Scientists warn: Humanity does not have effective tools to resist the tsunami
2021-05-03
An international team of scientists from 20 countries identified 47 problems that hinder the successful prevention and elimination of the consequences of the tsunami. Based on the carried out analysis, the world's leading experts on natural hazards have outlined directions for further scientific research. The research group's review is published in a special issue of the "Frontiers in Earth Science".
The main problems identified in the review are related to the large gaps and uncertainties in knowledge about tsunami, the lack of well-documented observations, and imperfect methods of processing available information. One of the reasons is the lack of coordination of the efforts of those countries for which the study and prediction of tsunamis, forecasting the corresponding risks, and preparation ...
European coordination needed to fight science disinformation, academies say
2021-05-03
Berlin, 3 May - In a new report, ALLEA, the European Federation of Academies of Sciences and Humanities, examines the potential of technical and policy measures to tackle science disinformation and calls for improved European exchange and coordination in this field.
While disinformation strategies are intoxicating public discourses in many fields, science disinformation is particularly dangerous to democratic governance and society at large. As highlighted by the ongoing pandemic, an undermining of trust in science poses a fundamental threat to political and individual decisions based on evidence and scientific knowledge.
Over ...
How to manage osteoporosis in hematologic stem cell transplant recipients
2021-05-03
Impaired bone health is among the most significant long-term consequences of hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT), a common therapy for patients with malignant and non-malignant haematological diseases.
To address this serious problem, the International Osteoporosis Foundation (IOF) expert Working Group on Cancer and Bone Disease has published a new Executive Summary of its authoritative state-of-the-art review. The review outlined the major factors affecting bone health in HSCT patients, and provided expert guidance for the monitoring, evaluation and treatment of bone loss in these patients. ...
Tailor-made therapy of multi-resistant tuberculosis
2021-05-03
Globally, tuberculosis is the most common bacterial infectious disease leading to death. The pathogen causing tuberculosis, Mycobacterium tuberculosis, has a number of peculiarities. One is that it is growing very slowly. While other typical pathogens, such as pneumococcal and pseudomonads, can already be identified by their growth in the microbiological laboratory in the first 72 hours, several weeks usually pass before tuberculosis bacteria grow in the lab. Thus it often takes one to two months before the efficacy of individual medicines can be tested.
However, these efficacy tests are essential for the effective treatment of multidrug-resistant tuberculosis (MDR-TB), which is becoming increasingly common. In these cases, the pathogen has become ...
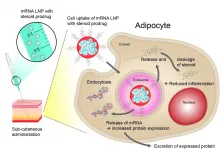
Research with neutrons for better mRNA medicines
2021-05-03
If not before, then certainly since the first messenger RNA (mRNA) vaccines to combat the SARS CoV2 virus were approved in Germany, mRNA has become a recognized term even outside scientific circles. What is less well known is that mRNA can be used to produce much more than just vaccines. Around 50 different procedures for the treatment of diseases including cancer are already being studied in clinical trials. Scientists from the pharmaceutical company AstraZeneca, with the support of neutron researchers from Forschungszentrum Jülich, have now discovered how the subcutaneous administration of mRNA can be improved. The goal is for chronically ill ...
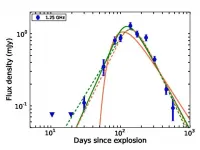
uGMRT reveals for the first time the patchy environment of a rare cosmic explosion
2021-05-03
Scientists from the National Centre for radio Astrophysics of the Tata Institute of Fundamental Research (NCRA-TIFR) Pune used the upgraded Giant Metrewave Radio Telescope (uGMRT) to determine that AT 2018 cow, the first of a newly discovered class of cosmic explosions, has an extremely patchy environment. Sources like AT 2018cow release an enormous amount of energy, nonetheless fade extremely rapidly. This along with their extremely blue color has led to them being called FBOTs for Fast Blue Optical Transient. This is the first observational evidence of inhomogeneous emission from an FBOT. The origins of FBOTs are still under debate, but proposed models include explosion of a massive star, collision of an accreting neutron star and ...
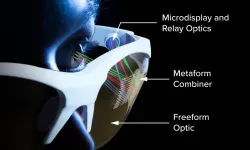
A new way to make AR/VR glasses
2021-05-03
"Image" is everything in the $20 billion market for AR/VR glasses. Consumers are looking for glasses that are compact and easy to wear, delivering high-quality imagery with socially acceptable optics that don't look like "bug eyes."
University of Rochester researchers at the Institute of Optics have come up with a novel technology to deliver those attributes with maximum effect. In a paper in Science Advances, they describe imprinting freeform optics with a nanophotonic optical element called "a metasurface."
The metasurface is a veritable forest of tiny, silver, nanoscale structures on a thin metallic film that conforms, in this advance, to the freeform shape of ...
Researchers promote usability for everyone, everywhere
2021-05-03
According to Michael Twidale, professor in the School of Information Sciences at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign, bad usability can be an irritation for everyone but "especially awful" for the underprivileged. In "Everyone Everywhere: A Distributed and Embedded Paradigm for Usability," which was recently published in the Journal of the Association for Information Science and Technology (JASIST), Twidale and coauthors David M. Nichols (University of Waikato, New Zealand) and Christopher P. Lueg (Bern University of Applied Sciences, Switzerland) present a new paradigm to address the persistence of difficulties that people have ...
As wildfires increase in severity, experts call for coordinated federal response
2021-05-03
(New York, NY) - May 3, 2021 - In advance of a wildfire season projected to be among the worst, the American Thoracic Society has released a report that calls for a unified federal response to wildfires that includes investment in research on smoke exposure and forecasting, health impacts of smoke, evaluation of interventions, and a clear and coordinated communication strategy to protect public health.
The report, Respiratory Impacts of Wildland Fire Smoke: Future Challenges and Policy Opportunities, was published online ahead of print in the Annals of the American Thoracic Society on May 3, 2021.
The report comes at a time when the U.S. is experiencing an increasing frequency of very large destructive wildfires, due to years ...
Applying UV light to common disinfectants makes them safer to use
2021-05-03
Over 400 common disinfectants currently in use could be made safer for people and the environment and could better fight the COVID-19 virus with the simple application of UVC light, a new study from the University of Waterloo shows.
Benzalkonium chloride (BAK) is the most common active ingredient in many disinfectants regularly used in hospitals, households, and food processing plants to protect against a wide range of viruses and bacteria - including all strains of SARS-CoV-2, the coronavirus that causes COVID-19 - but its toxicity means that it can't be used in high concentrations. It also means that products containing BAK are harmful to humans ...
Personalised follow-up care needed to address varying health burdens in breast cancer pts
2021-05-03
LUGANO, Switzerland, 3 May 2021 - As breast cancer becomes a largely curable disease, with more than 70% of women surviving at least 10 years after diagnosis across most of Europe thanks to early detection and treatment, (1) the quality of life after cancer has become an important aspect of the patient journey - one that may be inadequately addressed with current standards of follow-up. A study presented at the ESMO Breast Cancer 2021 Virtual Congress (2) has shown that breast cancer survivors differ widely in the burden of symptoms they experience after the end of treatment and thereby revealed an unmet need for tailored approaches to follow-up care. (3)
Lead author Kelly de Ligt ...
Team from UHN, CAMH identify unique characteristics of human neurons
2021-05-03
TORONTO - Scientists at the Krembil Brain Institute, part of University Health Network (UHN), in collaboration with colleagues at the Centre for Addiction and Mental Health (CAMH), have used precious and rare access to live human cortical tissue to identify functionally important features that make human neurons unique.
This experimental work is among the first of its kind on live human neurons and one of the largest studies of the diversity of human cortical pyramidal cells to date.
"The goal of this study was to understand what makes human brain cells 'human,' and how human neuron circuitry functions as it does," says Dr. Taufik Valiante, neurosurgeon, scientist at the Krembil Brain Institute at UHN and co-senior author on the paper.
"In our study, we wanted ...
Personalised medications possible with 3D printing
2021-05-03
Customised medicines could one day be manufactured to patients' individual needs, with University of East Anglia (UEA) researchers investigating technology to 3D 'print' pills.
The team, including Dr Andy Gleadall and Prof Richard Bibb at Loughborough University, identified a new additive manufacturing method to allow the 3D printing of medicine in highly porous structures, which can be used to regulate the rate of drug release from the medicine to the body when taken orally.
Dr Sheng Qi, a Reader in Pharmaceutics at UEA's School of Pharmacy, led the research. The project findings, 'Effects of porosity on drug release kinetics of swellable and erodible porous pharmaceutical solid dosage forms ...
Same drug can have opposite effects on memory according to sexual differences
2021-05-03
A research team from the Institut de Neurociències at the Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona (INc-UAB) has showed that inhibition through a drug of the Tac2 neuronal circuit, involved in the formation of the memory of fear, has opposite effects on the ability to remember aversive events in mice according to sex: it is reduced in male mice and increased in female mice.
Is the first time that a drug has been shown to produce this opposite effect on the memory of male and female mice. The study also evidences that opposing molecular mechanisms and behaviours can occur ...
Oceans' microscopic plants -- diatoms -- capture carbon dioxide via biophysical pathways
2021-05-03
Diatoms are tiny unicellular plants -- no bigger than half a millimeter -- which inhabit the surface water of the world's oceans where sunlight penetration is plenty. Despite their modest size, they are one of the world's most powerful resources for removing carbon dioxide (CO2) from the atmosphere. They currently remove, or "fix," 10-20 billion metric tons of CO2 every year by the process of photosynthesis. But not much is known about which biological mechanisms diatoms use, and whether these processes might become less effective with rising ocean acidity, temperatures, and, in particular, CO2 concentrations. A new study in Frontiers in Plant Science shows that diatoms predominantly ...
Planned cesarean births safe for low-risk pregnancies
2021-05-03
New research shows that planned cesarean deliveries on maternal request are safe for low-risk pregnancies and may be associated with a lower risk of adverse delivery outcomes than planned vaginal deliveries. The study is published in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal).
The study used province-wide data from the Better Outcomes Registry & Network (BORN), Ontario's provincial birth registry. The authors analyzed data on 422,210 low-risk pregnancies over 6 years (2012 to 2018). There were 46,533 cesarean deliveries, of which 1827 (3.9%) were planned at the request of the mother; this proportion was unchanged during the years of study. Mothers who requested cesarean delivery ...
Structural racism contributes to the racial inequities in social determinants of psychosis
2021-05-03
The legacy of systemic racism in the U.S impacts psychosis risk at the individual and neighborhood level, according to a definitive review published online today. Researchers examined U.S. based evidence connecting social and environmental factors with outcomes relating to psychotic experiences, including schizophrenia.
The review examined potential risk factors and influence of structural racism within three key areas. These included disparities in neighborhoods; trauma and stress experienced at both collective and individual levels; and complications experienced around pregnancy.
Disparities in U.S. neighborhoods perpetuate disadvantage for racially minoritized ...
Election campaigns: attacks and smearing backfire and can benefit other candidates
2021-05-03
Candidates often give in to temptation to attack opponents in electoral campaigns through negative ads (more than 55% of the ads aired by the Clinton and Trump campaigns in 2016 were negative), even if evidence of this tactic effectiveness is, at least, mixed. A study by Bocconi University professors Vincenzo Galasso, Tommaso Nannicini and Salvatore Nunnari, just published in the American Journal of Political Science, reveals the backlash of electoral smearing and shows that, in a three-candidate race, it's the "idle candidate" (the one neither attacking nor being attacked) to have the upper hand.
During a three-candidate mayoral race in a mid-sized Italian town in 2015, the authors ...
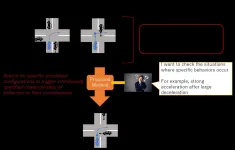
Technique to automatically discover simulation configurations for behaviors hard to test
2021-05-03
The research team led by Fuyuki Ishikawa at the National Institute of Informatics (NII, Japan) developed a technique to search automatically for simulation configurations that test various behaviors of automated driving systems. This research was conducted under the ERATO-MMSD project (*1) funded by the Japan Science and Technology Agency (JST, Japan). The proposed technique iterates trials on simulations using an optimization method called evolutionary computation so that it discovers simulation configurations that lead to specific features of driving behaviors such as high acceleration, deceleration, and steering operation. The outcome of this research was presented in ICST 2021 (*2), a flagship conference on software testing ...
Screening healthcare workers could serve as early warning system for future viruses
2021-05-03
New research has shown that COVID-19 infections in healthcare workers during the first wave of the pandemic provided an accurate sample of the general population, suggesting that data from healthcare workers could be used to estimate the severity of future viruses more quickly.
The study, led by researchers from RCSI University of Medicine and Health Sciences in collaboration with IBM Research, is published in PLOS ONE.
The researchers analysed the infection data from healthcare workers and the progression of the first wave of the COVID-19 outbreak using the reported daily infection numbers in Ireland. Using similar data in four other countries (Germany, UK, South Korea and Iceland), computer models showed how the disease progressed in different countries related to ...
Volunteer firefighters have higher levels of 'forever chemicals'
2021-05-03
Volunteer firefighters -- who comprise more than 65 percent of the U.S. fire service -- have higher levels of "forever chemicals," per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS), in their bodies than the general public, according to a Rutgers study.
The study, which was published in the International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, compared the levels of nine PFAS chemicals in the blood of volunteer firefighters against levels in the general population.
It is the first study to evaluate volunteer firefighters' exposure to PFAS, which are chemicals that accumulate in human bodies and in the environment and ...
Study finds heart transplantation using donation after cardiac death with NRP
2021-05-02
Boston, MA (May 2, 2021) - A new study, presented today at the AATS 101st Annual Meeting, found that heart transplantation using donation after cardiac death (DCD) with normothermic regional perfusion (NRP) is feasible in the United States. Broader application of DCD heart transplantation has the potential to increase cardiac allograft availability by 20-30 percent. Over a one-year period, from January 2020 to January 2021, eight heart transplants were performed using cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB) for immediate regional reperfusion and cardiac unloading to accomplish optimal myocardial salvage. All hearts ...
AATS Foundation scholarships shown to support success in academic surgery
2021-05-02
Boston, MA (May 2, 2021) - A new study, presented today at the AATS 101st Annual Meeting, finds that AATS Foundation fellowships support success in academic surgery career tracks. The AATS Foundation has two primary grant funding mechanisms: the AATS Foundation Scholarship and the Surgical Investigator Award. The study looked at publications, citations, NIH funding, and leadership position of awardees, among other factors.
Results show that recipients of both the AATS Surgical Investigator award and the Foundation Scholarship demonstrate sustained scholarship ...
Atrial fenestration during AVSD repair is associated with increased mortality
2021-05-02
Boston, MA (May 2, 2021) - A new study, presented today at the AATS 101st Annual Meeting, shows an association between decreased survival at five years and leaving an atrial communication at biventricular repair of unbalanced AVSD after adjusting for other known risk factors. During repair of atrioventricular septal defect (AVSD), surgeons may leave an atrial level shunt when they have concerns about postoperative pulmonary hypertension, a hypoplastic right ventricle (RV), hypoplastic left ventricle (LV), or as part of their routine practice. The study sought to determine factors associated with mortality after biventricular repair of AVSD.
The study included 581 patients enrolled from 31 Congenital Heart Surgeons' ...
Pulmonary endarterectomy achieves excellent results for patients with segmental CTEPH
2021-05-02
Boston, MA (April 30, 2021) - A new study, presented today at the AATS 101st Annual Meeting, found that patients treated surgically for segmental Chronic Thromboembolic Pulmonary Hypertension (CTEPH) had excellent outcomes with the vast majority doing very well in the long term without any additional treatment other than surgery. In addition, the study found that the proportion of CTEPH patients with segmental disease increased dramatically during the study period - from 2005 to 2020. At the beginning of the study, roughly seven percent of patients were diagnosed with segmental disease. During the last five years of the study, the proportion ...
[1] ... [2363]
[2364]
[2365]
[2366]
[2367]
[2368]
[2369]
[2370]
2371
[2372]
[2373]
[2374]
[2375]
[2376]
[2377]
[2378]
[2379]
... [8818]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.