Changes in diet quality of food sources among US children, adults
2021-04-12
What The Study Did: Changes in quality of diet from different sources of food among U.S. children and adults from 2003 to 2018 were examined in this survey study.
Authors: Junxiu Liu, Ph.D., of the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in New York, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.5262)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflicts of interest and funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions ...
Prenatal opioid exposure, risk of infant death
2021-04-12
What The Study Did: Researchers compared the risk of death between infants with and without prenatal opioid exposure and also the difference in risk if diagnosed with neonatal opioid withdrawal syndrome.
Authors: JoAnna K. Leyenaar, M.D., Ph.D., M.P.H., of Children's Hospital at Dartmouth-Hitchcock Medical Center in Lebanon, New Hampshire, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamapediatrics.2021.6364)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflict of interest and funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including ...
Postoperative in-hospital morbidity, mortality of patients with COVID-19 compared to patients without
2021-04-12
What The Study Did: This study used data from a national database to compare clinical outcomes of surgical patients with and without COVID-19.
Authors: Max R. Haffner, M.D., of the University of California, Davis, in Sacramento, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.5697)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflicts of interest and funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
INFORMATION:
Media advisory: The full study is linked to this news release.
Embed this link ...
Estimation of colorectal cancer screening, outcomes during COVID-19 pandemic
2021-04-12
What The Study Did: This modeling study estimates COVID-19-related changes in rates of colorectal cancer screenings and associated outcomes and estimates the degree to which expanded fecal immunochemical testing could potentially mitigate these outcomes.
Authors: Rachel B. Issaka, M.D., M.A.S., of the Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center in Seattle, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.6454)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflict of interest and funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and ...
Researchers find genes, corresponding proteins that may lead to new depression treatments
2021-04-12
Using an innovative protein-based approach, researchers at the Atlanta Veterans Affairs Medical Center and nearby Emory University have found genes and corresponding proteins that could point the way to new depression treatments.
Using a proteome-wide association study (PWAS) that integrated genome-wide association study (GWAS) data with human brain proteomic and genetic data, researchers have identified 19 genes that may lead to depression by altering brain protein levels. They also pinpointed 25 such proteins that offer promise as potential targets for new depression treatments.
The researchers detail their approach and findings in April 2021 in the journal Nature ...
For tomato genes, one plus one doesn't always make two
2021-04-12
Both people and tomatoes come in different shapes and sizes. That is because every individual has a unique set of genetic variations--mutations--that affect how genes act and function. Added together, millions of small genetic variations make it hard to predict how a particular mutation will impact any individual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory (CSHL) Professor and Howard Hughes Medical Institute Investigator Zach Lippman showed how genetic variations in tomatoes can influence the way a specific mutation affects the plant. He is working toward being able to predict the effects of mutations on different tomato varieties.
In this study, Lippman and his team used CRISPR, a highly accurate and targeted gene-editing tool, on two tomato genes that control fruit ...
Cancer DNA blood tests validated by international research team
2021-04-12
An international team today reports the findings of an independent assessment of five commercially-available assays for tumour DNA sequencing - a fast, cheap and less invasive method to diagnose and monitor cancer.
The researchers revealed that all assays could reliably detect so-called circulating tumour DNA (ctDNA) when it made up 0.5% of the total DNA in blood, a level of sensitivity that allows detection, genetic analysis and monitoring of late-stage and metastatic tumours.
Published in the journal Nature Biotechnology, the study is a major milestone for the use of ctDNA assays as cancer diagnostics, outlining best-practice guidelines ...
Unusual fossil reveals last meal of prehistoric pollinator
2021-04-12
An amber fossil of a Cretaceous beetle has shed some light on the diet of one of the earliest pollinators of flowering plants.
The animal's remains were unearthed by researchers at the University of Bristol and the Nanjing Institute of Geology and Palaeontology of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (NIGPAS) who were able to study its fossil faecal matter, which was composed solely of pollen.
Besides being a visitor of angiosperms - flowering plants - researchers now have conclusive evidence that the new fossil named Pelretes vivificus also fed on their pollen. Details of this discovery have been published ...
Drug testing approach uncovers effective combination for treating small cell lung cancer
2021-04-12
Researchers from the National Institutes of Health have identified and tested a drug combination that exploits a weakness in small cell lung cancer (SCLC), an aggressive, dangerous cancer. The scientists targeted a vulnerability in how the cancer cells reproduce, increasing already high levels of replication stress ¬¬-- a hallmark of out-of-control cell growth in many cancers that can damage DNA and force cancer cells to constantly work to repair themselves. In a small clinical trial, the drug duo shrank the tumors of SCLC patients. The team reported its findings April 12 in Cancer Cell.
While many patients with small cell lung cancer initially respond to chemotherapy, they lack an effective follow-up treatment. These patients usually live a matter of weeks after their ...
New test better detects reservoir of virus in HIV patients
2021-04-12
A new test that measures the quantity and quality of inactive HIV viruses in the genes of people living with HIV may eventually give researchers a better idea of what drugs work best at curing the disease.
Currently no cure exists for HIV and AIDS, but antiretroviral therapy drugs, or ARTs, effectively suppress the virus to undetectable levels.
Published today in Cell Reports Medicine, the study discusses how a new test, developed jointly by scientists at the University of Washington School of Medicine and Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center, will ...
Scientists uncover the last meal of a cretaceous pollinator
2021-04-12
While pollinators such as bees and butterflies provide crucial ecosystem services today, little is known about the origin of the intimate association between flowering plants and insects.
Now, a new amber fossil unearthed by researchers from the Nanjing Institute of Geology and Palaeontology of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (NIGPAS) and the University of Bristol sheds light on some of the earliest pollinators of flowering plants.
The study was published in Nature Plants on April 12.
Two hundred million years ago the world was as green as today, overgrown with dense vegetation, but it was not as colorful. Flowering plants (angiosperms) that make up over 80% of all plant species today, only began to diversify in the Cretaceous, about 125 million years ago.
Some scientists have attributed ...
New Jurassic flying reptile reveals the oldest opposed thumb
2021-04-12
A new 160-million-year-old arboreal pterosaur species, dubbed 'Monkeydactyl', has the oldest true opposed thumb - a novel structure previously not known in pterosaurs.
An international team of researchers from China, Brazil, UK, Denmark and Japan have described a new Jurassic pterosaur Kunpengopterus antipollicatus, which was discovered in the Tiaojishan Formation of Liaoning, China.
It is a small-bodied darwinopteran pterosaur, with an estimated wingspan of 85 cm. Most importantly, the specimen was preserved with an opposed pollex ("thumb") on both hands.
The species name 'antipollicatus' ...
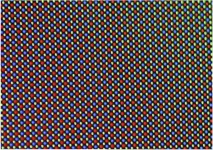
SMART discovers the science behind varying performance of different colored LEDs
2021-04-12
Singapore, 12 April 2021 - Researchers from the Low Energy Electronic Systems (LEES) Interdisciplinary Research Group (IRG) at Singapore-MIT Alliance for Research and Technology (SMART), MIT's research enterprise in Singapore, together with Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) and National University of Singapore (NUS) have found a method to quantify the distribution of compositional fluctuations in the indium gallium nitride (InGaN) quantum wells (QWs) at different indium concentrations.
InGaN light emitting diodes (LEDs) have revolutionised the field ...
Global warming could lead to the melting of more than a third of Antarctic ice shelves
2021-04-12
A new study conducted jointly by the Univerisyt of Liege (Belgium) and the University of Reading (England) suggests that 34% of the Antarctic ice shelves could disappear by the end of the century if the planet warms up by 4°C compared with pre-industrial temperatures. This melting could lead to a significant rise in sea levels. This study is published in the journal Geophysical Research Letters.
Since the early 2000s, scientists have observed that the Antarctic ice sheet is losing mass at a rate that is accelerating. The ice sheet is a very thick expanse of ice that can cover an entire continent. There are only two ice sheets on Earth: the Greenland ice sheet, which is limited to the ...
Study showing how the brain retrieves facts and may help people with memory problems
2021-04-12
A shared set of systems in the brain may play an important role in controlling the retrieval of facts and personal memories utilised in everyday life, new research shows.
Scientists from the University of York say their findings may have relevance to memory disorders, including dementia, where problems remembering relevant information can impact on the daily life of patients.
Researchers say the findings may also have important implications for the development of a new generation of artificial intelligence systems, which use long-term memory in solving computational problems.
The brain's long-term memory stores are categorised into two: factual memory ...
Is a calorie a calorie? Not always, when it comes to almonds
2021-04-12
Researchers at the University of Toronto have found that a calorie labelled is not the same as a calorie digested and absorbed, when the food source is almonds.
The findings should help alleviate concerns that almonds contribute to weight gain, which persist despite the widely recognized benefits of nuts as a plant-based source of protein, vitamins and minerals.
"Nuts have generally been thought of as healthy the last two decades, but the messaging around nuts has often come with a disclaimer that they are high in fat and energy," said John Sievenpiper, ...
World's first study to evaluate greenhouse gas emissions from Chinese inland waters
2021-04-12
Inland waters are an important component of the global carbon cycle and function as active reactors, transporting and transforming large quantities of naturally- and anthropogenically-derived carbon. Previous studies suggest that inland waters are major sources for greenhouse gas emissions to the atmosphere, yet these emissions are poorly constrained (Note 1).
As a primary greenhouse gas that drives global climate change, carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions from inland waters play a key role in assessing global carbon cycle. While most efforts over the last decade have focused on refining the emission flux estimates at the regional and global scales, scientists do not fully understand the responsiveness of regional ...
Having employees overseas helps companies reap US tax benefits
2021-04-12
A recent study finds U.S. companies that have a substantial number of employees in foreign jurisdictions with lower tax rates are more likely than their peers to "artificially" locate earnings in those jurisdictions - and the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) is less likely to challenge these complex tax-planning activities.
"Many politicians seek to encourage domestic employment and discourage sending jobs overseas," says Nathan Goldman, co-author of the study and an assistant professor of accounting in North Carolina State University's Poole College of Management. "To do that, they'll need to address elements of corporate tax policy that effectively encourage ...
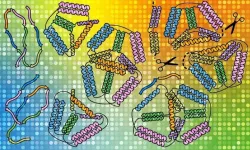
Lighting the way to folding next-level origami
2021-04-12
Origami may sound more like art than science, but a complex folding pathway that proteins use to determine their shape has been harnessed by molecular biologists, enabling them to build some of the most complex synthetic protein nanostructures to date.
Using EMBL Hamburg's world-class beamline P12 at DESY's PETRA III synchrotron, a team of Slovenian researchers, in collaboration with EMBL's Svergun group, directed powerful X-ray beams at artificial proteins called coiled-coil origami. The proteins were designed to fold into a particular shape based on short modules that interact ...
Early cannabis use linked to heart disease
2021-04-12
Smoking cannabis when you're young may increase your risk of developing heart disease later, according to a recent University of Guelph study.
In the first study to look at specific risk indicators for cardiovascular disease (CVD) in young, healthy cannabis users, researchers found subtle but potentially important changes in heart and artery function.
Cigarette smoking is known to affect cardiovascular health, causing changes to blood vessels and the heart. Less is known about the impact of smoking cannabis on long-term CVD risk, even as use of the substance grows in Canada and abroad. Cannabis is the most commonly used recreational substance worldwide after ...
CNIC researchers explain how high blood pressure, the most important cause of disease worldwide, acc
2021-04-12
High blood pressure, the most important cause of disease worldwide, accelerates atherosclerosis but the mechanism is unknown. Using gene modified minipigs, researchers from the Centro Nacional de Investigaciones Cardiovasculares (CNIC) and Aarhus University (Denmark), demonstrate that high blood pressure alters the structure of arteries leading to more accumulation of LDL cholesterol and faster development of atherosclerosis. The study has been published in The Journal of the American College of Cardiology (JACC).
Blood pressure-lowering drugs are routinely used to prevent the development of atherosclerosis and heart disease, but the mechanism of this effect is still ...
Breakthrough in plant protection: RNAi pesticides affect only one pest species
2021-04-12
The detrimental impact of pesticides on non-target organisms is one of the most urgent concerns in current agriculture. Double-stranded RNAs (dsRNAs) represent the most species-specific class of pesticides to date, potentially allowing control of a target pest without effecting other species. The unprecedented target-specificity of dsRNA is due to its nucleotide sequence-specific mode of action that results in post-transcriptional gene silencing, or RNA interference (RNAi), in the target species. The development and field use of dsRNAs, via both the insertion of transgenes into the plant genome and the application ...
Brain damage caused by plasticisers
2021-04-12
The plasticisers contained in many everyday objects can impair important brain functions in humans. Biologists from the University of Bayreuth warn of this danger in an article in Communications Biology. Their study shows that even small amounts of the plasticisers bisphenol A and bisphenol S disrupt the transmission of signals between nerve cells in the brains of fish. The researchers consider it very likely that similar interference can also occur in the brains of adult humans. They therefore call for the rapid development of alternative plasticisers that do ...
The COVID-19 pandemic has been linked with six unhealthy eating behaviors
2021-04-12
MINNEAPOLIS/ST.PAUL (04/12/2021) -- A new probe into the lingering impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic revealed correlations to six unhealthy eating behaviors, according to a study by the University of Minnesota Medical School and School of Public Health. Researchers say the most concerning finding indicates a slight increase or the re-emergence of eating disorders, which kill roughly 10,200 people every year -- about one person every 52 minutes.
U of M Medical School's Melissa Simone, PhD, a postdoctoral research fellow in the Department of Psychiatry and Behavioral Sciences, collaborated with School of Public Health ...
Pain receptors linked to the generation of energy-burning brown fat cells
2021-04-12
BOSTON - (April 12, 2021) - A new source of energy expending brown fat cells has been uncovered by researchers at the Joslin Diabetes Center, which they say points towards potential new therapeutic options for obesity. According to the new report, published today by Nature Metabolism, the key lies in the expression of a receptor called Trpv1 (temperature-sensitive ion channel transient receptor potential cation subfamily V member 1) -- a protein known to sense noxious stimuli, including pain and temperature.
Specifically, the authors point to smooth muscle cells expressing the Trpv1 receptor and identify them as a novel source of energy-burning brown fat cells (adipocytes). This should translate into increased overall energy ...
[1] ... [2428]
[2429]
[2430]
[2431]
[2432]
[2433]
[2434]
[2435]
2436
[2437]
[2438]
[2439]
[2440]
[2441]
[2442]
[2443]
[2444]
... [8815]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.