Study: ISCHEMIA trial represents small fraction of patients undergoing intervention
2021-04-29
WASHINGTON, D.C. (APRIL 29, 2021) - Results from a new study find a broad range of patients who typically undergo revascularization for stable ischemic heart disease (SIHD) in the U.S. did not meet enrollment criteria for the ISCHEMIA trial. The data, which was presented today as late-breaking clinical science at the Society for Cardiovascular Angiography & Interventions (SCAI) 2021 Scientific Sessions, demonstrates a minority of SIHD patients referred for coronary intervention in contemporary practice clearly resemble those enrolled in the ISCHEMIA trial.
Ischemic heart disease impacts more than 13 million people in the United States and is the leading cause ...
Study reveals need for equitable access of minimally invasive heart procedure
2021-04-29
WASHINGTON, D.C, (April 29, 2021) - An analysis of growth patterns in transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR) programs across United States hospitals is being presented as late-breaking clinical science at the Society for Cardiovascular Angiography& Interventions (SCAI) 2021 Scientific Sessions. The findings indicate that TAVR hospital programs are predominately located in metropolitan areas serving patients with higher socioeconomic status, potentially contributing to the disparities in cardiac care.
TAVR is a minimally invasive procedure for patients in need of a valve repair or replacement and is an alternative to surgical aortic valve replacement (SAVR), a treatment ...
Two studies demonstrate new PCI approaches offer benefits to patients and physicians
2021-04-29
Washington, D.C., April 29, 2021 - Two studies related to percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) evaluating the use of risk-avoidance strategies and robotic-assisted technology, respectively, are being presented as late-breaking clinical science at the Society for Cardiovascular Angiography & Interventions (SCAI) 2021 Scientific Sessions. An analysis of strategically avoiding high-risk PCI cases indicates systematic risk-avoidance does not improve, and may worsen, the quality of hospital PCI programs. A study of a robotic-assisted PCI shows the technology is safe and effective for the treatment of both simple and complex lesions; this has the potential to address the occupational ...
Lateral flow testing should not be used as a green light for activities
2021-04-29
The United Kingdom government plans to implement mass scale population testing for SARS-CoV-2 infection using Lateral Flow Devices (LFDs), yet the devices' sensitivity is unknown. A study published in the open access journal PLOS Biology by Alan McNally at University of Birmingham, UK, and colleagues suggests while LFDs are highly effective in identifying SARS-CoV-2 in individuals with high quantities of viral RNA present on the test swab, they are inaccurate at diagnosing infections in individuals with lower viral loads.
LFDs are increasingly used to increase testing capacity and screen asymptomatic populations for SARS-CoV-2 infection in mass surveillance programs, yet there are few data ...
Fish have been swallowing microplastics since the 1950s
2021-04-29
Forget diamonds--plastic is forever. It takes decades, or even centuries, for plastic to break down, and nearly every piece of plastic ever made still exists in some form today. We've known for a while that big pieces of plastic can harm wildlife--think of seabirds stuck in plastic six-pack rings--but in more recent years, scientists have discovered microscopic bits of plastic in the water, soil, and even the atmosphere. To learn how these microplastics have built up over the past century, researchers examined the guts of freshwater fish preserved in museum collections; they found that fish have been swallowing microplastics since the 1950s and that the concentration of microplastics in their guts ...
Hubble watches how a giant planet grows
2021-04-29
NASA's Hubble Space Telescope is giving astronomers a rare look at a Jupiter-sized, still-forming planet that is feeding off material surrounding a young star.
"We just don't know very much about how giant planets grow," said Brendan Bowler of the University of Texas at Austin. "This planetary system gives us the first opportunity to witness material falling onto a planet. Our results open up a new area for this research."
Though over 4,000 exoplanets have been cataloged so far, only about 15 have been directly imaged to date by telescopes. And the planets are so far away and small, they are simply dots in the best photos. The team's fresh technique for using Hubble to directly image this planet paves a new route for further exoplanet ...
New Geology articles published online ahead of print in April
2021-04-29
Boulder, Colo., USA: Thirty-one new articles were published online ahead of
print for Geology in April. Topics include shocked zircon from the
Chicxulub impact crater; the Holocene Sonoran Desert; the architecture of
the Congo Basin; the southern Death Valley fault; missing water from the
Qiangtang Basin; sulfide inclusions in diamonds; how Himalayan collision
stems from subduction; ghost dune hollows; and the history of the Larsen C Ice Shelf. These Geology articles are online at END ...
Plankton have a genome like no other
2021-04-29
The genome of single-celled plankton, known as dinoflagellates, is organized in an incredibly strange and unusual way, according to new research. The findings lay the groundwork for further investigation into these important marine organisms and dramatically expand our picture of what a eukaryotic genome can look like.
Researchers from KAUST, the U.S. and Germany have investigated the genomic organization of the coral-symbiont dinoflagellate Symbiodinium microadriaticum. The S. microadriaticum genome had already been sequenced and assembled into segments known as scaffolds but lacked a chromosome-level assembly.
The team used a technique known as Hi-C to detect ...
Baby mantis shrimp don't pull their punches
2021-04-29
DURHAM, N.C. - Mantis shrimp don't need baby food. They start their life as ferocious predators who know how to throw a lethal punch.
A new study appearing April 29 in the Journal of Experimental Biology shows that larvae of the Philippine mantis shrimp (Gonodactylaceus falcatus) already display the ultra-fast movements for which these animals are known, even when they are smaller than a short grain of rice.
Their ultra-fast punching appendages measure less than 1 mm, and develop right when the larva exhausts its yolk reserves, moves away from its nest and out into the big wide sea. It immediately begins preying on organisms smaller than a grain of sand.
Although they accelerate their arms almost 100 times faster than a Formula One car, Philippine mantis shrimp larvae are slower ...
Combining solar panels and lamb grazing increases land productivity, study finds
2021-04-29
CORVALLIS, Ore. - Land productivity could be greatly increased by combining sheep grazing and solar energy production on the same land, according to new research by Oregon State University scientists.
This is believed to be the first study to investigate livestock production under agrivoltaic systems, where solar energy production is combined with agricultural production, such as planting agricultural crops or grazing animals.
The researchers compared lamb growth and pasture production in pastures with solar panels and traditional open pastures. They found less overall but higher quality forage in the solar pastures and that lambs raised in each pasture type ...
High vaccination rate is key to course of COVID-19 pandemic, modeling shows
2021-04-29
ROCHESTER, Minn. -- The Mayo Clinic data scientists who developed highly accurate computer modeling to predict trends for COVID-19 cases nationwide have new research that shows how important a high rate of vaccination is to reducing case numbers and controlling the pandemic.
Vaccination is making a striking difference in Minnesota and keeping the current level of positive cases from becoming an emergency that overwhelms ICUs and leads to more illness and death, according to a study published in Mayo Clinic Proceedings. The study, entitled "Quantifying the Importance of COVID-19 Vaccination to Our Future Outlook," outlines how Mayo's COVID-19 predictive modeling can assess future trends based on the pace of vaccination, and how vaccination trends are crucial ...
How long is a day on Venus? Scientists crack mysteries of our closest neighbor
2021-04-29
Venus is an enigma. It's the planet next door and yet reveals little about itself. An opaque blanket of clouds smothers a harsh landscape pelted by acid rain and baked at temperatures that can liquify lead.
Now, new observations from the safety of Earth are lifting the veil on some of Venus' most basic properties. By repeatedly bouncing radar off the planet's surface over the last 15 years, a UCLA-led team has pinned down the precise length of a day on Venus, the tilt of its axis and the size of its core. The findings are published today in the journal Nature Astronomy.
"Venus is our sister planet, and yet these fundamental properties have remained unknown," said Jean-Luc Margot, a UCLA professor of Earth, planetary and space sciences who led the research.
Earth ...
Smart cell therapies for solid cancers 'ready to move towards clinical trials'
2021-04-29
Immunotherapies that fight cancer have been a life-saving advancement for many patients, but the approach only works on a few types of malignancies, leaving few treatment options for most cancer patients with solid tumors. Now, in two related papers published April 28, 2021 in Science Translational Medicine, researchers at UCSF have demonstrated how to engineer smart immune cells that are effective against solid tumors, opening the door to treating a variety of cancers that have long been untouchable with immunotherapies.
By "programming" basic computational abilities into immune cells that are designed to attack cancer, the researchers have overcome a number of major hurdles that have kept these strategies ...
A psychologist's guide to donating more effectively to charities
2021-04-29
The decision to donate to a charity is often driven by emotion rather than by calculated assessments based on how to make the biggest impact. In a review article published on April 29 in the journal Trends in Cognitive Sciences, researchers look at what they call "the psychology of (in)effective altruism" and how people can be encouraged to direct their charitable contributions in ways that allow them to get more bang for the buck--and help them to have a larger influence.
"In the past, most behavioral science research that's looked at charitable giving has focused on quantity and how people might be motivated to give more money to charity, or to give at all," says first author Lucius Caviola (@LuciusCaviola), a postdoctoral researcher in the Department of Psychology at Harvard University. ...
Small generator captures heat given off by skin to power wearable devices
2021-04-29
Scientists in China have developed a small, flexible device that can convert heat emitted from human skin to electrical power. In their research, presented April 29 in the journal Cell Reports Physical Science, the team showed that the device could power an LED light in real time when worn on a wristband. The findings suggest that body temperature could someday power wearable electronics such as fitness trackers.
The device is a thermoelectric generator (TEG) that uses temperature gradients to generate power. In this design, researchers use the difference between the warmer body temperature and the relatively cooler ambient environment to generate power.
"This is a field with great potential," says corresponding author Qian Zhang of Harbin ...
Baby's first poop can help predict risk of developing allergies
2021-04-29
It may seem like an unusual place to go looking for answers, but the contents of a baby's first diaper can reveal a lot about a newborn's future health.
In a new study published today in Cell Reports Medicine, a team of University of British Columbia (UBC) researchers has shown that the composition of a baby's first poop--a thick, dark green substance known as meconium--is associated with whether or not a child will develop allergies within their first year of life.
"Our analysis revealed that newborns who developed allergic sensitization by one year of age had significantly less 'rich' meconium at birth, compared to those who didn't develop allergic sensitization," says the study's senior co-author Dr. Brett Finlay, a professor at the Michael Smith ...
New law of physics helps humans and robots grasp the friction of touch
2021-04-29
Although robotic devices are used in everything from assembly lines to medicine, engineers have a hard time accounting for the friction that occurs when those robots grip objects - particularly in wet environments. Researchers have now discovered a new law of physics that accounts for this type of friction, which should advance a wide range of robotic technologies.
"Our work here opens the door to creating more reliable and functional haptic and robotic devices in applications such as telesurgery and manufacturing," says Lilian Hsiao, an assistant professor of chemical and biomolecular engineering at North Carolina State University and corresponding author of a paper on the work.
At ...
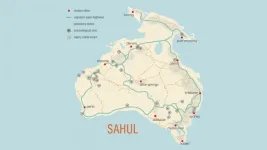
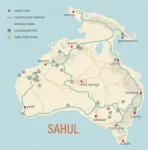
First Australian populations followed footpath 'superhighways' across the continent
2021-04-29
The best path across the desert is rarely the straightest. For the first human inhabitants of Sahul -- the super-continent that underlies modern Australia and New Guinea -- camping at the next spring, stream, or rock shelter allowed them to thrive for hundreds of generations. Those who successfully traversed the landmarks made their way across the continent, spreading from their landfall in the Northwest across the continent, making their way to all corners of Australia and New Guinea.
By simulating the physiology and decisions of early way-finders, an international team* of archaeologists, geographers, ecologists, and computer scientists has mapped the probable "superhighways" that led ...
For young breast cancer patients, fertility concerns influence therapy decisions
2021-04-29
BOSTON - Concerns about fertility often influence how young women with breast cancer approach treatment decisions and are a reason for forgoing or delaying hormone-blocking therapy, a new study by Dana-Farber Cancer Institute investigators shows.
The findings, published online today by the journal Cancer, reinforce the need for physicians to talk with patients about their fertility-related priorities and address them in treatment plans, the study authors write. Such conversations are important not only at the start of treatment but during its entire course, as patients' goals ...
Machine learning algorithm helps unravel the physics underlying quantum systems
2021-04-29
Scientists from the University of Bristol's Quantum Engineering Technology Labs (QETLabs) have developed an algorithm that provides valuable insights into the physics underlying quantum systems - paving the way for significant advances in quantum computation and sensing, and potentially turning a new page in scientific investigation.
In physics, systems of particles and their evolution are described by mathematical models, requiring the successful interplay of theoretical arguments and experimental verification. Even more complex is the description of systems of particles interacting with each other at the quantum mechanical level, which is often done using a Hamiltonian model. The process of formulating Hamiltonian models from observations is made even harder by the nature ...
Mapping the 'superhighways' travelled by the first Australians
2021-04-29
'Superhighways' used by a population of up to 6.5 million Indigenous Australians to navigate the continent tens of thousands of years ago have been revealed by new research using sophisticated modelling of past people and landscapes.
The new insights into how people not only survived, but thrived, in harsh environments provide further evidence of the capacity and resilience of the ancestors of Indigenous people, and help paint a picture of large, well-organised groups navigating tough terrain.
The 'peopling' of Sahul -- the combined mega continent that joined Australia with New Guinea when ...
The Arctic's greening, but it won't save us
2021-04-29
There was a hope that as more plants start to grow in Arctic and boreal latitudes as our warming climate makes those regions more hospitable for plants, those photosynthesizing plants would work to help sequester the atmospheric carbon dioxide that helped them flourish in the first place. But new research led by scientists at UC Irvine and Boston University, out in Nature Climate Change, suggests that all the new green biomass is not as large a carbon sink as scientists had hoped.
"What does greening really mean? Can we really trust it to save us from climate change?" said Jon Wang, an Earth system scientist at UCI who the led the work alongside BU Earth & Environment professor Mark Friedl. "A big question is: What'll happen to the carbon that's currently ...
Caregiver perceptions of children's psychological well-being during COVID-19 pandemic
2021-04-29
What The Study Did: This survey study examines the associations of school closure and exposure to COVID-19-related stressors with caregivers' perceptions of their children's mental well-being.
Authors: Tali Raviv, Ph.D., of the Ann and Robert H. Lurie Children's Hospital of Chicago, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.11103)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflict of interest disclosures. Please see the article ...
Association of cancer screening decline with COVID-19
2021-04-29
What The Study Did: Using insurance claims data, the change in screening rates for breast, colorectal and prostate cancers during the COVID-19 pandemic were estimated as well as the overall decline in cancer screening last year among the U.S. population.
Authors: Ronald Chen, M.D., M.P.H., of the University of Kansas in Kansas City, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamaoncol.2021.0884)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflicts of interest disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
INFORMATION:
Media ...
Complications of COVID-19 nasopharyngeal swab test
2021-04-29
What The Study Did: This case series investigates the frequency and type of SARS-CoV-2 nasopharyngeal test complications in Helsinki, Finland.
Authors: Anni Koskinen, M.D., Ph.D., of the Helsinki University Hospital in Finland, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamaoto.2021.0715)
Editor's Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
INFORMATION:
Media advisory: The full article is linked to this news release.
Embed this link to provide your readers free access to the full-text article This ...
[1] ... [2362]
[2363]
[2364]
[2365]
[2366]
[2367]
[2368]
[2369]
2370
[2371]
[2372]
[2373]
[2374]
[2375]
[2376]
[2377]
[2378]
... [8813]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.