Study reveals the gateway to conscious awareness
2021-05-04
During our waking hours, the brain is receiving a near-constant influx of sensory signals of various strengths. For decades, scientists have wondered why some signals rise to the light of conscious awareness while other signals of a similar strength remain in the dark shadows of unconsciousness. What controls the gate that separates the shadows and the light?
In a new study from the Department of Anesthesiology and Center for Consciousness Science at Michigan Medicine, researchers identify a key area in the cortex that appears to be the gate of conscious awareness.
"Information processing in the brain ...
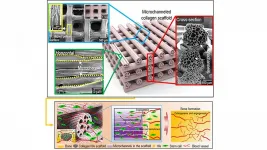
Using 4D printing to enable vascularization, bone tissue regeneration, spinal fusion
2021-05-04
WASHINGTON, May 4, 2021 -- Spinal fusion is frequently performed to restore spinal stability in patients with spinal diseases, such as spinal stenosis, vertebral fractures, progressive deformities, and instability. In the past two decades, there has been marked increase in the number of people over 65 years in age who have needed spinal fusion surgery.
While autogenous bone grafts have long been considered the reference standard for spinal fusion, painful pseudoarthrosis remains a leading cause of poor clinical outcomes. Many researchers have consequently focused on ...
Cellphone converts into powerful chemical detector
2021-05-04
WASHINGTON, May 4, 2021 -- Scientists from Texas A&M have developed an extension to an ordinary cellphone that turns it into an instrument capable of detecting chemicals, drugs, biological molecules, and pathogens. The advance is reported in Reviews of Scientific Instruments, by AIP Publishing.
Modern cellphones include high-quality cameras capable of detecting low levels of light and eliminating digital noise through software processing of the captured images. Recent work has taken advantage of this sensitivity to produce cellphone cameras that ...
Surgery to prevent breast cancer requires a patient-doctor dialogue about risks, benefits
2021-05-04
SAN ANTONIO (May 4, 2021) - Risk-reducing mastectomy saves lives of women who, because of hereditary or other risk factors, may have a very high lifetime risk of developing breast cancer, according to two new journal articles written to guide physicians and patients. All of these women should also discuss with their physicians nonsurgical options such as screening and medications to reach the best, customized treatment strategy, the essays mention.
Both articles, published May 4 in the Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA), are by END ...
Original investigation: When drug companies raise list prices, out-of-pocket costs for patients
2021-05-04
WHO Benjamin Rome, MD, Instructor of Medicine at Harvard Medical School and researcher in the Program On Regulation, Therapeutics, And Law (PORTAL) in the Division of Pharmacoepidemiology and Pharmacoeconomics, Brigham and Women's Hospital; corresponding author of a paper published in JAMA Network Open.
WHAT When drug manufacturers raise the list price for brand-name prescription drugs, do patients' out-of-pocket costs rise too? A new study published in JAMA Network Open by Dr. Benjamin Rome and colleagues in the Brigham's Division of Pharmacoepidemiology and Pharmacoeconomics finds that more than half of patients may experience increases in out-of-pocket spending when drug ...
Team cracks century-old mystery over the health struggles of explorer Ernest Shackleton
2021-05-04
BOSTON - Researchers from Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) appear to have solved the 120-year-old mystery surrounding the failing health of famed Antarctic explorer Sir Ernest Shackleton over the course of his daring expeditions to Antarctica in the early part of the twentieth century. In a paper published online in the END ...
Do people aged 105 and over live longer because they have more efficient DNA repair?
2021-05-04
Researchers have found that people who live beyond 105 years tend to have a unique genetic background that makes their bodies more efficient at repairing DNA, according to a study published today in eLife.
This is the first time that people with 'extreme longevity' have had their genomes decoded in such detail, providing clues as to why they live so long and manage to avoid age-related diseases.
"Aging is a common risk factor for several chronic diseases and conditions," explains Paolo Garagnani, Associate Professor at the Department of Experimental, Diagnostic ...
Changes in proteins play important role in aging kidneys
2021-05-04
Studying protein changes in the kidneys as we age, as well as the transcription of genes into proteins, helps provide a full picture of the age-related processes that take place in these organs, says a study in mice published today in eLife.
Aging causes many changes in the body and in essential organs such as the kidneys, which function less efficiently later in life. Age-related changes in the kidneys have mostly been reported by looking at the transcription of genes - the process by which a segment of DNA is copied into RNA. The current study suggests that this approach, combined with studying changes in proteins, gives us a better understanding of age-related changes in the kidney and may point to new approaches for treating ...
New neuroimaging technique studies brain stimulation for depression
2021-05-04
TAMPA, Fla. (May 4, 2021) -- Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation, or rTMS, was FDA approved in 2008 as a safe and effective noninvasive treatment for severe depression resistant to antidepressant medications. A small coil positioned near the scalp generates repetitive, pulsed magnetic waves that pass through the skull and stimulate brain cells to relieve symptoms of depression. The procedure has few side effects and is typically prescribed as an alternative or supplemental therapy when multiple antidepressant medications and/or psychotherapy do not work.
Despite increased use ...
Population-based study shows air pollution exposure contributes to childhood asthma
2021-05-04
LONDON, ON - New findings from Ontario have shown that children born in Sarnia have a higher risk of developing asthma compared to neighbouring cities. A research team from Lawson Health Research Institute and Western University, using provincial data from ICES, found that higher air pollution exposure in the first year of life very likely contributed to this higher risk. Their results are published today in CMAJ Open.
Summary of study results:
-Children born in Sarnia in the 1990s and early 2000s were disproportionally at a higher risk of developing asthma in the first few years of life, compared to neighbouring cities.
-Air pollution exposure ...
Forest fires drive expansion of savannas in the heart of the Amazon
2021-05-04
Agência FAPESP – White-sand savannas are expanding in the heart of the Amazon as a result of recurring forest fires, according to a study published in the journal Ecosystems.
The study was supported by FAPESP, and conducted by Bernardo Monteiro Flores, currently a postdoctoral fellow in ecology at the Federal University of Santa Catarina (UFSC) in Brazil, and Milena Holmgren, a professor in the Department of Environmental Sciences at Wageningen University in the Netherlands.
“The edges of the Amazon Rainforest have long been considered the ...
Researchers identify potential combination therapy for aggressive lung cancer
2021-05-04
FINDINGS
A new study by researchers at the UCLA Jonsson Comprehensive Cancer Center has identified a novel combination therapy to potentially help overcome resistance to immunotherapy in people diagnosed with advanced lung cancer. The combination approach uses immune checkpoint inhibitors with ATRA, a safe medication that is widely used to treat leukemia. The team found the combination therapy led to eradication of over 70% of tumors when tested in mice with LKB1-deficient lung cancer. It also generated durable tumor-specific immunity.
BACKGROUND
Immune checkpoint inhibitors have substantially ...
One step closer to efficient cannabis production
2021-05-04
As nurseries and garden centers fill up with spring landscaping plants, home gardeners owe a lot to a technique called micropropagation, which has proven beneficial to many plants - perhaps soon to include cannabis, thanks to work by UConn researchers in the College of Agriculture, Health, and Natural Resources.
Micropropagation is a technique used for growing large quantities of new plants from fewer "parent" plants, yielding clones with the same, predictable qualities. The cannabis (Cannabis sativa) industry, however, has been largely left out of this beneficial technique, because this species of plant is extremely difficult to micropropagate.
Researchers from UConn - including Associate Professor Jessica Lubell-Brand, Ph.D. student Lauren Kurtz, and Professor Mark ...
Forty years of nursing science in HIV/AIDS: JANAC marks progress and challenges
2021-05-04
May 4, 2021 - From the very beginning of the AIDS epidemic in 1981, nurses have been at the forefront of patient care, advocacy, and research. But even in the age of antiretroviral therapy and pre-exposure prophylaxis, many challenges remain in reducing the impact of HIV and AIDS, according to the special May/June issue of END ...
Bringing up baby: A crocodile's changing niche
2021-05-04
Relatives of the giant crocodile might have been kings of the waterways during the Cretaceous period, eating anything--including dinosaurs--that got a little too close to the water's edge, but the largest of these apex predators still started off small. Figuring out how these little crocs grew up in a world surrounded by giants is no small task. Now crocs fossils from Texas are shedding light on how these animals changed their diets as they grew, helping them find a place of their own in environments alongside their bigger, badder relatives.
According to the study, published by Cambridge University Press, the crocodiless in question are members of the Deltasuchus motherali and lived along the coastline of Texas 96 million years ...
Why does heart scarring cause abnormal rhythms in some people but not others?
2021-05-04
Scientists have shed light on why some people who have a stroke do not also have abnormal heart rhythms, even though their hearts contain similar scar tissue.
Their results, published today in eLife, could help identify the best treatments for people who might be at risk of recurrent stroke, new heart disorders, or both.
Strokes are often caused by abnormal blood flow resulting from rapid, irregular beating in the upper chamber of the heart. This is also called atrial fibrillation (AFib). But some people have strokes that appear to have been caused by the heart, ...
Endothelial function biomarker bio-ADM for risk stratification and management of COVID-19 patients
2021-05-04
Aachen, Germany and Hennigsdorf/Berlin, Germany, May 4, 2021 - German University Hospital Uniklinik RWTH Aachen ("Uniklinik RWTH Aachen") and diagnostics company SphingoTec GmbH ("SphingoTec") today announced that the endothelial function biomarker bio-ADM aids in the early risk stratification and management of patients suffering from severe COVID-19, in need for escalated intensive care treatment (1). A team lead by the clinical researchers at Uniklinik RWTH Aachen has shown that high bio-ADM levels indicate the severity of the acute respiratory distress ...
Staying down on the farm
2021-05-04
Tokyo, Japan - Researchers at Tokyo University of Agriculture and Technology (TUAT) modeled the dynamic instability--the so-called "power hop"--that can cause uncontrollable bouncing and damage tractors when they plow dry ground. The team found that self-excited oscillations can arise when the tractor pushes against the ground.
Plowing a field on a tractor may seem like a serene occupation, but sudden vibrations can grow unexpectedly and threaten to topple you under certain conditions. The problem is that in nonlinear systems with coupled components, as with a mechanical tractor, ...
Closing in on state-of-the-art semiconductor solar cells
2021-05-04
A synthetic approach that improves absorber layers in perovskite solar cells could help them achieve their full potential and draw closer to the performance of leading gallium arsenide devices.
Solar cells that rely on perovskite thin films to capture sunlight are the fastest growing photovoltaic technology. Cheaper and easier to manufacture and incorporate into devices than conventional semiconductors, lead halide perovskites also effectively absorb visible light and display long charge carrier diffusion lengths -- an indicator of their ability to maintain light-induced electrons and holes separation and facilitate charge transport.
Performance ...
Aryl hydrocarbon receptor suppresses immunity to oral cancer through immune checkpoint regulation
2021-05-04
A new Boston University School of Public Health (BUSPH) study has identified for the first time how the aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR), an environmental chemical receptor, drives immunosuppression in oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC)--and that its removal from malignant cells can result in tumor rejection.
Published in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, the study findings provide new insight into the biology of cancer immunosuppression, and identify a new target for cancer immunotherapy treatment.
Immune checkpoint inhibitors (immunotherapy drugs) are some of the most important treatments that have emerged for treating many cancers, including OSCC. Targeting immune checkpoint molecules such as PD-1, ...
Polarization and mobilization on social media affect infection figures
2021-05-04
Measures to contain the Corona pandemic are the subject of politically charged debate and tend to polarize segments of the population. Those who support the measures motivate their acquaintances to follow the rules, while those who oppose them call for resistance in social media. But how exactly do politicization and social mobilization affect the incidence of infection? Researchers at the Max Planck Institute for Human Development have examined this question using the USA as an example. Their findings were published in Applied Network Science.
Limit crowds, keep a safe distance, and wear masks. Such non-pharmaceutical ...
The micro-environment of breast cancer in three dimensions
2021-05-04
Cancerous tumors thrive on blood, extending their roots deep into the fabric of the tissue of their host. They alter the genetics of surrounding cells and evolve to avoid the protective attacks of immune cells. Now, Penn State researchers have developed a way to study the relationship between solid, difficult-to-treat tumors and the microenvironment they create to support their growth.
The method has the potential to act as a testbed for drugs and other anticancer treatments, according to Ibrahim T. Ozbolat, associate professor of engineering science and mechanics and biomedical engineering, who led the research. The details of the approach were published in Advanced Biology.
Using ...
Snakeskin can inspire to safer buildings
2021-05-04
Despite human inventiveness and ingenuity, we still lag far behind the elegant and efficient solutions forged by nature over millions of years of evolution.
This also applies for buildings, where animals and plants, have developed extremely effective digging methods, for example, that are far more energy-efficient than modern tunnelling machines, and even self-repairing foundations that are unusually resistant to erosion and earthquakes (yep, we're talking about roots here).
Researchers from all over the world are therefore seeking inspiration in nature to develop the buildings of the future, and researchers from Aarhus University ...
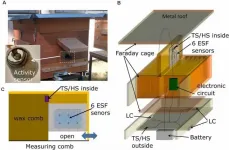
The secret life of bee signals can communicate colony health
2021-05-04
Honeybees have a complex communication system. Between buzzes and body movements, they can direct hive mates to food sources, signal danger, and prepare for swarming - all indicators of colony health. And now, researchers are listening in.
Scientists based in Germany - with collaborators in China and Norway - have developed a way to monitor the electrostatic signals that bees give off. Basically, their wax-covered bodies charge up with electrostatic energy due to friction when flying, similar to how rubbing your hair can make it stand on end. That energy then gets emitted during communications.
"We were thrilled by the ...
Fertility apps with hundreds of millions of users collect and share excessive information
2021-05-04
The majority of top-rated fertility apps collect and even share intimate data without the users' knowledge or permission, a collaborative study by Newcastle University and Umea University has found.
Researchers are now calling for a tightening of the categorisation of these apps by platforms to protect women from intimate and deeply personal information being exploited and sold.
For hundreds of millions of women fertility tracking applications offer an affordable solution when trying to conceive or manage their pregnancy. But as this technology grows in popularity, experts have revealed that most of the top-rated fertility apps collect and share sensitive ...
[1] ... [2370]
[2371]
[2372]
[2373]
[2374]
[2375]
[2376]
[2377]
2378
[2379]
[2380]
[2381]
[2382]
[2383]
[2384]
[2385]
[2386]
... [8832]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.