Brachytherapy may continue following uterine perforation in cervical cancer patients
2021-04-13
A new study finds that brachytherapy, a common procedure that delivers radiation directly to cancer cells, may continue safely, potentially without delay or antibiotics, in cervical cancer patients following uterine perforation.
According to the World Health Organization, cervical cancer is the fourth most common cancer in women. Treatment for cervical cancer often involves brachytherapy combined with daily radiation therapy. Brachytherapy delivers radiation directly to cancer cells through a tube placed within the uterus. "At times this tube can pierce the uterus and lead to a perforation," said William Small, Jr., MD, lead study author and professor and chair of radiation ...
World's protected areas need more than a 'do not disturb' sign
2021-04-13
Lessons learned from the world's protected forests: Just declaring a plot of land protected isn't enough - conservation needs thoughtful selection and enforcement.
A group of scientists, many tied to Michigan State University, examined nearly 55,000 protected areas across the world to understand what it took to effectively protect their forests - a key benchmark to protecting habitat and preserving natural resources. They conclude that it's important to protect the forests exposed to the most threats in areas close to cities and be prepared to be strict in enforcing rules intended to stop deforestation.
In a recent issue of Science of the Total Environment, researchers noted that more than 4 million square kilometers ...
Stellar feedback and an airborne observatory; scientists determine a nebula younger than believed
2021-04-13
In the southern sky, situated about 4,300 light years from Earth, lies RCW 120, an enormous glowing cloud of gas and dust. This cloud, known as an emission nebula, is formed of ionized gases and emits light at various wavelengths. An international team led by West Virginia University researchers studied RCW 120 to analyze the effects of stellar feedback, the process by which stars inject energy back into their environment. Their observations showed that stellar winds cause the region to expand rapidly, which enabled them to constrain the age of the region. These findings indicate that RCW 120 must be less than 150,000 years old, which is very young for such ...
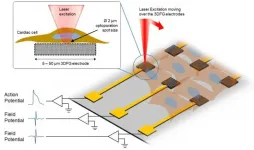
Unlocking richer intracellular recordings
2021-04-13
Behind every heartbeat and brain signal is a massive orchestra of electrical activity. While current electrophysiology observation techniques have been mostly limited to extracellular recordings, a forward-thinking group of researchers from Carnegie Mellon University and Istituto Italiano di Tecnologia has identified a flexible, low-cost, and biocompatible platform for enabling richer intracellular recordings.
The group's unique "across the ocean" partnership started two years ago at the Bioelectronics Winter School (BioEl) with libations and a bar napkin sketch. It has evolved into research published today in Science ...
UBCO engineer cautions pregnant women about speed bumps
2021-04-13
Slow down. Baby on board.
So says UBC Okanagan researcher and Associate Professor of Mechanical Engineering Hadi Mohammadi. His new research, conducted in collaboration with Sharif University of Technology, determines that accelerating over speed bumps poses a danger for pregnant women and their fetuses.
"There is lots of research about the importance of movement for women during pregnancy," explains Mohammadi, who teaches in the School of Engineering. "Our latest research looked specifically at the impacts of sudden acceleration on a pregnant woman."
Using new modelling based on data from ...
Finding resiliency in local, community news gathering
2021-04-13
When the Webster-Kirkwood Times, a community newspaper in the greater St. Louis, Missouri area, had to endure layoffs and stop publishing its print edition -- due to a loss in revenue as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic -- its readers felt the loss and began supporting the newspaper in earnest.
"A lot of times people don't know what they've got until it's gone," said Jaime Mowers, editor-in-chief of the Webster-Kirkwood Times. "Now, there is such a newfound appreciation for the newspaper. It's amazing to have the community's support, knowing we are loved that much and appreciated enough to ...
Mindfulness can make you selfish
2021-04-13
BUFFALO, N.Y. - Mindfulness is big business. Downloads of mindfulness apps generate billions of dollars annually in the U.S., and their popularity continues to rise. In addition to what individual practitioners might have on their phones, schools and prisons along with 1 in 5 employers currently offer some form of mindfulness training.
Mindfulness and meditation are associated with reducing stress and anxiety, while increasing emotional well-being. Plenty of scholarship supports these benefits. But how does mindfulness affect the range of human behaviors -- so-called prosocial behaviors -- that can potentially help or benefit other people? What happens when the research looks outwardly at social effects of mindfulness rather than inwardly at its personal effects?
It's ...
Human screams communicate at least six emotions
2021-04-13
Human screams signal more than fear and are more acoustically diverse than previously thought, according to a study published April 13th 2021 in the open-access journal PLOS Biology by Sascha Fru?hholz of the University of Zurich, and colleagues. Remarkably, non-alarming screams are perceived and processed by the brain more efficiently than alarming screams.
In nonhuman primates and other mammalian species, scream-like calls are frequently used as an alarm signal exclusively in negative contexts, such social conflicts or the presence of predators or other environmental threats. Humans are also assumed to use screams to signal danger and to scare predators. But humans scream not only when they are ...
The Lancet Psych: No evidence of an increase in risk of suicide in first months of the pandemic, but continued monitoring needed
2021-04-13
First study to examine suicides occurring around the world during the COVID-19 pandemic finds that - in high-income and upper-middle-income countries - suicide numbers have remained largely unchanged or have declined in the early months of the pandemic, compared with expected levels.
However, the authors stress that governments must remain vigilant as the longer-term mental health and economic effects of the pandemic unfold and be poised to respond if the situation changes.
Study looked at numbers of suicides in 21 countries between 1 April and 31 July 2020 and compared these with trends in the previous one to four years.
A new observational study ...
Joyful screams perceived more strongly than screams of fear or anger
2021-04-13
Screaming can save lives. Non-human primates and other mammalian species frequently use scream-like calls when embroiled in social conflicts or to signal the presence of predators and other threats. While humans also scream to signal danger or communicate aggression, they scream when experiencing strong emotions such as despair or joy as well. However, past studies on this topic have largely focused on alarming fear screams.
Humans respond to positive screams more quickly and with higher sensitivity
In a new study, a team at the University of Zurich Department of Psychology led by Sascha Frühholz ...
Life expectancy lower near superfund sites
2021-04-13
Living near a hazardous waste or Superfund site could cut your life short by about a year, reports Hanadi S. Rifai, John and Rebecca Moores Professor of Civil and Environmental Engineering at the University of Houston. The study, published in Nature Communications and based on evaluation of 65,226 census tracts from the 2018 Census, is the first nationwide review of all hazardous waste sites and not just the 1,300 sites on the national priority list managed by the federal government.
The analysis shows a decrease of more than two months in life expectancy for those living near a Superfund site. When coupled with high disadvantage of sociodemographic factors like age, sex, marital status and income, the decrease could be nearly 15 months, ...
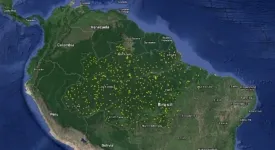
Airborne laser scanning of gaps in Amazon rainforest helps explain tree mortality
2021-04-13
A group of researchers led by Brazilians has used an innovative model to map gaps in the Amazon rainforest and identify factors that contribute to tree mortality. Water stress, soil fertility, and anthropic forest degradation have the most influence on gap dynamics in the world's largest and most biodiverse tropical rainforest, according to an article on the study published in Scientific Reports.
Forest gaps are most frequent in the areas with the highest levels of soil fertility, possibly because the abundance of organic material drives faster tree growth and shorter life cycles.
The main method of data collection ...
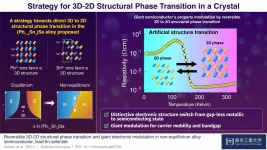
Giant electronic conductivity change driven by artificial switch of crystal dimensionality
2021-04-13
The electronic properties of solid materials are highly dependent on crystal structures and their dimensionalities (i.e., whether the crystals have predominantly 2D or 3D structures). As Professor Takayoshi Katase of Tokyo Institute of Technology notes, this fact has an important corollary: "If the crystal structure dimensionality can be switched reversibly in the same material, a drastic property change may be controllable." This insight led Prof. Katase and his research team at Tokyo Institute of Technology, in partnership with collaborators at Osaka University and National Institute for Materials Science, to embark on research into the possibility of switching the crystal structure dimensionality of a lead-tin-selenide alloy semiconductor. Their results appear in a paper published ...
Smoking cannabis significantly impairs vision, study finds
2021-04-13
A study carried out by the University of Granada indicates that smoking cannabis significantly alters key visual functions, such as visual acuity, contrast sensitivity, three-dimensional vision (stereopsis), the ability to focus, and glare sensitivity
Yet, more than 90% of users believe that using cannabis has no effect on their vision, or only a slight effect
A group of researchers from the Department of Optics of the University of Granada (UGR) has studied the effects of smoking cannabis on various visual parameters compared to the effect that the users themselves perceive the drug to have on their vision.
This study, led by Carolina Ortiz Herrera and Rosario González Anera, has been published in the journal Scientific Reports. Its main author, Sonia Ortiz Peregrina, explains that ...
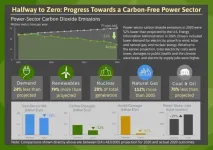
US power sector is halfway to zero carbon emissions
2021-04-13
Concerns about climate change are driving a growing number of states, utilities, and corporations to set the goal of zeroing out power-sector carbon emissions. To date 17 states plus Washington, D.C. and Puerto Rico have adopted laws or executive orders to achieve 100% carbon-free electricity in the next couple of decades. Additionally, 46 U.S. utilities have pledged to go carbon free no later than 2050. Altogether, these goals cover about half of the U.S. population and economy.
These are ambitious targets, but a new look at the past 15 years in the electricity sector shows that large reductions in emissions are possible.
New research from the Department of Energy's Lawrence ...
Northern Star Coral study could help protect tropical corals
2021-04-13
As the Rhode Island legislature considers designating the Northern Star Coral an official state emblem, researchers are finding that studying this local creature's recovery from a laboratory-induced stressor could help better understand how to protect endangered tropical corals.
A new study published today in mSystems, a journal of the American Society for Microbiology, investigates antibiotic-induced disturbance of the coral (Astrangia poculata) and shows that antibiotic exposure significantly altered the composition of the coral's mucus bacterial microbiome, but that all the treated corals recovered ...
Study of US tuna fisheries explores nexus of climate change, sustainable seafood
2021-04-13
A new study published in Elementa by researchers at the University of California, Santa Cruz and NOAA examines traditional aspects of seafood sustainability alongside greenhouse gas emissions to better understand the "carbon footprint" of U.S. tuna fisheries.
Fisheries in the United States are among the best managed in the world, thanks to ongoing efforts to fish selectively, end overfishing, and rebuild fish stocks. But climate change could bring dramatic changes in the marine environment that threaten seafood productivity and sustainability. That's one reason why researchers ...
Researchers develop new method for putting quantum correlations to the test
2021-04-13
Physicists from Swansea University are part of an international research collaboration which has identified a new technique for testing the quality of quantum correlations.
Quantum computers run their algorithms on large quantum systems of many parts, called qubits, by creating quantum correlations across all of them. It is important to verify that the actual computation procedures lead to quantum correlations of desired quality.
However, carrying out these checks is resource-intensive as the number of tests required grows exponentially with the number of qubits involved.
Researchers from the College of Science, working with colleagues from Spain ...
Novel guidelines help select optimal deconvolution method
2021-04-13
Biomedical scientists are increasingly using deconvolution methods, those used to computationally analyze the composition of complex mixtures of cells. One of their challenges is to select one method that is appropriate for their experimental conditions among nearly 50 available.
To help with method selection, researchers at Baylor College of Medicine and the Jan and Dan Duncan Neurological Research Institute at Texas Children's Hospital have extensively evaluated 11 deconvolution methods that are based on RNA-sequencing (RNA-seq) data analysis, determining each method's ...
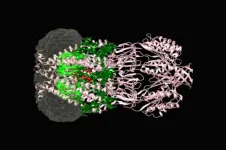
Inside the protein channel that keeps bacteria alive
2021-04-13
Almost all bacteria rely on the same emergency valves--protein channels that pop open under pressure, releasing a deluge of cell contents. It is a last-ditch effort, a failsafe that prevents bacteria from exploding and dying when stretched to the limit. If we understood how those protein channels worked, antibiotic drugs could be designed to open them on demand, draining a bacterium of its nutrients by exploiting a floodgate common to many species.
But these channels are tricky to operate in the lab. And how precisely they open and close, passing through a sub-conducting state and ending in a desensitized state under the influence of mechanical forces, remains poorly understood. Now, new research from ...
COVID-19 in our dust may help predict outbreaks, study finds
2021-04-13
A study done in rooms where COVID-19 patients were isolated shows that the virus's RNA - part of the genetic material inside a virus - can persist up to a month in dust.
The study did not evaluate whether dust can transmit the virus to humans. It could, however, offer another option for monitoring COVID-19 outbreaks in specific buildings, including nursing homes, offices or schools.
Karen Dannemiller, senior author of the study, has experience studying dust and its relationship to potential hazards like mold and microbes.
"When the pandemic started, we really wanted to find a way that we could help ...
NIH experts discuss post-acute COVID-19
2021-04-13
WHAT:
Many people who have COVID-19 make a full recovery and return to their baseline state of health; however, some people have symptoms or other sequelae weeks or months after initial SARS-CoV-2 infection. These heterogeneous symptoms were the subject of the virtual "Workshop on Post-acute Sequelae of COVID-19" hosted on Dec. 2 and 4, 2020, by the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), in collaboration with other institutes and centers of the National Institutes of Health. A paper published recently in Annals of Internal Medicine ...
Researchers reveal aging signatures across diverse tissue cells in mice
2021-04-13
Researchers have identified molecular signatures of the aging process in mice, publishing their results today in the open-access eLife journal.
Their analyses provide one of the most comprehensive characterisations of the molecular signatures of aging across diverse types of cells from different tissues in a mammal, and will aid future studies on aging and related topics.
Aging leads to the decline of major organs and is the main risk factor for many diseases, including cancer, cardiovascular and neurodegenerative diseases. While previous studies have highlighted different hallmarks of the aging process, the underlying molecular and cellular mechanisms ...
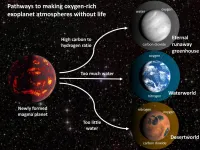
Study warns of 'oxygen false positives' in search for signs of life on other planets
2021-04-13
In the search for life on other planets, the presence of oxygen in a planet's atmosphere is one potential sign of biological activity that might be detected by future telescopes. A new study, however, describes several scenarios in which a lifeless rocky planet around a sun-like star could evolve to have oxygen in its atmosphere.
The new findings, published April 13 in AGU Advances, highlight the need for next-generation telescopes that are capable of characterizing planetary environments and searching for multiple lines of evidence for life in addition to detecting oxygen.
"This ...
What's in it for us: added value-based approach towards telehealth
2021-04-13
After interviewing various stakeholders from public and private healthcare systems (in Lithuania and the US), researchers Dr Agne Gadeikiene, Prof Asta Pundziene, Dr Aiste Dovaliene from Kaunas University of Technology (KTU), Lithuania designed a detailed structure revealing added value of remote healthcare services, i.e. telehealth. Adopting the concept of value co-creation common in business research to healthcare, the scientists claim that this is the first comprehensive analysis of this kind in the healthcare field involving two different healthcare systems.
According to the researchers, although in the US the consultations via phone with physician have been available for more than fifty ...
[1] ... [2422]
[2423]
[2424]
[2425]
[2426]
[2427]
[2428]
[2429]
2430
[2431]
[2432]
[2433]
[2434]
[2435]
[2436]
[2437]
[2438]
... [8815]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.