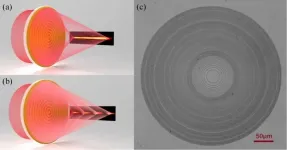
Science Advances publishes proteomics technology from Oblique Therapeutics AB
2021-04-16
Science Advances publishes proteomics technology from Oblique Therapeutics AB with a potential to bring several novel antibody medicines to large patient populations in multiple disease areas
Gothenburg, Sweden, April 16th, 2021 - Oblique Therapeutics AB, a Sweden-based biotech company, in collaboration with Karolinska Institutet (Stockholm, Sweden), Gothenburg University (Sweden) and several local biotechs published promising research results in the highly-acclaimed scientific journal Science Advances (AAAS) entitled: Rational Antibody design for Undruggable Targets using Kinetically Controlled Biomolecular ...
Female protective effect: Yale researchers find clues to sex differences in autism
2021-04-16
New Haven, Conn. -- It is well established that autism occurs much more frequently in boys than in girls, and that girls seem to have a greater resilience to developing the condition. It has been unclear, however, why that is.
In a new Yale-led study, researchers find that autism may develop in different regions of the brain in girls than boys and that girls with autism have a larger number of genetic mutations than boys, suggesting that they require a larger "genetic hit" to develop the disorder.
The findings appear in the April 16 edition of the journal ...
Researchers revise indicator of mobility limitation in older adults
2021-04-16
Aging entails a loss of muscle mass and strength, which in some cases impairs mobility, hinders walking or performance of day-to-day tasks, and exposes the elderly to the risk of falls and hospitalizations.
In clinical practice, handgrip measurement is the most widely used method to identify loss of overall muscular strength in older people. Values below 26 kg for men and 16 kg for women have for some time been considered an indication of risk-associated weakness, but these parameters are being revised.
Researchers at the Federal University of São Carlos (UFSCar) in the state of São Paulo, Brazil, collaborating with colleagues at other institutions in the same state such as the University of São Paulo's Ribeirão Preto Medical School (FMRP-USP), Nursing School ...
Study shows past COVID-19 infection doesn't fully protect young people against reinfection
2021-04-16
Although antibodies induced by SARS-CoV-2 infection are largely protective, they do not completely protect against reinfection in young people, as evidenced through a longitudinal, prospective study of more than 3,000 young, healthy members of the US Marines Corps conducted by researchers at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai and the Naval Medical Research Center, published April 15 in The Lancet Respiratory Medicine.
"Our findings indicate that reinfection by SARS-CoV-2 in health young adults is common" says Stuart Sealfon, MD, the Sara B. and Seth M. Glickenhaus Professor of Neurology at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai and senior author of the paper. "Despite a prior COVID-19 infection, young people can catch the virus ...
A new super-Earth detected orbiting a red dwarf star
2021-04-16
In recent years there has been an exhaustive study of red dwarf stars to find exoplanets in orbit around them. These stars have effective surface temperatures between 2400 and 3700 K (over 2000 degrees cooler than the Sun), and masses between 0.08 and 0.45 solar masses. In this context, a team of researchers led by Borja Toledo Padrón, a Severo Ochoa-La Caixa doctoral student at the Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias (IAC), specializing in the search for planets around this type of stars, has discovered a super-Earth orbiting the star GJ 740, a red dwarf star situated some 36 light years from the Earth.
The planet orbits its star with a period of 2.4 days and its mass is around 3 ...
Differences in national food security best explained by household income, not agriculture
2021-04-16
One of the most comprehensive statistical analyses of drivers of food insecurity across 65 countries has concluded that household income consistently explains more discrepancy in food security than any other factor, including agricultural land resources and production. The Thayer School of Engineering at Dartmouth study, "Cross-national analysis of food security drivers: comparing results based on the Food Insecurity Experience Scale and Global Food Security Index," was recently published by the peer-reviewed journal Food Security.
Given the persistent issue of food insecurity--one of the United Nation's sustainable development goals is to achieve zero hunger--the study's results are vital in determining how best to tackle the complex problem.
"We're ...
Hidden magma pools pose eruption risks that we can't yet detect
2021-04-16
Boulder, Colo., USA: Volcanologists' ability to estimate eruption risks is largely reliant on knowing where pools of magma are stored, deep in the Earth's crust. But what happens if the magma can't be spotted?
Shane Rooyakkers, a postdoctoral scholar at GNS Science in New Zealand, grew up in the shadow of Mount Taranaki on the country's North Island, hiking on the island's many volcanoes. Today, his research is revealing hidden dangers that may have been beneath his feet all along.
A new study, published yesterday in Geology, explores a threat volcanologists discovered only recently: surprisingly shallow magma pools that are too small to be detected with common volcano monitoring equipment. Such a magma body was ...
COVID-19: Scientists identify human genes that fight infection
2021-04-16
LA JOLLA, CALIF. - April 16, 2021 - Scientists at Sanford Burnham Prebys have identified a set of human genes that fight SARS-CoV-2 infection, the virus that causes COVID-19. Knowing which genes help control viral infection can greatly assist researchers' understanding of factors that affect disease severity and also suggest possible therapeutic options. The genes in question are related to interferons, the body's frontline virus fighters.
The study was published in the journal Molecular Cell.
"We wanted to gain a better understanding of the cellular response to SARS-CoV-2, including what drives a strong or weak response to infection," says Sumit K. Chanda, Ph.D., professor and director of the Immunity and Pathogenesis Program at Sanford Burnham Prebys and lead ...
New CRISPR technology offers unrivaled control of epigenetic inheritance
2021-04-16
Scientists have figured out how to modify CRISPR's basic architecture to extend its reach beyond the genome and into what's known as the epigenome -- proteins and small molecules that latch onto DNA and control when and where genes are switched on or off.
In a paper published April 9, 2021, in the journal Cell, researchers at UC San Francisco and the Whitehead Institute describe a novel CRISPR-based tool called "CRISPRoff," which allows scientists to switch off almost any gene in human cells without making a single edit to the genetic code. The researchers also show that once a gene is switched off, it remains inert in the cell's descendants for hundreds of generations, unless ...
How tangled proteins kill brain cells, promote Alzheimer's, CTE
2021-04-16
Look deep inside the brain of someone with Alzheimer's disease, most forms of dementia or the concussion-related syndrome known as chronic traumatic encephalopathy (CTE) and you'll find a common suspected culprit: stringy, hairball-like tangles of a protein called tau.
Such conditions, collectively known as "tauopathies" strike scores of people across the globe, with Alzheimer's alone affecting six million people in the United States.
But more than a century after German psychiatrist Alois Alzheimer discovered tau tangles, scientists still have much to ...
Fitted filtration efficiency of double masking during COVID-19 pandemic
2021-04-16
What The Study Did: The fitted filtration efficiency of commonly available masks worn singly, doubled or in combinations was evaluated in this study.
Authors: Emily E. Sickbert-Bennett, Ph.D., M.S., of the UNC Medical Center in Chapel Hill, North Carolina, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2021.2033)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflict of interest and funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of ...
Fit matters most when double masking to protect yourself from COVID-19
2021-04-16
CHAPEL HILL, NC - A study published today in JAMA Internal Medicine shows that wearing two face coverings can nearly double the effectiveness of filtering out SARS-CoV-2-sized particles, preventing them from reaching the wearer's nose and mouth and causing COVID-19. The reason for the enhanced filtration isn't so much adding layers of cloth, but eliminating any gaps or poor-fitting areas of a mask.
"The medical procedure masks are designed to have very good filtration potential based on their material, but the way they fit our faces isn't perfect," said Emily ...
Thermoelectric material discovery sets stage for new forms of electric power in the future
2021-04-16
Thermoelectrics directly convert heat into electricity and power a wide array of items -- from NASA's Perseverance rover currently exploring Mars to travel coolers that chill beverages.
A Clemson University physicist has joined forces with collaborators from China and Denmark to create a new and potentially paradigm-shifting high-performance thermoelectric compound.
A material's atomic structure, which is how atoms arrange themselves in space and time, determines its properties. Typically, solids are crystalline or amorphous. In crystals, atoms are in an orderly and symmetrical pattern. Amorphous materials have randomly distributed atoms.
Clemson researcher Jian He and the international team created a new hybrid compound in which the crystalline and ...
Researchers develop microscopic theory of polymer gel
2021-04-16
Russian scientists have proposed a theory of phase transformation in polymer gels. It explains the mechanisms of the dramatic reduction in volume of zwitterionic hydrogels when they are cooled. The results are published in the journal Chemical Communications (ChemComm).
Polymer gels have unusual properties, including the ability to absorb water in volumes hundreds of times greater than their own. For example, some hydrogels are capable of holding up to two kilograms of water per gram of dry gel. By changing the temperature or adding solvents, various desired properties can be achieved. This is why polymer gels are used in industry and biomedicine, including for the targeted delivery of medication, creation of artificial skin, children's toys, etc.
If you take ...
Studies suggest people with blood cancers may not be optimally protected after COVID-19 vaccination
2021-04-16
Two new studies published in Blood suggest that the mRNA COVID-19 vaccine may have reduced efficacy in individuals with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) and multiple myeloma, two types of blood cancer. According to researchers, these studies could help inform the ideal time for vaccination of these populations.
Study suggests two-dose COVID-19 vaccine is less effective for people with CLL as compared to healthy controls
The first study reports that people with CLL had markedly lower immune response rates to the two-dose mRNA COVID-19 vaccine than healthy individuals ...
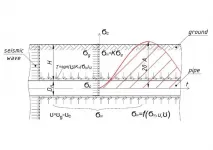
Are our oil and gas pipelines safe during an earthquake?
2021-04-16
Underground pipelines that transport oil and gas are very important engineering communications worldwide. Some of these underground communications are built and operated in earthquake-prone areas.
Seismic safety or seismic stability of underground pipelines began to be intensively studied since the 1950s.
Since then, a number of methodologies were proposed for calculating stress received by an underground pipeline during an earthquake. The purpose of these methodologies was to make an accurate prediction on the structural stress received by a pipeline during an earthquake, and thus it would allow to decide ...
Virtual humans are equal to real ones in helping people practice new leadership skills
2021-04-16
A virtual human can be as good as a flesh-and-blood one when it comes to helping people practice new leadership skills. That's the conclusion from new research published in the journal Frontiers in Virtual Reality that evaluated the effectiveness of computer-generated characters in a training scenario compared to real human role-players in a conventional setting.
Practice-based training techniques, including role-playing, are sometimes used to help improve training outcomes. However, these methods can be expensive to implement, and often require specialized knowledge and even professional actors to create realistic training environments. In addition, some ...
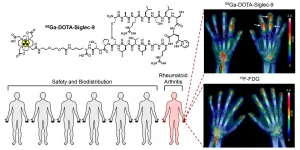
Promising results from first-in-humans study of a novel PET radiopharmaceutical
2021-04-16
The preliminary trial results of a novel radiopharmaceutical for PET imaging of inflammation developed at the University of Turku, Finland, have been published. The compound, which targets the vascular adhesion protein 1 (VAP-1) that regulates inflammatory cell traffic, is the first radiopharmaceutical that has been developed completely in Finland and has advanced to clinical trials. In the study that started with healthy volunteers, the radiopharmaceutical was found to be well tolerated and safe.
The radiopharmaceutical is 68Ga-labelled Siglec-9 peptide.
"The dose of the radiopharmaceutical ...
Leonardo da Vinci definitely did not sculpt the Flora bust
2021-04-16
"It is machination, it is deception," said the Director General of the Berlin Royal Museums in his defence when criticized for buying a fake. Wilhelm Bode did not budge an inch: the sculpture he acquired in 1909 was an as yet unknown production of the great Renaissance master, Leonardo da Vinci. After one hundred years and numerous controversies, a group of scientists led by a CNRS researcher* has just proven him wrong once and for all. The Flora wax bust, conserved at the Bode Museum in Berlin, recently underwent radiocarbon (14C) dating, which provided both a precise date and an incontrovertible result: it was made in the nineteenth century, nearly 300 years after da Vinci's death. As the sculpture was made primarily from spermaceti, ...
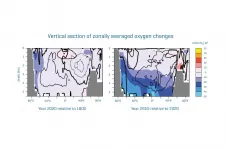
Long-term consequences of CO2 emissions
2021-04-16
The life of almost all animals in the ocean depends on the availability of oxygen, which is dissolved as a gas in seawater. However, the ocean has been continuously losing oxygen for several decades. In the last 50 years, the loss of oxygen accumulates globally to about 2% of the total inventory (regionally sometimes significantly more). The main reason for this is global warming, which leads to a decrease in the solubility of gases and thus also of oxygen, as well as to a slowdown in the ocean circulation and vertical mixing. A new study published today in the scientific journal Nature Communications ...
Generation of super-resolved optical needle and multifocal array using graphene oxide metalenses
2021-04-16
In a new publication from Opto-Electronic Advances; DOI https://doi.org/10.29026/oea.2021.200031, Researchers led by Professor Baohua Jia at Swinburne University of Technology, Victoria, Australia, Professor Cheng-Wei Qiu at National University of Singapore, Singapore and Professor Tian Lan at Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing, China considered the generation of super-resolved optical needle and multifocal array using graphene oxide metalenses.
Ultrathin and lightweight, metalenses are becoming increasingly significant for their use in photonic chips, biosensors and micro imaging systems such as smart phone cameras.
Compared to conventional lenses, metalenses can improve the image quality of current cameras, ...
Egg and sperm cell size evolved from competition
2021-04-16
In most living animals, egg cells are vastly larger than sperm cells. In humans, for example, a single egg is 10 million times the volume of a sperm cell.
In a new study, Northwestern University researchers found that competition and natural selection drove this curious size discrepancy.
Using mathematical modeling, the researchers considered a time very early in evolution when primordial species reproduced using external fertilization. In the model, bigger reproductive cells, or gametes, presented a competitive edge because they could hold more nutrients for a potential zygote. Smaller gametes, however, required fewer resources to make, which put less stress on the parent.
"Organisms either needed to produce the biggest gametes with the most provisions ...
Experiments cast doubts on the existence of quantum spin liquids
2021-04-16
When temperatures drop below zero degrees Celsius, water turns to ice. But does everything actually freeze if you just cool it down enough? In the classical picture, matter inherently becomes solid at low temperatures. Quantum mechanics can, however, break this rule. Therefore, helium gas, for example, can become liquid at -270 degrees, but never solid under atmospheric pressure: There is no helium ice.
The same is true for the magnetic properties of materials: at sufficiently low temperatures, the magnetic moments known as 'spins', for example, arrange themselves in such a way that they are oriented opposite/antiparallel to their respective neighbors. One can think of this as arrows pointing alternating up and down along a chain or in a checkerboard pattern. It ...
Alpine plants are losing their white "protective coat"
2021-04-16
Snow cover in the Alps has been melting almost three days earlier per decade since the 1960s. This trend is temperature-related and cannot be compensated by heavier snowfall. By the end of the century, snow cover at 2,500 meters could disappear a month earlier than today, as simulations by environmental scientists at the University of Basel demonstrate.
Global warming demands huge adjustments in tourism, hydropower generation and agriculture in alpine areas. But the fauna and flora also have to adapt to rising temperatures. By the end of the century, ...
Dust at work can lead to rheumatic diseases
2021-04-16
If you are exposed to silica (quartz) dust at work - e.g. from working with concrete and granite - you have a greater risk of certain types of rheumatic disease. This is shown by results from Aarhus University and Aarhus University Hospital, which have just been published in the International Journal of Epidemiology.
Exposure to silica dust at work, which is the case especially at workplaces within construction and industry, may lead to autoimmune rheumatic diseases. Photo: Unsplash.
Exposure to silica dust at work, which is the case especially at workplaces within construction and industry, may lead to autoimmune rheumatic diseases. Photo: Unsplash.
As the research results from Aarhus University show, exposure to ...
[1] ... [2409]
[2410]
[2411]
[2412]
[2413]
[2414]
[2415]
[2416]
2417
[2418]
[2419]
[2420]
[2421]
[2422]
[2423]
[2424]
[2425]
... [8815]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.