Lung cancer screening predicts risk of death from heart disease
2021-04-15
OAK BROOK, Ill. - A deep learning algorithm accurately predicts the risk of death from cardiovascular disease using information from low-dose CT exams performed for lung cancer screening, according to a study published in Radiology: Cardiothoracic Imaging.
Cardiovascular disease is the leading cause of mortality worldwide. It even outpaces lung cancer as the leading cause of death in heavy smokers.
Low-dose CT lung scans are used to screen for lung cancer in high-risk people such as heavy smokers. These CT scans also provide an opportunity to screen for cardiovascular disease by extracting information about calcification ...
Potential ways to improve survival for cancer patients who receive fragmented care
2021-04-15
Key takeaways
Pancreatic, liver, bile duct, and stomach cancer operations are inherently complex and initially often take place at large cancer centers where surgical teams perform a large volume of procedures.
Readmission to a different hospital from where patients had these operations initially performed markedly increases death risk.
There are ways to address care fragmentation with newly identified risk factors for readmission; cancer hospitals should seek to determine safe sites of care for readmissions after these types of operations.
CHICAGO: New research reveals that 28 percent of patients who are readmitted ...
Patients who are overweight or obese at risk of more severe COVID-19
2021-04-15
Patients who are overweight or obese have more severe COVID-19 and are highly likely to require invasive respiratory support, according to a new international study.
The research, led by the Murdoch Children's Research Institute (MCRI) and The University of Queensland and published in Diabetes Care, found obese or overweight patients are at high risk for having worse COVID-19 outcomes. They are also more likely to require oxygen and invasive mechanical ventilation compared to those with a healthy weight.
MCRI researcher Dr Danielle Longmore said the findings, which highlighted the relationship between obesity and increased COVID-19 disease burden, showed the need to urgently introduce strategies to address ...
Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B Volume 11, Issue 3 publishes
2021-04-15
https://www.sciencedirect.com/journal/acta-pharmaceutica-sinica-b/vol/11/issue/3
The Journal of the Institute of Materia Medica, the Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and the Chinese Pharmaceutical Association, Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B (APSB) is a monthly journal, in English, which publishes significant original research articles, rapid communications and high quality reviews of recent advances in all areas of pharmaceutical sciences -- including pharmacology, pharmaceutics, medicinal chemistry, natural products, pharmacognosy, pharmaceutical analysis and pharmacokinetics.
Featured papers in this issue are:
Isorhapontigenin protects against doxorubicin-induced ...
BIO Integration Journal, Volume 2, Issue Number 1, publishes
2021-04-15
Guangzhou, April 8, 2021: New journal BIO Integration (BIOI) publishes its fifth issue, volume 2, issue 1. BIOI is a peer-reviewed, open access, international journal, which is dedicated to spreading multidisciplinary views driving the advancement of modern medicine. Aimed at bridging the gap between the laboratory, clinic, and biotechnology industries, it will offer a cross-disciplinary platform devoted to communicating advances in the biomedical research field and offering insights into different areas of life science, to encourage cooperation and exchange among scientists, clinical researchers, and health care providers.
The issue contains an editorial, two mini review articles, two opinion articles and an interview offering ...
Keep calm! How blood vessels are kept in check
2021-04-15
The inner surface of blood vessels is lined by a wafer-thin layer of cells known as the endothelium, which forms a crucial barrier between blood and the surrounding tissue. The single-layered cell structure promotes the exchange of oxygen and nutrients, while simultaneously preventing the uncontrolled leakage of blood components. Only when the metabolic needs of the surrounding tissue increase, e.g., during growth, wound healing or tumor development, do endothelial cells abandon this stable cell association in order to divide and form new blood vessels. The signals that trigger this activation have been ...
New way of diagnostics detects 'undetectable' genetic defects
2021-04-15
Detecting hidden genetic defects by applying an existing method to an existing datasets. Researchers at Radboud university medical center have succeeded: they showed that the 'Expansion Hunter' method can detect errors in the DNA that lead to repeat expansion diseases, such as the movement disorder ataxia. This result provides guidance to fellow researchers worldwide on how to use this method to diagnose patients with genetic disorders.
With current diagnostic technology for genetic disorders, it is possible to map all 20,000 genes in our DNA at once. Doctors are increasingly opting for this so-called exome technique: it is widely applicable and increasingly provides molecular diagnoses. ...
Keeping fit with HIIT really does work
2021-04-15
High intensity interval training has become increasingly popular as it's a quick and effective way to improve health. This is all the more important as countries around the world emerge from lockdowns due to coronavirus and are looking for quick and easy way to exercise again.
Recently, researchers have been studying whether shorter variations of HIIT, involving as little as 4-min of high intensity exercise per session (excluding a warm up and cool down), also improve health.
A new review paper published in the Journal of Physiology collates a decade's worth of research ...
A study identifies a universal property for efficient communication
2021-04-15
Words categorize the semantic fields they refer to in ways that maximize communication accuracy while minimizing complexity. Recent studies have shown that human languages are optimally balanced between accuracy and complexity. For example, many languages have a word that denotes the colour red, but no language has individual words to distinguish ten different shades of the colour. These additional words would complicate the vocabulary and rarely would they be useful to achieve precise communication.
A study published on 23 March in the journal Proceedings of the ...
Fewer advertisers but more subscribers to the Nordic news media during the pandemic
2021-04-15
The corona pandemic has had a major impact on the Nordic news media. At the same time as advertising revenues have fallen drastically, interest among the audience for professional news coverage has increased, according to a new report from Nordicom at the University of Gothenburg. Several Nordic media companies have also reported record sales of digital subscriptions as a result of the pandemic.
Covid-19 swept over the Nordic region and the rest of the world with full force in the spring of 2020. A year later, the pandemic still has the world in a strong grip. However, both the health-related ...
eBird data used to shape eagle management
2021-04-15
ITHACA, N.Y. - Millions of people donate billions of dollars' worth of their time to citizen-science projects each year. While these efforts have broadened our understanding of everything from birds to bees to bracken ferns, rarely has citizen-science data informed policy at the highest levels of government. But that may be changing.
One of the world's largest citizen-science efforts, the Cornell Lab of Ornithology's eBird, is now helping the federal government streamline and refine its process for assessing eagle populations and informing eagle management.
New research out this week in the Journal of ...
Trial shows York leishmaniasis vaccine safe and induces immune responses in patients
2021-04-15
The results of the first clinical trial of a new vaccine for a neglected tropical disease have demonstrated that it is safe and induces immune responses in patients with the infection.
There are currently no vaccines to prevent leishmaniasis which is spread by the bite of sand flies and existing drugs have many side effects and are difficult to administer.
The potential new vaccine was developed by researchers at the Hull York Medical School, which is the joint medical school of the Universities of Hull and York.
Professor Paul Kaye from the Hull York Medical School was the principal investigator on the Wellcome Trust Translation Award that funded the development of the vaccine.
Professor Kaye said: ...
CHOP-led research study identifies key target in treatment-resistant hemophilia A
2021-04-15
Philadelphia, April 15, 2021--Researchers at Children's Hospital of Philadelphia (CHOP) have identified a key target that may be responsible for treatment failure in about 30% of patients with hemophilia A. The target, known as B cell activating factor (BAFF), appears to promote antibodies against and inhibitors of the missing blood clotting factor that is given to these patients to control their bleeding episodes. The findings, published in the Journal of Clinical Investigation, raise the possibility of using anti-BAFF therapies, potentially in combination with immune tolerance therapies, to tame the immune response in some patients with severe hemophilia A.
Hemophilia A is the most common inherited bleeding disorder, affecting ...
Visio-vestibular examination is critical part of diagnosing concussion in young athletes
2021-04-15
Philadelphia, April 15, 2021 - Early and accurate diagnosis leads to optimal recovery from concussion. Over the past year across a series of studies, the Minds Matter Concussion Program research team at Children's Hospital of Philadelphia (CHOP) has systematically evaluated the use of the visio-vestibular examination (VVE) and its ability to enhance concussion diagnosis and management. The latest of these studies published online today in the Clinical Journal of Sports Medicine.
The VVE involves a series of brief eye movement and balance tests intended to identify deficits in brain function involving the visual and vestibular systems. Researchers found that the VVE presents several advantages over current clinical measures, moving beyond subjective symptoms ...
No increase in brain health problems in middle age for men who played football in high school
2021-04-15
April 15, 2021 - Decades after their days on the gridiron, middle-aged men who played football in high school are not experiencing greater problems with concentration, memory, or depression compared to men who did not play football, reports a study in Clinical Journal of Sport Medicine. The journal is published in the Lippincott portfolio by Wolters Kluwer.
"Men who played high-school football did not report worse brain health compared with those who played other contact sports, noncontact sports, or did not participate in sports during high school," according to the new research, led by Grant L. Iverson, PhD, of Harvard Medical School. The study offers reassurance that playing high-school football is not, in itself, a risk factor for cognitive or mood ...
CityU biologists discover super-enhancers that switch on breast cancer genes
2021-04-15
Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) is an aggressive type of breast cancer with a high fatality rate. Currently, chemotherapy is the major treatment option, but the clinical result is unsatisfactory. A research team led by biologists at City University of Hong Kong (CityU) has identified and characterised a set of specific super-enhancers that stimulate the activity of the related critical cancer genes. The research has also discovered that the deletion of certain specific super-enhancers can reduce tumour cell growth. The latest findings may help discover new effective drug targets for TNBC patients to improve their survival chance.
Traditionally, cancer research ...
Counting pedestrians to make pedestrians count
2021-04-15
A key portion of MIT's campus overlaps with Kendall Square, the bustling area in East Cambridge where students, residents, and tech employees scurry around in between classes, meetings, and meals. Where are they all going? Is there a way to make sense of this daily flurry of foot traffic?
In fact, there is: MIT Associate Professor Andres Sevtsuk has made Kendall Square the basis of a newly published model of pedestrian movement that could help planners and developers better grasp the flow of foot traffic in all cities.
Sevtsuk's work emphasizes the functionality of a neighborhood's elements, above and beyond its physical form, making the model one that could be ...
Making waves in oceanography
2021-04-15
A new scientific discovery in Australia by Flinders University has recorded for the first time how ghost currents and sediments can 'undo' the force of gravity.
The new theory, just published in the Journal of Marine Systems, helps explain obscure events in which suspended sediment particles mysteriously move upward, not downward, on the slope of submarine canyons of the deep sea.
While this activity seems to contradict the laws of gravity, Flinders University physical oceanographer Associate Professor Jochen Kaempf has found an answer, devising the first scientific explanation of the observed upslope sediment transport.
"To put it simply, the vehicle of this transport are currents that, while carrying ...
With impressive accuracy, dogs can sniff out coronavirus
2021-04-15
Many long for a return to a post-pandemic "normal," which, for some, may entail concerts, travel, and large gatherings. But how to keep safe amid these potential public health risks?
One possibility, according to a new study, is dogs. A proof-of-concept investigation published today in the journal PLOS ONE suggests that specially trained detection dogs can sniff out COVID-19-positive samples with 96% accuracy.
"This is not a simple thing we're asking the dogs to do," says Cynthia Otto, senior author on the work and director of the University of Pennsylvania School of Veterinary Medicine Working Dog Center. "Dogs have to ...
Novak Djokovic now has a tiny new snail species named after him
2021-04-15
Do freshwater snails make good tennis players? One of them certainly has the name for it.
Enter Travunijana djokovici, a new species of aquatic snail named after famous Serbian ten­nis player Novak Djokovic.
Slovak biospeleologist Jozef Grego and Montenegrin zoologist Vladimir Pesic of the University of Montenegro discovered the new snail in a karstic spring near Podgorica, the capital of Montenegro, during a field trip in April 2019. Their scientific article, published in the open-access, peer-reviewed journal Subterranean Biology, says they named it after Djokovic "to acknowledge his inspiring enthusiasm and energy."
"To discover some of the world's rarest animals that inhabit the unique underground habitats of the Dinaric karst, to reach inaccessible cave and spring habitats ...
Norovirus clusters are resistant to environmental stresses and UV disinfection, new study finds
2021-04-15
WASHINGTON (April 15, 2021) -- Clusters of a virus known to cause stomach flu are resistant to detergent and ultraviolet disinfection, according to new research co-led by END ...
German National HPC Centre provides resources to look for cracks in the standard model
2021-04-15
Since the 1970s, the Standard Model of Physics has served as the basis from which particle physics are investigated. Both experimentalists and theoretical physicists have tested the Standard Model's accuracy, and it has remained the law of the land when it comes to understanding how the subatomic world behaves.
This week, cracks formed in that foundational set of assumptions. Researchers of the "Muon g-2" collaboration from the Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory (FNAL) in the United States published further experimental findings that show that muons--heavy subatomic relatives of electrons--may have a larger "magnetic moment" than earlier Standard Model estimates had predicted, indicating that an unknown particle or force might be influencing ...
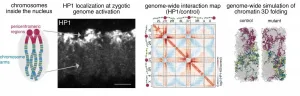
The architect of genome folding
2021-04-15
The DNA molecule is not naked in the nucleus. Instead, it is folded in a very organized way by the help of different proteins to establish a unique spatial organization of the genetic information. This 3D spatial genome organization is fundamental for the regulation of our genes and has to be established de novo by each individual during early embryogenesis. Researchers at the MPI of Immunobiology and Epigenetics in Freiburg in collaboration with colleagues from the Friedrich Mischer Institute in Basel now reveal a yet unknown and critical role of the protein HP1a in the 3D genome re-organization after fertilisation. The study published in the scientific journal Nature identifies HP1a as an epigenetic regulator that is involved in establishing ...
Potential impact of pass/fail USMLE Step 1 scoring on radiology residency applications
2021-04-15
Leesburg, VA, April 15, 2021--A Scientific E-Poster to be presented at the 2021 ARRS Virtual Annual Meeting found that as the United States Medical Licensing Examination (USMLE) Step 1 transitions from a numerical score to pass or fail--as early as January 2022--radiology residency program directors will likely rely on USMLE Step 2 Clinical Knowledge (CK) scores as an objective and standardized metric to screen applicants.
"However," wrote lead investigator Rebecca Zhang of the University of Maryland School of Medicine in Baltimore, "program directors remain unsure whether they will ...
Outcome predictive performance of admission chest radiographs in COVID-19 patients
2021-04-15
Leesburg, VA, April 15, 2021--A Scientific E-Poster to be presented at the 2021 ARRS Virtual Annual Meeting found that in the setting of a high pretest probability of COVID-19 infection or with a quick turnaround of the rapid real-time reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) COVID-19 test, a chest x-ray (CXR) scoring system may be used prospectively to predict patient outcomes.
"We developed an accurate and reliable tool for classifying COVID-19 severity, which can be used both at the attending chest radiologist and junior resident level. This study identifies the laboratory, clinical and radiographic data that predict important patient outcomes such as death, intubation, and the need for chronic renal replacement ...
[1] ... [2415]
[2416]
[2417]
[2418]
[2419]
[2420]
[2421]
[2422]
2423
[2424]
[2425]
[2426]
[2427]
[2428]
[2429]
[2430]
[2431]
... [8815]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.