Gaps in genetic knowledge affect kiwi conservation efforts
2021-04-21
Kiwi are iconic birds that have been severely impacted by deforestation and predation from invasive mammals since the arrival of humans in New Zealand. The remaining kiwi can be split into 14 clusters that are now treated as separate conservation management units. A review published in Ibis examines the latest information on kiwi genetics to investigate the legitimacy for maintaining these differences.
Although studies indicate that kiwi differ genetically between areas, there is little understanding of the extent of local adaptations and breeding changes on populations. The work highlights the need for a more detailed understanding of the genetics of different species for wildlife conservation.
"Using kiwi as an example, we hope to convey that results ...
Mobility in terrestrial and underwater wireless sensor networks
2021-04-21
A Wireless Sensor Network--a set of sensor nodes placed in different locations that sense their surroundings and transmit sensed data--can have a range of applications related to the environment, healthcare, transportation, security, and other areas. An analysis of published research provides an overview of the ability of "mobile elements" to improve terrestrial and underwater Wireless Sensor Networks.
As described in the analysis published in the International Journal of Communication Systems, mobile elements improve communication between sensor nodes by visiting static sensor nodes and collecting their data. This leads to a decrease in energy ...
NASA NeMO-Net video game helps researchers understand global coral reef health
2021-04-21
Marine ecosystems are in the midst of a conservation crisis, with coral reefs in particular facing numerous challenges as a result of climate change. In an effort to better understand these environments and the threats they face, researchers collect huge image libraries of these underwater environments, using 3D imagery collected from divers and snorkelers, as well as 2D images collected from satellites. These approaches provide researchers with huge amounts of data, but to extract value from these libraries requires a method to quickly analyze for patterns or 'classifications'.
In a new study in Frontiers in Marine Science, researchers at NASA's Ames Research Center's Laboratory ...
A good night's sleep could do wonders for your sex life
2021-04-21
CLEVELAND, Ohio (April 21, 2021)--The importance of getting a good night's sleep cannot be overstated. Lack of sleep can lead to a number of health problems and affect a woman's overall quality of life. A new study suggests that insufficient quality sleep also may lead to problems in the bedroom in the form of female sexual dysfunction. Study results are published online today in Menopause, the journal of The North American Menopause Society (NAMS).
Both sleep and sexual function problems are common in women during midlife. More than 26% of midlife women experience significant sleep symptoms that meet the criteria for insomnia, ...
Walk the dinosaur! New biomechanical model shows Tyrannosaurus rex in a swinging gait
2021-04-21
Humans and animals have a preferred walking speed. This is, in part, influenced by the amount of energy required: they prefer to walk at the speed at which they use the lowest possible amount of energy. One of the ways to achieve this is using something called resonance.
You already know how it works: when you are on a swing, you can't just swing at any speed. If you want to do it properly, you have to get the timing right, and swing in the rhythm of the swing. In other words: you have to resonate with it. And when you're on a nice relaxing walk, the parts of your body resonate, too. Walking slightly slower doesn't require less energy: you ...
Music improves older adults' sleep quality
2021-04-21
Listening to music before going to be can improve sleep quality among older adults, according to an analysis of all relevant published clinical trials.
In the analysis, which is published in the Journal of the American Geriatrics Society, five randomized trials met the investigators' criteria. Older adults who listened to music experienced significantly better sleep quality than those who did not listen to music. Also, older adults who listened to sedative music experienced a greater improvement in sleep quality than those who listened to more rhythmic music. Furthermore, listening to music for longer than four weeks was especially effective at improving sleep quality.
"Music intervention is an effective strategy and is easy to administer by a caregiver or healthcare worker," ...
Augmented reality in retail and its impact on sales
2021-04-21
Augmented reality (AR) is a technology that superimposes virtual objects onto a live view of physical environments, helping users visualize how these objects fit into their physical world. Researchers from City University of Hong Kong and Singapore Management University published a new paper in the Journal of Marketing that identifies four broad uses of AR in retail settings and examines the impact of AR on retail sales.
The study, forthcoming in the Journal of Marketing, is titled "Augmented Reality in Retail and Its Impact on Sales" and is authored by Yong-Chin Tan, Sandeep Chandukala, and Srinivas Reddy. The researchers discuss the following uses of AR in retail settings: ...
Shift-work causes negative impacts on health, affects men and women differently
2021-04-21
Shift-work and irregular work schedules can cause several health-related issues and affect our defence against infection, according to new research from the University of Waterloo.
These health-related issues occur because the body's natural clock, called the circadian clock, can be disrupted by inconsistent changes in the sleep-wake schedule and feeding patterns often caused by shift work. To study this, researchers at Waterloo developed a mathematical model to look at how a disruption in the circadian clock affects the immune system in fighting off illness.
"Because our immune system is affected by the circadian clock, our ability to mount ...
Carleton's Dominque Roche investigates why researchers are wary of sharing data
2021-04-21
Carleton University's Marie Curie Global Fellow Dominique Roche has co-authored a paper on the barriers researchers face to publicly sharing their data, an issue that has gained prominence during the COVID-19 pandemic. The article, Reported Individual Costs and Benefits of Sharing Open Data among Canadian Academic Faculty in Ecology and Evolution, was published in the journal BioScience.
"The COVID-19 pandemic has made people from all over the world grasp the importance of sharing research data to speed up scientific discoveries," said Roche. "Clearly, open data have been key in fighting the pandemic, but they're also really important to tackle other urgent problems, like climate change and biodiversity loss."
Roche and co-author Sandrine ...
Environmental DNA and RNA may be key in monitoring pathogens such as SARS-CoV-2
2021-04-21
Real-world disease and parasite monitoring is often hampered by the inability of traditional approaches to easily sample broad geographical areas and large numbers of individuals. This can result in patchy data that fall short of what researchers need to anticipate and address outbreaks. Writing in BioScience, Jessica Farrell (University of Florida), Liam Whitmore (University of Limerick), and David Duffy (University of Florida) describe the promise of novel molecular techniques to overcome these shortcomings.
By sampling environmental DNA and RNA (eDNA and eRNA), the authors say, researchers will be better able to ...
Simple treatment during pregnancy can protect baby from memory problems in later life
2021-04-21
A new study in laboratory rats has discovered a direct link between low oxygen in the womb and impaired memory function in the adult offspring. It also finds that anti-oxidant supplements during pregnancy may protect against this.
Low oxygen in the womb - known as chronic fetal hypoxia - is one of the most common complications in human pregnancy. It can be diagnosed when a routine ultrasound scan shows that the baby is not growing properly and is caused by a number of conditions including pre-eclampsia, infection of the placenta, gestational diabetes or maternal obesity.
The new results show that chronic fetal hypoxia leads to a reduced density of blood vessels, and a reduced number of nerve cells and their connections in parts of the ...
Handwashing responsible for bacteria in sinks, largest non-hospital study shows
2021-04-21
Handwashing is shaping communities of bacteria that live and grow in the plumbing of domestic sinks, scientists have found.
In the largest study of sink bacteria conducted outside of hospitals, scientists at the University of Reading discovered communities of similar bacteria that largely remain down our drains after hand washing.
The researchers found that there are significant differences between families of dominant bacteria depending on the location in the sink drains, and that plumbing systems such as P-trap or U-bend provides ideal environments for bacteria to grow.
Dr Hyun Soon Gweon, Lecturer in Bioinformatics for Genomics at the University of Reading, said:
"The mantra to 'wash your hands' to fight coronavirus transmission has highlighted the importance of ...
Simple oral hygiene could help reduce COVID-19 severity - study
2021-04-21
COVID-19 could pass into people's lungs from saliva with the virus moving directly from mouth to bloodstream - particularly if individuals are suffering from gum disease, according to new research.
Evidence shows that blood vessels of the lungs, rather than airways, are affected initially in COVID-19 lung disease with high concentrations of the virus in saliva and periodontitis associated with increased risk of death.
The researchers propose that dental plaque accumulation and periodontal inflammation further intensify the likelihood of the SARS-CoV-2 virus reaching the lungs and causing more severe cases of the infection.
Experts say this discovery could make effective oral healthcare ...
Medical and ethical experts say 'make general anaesthesia more widely available for dying patients'
2021-04-21
General anaesthesia is widely used for surgery and diagnostic interventions, to ensure the patient is completely unconscious during these procedures. However, in a paper published in Anaesthesia (a journal of the Association of Anaesthetists) ethics and anaesthesia experts from the University of Oxford say that general anaesthesia should be more widely available for patients at the end of their lives.
Painkilling medications (analgesia) are commonly given to dying patients. But they may not be enough, leading to the use of continuous deep sedation (also known as "palliative" or "terminal" sedation).
"However, for some patients these common interventions are not enough. Other patients may express a clear desire to be completely unconscious as they die," explains ...
Study finds dramatic gains in life expectancy for people with HIV in Latin America
2021-04-21
In 2003 in Haiti, a 20-year-old in treatment for HIV could have expected to live to 34. But as of 2017, life expectancy for a 20-year-old in treatment for HIV in Haiti is now 61, compared to 70 for Haiti's general population.
A research team from Vanderbilt University Medical Center and institutions across Latin America today reports what looks to be far the largest study to date of life expectancy for people living with HIV infection in low-income or middle-income countries.
With a focus on 30,688 people treated for HIV between 2003 and 2017 in seven Latin American countries, the study, published ...
Significant life expectancy increase for adults living with HIV on ART in Latin America
2021-04-21
Study of 30,000 adults living with HIV receiving antiretroviral therapy (ART) in Latin America and the Caribbean finds life expectancy has increased to within 10 years of the general population in these countries over the last two decades.
Disparities in life expectancy due to demographic and clinical factors at the point participants began ART (including sexual HIV transmission risk, low CD4 cell count, and history of tuberculosis) highlight an ongoing need to reach vulnerable populations in the region.
Life expectancy among adults living with HIV receiving antiretroviral therapy (ART) ...
Drug development platform could provide flexible, rapid and targeted antimicrobials
2021-04-21
When disease outbreaks happen, response time in developing and distributing treatments is crucial to saving lives. Unfortunately, developing custom drugs as countermeasures is often a slow and difficult process.
But researchers at the University of Colorado Boulder have created a platform that can develop effective and highly specific peptide nucleic acid therapies for use against any bacteria within just one week. The work is detailed in Nature Communications Biology and could change the way we respond to pandemics and how we approach increasing cases of antibiotic resistance globally.
The Facile Accelerated Specific Therapeutic (FAST) platform was created by Associate Professor Anushree Chatterjee ...
The COVID-19 is a unique opportunity to move towards more sustainable and equitable society
2021-04-20
Researchers at the University of Jyväskylä highlight how the struggles caused by the COVID-19 pandemic can guide us towards an equitable use of our shared environment and a transition towards sustainability.
COVID-19 crisis has emphasized how poorly prepared humanity is to cope with global disasters and to face the new ecological norm under climate change, degraded ecosystems, and biodiversity loss. The final consequences of COVID-19 crisis on sustainability are not yet known. However, this crisis offers a unique opportunity to move towards a greener, ...
Using engineering methods to track the imperceptible movements of stony corals
2021-04-20
Coral reefs around the world are under threat from rising sea temperatures, ocean acidification, disease and overfishing, among other reasons.
Tracking signs of stress and ill health is difficult because corals -- an animal host coexisting with algae, bacteria, viruses and fungi -- are dynamic organisms that behave differently depending on what's happening in their environment. Some scientists wonder if recording changes in coral movements over time could help with monitoring a coral reef's health.
This is not always a straightforward task. Some coral species wave and pulse in ...
E-cigarette users in rural Appalachia develop more severe lung injuries
2021-04-20
Just as e-cigarette ingredients can vary from one region to another, the health effects of vaping can have regional characteristics as well. A new study out of West Virginia University suggests that rural e-cigarette users are older--and often get sicker--than their urban counterparts.
Researchers with the WVU School of Medicine are investigating severe lung injuries occurring among e-cigarette users in rural Appalachia. In a recent study, Sunil Sharma--section chief of pulmonary/critical care and sleep medicine at the School of Medicine--and his colleagues present a case study of patients with EVALI (electronic cigarettes and vaping-associated lung injury) admitted to WVU hospitals from August 2019 to March 2020. ...
The immune link between a leaky blood-brain barrier and schizophrenia
2021-04-20
Like a stern bodyguard for the central nervous sytem, the blood-brain barrier keeps out anything that could lead to disease and dangerous inflammation--at least when all is functioning normally.
That may not be the case in people with schizophrenia and other mental disorders, suggest new findings from a team led by researchers from the School of Veterinary Medicine, Perelman School of Medicine, and Children's Hospital of Philadelphia (CHOP). In these individuals, a more permissive barrier appears to allow the immune system to get improperly involved in the central nervous system, the researchers showed. The inflammation that arises likely contributes to the clinical manifestations of neuropsychiatric conditions.
"Our hypothesis was that, if the immune function of the blood-brain ...
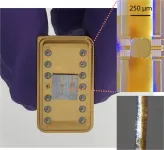
Tiny chip-based device performs ultrafast modulation of X-rays
2021-04-20
WASHINGTON -- Researchers have developed new x-ray optics that can be used to harness extremely fast pulses in a package that is significantly smaller and lighter than conventional devices used to modulate x-rays. The new optics are based on microscopic chip-based devices known as microelectromechanical systems (MEMS).
"Our new ultrafast optics-on-a-chip is poised to enable x-ray research and applications that could have a broad impact on understanding fast-evolving chemical, material and biological processes," said research team leader Jin Wang from the U.S Department of Energy's Argonne National Laboratory. "This could aid in the development of more efficient solar cells and batteries, advanced computer storage materials and devices, ...
Helpful, engineered 'living' machines in the future?
2021-04-20
Engineered, autonomous machines combined with artificial intelligence have long been a staple of science fiction, and often in the role of villain like the Cylons in the "Battlestar Galactica" reboot, creatures composed of biological and engineered materials. But what if these autonomous soft machines were ... helpful?
This is the vision of a team of Penn State and U.S. Air Force researchers, outlined in a recent paper in Nature Communications. These researchers produced a soft, mechanical metamaterial that can "think" about how forces are applied to it and respond via programmed reactions. ...
Large numbers of regular drug users report increased substance use during COVID-19
2021-04-20
People who regularly use psychoactive substances report experiencing a variety of negative impacts since the COVID-19 pandemic began, including increased usage and fear of relapse or overdose, highlighting the need for improved supports and services, including better access to safe supply programs, according to a new CAMH survey published in the International Journal of Drug Policy.
"People who use drugs have been negatively impacted by the pandemic in ways that put them at greater risk for experiencing substance and health-related harms, including overdoses and a decreased ability to mitigate risk behaviours," ...
Diagnostic yield of non-contrast pituitary MRI for pediatric pathologies
2021-04-20
Leesburg, VA, April 20, 2021--An award-winning Scientific Electronic Exhibit to be presented at the ARRS 2021 Virtual Annual Meeting found non-contrast pituitary MRI for central precocious puberty (CPP), growth hormone deficiency (GHD), and short stature (SS) has similar diagnostic yield compared to the standard contrast-enhanced protocol.
"Microadenomas, a common justification for contrast administration, may not influence management in this patient population," wrote first author Jennifer Huang of Vanderbilt University in Nashville, TN, adding "minimal inconvenience would be added for the few patients who would need to return for contrast-enhanced MRI for definitive diagnosis."
Huang and colleagues performed a retrospective review of pediatric pituitary MRI studies from 2010-2019 ...
[1] ... [2398]
[2399]
[2400]
[2401]
[2402]
[2403]
[2404]
[2405]
2406
[2407]
[2408]
[2409]
[2410]
[2411]
[2412]
[2413]
[2414]
... [8814]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.