Leg muscle action assists blood flow independently of age
2021-04-19
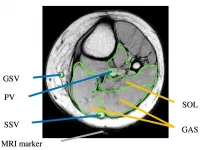
Chronic lower-limb edema (CLE) -- the permanent accumulation of fluid in the leg -- often occurs in elderly people. The condition leads to various physical and mental problems, including difficulty in walking or moving, fatigue and anxiety. One cause of CLE is the lack of physical activity, which is associated with a decrease in muscle pump action. The latter refers to the leg muscle's acting as a blood pump: when contracted, the muscle squeezes veins together, forcing blood to flow. The question whether muscle pump action systematically changes with age has not been thoroughly investigated; now, Junko Sugama from Kanazawa University and colleagues have addressed this issue. In addition, they studied how leg posture affects muscle pump action.
For their study, Sugama ...
Mirror, mirror...viewing your own face, even subconsciously, is rewarding
2021-04-19
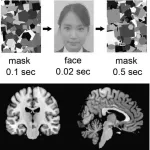
Osaka, Japan - As humans, we each have a powerful ability to easily recognize our own face. But now, researchers from Japan have uncovered new information about how our cognitive systems enable us to distinguish our own face from those of others, even when the information is presented subliminally.
In a study published this month in Cerebral Cortex, researchers from Osaka University have revealed that a central element of the dopamine reward pathway in the brain was activated when participants were subliminally shown images of their face. This provides new clues regarding the underlying processes of the brain involved in self-facial recognition.
When we are ...
Evidence for glaciation predating MIS-6 in the eastern Nyainqêntanglha, southeastern Tibet
2021-04-19
Southeastern Tibet is one of the most glaciated regions on the Tibetan Plateau both at present and during the Quaternary. Numerical dating of glacial deposits has allowed the establishment of a provisional chronology of Quaternary glacial fluctuations in this region, with the oldest glaciation (Guxiang Glaciation) occurring in marine oxygen isotope stage 6 (MIS-6). However, glaciations predating MIS-6 have been identified at many locations on the Tibetan Plateau and its surrounding mountains, posing the question: as a major glaciation center both at present and during the Quaternary, did a glaciation prior to MIS-6 ever occur in southeastern Tibet?
Zhou et al. (2021) provide evidence for a glacier advance in the Bodui Zangbo River ...
Where's my horse-sized rabbit?
2021-04-19
Japan -- Next to cat videos, watching small and cuddly rabbits is probably one of the most popular internet pastimes. Plus they appear in literature as well as in traditional folklore spanning numerous cultures, thanks likely to the fact that rabbits reside on every continent except Antarctica.
Yet despite their ubiquity, lagomorphs -- including rabbits, hares, and pikas -- are rather limited in their size diversity. Compare this to their evolutionary sisters, the rodents, which vary in size from the four-gram pygmy mouse to capybaras weighing as much as 50 kilograms.
So why don't we see rabbits rivaling the sizes of horses?
To answer this question, a research team ...
Where are the women on the Spanish-language Wikipedia site?
2021-04-19
With its more than 40 million articles in 301 different languages, Wikipedia is one of the largest human collaboration efforts in history. One of the main pillars on which this wish to bring together the sum of all knowledge is based is the achievement of a neutral space. However, several studies suggest that the site suffers from a persistent gender bias as regards both content and the composition of its community. An analysis of the gender gap in the Spanish-language version of Wikipedia by an interdisciplinary team at the UOC has revealed that only 11.6% of its registered editors are women.
According to the new study, which has been published in the journal PLOS ONE, the difference could be partially due to female editors being less ...
Human land-use and climate change will have significant impact on animal genetic diversity
2021-04-19
Over the last 200 years, researchers have worked towards understanding the global distribution of species and ecosystems. But so far even the basic knowledge on the global geography of genetic diversity was limited.
That now changes with a recent paper from Globe Institute. Professor David Nogues Bravo and his team has spent the last eight years combining data from scientific gene banks with scenarios of future climate and land-use change. The result is the first ever global assessment of how it will impact the genetic diversity of mammals, e.g. when tropical forests are converted to agricultural land.
'Our study ...
SMART breakthrough to enhance travel behavior research with artificial neural networks
2021-04-19
Singapore, 19 April, 2021 - Researchers at the Future Urban Mobility (FM) Interdisciplinary Research Group (IRG) at Singapore-MIT Alliance for Research and Technology (SMART), MIT's research enterprise in Singapore, have created a synthetic framework known as theory-based residual neural network (TB-ResNet), which combines discrete choice models (DCMs) and deep neural networks (DNNs), also known as deep learning, to improve individual decision-making analysis used in travel behaviour research.
In this research paper, Theory-based residual neural networks: A synergy of discrete choice models and deep neural networks, ...
Understanding interfaces of hybrid materials with machine learning
2021-04-19
The production of nanomaterials involves self-assembly processes of functionalized (organic) molecules on inorganic surfaces. This combination of organic and inorganic components is essential for applications in organic electronics and other areas of nanotechnology.
Until now, certain desired surface properties were often achieved on a trial-and-error basis. Molecules were chemically modified until the best result for the desired surface property was found. However, the processes controlling the self-assembly of molecules at interfaces are so complex ...
Active liquid crystal systems examined in search of autonomous materials systems
2021-04-19
Liquid Crystals (LC) are widely deployed in display technology and optical fibres. From smartphones in your pockets to large screen TVs, LCs are everywhere, as this special state of matter has been found in colorful soap bubbles as well as certain living tissues.
But LCs are by no means limited to use in gadgets or electronic devices. For quite some time, scientists have been studying the possibility of creating "active nematics", a particular class of active LCs, which consist of self-driven units capable of converting chemical or other forms of energy into motion. When administered the proper stimuli, scientists have found that they can generate a predictable response from different LCs, which allows for design of smart, multifunctional ...
Bad to the bone: Hebrew University reveals impact of junk food on kids' skeletal development
2021-04-19
A team of researchers from the Hebrew University of Jerusalem has proven the linkages between ultra-processed foods and reduced bone quality, unveiling the damage of these foods particularly for younger children in their developing years. The study, led by Professor Efrat Monsonego-Ornan and Dr. Janna Zaretsky from the Department of Biochemistry, Food Science and Nutrition at the University's Faculty of Agriculture, was published in the journal Bone Research and serves as the first comprehensive study of the effect of widely-available food products on skeleton development.
Ultra-processed foods--aka, junk food--are ...
Gender-affirming hormone therapy may increase risk of high blood pressure
2021-04-19
DALLAS, April 19, 2021 — Gender-affirming hormone therapy (GAHT) was associated with blood pressure changes in both transgender men and women, according to new research published today in Hypertension, an American Heart Association journal. Given the higher burden of heart attack, stroke and other cardiovascular conditions among transgender men and women, blood pressure screening and monitoring are important, especially after beginning hormone therapies.
Although doctors have prescribed gender-affirming hormone therapy to transgender men and women for more than 25 years, researchers and health care professionals know little about rates of hypertension and how the effects on blood ...
Scientists crack 'the Brazil-nut' puzzle, how do the largest nuts rise to the top?
2021-04-19
Scientists have for the first time captured the complex dynamics of particle movement in granular materials, helping to explain why mixed nuts often see the larger Brazil nuts gather at the top. The findings could have vital impact on industries struggling with the phenomenon, such as pharmaceuticals and mining.
Many people will have the experience of dipping their hands into a bag of mixed nuts only to find the Brazil nuts at the top. This effect can also be readily observed with cereal boxes, with the larger items rising to the top. Colloquially, this phenomenon of particles segregating by their size is known as the 'Brazil-nut effect' and also has huge implications for industries where uneven mixing can critically degrade product quality.
Now, for the first time, scientists at The ...
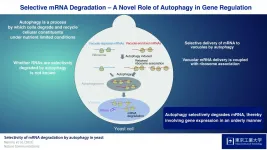
Selective mRNA degradation via autophagy: A novel role for autophagy in gene regulation
2021-04-19
Optimal cell function requires a fine balance between the synthesis and degradation of biomolecules. Autophagy is the process by which cells degrade and recycle their own components, helping to clean up and maintain the cell's internal environment and ensure the smooth functioning of cellular processes. Autophagy is strongly induced when cells are subjected to stresses like nutrient deprivation, acting under such conditions to supply nutrients through its breakdown of unneeded cellular material.
Autophagy substrates are delivered to vacuoles in yeast or lysosomes in mammals for degradation by double-membrane vesicles called "autophagosomes". While autophagy was originally considered a non-selective process that isolates substrates in the cytoplasm of ...
As plant/animal diversity wanes, is microbial life changing too? A perilously 'profound Ignorance'
2021-04-19
With alarms sounding about the declining diversity of plants and animals, a related concern with equally profound implications is posed: is the variety of microbial life, including viruses, changing too -- and if so, in which direction and how fast?
In a paper published today, David S. Thaler of the University of Basel, Switzerland, and Guest Investigator at The Rockefeller University's Programme for the Human Environment (PHE), notes the well-documented, "clearly downwards" trajectory of plant and animal diversity, constituting "a key issue of the Anthropocene."
Whether change is underway also in the world of microbes -- the tiniest cogs in planetary functioning -- is "a complete unknown. We have no idea whether global microbial diversity is increasing, decreasing, or staying ...
Under 30 and sexually active? It's a good idea to get tested for chlamydia and gonorrhea
2021-04-19
Anyone sexually active under age 30 should be offered testing for chlamydia and gonorrhea, according to a new guideline from the Canadian Task Force on Preventive Health Care published in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal).
Chlamydia and gonorrhea are the most commonly reported sexually transmitted bacterial infections (STIs) in Canada and are treatable with antibiotics. Without treatment, these infections can lead to pelvic inflammatory disease, pain and possibly infertility.
"If people are under 30 and sexually active, it's a good idea to get tested," says Dr. Ainsley Moore, a family physician and associate clinical professor, Department of Family Medicine, McMaster University, and chair of the task force chlamydia ...
Videoconferences more exhausting when participants don't feel group belonging
2021-04-19
Videoconferences may be less exhausting if participants feel some sense of group belonging, according to new research published by the American Psychological Association.
As remote work and the use of videoconferences have dramatically increased during the coronavirus pandemic, more people are fatigued from meeting through computer screens instead of in person. In this study, 55 employees in various fields in the United States were surveyed about their feelings about videoconferences. The researchers thought longer meetings and being on video would cause the most fatigue, but their findings surprised them, said lead researcher Andrew Bennett, PhD, an assistant professor at Old Dominion University.
"We expected that aspects of being on video would be related to fatigue, such ...
Common plants and pollinators act as anchors for ecosystems
2021-04-19
The next time you go for a hike, take an extra moment to appreciate the seemingly ordinary life all around you. A house fly, humble yarrow weed and other "generalist" plants and pollinators play a crucial role in maintaining biodiversity and may also serve as buffers against some impacts of climate change, finds new University of Colorado Boulder research.
The findings, published this month in Ecology, provide valuable insights for prioritizing the conservation of species that contribute to the strength of ecological communities.
"A lot of times, conservation efforts are geared toward things that are rare. But oftentimes, species that are common are also in decline and could go extinct, and that could have really big repercussions for maintaining biodiversity," ...
Online farmers' markets valuable when crisis events like COVID occur
2021-04-19
New research is shining light on the importance of farmers' markets' ability to mitigate potential disruptions to distribution networks in the face of system shocks like the COVID-19 pandemic.
In a recent study, the researchers found the markets' regional characteristics play a key role in the decision to move all or parts of their operations online -- and how that decision can help or hinder its surrounding community.
"By building online communities through their social media and website tools, farmers' markets can play a role in keeping the community connected and supporting a sustainable and just food system through the pandemic and beyond," said researcher Josalyn Radcliffe, a PhD student in Waterloo's School of Public Health and ...
Heart patients advised to move more to avoid heart attacks and strokes
2021-04-17
Sophia Antipolis - 17 April 2021: Elevated blood pressure, high cholesterol and diabetes increase the risk of heart disease. But a large study today reveals that in people with these conditions, increasing activity levels is associated with a reduced likelihood of heart events and mortality. The research is presented at ESC Preventive Cardiology 2021, an online scientific congress of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC).1
Study author Dr. Esmée Bakker of Radboud University Medical Center, Nijmegen, the Netherlands said: "Previous research showed that improvements in physical activity are beneficial to health. However, those studies were performed in the general population. In our study, we were interested to see if there were similar effects in individuals with cardiovascular ...
New amphibious centipede species discovered in Okinawa and Taiwan
2021-04-17
Tokyo, Japan - Researchers from Tokyo Metropolitan University and Hosei University have discovered a new species of large, tropical centipede of genus Scolopendra in Okinawa and Taiwan. It is only the third amphibious centipede identified in the world, and is the largest in the region, 20 cm long and nearly 2 cm thick. It is also the first new centipede to be identified in Japan in 143 years, testament to the incredible biodiversity of the Ryukyu Archipelago.
Scolopendra is a genus of large, tropical centipede, one of the original genera named by the father of modern taxonomy himself, Carl Linnaeus. They are strong predators in any soil ecosystems they inhabit, with around 100 different species found in tropical regions around the world. Of these, only five have been ...
Scientists may detect signs of extraterrestrial life in the next 5 to 10 years
2021-04-16
Research shows that a new telescope could detect a potential signature of life on other planets in as little as 60 hours.
"What really surprised me about the results is that we may realistically find signs of life on other planets in the next 5 to 10 years," said Caprice Phillips, a graduate student at The Ohio State University, who will share preliminary findings at a END ...
The fate of the planet
2021-04-16
From engineered pandemics to city-toppling cyber attacks to nuclear annihilation, life on Earth could radically change, and soon. Scientists will forecast the fate of the planet at a END ...
Tarantula's ubiquity traced back to the cretaceous
2021-04-16
Tarantulas are among the most notorious spiders, due in part to their size, vibrant colors and prevalence throughout the world. But one thing most people don't know is that tarantulas are homebodies. Females and their young rarely leave their burrows and only mature males will wander to seek out a mate. How then did such a sedentary spider come to inhabit six out of seven continents?
An international team of researchers, including Carnegie Mellon University's Saoirse Foley, set out on an ancestry.com-like investigation to find the answer to this question. They looked to the transcriptomes, ...
On the pulse of pulsars and polar light
2021-04-16
Faced with the tragic loss of the Arecibo observatory in Puerto Rico and the often prohibitive cost of satellite missions, astronomers are searching for savvy alternatives to continue answering fundamental questions in physics.
At a END ...
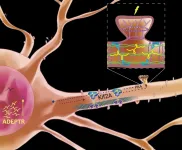
Neural plasticity depends on this long noncoding RNA's journey from nucleus to synapse
2021-04-16
JUPITER, FL--Making memories involves more than seeing friends or taking photos. The brain constantly adapts to new information and stores memories by building connections among neurons, called synapses. How neurons do this--reaching out arm-like dendrites to communicate with other neurons--requires a ballet of genes, signaling molecules, cellular scaffolding and protein-building machinery.
A new study from scientists at Scripps Research and the Max Planck Florida Institute for Neuroscience finds a central role for one signaling molecule, a long, noncoding RNA that the scientists named ADEPTR.
Using a variety of technologies, including confocal and two-photon microscopy, they track ADEPTR's moves, watching as it forms, travels, amasses at the ...
[1] ... [2408]
[2409]
[2410]
[2411]
[2412]
[2413]
[2414]
[2415]
2416
[2417]
[2418]
[2419]
[2420]
[2421]
[2422]
[2423]
[2424]
... [8815]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.