May Day: How electricity brought power to strikes
2021-04-28
Areas in Sweden with early access to electricity at the start of the 1900s underwent rapid change. Electrification led to more strikes, but it was not those who were threatened by the new technology who protested. Instead, it was the professional groups who had acquired a stronger negotiating position - thanks to technological development, according to new research from Lund University.
Labour market conditions are affected by new technology. Currently, the impact of automation on the labour market is often discussed, whether jobs will disappear as computers take over, or whether digitalisation drives development towards a gig economy with uncertain employment conditions. One fear is that the technological development could generate social unrest and a risk of increased ...
Measuring the Moon's nano dust is no small matter
2021-04-28
Like a chameleon of the night sky, the Moon often changes its appearance. It might look larger, brighter or redder, for example, due to its phases, its position in the solar system or smoke in Earth's atmosphere. (It is not made of green cheese, however.)
Another factor in its appearance is the size and shape of moon dust particles, the small rock grains that cover the moon's surface. Researchers at the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) are now measuring tinier moon dust particles than ever before, a step toward more precisely explaining the Moon's apparent color ...
New method might improve prostate cancer and high cholesterol treatments
2021-04-28
Researchers from the University of Copenhagen, in collaboration with their Swiss colleagues at the University Hospital of Bern, have cracked the code for controlling a group of enzymes that affect our metabolism.
The researchers' findings could help us avoid diseases ranging from high cholesterol to infertility to certain types of cancer, which are all due, among other things, to hormonal imbalances.
They have found a way to influence a special protein called cytochrome P450 reductase (POR) -- popularly characterized as the 'conductor' of the body's protein orchestra, which helps regulate our hormones and makes it possible to break down medicinal products in the liver.
"We have developed a method to ...
How can we stop mankind from stagnating?
2021-04-28
Fast growth of the global human population has long been regarded as a major challenge that faces mankind. Presently, this challenge is becoming even more serious than before, in particular because many natural resources are estimated to deplete before the end of this century.
The increasing population pressure on agriculture and ecosystems and the environment more generally is predicted to result in worldwide food and water shortages, pollution, lack of housing, poverty and social tension. The situation is exacerbated by global climate change as considerable areas of land are predicted to be flooded and hence taken out of human's use.
It is widely believed ...
Show me your playlist and I'll tell you who you are
2021-04-28
According to the researchers, three songs from a playlist are enough to identify the person who chose the songs. Hence, companies like YouTube and Spotify can accumulate a great deal of information about their users based only on their musical preferences.
The study was led by Dr. Ori Leshman of the Jaime and Joan Constantiner School of Education at Tel Aviv University and Dr. Ron Hirschprung of the Department of Management and Industrial Engineering at Ariel University. The study was published in the journal Telematics and Informatics.
The study included ...
Christmas Eve coke works fire followed by asthma exacerbations
2021-04-28
PITTSBURGH, April 28, 2021 - Asthma exacerbations rose following a catastrophic Christmas Eve fire two years ago that destroyed pollution controls at the Clairton Coke Works--the largest such facility in the nation, a University of Pittsburgh Graduate School of Public Health analysis concludes.
The study, published in the Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology, was possible because of a collaboration with the University of Pittsburgh Asthma and Environmental Lung Health Institute at UPMC and the Allegheny County Health Department, with funding from The Heinz Endowments.
"In addition to verifying that people living within a 10-mile radius of the coke works had higher rates of asthma exacerbations and use of albuterol rescue medication than those living outside the radius, we learned ...
Socioeconomic deprivation modifies genetic influence on higher education
2021-04-28
A comprehensive study from Uppsala University demonstrates that socioeconomic deprivation modifies genetic effects on higher education and abstract reasoning. The paper illustrates how genes play a greater role in educational attainment in more socioeconomically deprived regions of the United Kingdom. The study was recently published in the American Journal of Psychiatry.
Education is an important factor in an individual's life and strongly linked to economic outcomes and quality of life. The likelihood of completing higher education is partly determined by genetic factors. Common genetic variants have previously been estimated to contribute 11-13% ...
Job changes following breast cancer are frequent in some cases
2021-04-28
Breast cancer diagnosis: Around 88 percent of patients survive the dangerous disease in the first five years. Work is important for getting back to normality. Researchers from the University of Bonn and the German Cancer Society investigated how satisfied former patients are with their occupational development over a period of five to six years since diagnosis. About half experienced at least one job change during the study period. Around ten percent of those affected even report involuntary changes. The researchers conclude that there is a need for long-term support measures for patients. The study is now published in the Journal of Cancer Survivorship.
Breast cancer is the most commonly occurring cancer in women. ...
New model may explain the mystery of asymmetry in Parkinson's disease
2021-04-28
Amsterdam, April 28, 2021 - Parkinson's disease (PD) is characterized by slowness of movement and tremors, which often appear asymmetrically in patients. The new model of PD described in this review article published in the Journal of Parkinson's Disease may explain these perplexing asymmetrical motor symptoms and other known variations such as different degrees of constipation and sleep disorders.
PD is a heterogenous disorder. Symptoms and the speed with which symptoms progress vary greatly among patients. In three-quarters of patients, motor symptoms initially appear in one side of the body. Some ...
A pioneering study: Plant roots act like a drill
2021-04-28
In an interdisciplinary research project carried out at Tel Aviv University, researchers from the School of Plant Sciences affiliated with the George S. Wise Faculty of Life Sciences collaborated with their colleagues from the Sackler Faculty of Medicine in order to study the course of plant root growth. The plant researchers were aided by a computational model constructed by cancer researchers studying cancer cells, which they adapted for use with plant root cells.
The fascinating and groundbreaking findings: For the first time in the world, it has been demonstrated, at the resolution of a single cell, that the root grows ...
A path to graphene topological qubits
2021-04-28
In the quantum realm, electrons can group together to behave in interesting ways. Magnetism is one of these behaviors that we see in our day-to-day life, as is the rarer phenomena of superconductivity. Intriguingly, these two behaviors are often antagonists, meaning that the existence of one of them often destroys the other. However, if these two opposite quantum states are forced to coexist artificially, an elusive state called a topological superconductor appears, which is exciting for researchers trying to make topological qubits.
Topological qubits are exciting as one of the potential technologies for future quantum computers. In particular, topological qubits provide the basis for topological quantum ...
Brazilian coronavirus variant likely to be more transmissible and able to evade immunity
2021-04-28
Even though more and more vaccines against the coronavirus are being administered all over the world, many countries are still battling with outbreaks and face difficulties providing help to those in need.
One of those countries is Brazil. Here, they are facing a massive second wave outbreak, many daily deaths and instances of the health care systems collapsing. In the city of Manaus things have looked exceptionally bleak from December and through to the early spring.
The city was hit so hard by the first wave in 2020 that it was actually thought to be one of the few places in the world to have reached herd immunity. An estimated 75 percent of the population in the city had been infected. But then the second wave ...
Researchers develop comprehensive pregnancy care management plan among Chinese pregnant women type 1 diabetes
2021-04-28
The research team led by Prof. WENG Jianping from University of Science and Technology of China (USTC) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences has implemented a comprehensive preconception-to-pregnancy management plan, namely CARNATION study, for women with type1 diabetes (T1D), to reduce the risks of adverse pregnancy outcomes and improve the pregnancy care since 2015. The study was published in Diabetes Care.
The management plan, approved by the National Health and Family Planning Commission of the People's Republic of China, is made up of the checklist for the relevant health care providers (HCPs) covering 20 items of care in different ...
New algorithm makes it easier for computers to solve decision making problems
2021-04-28
Computer scientists often encounter problems relevant to real-life scenarios. For instance, "multiagent problems," a category characterized by multi-stage decision-making by multiple decision makers or "agents," has relevant applications in search-and-rescue missions, firefighting, and emergency response.
Multiagent problems are often solved using a machine learning technique known as "reinforcement learning" (RL), which concerns itself with how intelligent agents make decisions in an environment unfamiliar to them. An approach usually adopted in such an endeavor is policy iteration (PI), which starts off with a "base policy" and then improves on it to generate a "rollout policy" (with the process of generation ...
Spring forest flowers likely key to bumble bee survival, Illinois study finds
2021-04-28
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. -- For more than a decade, ecologists have been warning of a downward trend in bumble bee populations across North America, with habitat destruction a primary culprit in those losses. While efforts to preserve wild bees in the Midwest often focus on restoring native flowers to prairies, a new Illinois-based study finds evidence of a steady decline in the availability of springtime flowers in wooded landscapes.
The scarcity of early season flowers in forests - a primary food source for bumble bees at this time of year - likely endangers ...
Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions updates consensus guidelines on best practices
2021-04-28
WASHINGTON - The Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions (SCAI) has released an expert consensus statement providing cardiologists, cath lab directors, and hospital leadership guidance for contemporary cath lab standards. The document, "SCAI Expert Consensus Update on Best Practices in the Cardiac Catheterization Laboratory" will be presented today at the SCAI 2021 Virtual Scientific Sessions with simultaneous publication in Catheterization & Cardiovascular Interventions. The statement has been endorsed by the American College of Cardiology Clinical Policy Approval Committee, American Heart Association, ...
Novel imaging method to visualize respiratory activity of 3D tissue models
2021-04-28
Cells breathe, to an extent, exchanging gases, taking in energy sources from the environment and processing it. Now, researchers from Tohoku University in Japan have shone a light on the process in a new way.
Their demonstrated visualization method in model systems was made available online on March 12th in Biosensors and Bioelectronics, ahead of the June print edition.
The researchers used spheroids - cultured cells within a close-to-natural environment - to mimic a biological tissue using mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs). Due to MCSs' ability to self-renew and differentiate into various ...
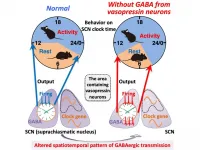
How behavioral rhythms are fine-tuned in the brain
2021-04-28
Our bodies and behaviors often seem to have rhythms of their own. Why do we go to the bathroom at the same time every day? Why do we feel off if we can't go to sleep at the right time? Circadian rhythms are a behind-the-scenes force that shape many of our behaviors and our health. Michihiro Mieda and his team at Kanazawa University in Japan are researching how the brain's circadian rhythm control center regulates behavior.
Termed the superchiasmatic nucleus, or SCN, the control center contains many types of neurons that transmit signals using the molecule GABA, but little is known about how each type contributes to our bodily rhythms. In their newest study, the researchers focused on GABA neurons that produce arginine vasopressin, a hormone that regulates ...
New device reduces hemostasis time following catheterization and improves efficiency
2021-04-28
WASHINGTON, D.C, (April 28, 2021) - A new study reveals the use of a potassium ferrate hemostatic patch (PFHP) reduces the time to hemostasis for patients receiving cardiac catherization. The findings indicate a faster approach to removing the compression band used during the procedure, without compromising safety. Positive results of the STAT2 trial follow an initial pilot study and are being presented as late-breaking clinical science at the Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions (SCAI) 2021 Virtual Scientific Sessions.
Cardiac ...
African Americans with coronary artery disease impacted by non-traditional risk factors
2021-04-28
WASHINGTON, D.C, (April 28, 2021) - A retrospective analysis of risk factors for coronary artery disease (CAD) in young African American patients is being presented today at the Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions (SCAI) 2021 Virtual Scientific Sessions. The findings reveal this specific patient segment, African-Americans under age 45, experiences greater CAD risk factors related to smoking, drug and alcohol abuse, HIV as well as mental health conditions including anxiety and depression.
CAD is the most common type of heart disease, with high blood pressure, obstructive sleep apnea and diabetes among traditional risk factors. African Americans are disproportionally ...
Study: Significant decline in heart attack patients who sought care at peak of pandemic
2021-04-28
WASHINGTON, D.C., (April 28, 2021) - Results from a retrospective observational study, presented today at Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions (SCAI) 2021 Virtual Scientific Sessions, reveal a 70% decline in the number of patients presenting with acute myocardial infarction (AMI) during April 2020 compared to April 2019. While the number of patients with AMI seeking care at hospitals dropped during the pandemic, those that did receive care experienced more severe symptoms because of delays in patients seeking emergency services.
AMI, commonly recognized as a heart attack, is responsible for more than one million deaths in the U.S. every year. For the best patient outcomes, seeking care within the ...
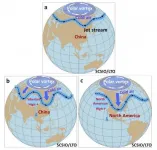
Causes of extreme weather and climate events in China during 2020/21
2021-04-28
During the summer of 2020, especially June and July, periods of extreme heavy rainfall occurred in China's Yangtze River Valley (YRV). These rain events caused the severest floods for the region since the summer of 1998. Despite this, the 2020 western North Pacific (WNP) typhoon season started slowly, but eventually produced 23 named tropical cyclones, still slightly below 27, the WNP seasonal average. As summer transitioned to winter, three severe cold surges swept most parts of China during late 2020 and early 2021, prompting the National Meteorological Center to issue its highest cold surge warning alert ...
Restricting internet searches causes stock market instability: study
2021-04-28
The research by RMIT University looked at the ramifications on the stock market following Google's withdrawal from mainland China in 2010.
It found access to unbiased information about companies' performance - aided by unrestricted internet search results - led to investors making more informed decisions.
On the flip side, search results manipulated to show overly positive information led to stocks for those companies being overvalued temporarily, increasing the stock market crash risk by 19%.
The study has been published in the Journal of Financial Economics.
Lead researcher Dr Gaoping Zheng, a lecturer in finance at RMIT, said the study showed search results influenced decisions, a challenge to previous thinking that they merely justified people's existing ideas.
"Until ...
Early MR scans found more people with broken-heart syndrome
2021-04-28
In almost ten per cent of myocardial infarctions, no obvious cause in the coronary artery can be found. Some of the patients are diagnosed with broken-heart syndrome, while others are left without a diagnosis. A new study from Karolinska Institutet in Sweden suggests that early magnetic resonance (MR) imaging of the heart can greatly increase the rate of diagnosis. The study has been published in the journal JACC Cardiovascular Imaging.
Myocardial infarction is one of the most common diseases in the West, and is usually caused by a blood clot that blocks the coronary artery on the heart's surface. However, in up to ten per cent of all myocardial infarctions, no obvious cause ...
The state of China's climate in 2020: Warmer and wetter again
2021-04-28
The National Climate Center (NCC) of China has just completed a report that gives an authoritative assessment of China's climate in 2020. It provides a summary of China's climate as well as the major weather and climate events that took place throughout the year. This is the third consecutive year that the NCC has published an annual national climate statement in Atmospheric and Oceanic Science Letters (AOSL).
"Against the background of global warming, extreme weather and climate events occur more frequently and have wide influence on society and economies. Last year, floods, droughts, typhoons, low-temperature freezing and snow disasters, and dust storms attacked ...
[1] ... [2393]
[2394]
[2395]
[2396]
[2397]
[2398]
[2399]
[2400]
2401
[2402]
[2403]
[2404]
[2405]
[2406]
[2407]
[2408]
[2409]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.