Hepatitis C drugs boost Remdesivir's antiviral activity against COVID-19
2021-04-27
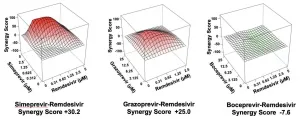
Remdesivir is currently the only antiviral drug approved in the U.S. for treating COVID-19 patients. In a paper published this week in Cell Reports, researchers from The University of Texas at Austin, Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute (RPI) and the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai showed that four drugs used to treat hepatitis C render remdesivir 10 times better at inhibiting the coronavirus in cell cultures.
These results indicate that a mixture containing remdesivir and a repurposed hepatitis C virus (HCV) drug could potentially function as a combination antiviral therapy for SARS-CoV-2. Such an antiviral could provide an immediate treatment for unvaccinated people who become infected and for vaccinated people whose immunity has waned.
Because these hepatitis drugs are already ...
Geographies of death: Study maps COVID-19 health disparities in Greater Santiago
2021-04-27
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. -- People up to age 40 living in economically depressed municipalities in the Greater Santiago, Chile, metropolitan area were three times more likely to die as a result of the infection than their counterparts in wealthier areas, researchers report in the journal Science. People ages 41-80 in low socioeconomic-status municipalities also suffered more from the pandemic than their peers in more affluent areas, the team found.
The study used new methods to analyze COVID-19 death counts, reported cases, testing rates and delays in testing results across location, time ...
New method preserves viable fruit fly embryos in liquid nitrogen
2021-04-27
Cryopreservation, or the long-term storage of biomaterials at ultralow temperatures, has been used across cell types and species. However, until now, the practical cryopreservation of the fruit fly (Drosophila melanogaster) -- which is crucial to genetics research and critical to scientific breakthroughs benefiting human health -- has not been available.
"To keep alive the ever-increasing number of fruit flies with unique genotypes that aid in these breakthroughs, some 160,000 different flies, laboratories and stock centers engage in the costly and frequent transfer of adults to fresh food, risking contamination and genetic drift," said Li Zhan, a postdoctoral associate with the University of Minnesota College of Science and Engineering and the Center for Advanced ...
UMD studies mangrove genetic diversity in Africa to conserve centers of biodiversity
2021-04-27
In collaboration with researchers at the Vrije Universiteit Brussel, a University of Maryland (UMD) postdoctoral researcher recently co-published a large-scale study examining the genetic diversity of mangroves over more than 1,800 miles of coastline in the Western Indian Ocean, including Eastern Africa and several islands. While the mangroves of Asia, Australia, and the Americas have been more extensively studied, little work has been done classifying and highlighting genetic diversity in African mangrove populations for conservation. Similar to other wetlands, mangrove ...
Researchers find breastfeeding linked to higher neurocognitive testing scores
2021-04-27
New research finds that children who were breastfed scored higher on neurocognitive tests. Researchers in the Del Monte Institute for Neuroscience at the University of Rochester Medical Center (URMC) analyzed thousands of cognitive tests taken by nine and ten-year-olds whose mothers reported they were breastfed, and compared those results to scores of children who were not.
"Our findings suggest that any amount of breastfeeding has a positive cognitive impact, even after just a few months." Daniel Adan Lopez, Ph.D. candidate in the Epidemiology program who is first author on the study recently ...
Women's football in Japan had a rich history before WWII
2021-04-27
A team of scientists has found that women's football was common across Japan between the Meiji restoration and the start of the Second World War. In the process, they also uncovered the oldest known photograph of women playing football in Japan, from 1916.
The history of men's football in Japan is well documented. In particular, the introduction of association football into Japan in the late 19th and 20th centuries has been extensively investigated. The same degree of attention had not been paid to women's football.
A team of researchers from six institutions, including Associate Professor Yoshihiro ...
Nature provides inspiration for breakthrough in self-regulating materials
2021-04-27
AMHERST Mass. - Scientists have long sought to invent materials that can respond to the external world in predictable, self-regulating ways. Now, new research conducted at the University of Massachusetts Amherst and appearing in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences brings us one step closer to that goal. For their inspiration, the scientists looked to nature.
Lampreys swimming, horses walking, and insects flying: each of these behaviors is made possible by a network of oscillators--mechanisms that produce a repetitive motion, such as wriggling a tail, taking a stride, or flapping a wing. What's more, these natural oscillators can respond to their environment in predictable ways. In ...
Switching to light
2021-04-27
Much as yeast serves in bakeries as single-celled helper, the bacterium Escherischia coli is a must in every biotechnology lab. A team led by Prof. Dr. Barbara Di Ventura, professor of biological signaling research at the University of Freiburg, has developed a new so-called optogenetic tool that simplifies a standard method in biotechnology: Instead of feeding the bacteria with sugar as commonly done, the researchers can now simply shine light on them. Di Ventura, Prof. Dr. Mustafa Hani Khammash from ETH Zurich/Switzerland and their teams, foremost first authors Edoardo Romano and Dr. Armin Baumschlager, ...
Anemia discovery points to more effective treatment approaches
2021-04-27
A combination of inexpensive oral medications may be able to treat fatigue-inducing anemias caused by chronic diseases and inflammation, a new discovery from the University of Virginia School of Medicine suggests.
This type of anemia is the second-most common kind, and it can be an added burden for organ-transplant recipients and people with autoimmune disorders, as well as patients battling cancer or kidney disease and others. In addition to causing severe fatigue, the anemia can trigger headaches, dizziness, rapid heartbeat and sweating.
"Not only do these anemias cause unpleasant ...
Impact of COVID-19 on racial-ethnic minorities among persons with opioid use disorder
2021-04-27
The COVID-19 pandemic has highlighted health disparities for people of color, who have been disproportionately affected by the pandemic. People with opioid use disorder (OUD) faced unique challenges when many mental health and addiction services were forced to scale back operations or temporarily close when social distancing guidelines were put in place.
A group of researchers in the College of Agriculture, Health and Natural Resources recently published their findings in the Journal of Substance Abuse and Treatment about the experiences of racial-ethnic minorities during the COVID-19 pandemic among people with OUD.
Doctoral ...
Middle East and North Africa: Heatwaves of up to 56 degrees Celsius without climate action
2021-04-27
The Middle East and North Africa Region (MENA) is a climate change hot spot where summers warm much faster than in the rest of the world. Some parts of the region are already among the hottest locations globally. A new international study predicts that ignoring the signals of climate change and continuing business-as-usual will lead to extreme and life-threatening heatwaves in the region. Such extraordinary heat events will have a severe impact on the people of the area.
The study, which aims at assessing emerging heatwave characteristics, was led by scientists from the Climate and Atmosphere Research Center (CARE-C) of The Cyprus Institute and the Max Planck Institute for Chemistry, with the contribution of researchers from the CMCC Foundation - Euro-Mediterranean ...
Study reports links between blood types and disease risks
2021-04-27
People with certain blood types are more likely to have blood clots or bleeding conditions, kidney stones, or pregnancy-induced hypertension, suggests a study published today in eLife.
The study confirms previously identified connections between certain blood types and the risk of blood clots and bleeding, and makes a new connection between kidney stones and having type B blood as compared to O. The discoveries may lead to new insights on how a person's blood type may predispose them to developing a certain disease.
Previous studies have found that people with blood type A or B were more likely to have cardiovascular disease or experience ...
Hepatitis C drugs multiply effect of COVID-19 antiviral Remdesivir
2021-04-27
TROY, N.Y. -- When combined with drugs currently used to treat hepatitis C, the antiviral remdesivir is 10 times more effective in treating cells infected with SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19.
Published this week in Cell Reports, this finding -- from Gaetano Montelione, a professor of chemistry and chemical biology at Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute, and his collaborators at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai and the University of Texas at Austin -- raises the potential for repurposing available drugs as COVID-19 antivirals in cases where a vaccine isn't practical or effective.
Remdesivir, which blocks viral replication by interfering with a viral polymerase, must ...
Army technique enhances robot battlefield operations
2021-04-27
ADELPHI, Md. -- Army researchers developed a technique that allows robots to remain resilient when faced with intermittent communication losses on the battlefield.
The technique, called α-shape, provides an efficient method for resolving goal conflicts between multiple robots that may want to visit the same area during missions including unmanned search and rescue, robotic reconnaissance, perimeter surveillance and robotic detection of physical phenomena, such as radiation and underwater concentration of lifeforms.
Researchers from the U.S. Army Combat Capabilities Development Command, known as DEVCOM, Army Research Laboratory and the University of Nebraska, Omaha ...
Anesthesia doesn't simply turn off the brain, it changes its rhythms
2021-04-27
In a uniquely deep and detailed look at how the commonly used anesthetic propofol causes unconsciousness, a collaboration of labs at The Picower Institute for Learning and Memory at MIT shows that as the drug takes hold in the brain, a wide swath of regions become coordinated by very slow rhythms that maintain a commensurately languid pace of neural activity. Electrically stimulating a deeper region, the thalamus, restores synchrony of the brain's normal higher frequency rhythms and activity levels, waking the brain back up and restoring arousal.
"There's a folk psychology or tacit assumption that what anesthesia does is simply 'turn off' the brain," said ...
Marine biodiversity: Enormous variety of animal life in the deep sea revealed
2021-04-27
Ecologists at the University of Cologne's Institute of Zoology have for the first time demonstrated the enormously high and also very specific species diversity of the deep sea in a comparison of 20 deep-sea basins in the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans. Over a period of 20 years, a research team led by Professor Dr Hartmut Arndt at the Institute of Zoology has compiled a body of data that for the first time allows for a comparison of the diversity of existing eukaryotes - organisms with a cell nucleus. Sediment samples from depths of 4000 to 8350 meters, ...
Horizontal transmission can cause severe and persistent eye inflammation
2021-04-27
Tokyo, Japan - Human T-cell lymphotropic virus type-1 (HTLV-1) is a retrovirus similar to human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) and has mostly been thought to be transmitted vertically (mother-to-child), or horizontally (sexually or parenterally (e.g. via blood transfusion)). The spread of this infection in metropolitan areas such as Tokyo is presumed to be due to horizontal transmission, especially sexual transmission.HTLV-1-associated diseases are thought to be caused mainly through vertical transmission. In a new study, clinicians from Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) describe that horizontal transmission route ...
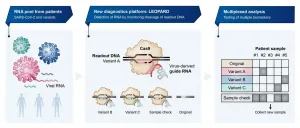
CRISPR discovery from Wuerzburg paves the way for novel COVID testing method
2021-04-27
Most conventional molecular diagnostics usually detect only a single disease-related biomarker. Great examples are the PCR tests currently used to diagnose COVID-19 by detecting a specific sequence from SARS-CoV-2. Such so-called singleplex methods provide reliable results because they are "calibrated" to a single biomarker. However, determining whether a patient is infected with a new SARS-CoV-2 variant or a completely different pathogen requires probing for many different biomarkers at one time.
Scientists from the Helmholtz Institute for RNA-based ...
EHR usability issues linked to nurse burnout and patient outcomes
2021-04-27
PHILADELPHIA (April 27, 2021) - Nurses and other clinicians rely heavily upon the electronic health record (EHR) to provide patient care. This includes clinical decision-making, care planning, patient surveillance, medication ordering and administration, and communication with other health care team members. While data show that EHR technology usability can put added burden on clinicians, the relationships between EHR usability and the job outcomes of hospital staff nurses and surgical patient outcomes have not been explored.
A new study from the University of ...
Hepatitis C drugs combined with Remdesivir show strong effectiveness against covid-19
2021-04-27
A combination of remdesivir, a drug currently approved in the United States for treating COVID-19 patients, and repurposed drugs for hepatitis C virus (HCV) was 10 times more effective at inhibiting SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19.
The combination therapy points a way toward a treatment for unvaccinated people who become infected, as well as for vaccinated people whose immunity has waned, for example due to the emergence of virus variants that escape this immune protection.
Four HCV drugs--simeprevir, vaniprevir, paritaprevir, and grazoprevir--in combination with remdesivir boosted the efficacy of remdesivir by as much as 10-fold, the researchers reported today in Cell Reports. The research team included scientists from Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, the ...
Majority of US faculty help students with mental health issues -- but few are trained for it
2021-04-27
Nearly 80 percent of higher education faculty report dealing with student mental health issues—issues that more than 90 percent of faculty believe have worsened or significantly worsened during the pandemic, according to a new nationwide survey led by a Boston University mental health researcher.
"The vast majority of faculty members, myself included, are not trained mental health professionals, but we have a role to play in supporting student well-being," says survey principal investigator Sarah Ketchen Lipson, a BU School of Public Health assistant professor of health law, policy, and management. "These data underscore a real opportunity to better equip faculty with knowledge ...
Material scientists find new angle toward better heat transfer
2021-04-27
UCLA materials scientists have developed a class of optical material that controls how heat radiation is directed from an object. Similar to the way overlapping blinds direct the angle of visible light coming through a window, the breakthrough involves utilizing a special class of materials that manipulates how thermal radiation travels through such materials.
Recently published in Science, the advance could be used to improve the efficiency of energy-conversion systems and enable more effective sensing and detection technologies.
"Our goal was to show that we could effectively beam thermal radiation -- the heat all objects emanate as electromagnetic waves -- ...
Following nature's cue, researchers build successful, sustainable industrial networks
2021-04-27
By translating the pattern of interconnections between nature's food chains to industrial networks, researchers at Texas A&M University have delineated guidelines for setting up successful industrial communities. The researchers said this guidance can facilitate economic growth, lower emissions and reduce waste while simultaneously ensure that partnering industries can recover from unexpected disturbances.
"Industries can often partner up to exchange byproducts and over time these industries might form bigger communities. While these networks sound quite beneficial to all industry partners within the community, they are not always successful," said Dr. Astrid Layton, assistant professor in the J. Mike Walker' ...
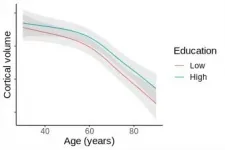
Higher education does not influence how the brain ages
2021-04-27
"This finding suggests that higher education does not influence brain aging" says Lars Nyberg from Umeå University in Sweden, first author of the study and also a part of the Lifebrain consortium.
Brains shrink at the same rate
All brains shrink with age, and the dominant view has been that more education slows the rate of shrinking. However, the evidence has been inconclusive because studies have not been able to track the rate of change over time. Until now.
Measured brain shrinkage over time
The researchers measured brain aging by measuring the ...
Alternative meats are not suppressing reliance on grazing animal sources
2021-04-27
EUGENE, Ore. -- April 27, 2021 -- The addition of meat alternatives such as poultry and fish is not reducing the global production and consumption of energy-gobbling land-based meats, according to new research.
That conclusion comes from an analysis of 53 years of international data by University of Oregon sociologist Richard York, who focuses on energy consumption in relationship to economic issues such as power and inequalities, and politics. His findings published April 26 in the journal Nature Sustainability.
"If you have increases in the production of poultry and fish, it doesn't tend to compete with or suppress other meat source consumption," York said. "It would be great if more ...
[1] ... [2397]
[2398]
[2399]
[2400]
[2401]
[2402]
[2403]
[2404]
2405
[2406]
[2407]
[2408]
[2409]
[2410]
[2411]
[2412]
[2413]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.