Predicting the onset of diseases
2021-04-20
A myriad of genetic factors can influence the onset of diseases like high blood pressure, heart diseases, and type 2 diabetes. If we were to know how the DNA influences the risk of developing such diseases, we, we could shift from reactive to more preventive care, not only improving patients' quality of living but also saving money in the health system. However, tracing the connections between the DNA and disease onset requires solid statistical models that reliably work on very large datasets of several hundred thousand patients.
Matthew Robinson, Assistant Professor at the Institute ...
Gut's immune response in COVID-19 may not provide efficient protection of other organs
2021-04-20
Our guts may not provide long-lasting systemic immunity from COVID-19, which is where immune cells circulate through the body to provide protection to other organs, finds a new study published in Frontiers in Immunology. An analysis of blood samples from patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 revealed that immune cells circulating in the blood, which were triggered by the gut's response to infection, were limited in number when compared to immune cells that had been triggered elsewhere in the body.
"Although the gut is considered an important portal of entry for the virus, the immune response in the blood of COVID-19 patients is dominated by ...
Understanding spoilage and quality issues may improve American artisan cheesemaking industry
2021-04-20
Philadelphia, April 20, 2021 - American artisan cheese has become increasingly popular over the past few decades. Understanding spoilage concerns and the financial consequences of defects can improve quality, profitability, and sustainability in the American artisan cheesemaking industry. In an article appearing in the END ...
Rock glaciers will slow Himalayan ice melt
2021-04-20
Some Himalayan glaciers are more resilient to global warming than previously predicted, new research suggests.
Rock glaciers are similar to "true" ice glaciers in that they are mixtures of ice and rock that move downhill by gravity - but the enhanced insulation provided by surface rock debris means rock glaciers will melt more slowly as temperatures rise.
Rock glaciers have generally been overlooked in studies about the future of Himalayan ice.
The new study, led by Dr Darren Jones at the University of Exeter, shows rock glaciers already account for about one twenty-fifth of Himalayan ...
Designing healthy diets - with computer analysis
2021-04-20
A new mathematical model for the interaction of bacteria in the gut could help design new probiotics and specially tailored diets to prevent diseases. The research, from Chalmers University of Technology in Sweden, was recently published in the journal PNAS.
"Intestinal bacteria have an important role to play in health and the development of diseases, and our new mathematical model could be extremely helpful in these areas," says Jens Nielsen, Professor of Systems Biology at Chalmers, who led the research.
The new paper describes how the mathematical model performed when making predictions ...
Better marketing for a better world
2021-04-20
Newly published research contained in the Special Issue of the Journal of Marketing features fourteen global author teams focused on the topic of Better Marketing for a Better World. Edited by Rajesh Chandy (London Business School), Gita Johar (Columbia University), Christine Moorman (Duke University), and John Roberts (University of New South Wales), this Special Issue brings together wide-ranging research to assess, illuminate, and debate whether, when, and how marketing contributes to a better world.
The Special Issue is built on the thesis that marketing has the power to improve lives, sustain livelihoods, strengthen societies, and benefit the world at large. It calls for a renewed ...
Efforts to reduce opioid prescriptions may be hindering end-of-life pain management
2021-04-20
PORTLAND, Ore. - Policies designed to prevent the misuse of opioids may have the unintended side effect of limiting access to the pain-relieving drugs by terminally ill patients nearing the end of their life, new research led by the Oregon State University College of Pharmacy suggests.
A study of more than 2,500 hospital patients discharged to hospice care over a nine-year period showed a decreasing trend of opioid prescriptions as well as an increase in the prescribing of less powerful, non-opioid analgesics, meaning some of those patients might have been undertreated for their pain compared to similar patients in prior years.
The findings, published in the Journal of Pain and Symptom Management, are an important step toward optimizing ...
Individualized training is key for autistic adolescents learning to drive
2021-04-20
Philadelphia, April 20, 2021 - A collaborative study from the Center for Injury Research and Prevention (CIRP) and the Center for Autism Research (CAR) at Children's Hospital of Philadelphia (CHOP) identified clear strengths and a series of specific challenges autistic adolescents experience while learning to drive. The findings were recently published by the American Journal of Occupational Therapy.
Researchers conducted in-depth interviews with 17 specialized driving instructors who were trained as occupational therapists, driving rehabilitation specialists, or licensed driving instructors and who had completed additional training related ...
Flushing a public toilet? Don't linger, because aerosolized droplets do
2021-04-20
Flushing a toilet can generate large quantities of microbe-containing aerosols depending on the design, water pressure or flushing power of the toilet. A variety of pathogens are usually found in stagnant water as well as in urine, feces and vomit. When dispersed widely through aerosolization, these pathogens can cause Ebola, norovirus that results in violent food poisoning, as well as COVID-19 caused by SARS-CoV-2.
Respiratory droplets are the most prominent source of transmission for COVID-19, however, alternative routes may exist given the discovery of small numbers of viable viruses in urine and stool samples. Public restrooms are especially cause for concern for transmitting COVID-19 because they are ...
Proportion of Black physicians in US has changed little in 120 years
2021-04-20
A new UCLA study finds that the proportion of physicians who are Black in the U.S. has increased by only 4 percentage points over the past 120 years, and that the share of doctors who are Black men remains unchanged since 1940.
The research also spotlights a significant income gap between white and Black male physicians -- a disparity, the researcher writes, that could reflect a combination of pay discrimination and unequal access for physicians to pursue careers in more lucrative specialties. The paper will be published April 19 in the peer-reviewed Journal of General Internal Medicine.
"These findings demonstrate how slow progress has been, and how far and fast we have to go, if we care about the diversity of the physician workforce and the health benefits such diversity brings ...
Omega-3 supplements do double duty in protecting against stress
2021-04-20
COLUMBUS, Ohio - A high daily dose of an omega-3 supplement may help slow the effects of aging by suppressing damage and boosting protection at the cellular level during and after a stressful event, new research suggests.
Researchers at The Ohio State University found that daily supplements that contained 2.5 grams of omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids, the highest dose tested, were the best at helping the body resist the damaging effects of stress.
Compared to the placebo group, participants taking omega-3 supplements produced less of the stress hormone cortisol and lower levels of a pro-inflammatory protein during a stressful event in the lab. And while levels of protective compounds sharply declined in the placebo group after the stressor, there were ...
Researchers find a way to mend a broken heart
2021-04-20
A Monash University study has uncovered for the first time a way to prevent and reverse damage caused by broken-heart syndrome, also known as Takotsubo cardiomyopathy.
Using mouse models, the pre-clinical study published in the acclaimed journal Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy, has shown the cardioprotective benefit of a drug called Suberanilohydroxamic acid, or SAHA, dramatically improved cardiac health and reversed the broken-heart. The landmark study used SAHA to target genes and is a world first for Takotsubo cardiomyopathy.
SAHA, currently used for cancer treatment, is approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and Australian Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA), works by providing a protective benefit to genes and ...
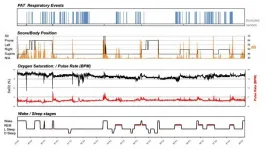
Disrupted sleep is linked to increased risk of death, particularly in women
2021-04-20
For the first time, a study has shown a clear link between the frequency and duration of unconscious wakefulness during night-time sleep and an increased risk of dying from diseases of the heart and blood vessels, and death from any cause, particularly in women.
The study of 8001 men and women, which is published today (Tuesday) in the European Heart Journal [1], found that women who experienced unconscious wakefulness most often and for longer periods of time had nearly double the risk of dying from cardiovascular disease during an average of between 6 and 11 years' ...
Multivits, omega-3, probiotics, vitamin D may lessen risk of positive COVID-19 test
2021-04-20
Taking multivitamins, omega-3, probiotics or vitamin D supplements may lessen the risk of testing positive for SARS-CoV-2, the virus responsible for COVID-19 infection--at least among women--indicates a large population study, published online in the journal BMJ Nutrition Prevention & Health.
But taking any of vitamin C, zinc, or garlic supplements wasn't associated with a lower risk of testing positive for the virus, the findings show.
There has been plenty of celebrity endorsement of the use of dietary supplements to both ward off and treat COVID-19 infection since the start of the pandemic, note the researchers.
In the UK alone, market share ...
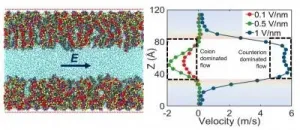
Surprising ionic and flow behaviors with functionalized nanochannels
2021-04-19
Nanochannels have important applications in biomedicine, sensing, and many other fields. Though engineers working in the field of nanotechnology have been fabricating these tiny, tube-like structures for years, much remains unknown about their properties and behavior.
Now, University of Maryland mechanical engineering associate professor Siddhartha Das and a group of his Ph.D. students have published surprising new findings in the journal ACS Nano. Using atomic-level simulations, Das and his team were able to demonstrate that charge properties as well as charge-induced fluid flow within a functionalized nanochannel does not always behave as expected.
"We've discovered a new context for nanochannels functionalized by grafting ...
How many Anthropocenes
2021-04-19
One of the marks of a successful idea in science is how quickly it can develop and evolve. In the case of the Anthropocene, the conceptual evolution has taken place with extraordinary speed. The strikingly influential hypothesis launched by the late Nobel laureate Paul Crutzen (Obituary, 24th Feb 2021) in 2000, was that the actions of an industrialised humanity has impacted the Earth so greatly as to trigger a new geological epoch. Originally developed within the Earth System science community in charting global environmental change, the Anthropocene then began ...
Science and need -- not wealth or nationality -- should guide vaccine allocation and prioritization
2021-04-19
April 19, 2021 -- Ensuring COVID-19 vaccine access for refugee and displaced populations, and addressing health inequities, is vital for an effective pandemic response. Yet, vaccine allocation and distribution has been neither equitable nor inclusive, despite that global leaders have stressed this as a critical aspect to globally overcoming the pandemic, according to a paper published by Columbia University Mailman School of Public Health. Read "Leave No-one Behind: Ensuring Access to COVID-19 vaccines for Refugee and Displaced Populations" in the journal Nature Medicine.
As of April 1st, high and upper-middle-income countries received 86 percent of the vaccine doses delivered worldwide, while ...
Tiny implantable tool for light-sheet imaging of brain activity
2021-04-19
Tools that allow neuroscientists to record and quantify functional activity within the living brain are in great demand. Traditionally, researchers have used techniques such as functional magnetic resonance imaging, but this method cannot record neural activity with high spatial resolution or in moving subjects. In recent years, a technology called optogenetics has shown considerable success in recording neural activity from animals in real time with single neuron resolution. Optogenetic tools use light to control neurons and record signals in tissues that are genetically modified ...
B cell activating factor possible key to hemophilia immune tolerance
2021-04-19
A group of scientists have just made a key discovery that could prevent and eradicate immune responses that lead to treatment failure in about one-third of people with severe hemophilia A.
Hemophilia is the most common severe inherited bleeding disorder in men. The disease affects 1 in 10,000 males worldwide and results from deficiency of blood clotting factor VIII (FVIII). Both children and adults with hemophilia A (80 percent of all hemophilia) receive treatment that involves infusing FVIII protein into the bloodstream. However, about 30 percent ...
Earth's biggest mass extinction took ten times longer on land than in the water
2021-04-19
Our planet's worst mass extinction event happened 252 million years ago when massive volcanic eruptions caused catastrophic climate change. The vast majority of animal species went extinct, and when the dust settled, the planet entered the early days of the Age of Dinosaurs. Scientists are still learning about the patterns of which animals went extinct and which ones survived, and why. In a new study in PNAS, researchers found that while extinctions happened rapidly in the oceans, life on land underwent a longer, more drawn-out period of extinctions.
"People assumed that because the marine extinction happened over a short period of time, life on land should have followed the same pattern, but we found that the marine extinction ...
Archaeological data demand new approaches to biodiversity conservation
2021-04-19
Professor Nicole Boivin, Director of the Department of Archaeology at the Max Planck Institute for the Science of Human History in Jena, Germany, is part of an international initiative to examine the implications of past land use for contemporary conservation efforts.
The multi-disciplinary team, which includes archaeologists, ecologists, anthropologists and conservation managers, has reconstructed ancient population and land use to show that already by 12,000 years ago, humans had re-shaped much of the terrestrial biosphere.
Their data challenge the idea that conservation ...
People have shaped Earth's ecology for at least 12,000 years, mostly sustainably
2021-04-19
New research published today in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS) shows that land use by human societies has reshaped ecology across most of Earth's land for at least 12,000 years. The research team, from over ten institutions around the world, revealed that the main cause of the current biodiversity crisis is not human destruction of uninhabited wildlands, but rather the appropriation, colonization, and intensified use of lands previously managed sustainably.
The new data overturn earlier reconstructions of global land use history, some of which indicated that most of Earth's land was uninhabited even as recently as 1500 CE. Further, ...
Clemson researchers find snake venom complexity is driven by prey diet
2021-04-19
Diversity in diet plays a role in the complexity of venom in pit vipers such as rattlesnakes, copperheads and cottonmouths.
But new collaborative research by Clemson University scientists found the number of prey species a snake ate did not drive venom complexity. Rather, it was how far apart the prey species were from each other evolutionarily.
"It's not just diet that drives the variation in venom across snakes. It's the breadth of diet," said Christopher Parkinson, a professor in the College of Science's Department of Biological Sciences. "If a snake eats 20 different species of mammals, its venom will not be very complex. But if it eats a centipede, a frog, a bird and a mammal, it's going to have a highly complex venom because each component of that venom ...
Defensive symbiosis leads to gene loss in bacterial partners
2021-04-19
Antibiotics on the cocoon protect the offspring of beewolves, a group of digger wasps, from detrimental fungi. These protective substances are produced by symbiotic bacteria of the genus Streptomyces, which live in these insects. In a new study in PNAS, researchers from the Max Planck Institute for Chemical Ecology and the University of Mainz, together with an international team, showed that these beneficial bacteria are losing genetic material that is no longer needed. The genome of these bacteria is of great interest for understanding the process of genome erosion and elucidating how the cooperation and the mutual benefit between bacteria and their host insects have evolved over long periods of time (PNAS, doi: 10.1073/pnas.2023047118, ...
Racial violence and the mental health of Black Americans
2021-04-19
Police violence against Black Americans is shamefully common in the United States and devastates communities. For incidents that get widespread media exposure, a collective trauma is felt across the nation, especially for Black individuals. Research supports that experiencing racism even vicariously can harm the mental and physical health of others of the same racial group, yet its effect on a population level is unclear.
A new study analyzed how highly publicized acts of racial violence impacted the mental health of Black Americans in the U.S. The authors identified 49 incidents that occurred between 2013 and 2017, including police killings of Black individuals, hate-crime murders and decisions not to indict or convict the officers involved. The researchers measured ...
[1] ... [2403]
[2404]
[2405]
[2406]
[2407]
[2408]
[2409]
[2410]
2411
[2412]
[2413]
[2414]
[2415]
[2416]
[2417]
[2418]
[2419]
... [8815]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.