforest evolution
2021-04-30
An international research group led by Prof. WANG Bo and Prof. SHI Gongle from the Nanjing Institute of Geology and Palaeontology of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (NIGPAS) collected approximately 25,000 fossil-containing amber samples and about 5,000 fossil plants in Zhangpu County, Fujian Province, southeast China from 2010 to 2019.
Their findings were published in Science Advances on April 30.
The Zhangpu biota, including amber biota and co-occurring megafossils, is the richest tropical seasonal rainforest biota discovered so far. It reveals that ...
Piecing together the LanCL puzzle
2021-04-30
Researchers from the Carl R. Woese Institute for Genomic Biology in collaboration with scientists at Oxford University have published a paper in Cell reporting the function of LanCL proteins. These proteins are found in eukaryotic cells but their function was previously unknown. The study is the first step towards understanding the importance of these ubiquitous proteins.
Bacteria contain enzymes called LanC that are capable of producing small proteins called lanthipeptides, which are characterized by the addition of a thiol group to a modified serine or threonine amino acid. Similar proteins--called LanC-like ...
Illnesses of controversial celebrities can negatively affect public health
2021-04-30
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa.-- Not all public figures are equally beloved, and sometimes when more controversial celebrities get sick, it may negatively affect people's health intentions. In a study of people's reactions to radio host Rush Limbaugh's announcement of a lung cancer diagnosis and Kentucky Sen. Rand Paul's announcement of a diagnosis of COVID-19, researchers at Penn State found that those who took pleasure in their misfortune were themselves less likely to take steps to prevent lung cancer or COVID-19.
"Schadenfreude is the emotion of feeling pleasure in another's misfortune," said Jessica Gall Myrick, associate professor of media studies. "In our study, after learning the news of a politician's ...
Tool to predict recidivism in federal inmates could make more prisoners eligible for early release
2021-04-30
Passed in 2018, the First Step Act sought to address re-entry challenges for inmates in the federal prison system. The legislation called for developing an assessment tool to identify inmates for release who had the lowest likelihood of recidivism. A new study assessed how the tool was developed and is used, finding that a greater proportion of inmates could reduce their risk and become eligible for early release over time if they participated in a re-entry program and did not incur infractions. This finding has implications for efforts to reduce prison populations during the COVID-19 pandemic.
The study, by researchers at the University of Nebraska ...
eNeuro publishes commentaries on upcoming documentary "In Silico"
2021-04-30
eNeuro is publishing a special collection of commentaries on April 30, 2021 on the neuroscience documentary In Silico. The collection, titled "Epistemological Lessons from the Blue and Human Brain Projects," features reactions to the documentary from leading neuroscientists as well as a discussion on brain modelling and massive research collaborations in general.
Noah Hutton's In Silico follows neuroscientist Henry Markram and his attempt to develop a computer model of the brain. The collaboration, called The Human Brain Project, received €1 billion in funding and pledged to build a full model within ten years. The documentary chronicles Markram and ...
Technology provides procedure efficiencies for congenital heart disease patients
2021-04-30
WASHINGTON, D.C, (April 30, 2021) - An analysis of a new international registry reveals benefits of using a longer covered stent for interventional procedures in congenital heart disease patients with Sinus Venosus Atrial Septal Defect (SVASD). The study was presented today as late-breaking clinical research at the Society for Cardiovascular Angiography & Interventions (SCAI) 2021 Scientific Sessions.
SVASD is a rare adult congenital heart disease which permits shunting of blood from the systemic to the pulmonary circulation , causing excessive blood flow to the lungs. Until now, open heart surgical repair was the gold standard approach to dealing with this condition but is necessarily invasive. Covered stent implantation is ...
Technology provides non-invasive treatment for congenital heart disease patients
2021-04-30
WASHINGTON, D.C., (April 30, 2021) - New study results validate the effectiveness of the Medtronic Harmony™ transcatheter pulmonary valve (TPV) system for patients with congenital heart disease (CHD) and severe pulmonary regurgitation (PR). The Harmony TPV is designed to be a less invasive treatment option for patients with irregularity in their right ventricular outflow tract (RVOT) needing pulmonary valve placement to restore valve function. The results of this study are being presented as late-breaking clinical science today at the Society for Cardiovascular Angiography & Interventions (SCAI) 2021 Scientific Sessions.
About 40,000 infants are born with CHD every year in the United States ...
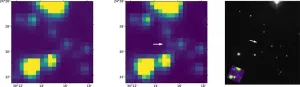
Not just for finding planets: Exoplanet-hunter TESS telescope spots bright gamma-ray burst
2021-04-30
DALLAS (SMU) - NASA has a long tradition of unexpected discoveries, and the space program's TESS mission is no different. SMU astrophysicist and her team have discovered a particularly bright gamma-ray burst using a NASA telescope designed to find exoplanets - those occurring outside our solar system - particularly those that might be able to support life.
It's the first time a gamma-ray burst has been found this way.
Gamma-ray bursts are the brightest explosions in the universe, typically associated with the collapse of a massive star and the birth of a black hole. They can produce as much radioactive energy as the sun will release during its entire 10-billion-year ...
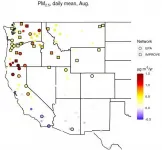
Wildfire smoke trends worsening for Western US
2021-04-30
From the Pacific Northwest to the Rocky Mountains, summers in the West are marked by wildfires and smoke. New research from the University of Utah ties the worsening trend of extreme poor air quality events in Western regions to wildfire activity, with growing trends of smoke impacting air quality clear into September. The work is published in Environmental Research Letters.
"In a big picture sense, we can expect it to get worse," says Kai Wilmot, lead author of the study and doctoral student in the Department of Atmospheric Sciences. "We're going to see more fire area burned in the Western U.S. between now and in 2050. If we extrapolate our trends forward, it seems to indicate that a lot ...
[1] ... [2364]
[2365]
[2366]
[2367]
[2368]
[2369]
[2370]
[2371]
2372
[2373]
[2374]
[2375]
[2376]
[2377]
[2378]
[2379]
[2380]
... [8818]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.