Finding new life for wine-grape residue
2021-04-23
California produces nearly 4 million tons of world-class wine each year, but with that comes thousands of tons of residue like grape skins, seeds, stems and pulp. What if scientists could harness that viticultural waste to help promote human health?
Maybe they can, according to new research from food scientists at the University of California, Davis. In a study published in the journal LWT - Food Science and Technology, the team discovered a wealth of potentially health-enhancing compounds and sugar molecules called oligosaccharides within chardonnay wine-grape pomace.
Oligosaccharides are found in many plant and animal tissues, including human breast milk. Recent advances have revealed oligosaccharides' vast potential ...
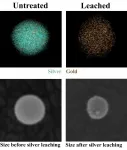
Silver ions hurry up, then wait as they disperse
2021-04-22
HOUSTON - (April 22, 2021) - There's gold in them thar nanoparticles, and there used to be a lot of silver, too. But much of the silver has leached away, and researchers want to know how.
Gold-silver alloys are useful catalysts that degrade environmental pollutants, facilitate the production of plastics and chemicals and kill bacteria on surfaces, among other applications. In nanoparticle form, these alloys could be useful as optical sensors or to catalyze hydrogen evolution reactions.
But there's an issue: Silver doesn't always stay put.
A new study by scientists at Rice University and the University ...
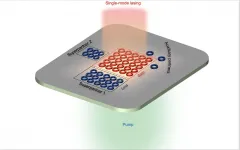
Army-funded research paves way for improved lasers, communications
2021-04-22
RESEARCH TRIANGLE PARK, N.C. -- New photonics research paves the way for improved lasers, high-speed computing and optical communications for the Army.
Photonics has the potential to transform all manners of electronic devices by storing and transmitting information in the form of light, rather than electricity. Using light's speed and the way information can be layered in its various physical properties can increase the speed of communication while reducing wasted energy; however, light sources such as lasers need to be smaller, stronger and more stable to achieve that, researchers ...
What Parkinson's disease patients reveal about how art is experienced and valued
2021-04-22
PHILADELPHIA-- Art appreciation is considered essential to human experience. While taste in art varies depending on the individual, cognitive neuroscience can provide clues about how viewing art affects our neural systems, and evaluate how these systems inform our valuation of art. For instance, one study shows that viewing art activates motor areas, both in clear representations of movement, like Adam and Eve in Michelangelo's Expulsion from Paradise, and in implied movement through brush strokes, like in Franz Kline's gestural paintings.
Altered neural functioning, like that experienced in patients with Parkinson's disease, changes the way ...
Law professor argues for removing police from traffic enforcement
2021-04-22
University of Arkansas law professor Jordan Blair Woods challenges the conventional wisdom that only police can enforce traffic laws.
In "Traffic Without Police," to be published in Stanford Law Review, Woods articulates a new legal framework for traffic enforcement, one that separates it from critical police functions, such as preventing and deterring crime, conducting criminal investigations and responding to emergencies.
If not the police, who then would enforce traffic laws? As Woods explains, jurisdictions would delegate most traffic enforcement to newly created traffic agencies. These public offices would operate independently from ...
Taking down human traffickers through online ads
2021-04-22
Researchers at Carnegie Mellon University and McGill University have adapted an algorithm first developed to spot anomalies in data, like typos in patient information at hospitals or errant figures in accounting, to identify similarities across escort ads.
The algorithm scans and clusters similarities in text and could help law enforcement direct their investigations and better identify human traffickers and their victims, said Christos Faloutsos, the Fredkin Professor in Artificial Intelligence at CMU's School of Computer Science, who led the team.
"Our algorithm can put the millions of advertisements together and highlight the common parts," Faloutsos said. "If they have a lot of things in common, it's not guaranteed, but it's highly likely that it ...
Life satisfaction among young people linked to collectivism
2021-04-22
An international group of scientists from Italy, the USA, China and Russia have studied the relationship between collectivism, individualism and life satisfaction among young people aged 18-25 in four countries. They found that the higher the index of individualistic values at the country level, the higher the life satisfaction of young people's lives. At the individual level, however, collectivism was more significant for young people. In all countries, young people found a positive association between collectivism, particularly with regard to family ties, and life satisfaction. This somewhat contradicts and at the same time clarifies the results ...
Use of e-cigarettes plus tobacco cigarettes linked to higher risk of respiratory symptoms
2021-04-22
BOSTON - Exclusively using (or "vaping") e-cigarettes can help people quit smoking, but many people using e-cigarettes to quit smoking continue to smoke cigarettes. New research led by investigators at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) reveals that respiratory symptoms--such as cough and wheeze--are more likely to develop when people use both e-cigarettes and tobacco cigarettes together compared with using either one alone. The findings are published in the American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine, the flagship journal of the American Thoracic Society.
The ...
Ancient Indigenous forest gardens promote a healthy ecosystem: SFU study
2021-04-22
A new study by Simon Fraser University historical ecologists finds that Indigenous-managed forests--cared for as "forest gardens"--contain more biologically and functionally diverse species than surrounding conifer-dominated forests and create important habitat for animals and pollinators. The findings are published today in Ecology and Society.
According to researchers, ancient forests were once tended by Ts'msyen and Coast Salish peoples living along the north and south Pacific coast. These forest gardens continue to grow at remote archaeological villages on Canada's northwest coast and are composed ...
Hungry fruit flies are extreme ultramarathon fliers
2021-04-22
In 2005, an ultramarathon runner ran continuously 560 kilometers (350 miles) in 80 hours, without sleeping or stopping. This distance was roughly 324,000 times the runner's body length. Yet this extreme feat pales in comparison to the relative distances that fruit flies can travel in a single flight, according to new research from Caltech.
Caltech scientists have now discovered that fruit flies can fly up to 15 kilometers (about 9 miles) in a single journey--6 million times their body length, or the equivalent of over 10,000 kilometers for the average human. In comparison to body length, this is further than many migratory species of birds can fly in a day. To discover this, the team conducted experiments in a dry lakebed ...
Pregnant women with COVID-19 face high mortality rate
2021-04-22
In a worldwide study of 2,100 pregnant women, those who contracted COVID-19 during pregnancy were 20 times more likely to die than those who did not contract the virus.
UW Medicine and University of Oxford doctors led this first-of-its-kind study, published today in JAMA Pediatrics. The investigation involved more than 100 researchers and pregnant women from 43 maternity hospitals in 18 low-, middle- and high-income nations; 220 of the women received care in the United States, 40 at UW Medicine. The research was conducted between April and August of 2020.
The study is unique because each woman affected by COVID-19 was compared with two uninfected pregnant women who gave birth during the same span in the same hospital.
Aside ...
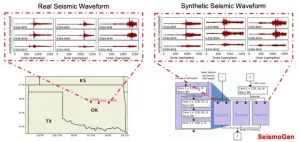
Machine learning model generates realistic seismic waveforms
2021-04-22
LOS ALAMOS, N.M., April 22, 2021--A new machine-learning model that generates realistic seismic waveforms will reduce manual labor and improve earthquake detection, according to a study published recently in JGR Solid Earth.
"To verify the e?cacy of our generative model, we applied it to seismic ?eld data collected in Oklahoma," said Youzuo Lin, a computational scientist in Los Alamos National Laboratory's Geophysics group and principal investigator of the project. "Through a sequence of qualitative and quantitative tests and benchmarks, we saw that our model can generate high-quality synthetic waveforms and improve machine learning-based earthquake detection algorithms."
Quickly and accurately detecting earthquakes can be a challenging task. Visual detection done ...
Study paves the way for new photosensitive materials
2021-04-22
Photocatalysts are useful materials, with a myriad of environmental and energy applications, including air purification, water treatment, self-cleaning surfaces, pollution-fighting paints and coatings, hydrogen production and CO2 conversion to sustainable fuels.
An efficient photocatalyst converts light energy into chemical energy and provides this energy to a reacting substance, to help chemical reactions occur.
One of the most useful such materials is knows as titanium oxide or titania, much sought after for its stability, effectiveness as a photocatalyst ...
Reprogramming fibroblasts could result in scar-free wound healing, suggests study in mice
2021-04-22
Researchers have determined a way to potentially minimize or eliminate scarring in wounded skin, by further decoding the scar-promoting role of a specific class of dermal fibroblast cells in mice. By preventing these cells from expressing the transcription factor Engrailed-1 (En-1), Shamik Mascharak and colleagues reprogrammed these cells to take on a different identity, capable of regenerating wounded skin - including the restoration of structures such as hair follicles and sweat glands that are absent in scarred skin tissue. With further development and testing, their discovery could lead to therapies to reduce or completely avoid scarring ...
China requires switch to zero-carbon energy to achieve more ambitious Paris Agreement goal, models S
2021-04-22
A new multi-model analysis suggests that China will need to reduce its carbon emissions by over 90% and its energy consumption by almost 40%, in order to meet the more ambitious target set by the 2016 Paris Agreement. The Agreement called for no more than a 1.5°Celsius (C) global temperature rise by 2050. These results provide a clear directive for China to deploy multiple strategies at once for long-term emission mitigation, the authors say. The findings also highlight the need for more research on the economic consequences of working toward a 1.5°C warming limit, arguing that current studies are far from adequate to inform the sixth assessment report (AR 6) on climate change planned for release by the United Nations' Intergovernmental ...
Medical record analysis links cannabis use disorder in pregnancy to infant health problems
2021-04-22
A new study of nearly five million live births recorded in California from 2001 to 2012 found that babies born to mothers diagnosed with cannabis use disorders at delivery were more likely to experience negative health outcomes, including preterm birth and low birth weight, compared to babies born to mothers without a cannabis use disorder diagnosis. The analysis, published today in Addiction and funded by the National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA), part of the National Institutes of Health, adds to a growing body of evidence that prenatal exposure to cannabis (marijuana) may be associated with poor birth outcomes, and sheds light on infant health one year after birth.
Recent studies have shown the ...
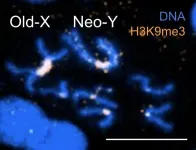
Toxic masculinity: Y chromosome contributes to a shorter lifespan in male flies
2021-04-22
Males may have shorter lifespans than females due to repetitive sections of the Y chromosome that create toxic effects as males get older. These new findings appear in a study by Doris Bachtrog of the University of California, Berkeley published April 22 in PLOS Genetics.
In humans and other species with XY sex chromosomes, females often live longer than males. One possible explanation for this disparity may be repetitive sequences within the genome. While both males and females carry these repeat sequences, scientists have suspected that the large number of repeats ...
Cannabis use disorder rate rose among pregnant women between 2001-2012
2021-04-22
A study of almost 5 million live births in California by researchers at the Herbert Wertheim School of Public Health and Human Longevity Science at University of California San Diego reports that babies born to mothers diagnosed with cannabis use disorder were more likely to experience negative health outcomes, such as preterm birth and low birth weight, than babies born to mothers without a cannabis use disorder diagnosis.
The findings are published online in the April 22, 2021 issue of the journal Addiction. The National Institute on Drug Abuse, part of the National Institutes of Health, funded the study.
Cannabis use disorder is a diagnostic term with specific criteria that defines continued cannabis use despite ...
Anti-aging compound improves muscle glucose metabolism in people
2021-04-22
A natural compound previously demonstrated to counteract aspects of aging and improve metabolic health in mice has clinically relevant effects in people, according to new research at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis.
A small clinical trial of postmenopausal women with prediabetes shows that the compound NMN (nicotinamide mononucleotide) improved the ability of insulin to increase glucose uptake in skeletal muscle, which often is abnormal in people with obesity, prediabetes or Type 2 diabetes. NMN also improved expression of genes that are involved in muscle structure and remodeling. However, the treatment did not lower blood glucose or blood pressure, improve blood lipid profile, increase insulin sensitivity in the liver, reduce fat ...
What does 1.5 °C warming limit mean for China?
2021-04-22
As part of the Paris Agreement, nearly all countries agreed to take steps to limit the average increase in global surface temperature to less than 2 °C, or preferably 1.5 °C, compared with preindustrial levels. Since the Agreement was adopted, however, concerns about global warming suggest that countries should aim for the "preferable" warming limit of 1.5 °C.
What are the implications for China of trying to achieve this lower limit?
Prof. DUAN Hongbo from the University of Chinese Academy of Sciences and Prof. WANG Shouyang from the Academy of Mathematics and Systems Science of the Chinese Academy ...
Researchers trace spinal neuron family tree
2021-04-22
LA JOLLA--(April 22, 2021) Spinal cord nerve cells branching through the body resemble trees with limbs fanning out in every direction. But this image can also be used to tell the story of how these neurons, their jobs becoming more specialized over time, arose through developmental and evolutionary history. Salk researchers have, for the first time, traced the development of spinal cord neurons using genetic signatures and revealed how different subtypes of the cells may have evolved and ultimately function to regulate our body movements.
The findings, published in ...
International research teams explore genetic effects of Chernobyl radiation
2021-04-22
In two landmark studies, researchers have used cutting-edge genomic tools to investigate the potential health effects of exposure to ionizing radiation, a known carcinogen, from the 1986 accident at the Chernobyl nuclear power plant in northern Ukraine. One study found no evidence that radiation exposure to parents resulted in new genetic changes being passed from parent to child. The second study documented the genetic changes in the tumors of people who developed thyroid cancer after being exposed as children or fetuses to the radiation released by the accident.
The findings, published around the ...
Scientists uncover a molecule that can help coronavirus escape antibodies
2021-04-22
Researchers have found that a natural molecule can effectively block the binding of a subset of human antibodies to SARS-CoV-2. The discovery may help explain why some COVID-19 patients can become severely ill despite having high levels of antibodies against the virus.
In their research, published in Science Advances today (22 April 2021), teams from the Francis Crick Institute, in collaboration with researchers at Imperial College London, Kings College London and UCL (University College London), found that biliverdin and bilirubin, natural molecules present in the body, can suppress the ...
Scientists unmask new neutralizing antibody target on SARS-CoV-2 spike protein
2021-04-22
Researchers have identified another potential target for neutralizing antibodies on the SARS-CoV-2 Spike protein that is masked by metabolites in the blood. As a result of this masking, the target may be inaccessible to antibodies, because they must compete with metabolite molecules to bind to the otherwise open region, the study authors speculate. This competitive binding activity may represent another method of immune evasion by the SARS-CoV-2 virus. Although further validation work is needed, the findings suggest that strategies to unmask this region - thus making it more visible and accessible to antibodies - may help lead to new vaccine designs. ...
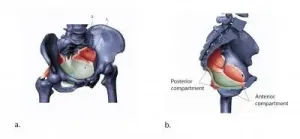
Why the human body has not evolved to make childbirth easier -- or has it?
2021-04-22
AUSTIN, Texas -- Despite advances in medicine and technology, childbirth isn't likely to get much easier on women from a biological perspective.
Engineers at The University of Texas at Austin and University of Vienna revealed in new research a series of evolutionary trade-offs that have created a near-perfect balance between supporting childbirth and keeping organs intact on a day-to-day basis. Human reproduction is unique because of the comparatively tight fit between the birth canal and baby's head, and it is likely to stay that way because of these competing biological imperatives.
The size of the pelvic floor and canal is key to keeping this balance. These opposing duties have constrained the ability of the pelvic floor to evolve over time to make childbirth easier because doing ...
[1] ... [2388]
[2389]
[2390]
[2391]
[2392]
[2393]
[2394]
[2395]
2396
[2397]
[2398]
[2399]
[2400]
[2401]
[2402]
[2403]
[2404]
... [8814]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.